简介
虽然netty很强大,但是使用netty来构建程序却是很简单,只需要掌握特定的netty套路就可以写出强大的netty程序。每个netty程序都需要一个Bootstrap,什么是Bootstrap呢?Bootstrap翻译成中文来说就是鞋拔子,在计算机世界中,Bootstrap指的是引导程序,通过Bootstrap可以轻松构建和启动程序。
在netty中有两种Bootstrap:客户端的Bootstrap和服务器端的ServerBootstrap。两者有什么不同呢?netty中这两种Bootstrap到底是怎么工作的呢? 一起来看看吧。
Bootstrap和ServerBootstrap的联系
首先看一下Bootstrap和ServerBootstrap这两个类的继承关系,如下图所示:
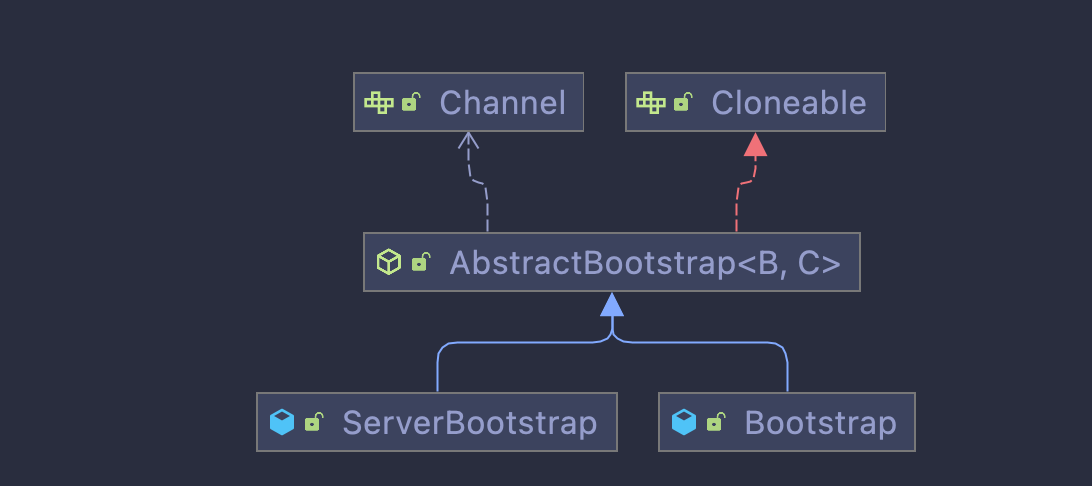
可以看到Bootstrap和ServerBootstrap都是继承自AbstractBootstrap,而AbstractBootstrap则是实现了Cloneable接口。
AbstractBootstrap
有细心的同学可能会问了,上面图中还有一个Channel,channel跟AbstractBootstrap有什么关系呢?
我们来看下AbstractBootstrap的定义:
public abstract class AbstractBootstrap<B extends AbstractBootstrap<B, C>, C extends Channel> implements Cloneable
AbstractBootstrap接受两个泛型参数,一个是B继承自AbstractBootstrap,一个是C继承自Channel。
我们先来观察一下一个简单的Bootstrap启动需要哪些元素:
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new FirstServerHandler());
}
})
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);
// 绑定端口并开始接收连接
ChannelFuture f = b.bind(port).sync();
// 等待server socket关闭
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
上面的代码是一个最基本也是最标准的netty服务器端的启动代码。可以看到和Bootstrap相关的元素有这样几个:
- EventLoopGroup,主要用来进行channel的注册和遍历。
- channel或者ChannelFactory,用来指定Bootstrap中使用的channel的类型。
- ChannelHandler,用来指定具体channel中消息的处理逻辑。
- ChannelOptions,表示使用的channel对应的属性信息。
- SocketAddress,bootstrap启动是绑定的ip和端口信息。
目前看来和Bootstrap相关的就是这5个值,而AbstractBootstrap的构造函数中也就定义了这些属性的赋值:
AbstractBootstrap(AbstractBootstrap<B, C> bootstrap) {
group = bootstrap.group;
channelFactory = bootstrap.channelFactory;
handler = bootstrap.handler;
localAddress = bootstrap.localAddress;
synchronized (bootstrap.options) {
options.putAll(bootstrap.options);
}
attrs.putAll(bootstrap.attrs);
}
示例代码中的group,channel,option等方法实际上都是向这些属性中赋值,并没有做太多的业务操作。
注意,AbstractBootstrap中只存在一个group属性,所以两个group属性是在ServerBootstrap中添加的扩展属性。
在Bootstrap中,channel其实是有两种赋值方法,一种是直接传入channel,另外一种方法是传入ChannelFactory。两者的本质都是一样的,我们看下channel是怎么转换成为ChannelFactory的:
public B channel(Class<? extends C> channelClass) {
return channelFactory(new ReflectiveChannelFactory<C>(
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(channelClass, "channelClass")
));
}
channelClass被封装在一个ReflectiveChannelFactory中,最终还是设置的channelFactory属性。
AbstractBootstrap中真正启动服务的方法就是bind,bind方法传入的是一个SocketAddress,返回的是ChannelFuture,很明显,bind方法中会创建一个channel。我们来看一下bind方法的具体实现:
private ChannelFuture doBind(final SocketAddress localAddress) {
final ChannelFuture regFuture = initAndRegister();
final Channel channel = regFuture.channel();
if (regFuture.cause() != null) {
return regFuture;
}
if (regFuture.isDone()) {
// At this point we know that the registration was complete and successful.
ChannelPromise promise = channel.newPromise();
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
return promise;
} else {
// Registration future is almost always fulfilled already, but just in case it's not.
final PendingRegistrationPromise promise = new PendingRegistrationPromise(channel);
regFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
Throwable cause = future.cause();
if (cause != null) {
// Registration on the EventLoop failed so fail the ChannelPromise directly to not cause an
// IllegalStateException once we try to access the EventLoop of the Channel.
promise.setFailure(cause);
} else {
// Registration was successful, so set the correct executor to use.
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2586
promise.registered();
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
}
}
});
return promise;
}
}
在doBind方法中,首先调用initAndRegister方法去初始化和注册一个channel。
channel是通过channelFactory的newChannel方法来创建的:
channel = channelFactory.newChannel();
接着调用初始化channel的init方法。这个init方法在AbstractBootstrap中并没有实现,需要在具体的实现类中实现。
有了channel之后,通过调用EventLoopGroup的register方法将channel注册到 EventLoop中,并将注册生成的ChannelFuture返回。
然后通过判断返回的regFuture的状态,来判断channel是否注册成功,如果注册成功,最后调用doBind0方法,完成最后的绑定工作:
private static void doBind0(
final ChannelFuture regFuture, final Channel channel,
final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
// This method is invoked before channelRegistered() is triggered. Give user handlers a chance to set up
// the pipeline in its channelRegistered() implementation.
channel.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (regFuture.isSuccess()) {
channel.bind(localAddress, promise).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE_ON_FAILURE);
} else {
promise.setFailure(regFuture.cause());
}
}
});
}
因为eventLoop本身是一个Executor,所以可以执行一个具体的命令的,在它的execute方法中,传入了一个新的Runnable对象,在其中的run方法中执行了channel.bind方法,将channel跟SocketAddress进行绑定。
到此,Bootstrap的bind方法执行完毕。
我们再来回顾一下bind方法的基本流程:
- 通过ChannelFactory创建一个channel。
- 将channel注册到Bootstrap中的EventLoopGroup中。
- 如果channel注册成功,则调用EventLoopGroup的execute方法,将channel和SocketAddress进行绑定。
是不是很清晰?
讲完AbstractBootstrap,接下来,我们再继续探讨一下Bootstrap和ServerBootstrap。
Bootstrap和ServerBootstrap
首先来看下Bootstrap,Bootstrap主要使用在客户端使用,或者UDP协议中。
先来看下Bootstrap的定义:
public class Bootstrap extends AbstractBootstrap<Bootstrap, Channel>
Bootstrap和AbstractBootstrap相比,主要多了一个属性和一个方法。
多的一个属性是resolver:
private static final AddressResolverGroup<?> DEFAULT_RESOLVER = DefaultAddressResolverGroup.INSTANCE;
private volatile AddressResolverGroup<SocketAddress> resolver =
(AddressResolverGroup<SocketAddress>) DEFAULT_RESOLVER;
AddressResolverGroup里面有一个IdentityHashMap,它的key是EventExecutor,value是AddressResolver:
private final Map<EventExecutor, AddressResolver<T>> resolvers =
new IdentityHashMap<EventExecutor, AddressResolver<T>>();
实际上AddressResolverGroup维护了一个EventExecutor和AddressResolver的映射关系。
AddressResolver主要用来解析远程的SocketAddress的地址。因为远程的SocketAddress可能并不是一个IP地址,所以需要使用AddressResolver解析一下。
这里的EventExecutor实际上就是channel注册的EventLoop。
另外Bootstrap作为一个客户端的应用,它需要连接到服务器端,所以Bootstrap类中多了一个connect到远程SocketAddress的方法:
public ChannelFuture connect(SocketAddress remoteAddress) {
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(remoteAddress, "remoteAddress");
validate();
return doResolveAndConnect(remoteAddress, config.localAddress());
}
connect方法和bind方法的逻辑类似,只是多了一个resolver的resolve过程。
解析完毕之后,会调用doConnect方法,进行真正的连接:
private static void doConnect(
final SocketAddress remoteAddress, final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise connectPromise) {
// This method is invoked before channelRegistered() is triggered. Give user handlers a chance to set up
// the pipeline in its channelRegistered() implementation.
final Channel channel = connectPromise.channel();
channel.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (localAddress == null) {
channel.connect(remoteAddress, connectPromise);
} else {
channel.connect(remoteAddress, localAddress, connectPromise);
}
connectPromise.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE_ON_FAILURE);
}
});
}
可以看到doConnect方法和doBind方法很类似,都是通过当前channel注册的eventLoop来执行channel的connect或许bind方法。
再看一下ServerBootstrap的定义:
public class ServerBootstrap extends AbstractBootstrap<ServerBootstrap, ServerChannel>
因为是ServerBootstrap用在服务器端,所以不选Bootstrap那样去解析SocketAddress,所以没有resolver属性。
但是对应服务器端来说,可以使用parent EventLoopGroup来接受连接,然后使用child EventLoopGroup来执行具体的命令。所以在ServerBootstrap中多了一个childGroup和对应的childHandler:
private volatile EventLoopGroup childGroup;
private volatile ChannelHandler childHandler;
因为ServerBootstrap有两个group,所以ServerBootstrap包含一个含有两个EventLoopGroup的group方法:
public ServerBootstrap group(EventLoopGroup parentGroup, EventLoopGroup childGroup)
还记得bind方法需要实现的init方法吗? 我们看下ServerBootstrap中init的具体逻辑:
void init(Channel channel) {
setChannelOptions(channel, newOptionsArray(), logger);
setAttributes(channel, newAttributesArray());
ChannelPipeline p = channel.pipeline();
final EventLoopGroup currentChildGroup = childGroup;
final ChannelHandler currentChildHandler = childHandler;
final Entry<ChannelOption<?>, Object>[] currentChildOptions = newOptionsArray(childOptions);
final Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object>[] currentChildAttrs = newAttributesArray(childAttrs);
p.addLast(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(final Channel ch) {
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
ChannelHandler handler = config.handler();
if (handler != null) {
pipeline.addLast(handler);
}
ch.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
pipeline.addLast(new ServerBootstrapAcceptor(
ch, currentChildGroup, currentChildHandler, currentChildOptions, currentChildAttrs));
}
});
}
});
}
首先是设置channel的一些属性,然后通过channel.pipeline方法获得channel对应的pipeline,然后向pipeline中添加channelHandler。
这些都是常规操作,我们要注意的是最后通过channel注册到的eventLoop,将ServerBootstrapAcceptor加入到了pipeline中。
很明显ServerBootstrapAcceptor本身应该是一个ChannelHandler,它的主要作用就是用来接受连接:
private static class ServerBootstrapAcceptor extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter
我们来看一下它的channelRead方法:
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
final Channel child = (Channel) msg;
child.pipeline().addLast(childHandler);
setChannelOptions(child, childOptions, logger);
setAttributes(child, childAttrs);
try {
childGroup.register(child).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
forceClose(child, future.cause());
}
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
forceClose(child, t);
}
}
因为server端接受的是客户端channel的connect操作,所以对应的channelRead中的对象实际上是一个channel。这里把这个接受到的channel称作child。通过给这个child channel添加childHandler,childOptions和childAttrs,一个能够处理child channel请求的逻辑就形成了。
最后将child channel注册到childGroup中,至此整个ServerBootstrapAcceptor接受channel的任务就完成了。
这里最妙的部分就是将客户端的channel通过server端的channel传到server端,然后在server端为child channel配备handler进行具体的业务处理,非常巧妙。
总结
通过具体分析AbstractBootstrap,Bootstrap和ServerBootstrap的结构和实现逻辑,相信大家对netty服务的启动流程有了大概的认识,后面我们会详细讲解netty中的channel和非常重要的eventLoop。
本文已收录于 http://www.flydean.com/03-1-netty-boots…-serverbootstrap/
最通俗的解读,最深刻的干货,最简洁的教程,众多你不知道的小技巧等你来发现!
欢迎关注我的公众号:「程序那些事」,懂技术,更懂你!