简介
使用Pandas的pivot方法可以将DF进行旋转变换,本文将会详细讲解pivot的秘密。
使用Pivot
pivot用来重组DF,使用指定的index,columns和values来对现有的DF进行重构。
看一个Pivot的例子:
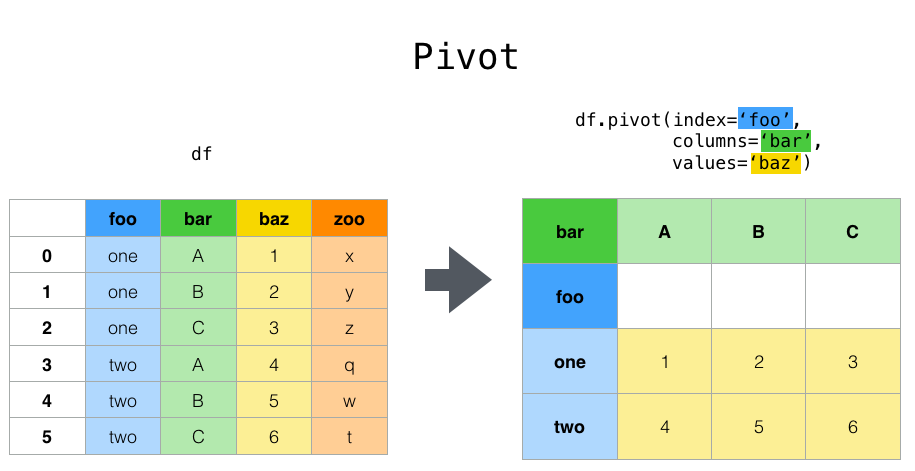
通过pivot变化,新的DF使用foo中的值作为index,使用bar的值作为columns,zoo作为对应的value。
再看一个时间变化的例子:
In [1]: df
Out[1]:
date variable value
0 2000-01-03 A 0.469112
1 2000-01-04 A -0.282863
2 2000-01-05 A -1.509059
3 2000-01-03 B -1.135632
4 2000-01-04 B 1.212112
5 2000-01-05 B -0.173215
6 2000-01-03 C 0.119209
7 2000-01-04 C -1.044236
8 2000-01-05 C -0.861849
9 2000-01-03 D -2.104569
10 2000-01-04 D -0.494929
11 2000-01-05 D 1.071804
In [3]: df.pivot(index='date', columns='variable', values='value')
Out[3]:
variable A B C D
date
2000-01-03 0.469112 -1.135632 0.119209 -2.104569
2000-01-04 -0.282863 1.212112 -1.044236 -0.494929
2000-01-05 -1.509059 -0.173215 -0.861849 1.071804
如果剩余的value,多于一列的话,每一列都会有相应的columns值:
In [4]: df['value2'] = df['value'] * 2
In [5]: pivoted = df.pivot(index='date', columns='variable')
In [6]: pivoted
Out[6]:
value value2
variable A B C D A B C D
date
2000-01-03 0.469112 -1.135632 0.119209 -2.104569 0.938225 -2.271265 0.238417 -4.209138
2000-01-04 -0.282863 1.212112 -1.044236 -0.494929 -0.565727 2.424224 -2.088472 -0.989859
2000-01-05 -1.509059 -0.173215 -0.861849 1.071804 -3.018117 -0.346429 -1.723698 2.143608
通过选择value2,可以得到相应的子集:
In [7]: pivoted['value2']
Out[7]:
variable A B C D
date
2000-01-03 0.938225 -2.271265 0.238417 -4.209138
2000-01-04 -0.565727 2.424224 -2.088472 -0.989859
2000-01-05 -3.018117 -0.346429 -1.723698 2.143608
使用Stack
Stack是对DF进行转换,将列转换为新的内部的index。
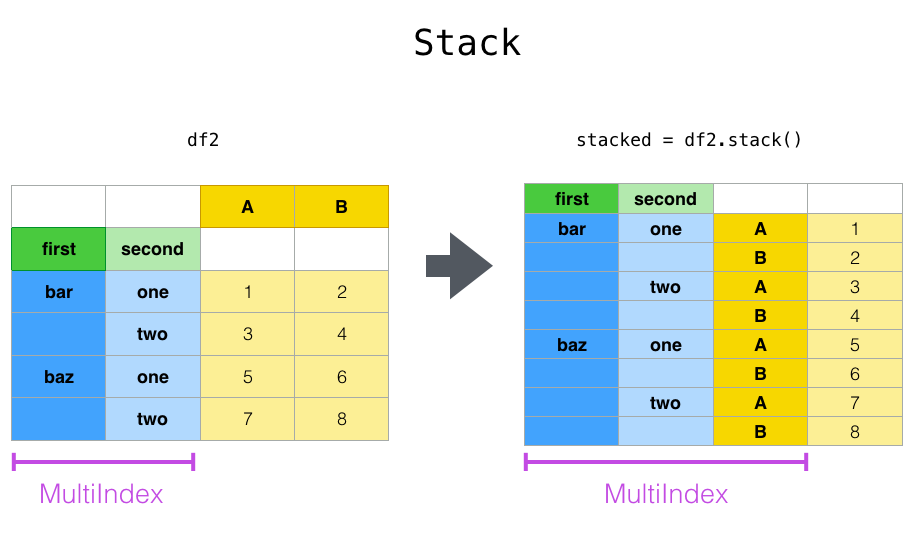
上面我们将列A,B转成了index。
unstack是stack的反向操作,是将最内层的index转换为对应的列。
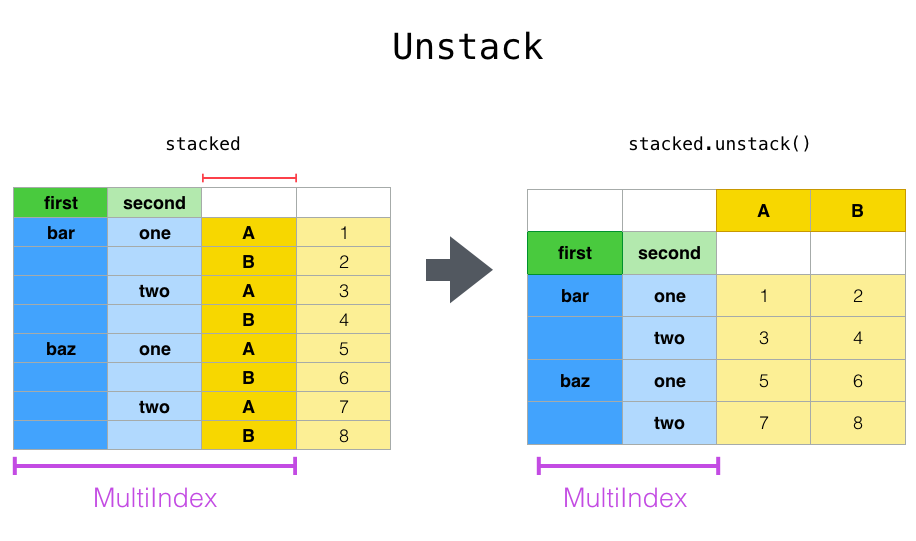
举个具体的例子:
In [8]: tuples = list(zip(*[['bar', 'bar', 'baz', 'baz',
...: 'foo', 'foo', 'qux', 'qux'],
...: ['one', 'two', 'one', 'two',
...: 'one', 'two', 'one', 'two']]))
...:
In [9]: index = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples(tuples, names=['first', 'second'])
In [10]: df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(8, 2), index=index, columns=['A', 'B'])
In [11]: df2 = df[:4]
In [12]: df2
Out[12]:
A B
first second
bar one 0.721555 -0.706771
two -1.039575 0.271860
baz one -0.424972 0.567020
two 0.276232 -1.087401
In [13]: stacked = df2.stack()
In [14]: stacked
Out[14]:
first second
bar one A 0.721555
B -0.706771
two A -1.039575
B 0.271860
baz one A -0.424972
B 0.567020
two A 0.276232
B -1.087401
dtype: float64
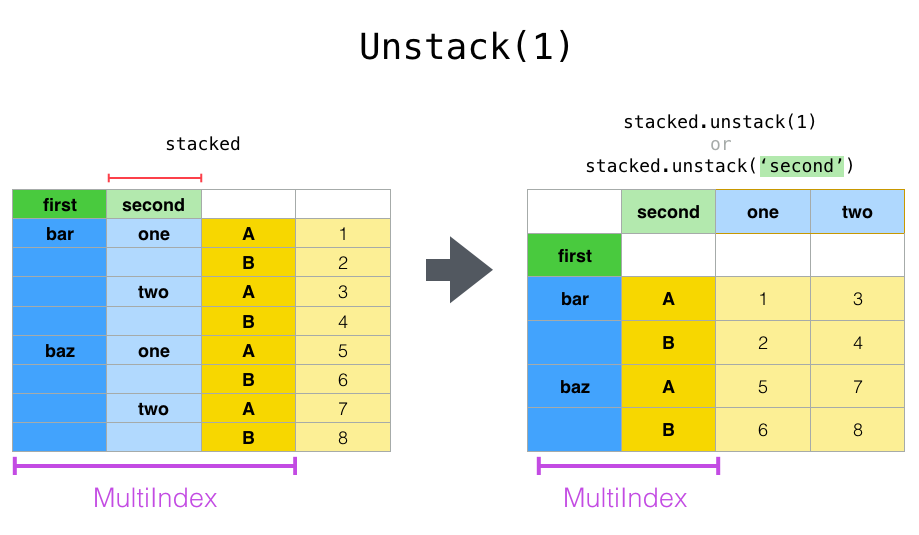
默认情况下unstack是unstack最后一个index,我们还可以指定特定的index值:
In [15]: stacked.unstack()
Out[15]:
A B
first second
bar one 0.721555 -0.706771
two -1.039575 0.271860
baz one -0.424972 0.567020
two 0.276232 -1.087401
In [16]: stacked.unstack(1)
Out[16]:
second one two
first
bar A 0.721555 -1.039575
B -0.706771 0.271860
baz A -0.424972 0.276232
B 0.567020 -1.087401
In [17]: stacked.unstack(0)
Out[17]:
first bar baz
second
one A 0.721555 -0.424972
B -0.706771 0.567020
two A -1.039575 0.276232
B 0.271860 -1.087401
默认情况下stack只会stack一个level,还可以传入多个level:
In [23]: columns = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples([
....: ('A', 'cat', 'long'), ('B', 'cat', 'long'),
....: ('A', 'dog', 'short'), ('B', 'dog', 'short')],
....: names=['exp', 'animal', 'hair_length']
....: )
....:
In [24]: df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(4, 4), columns=columns)
In [25]: df
Out[25]:
exp A B A B
animal cat cat dog dog
hair_length long long short short
0 1.075770 -0.109050 1.643563 -1.469388
1 0.357021 -0.674600 -1.776904 -0.968914
2 -1.294524 0.413738 0.276662 -0.472035
3 -0.013960 -0.362543 -0.006154 -0.923061
In [26]: df.stack(level=['animal', 'hair_length'])
Out[26]:
exp A B
animal hair_length
0 cat long 1.075770 -0.109050
dog short 1.643563 -1.469388
1 cat long 0.357021 -0.674600
dog short -1.776904 -0.968914
2 cat long -1.294524 0.413738
dog short 0.276662 -0.472035
3 cat long -0.013960 -0.362543
dog short -0.006154 -0.923061
上面等价于:
In [27]: df.stack(level=[1, 2])
使用melt
melt指定特定的列作为标志变量,其他的列被转换为行的数据。并放置在新的两个列:variable和value中。
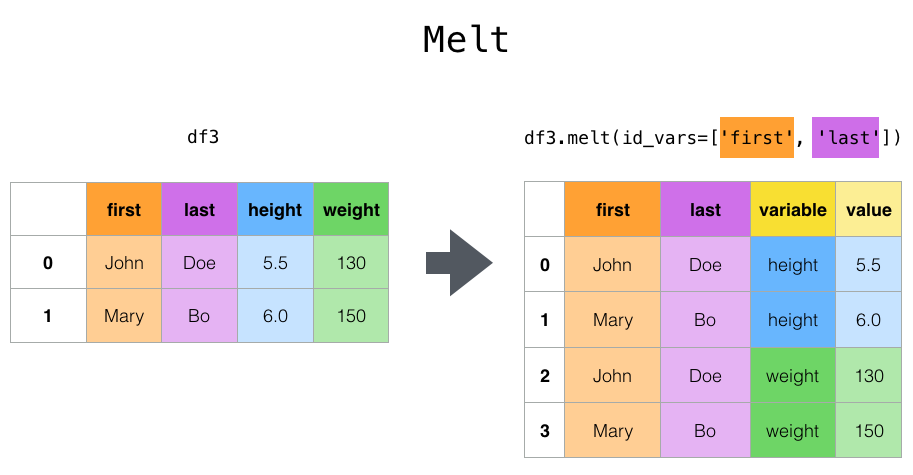
上面例子中我们指定了两列first和last,这两列是不变的,height和weight被变换成为行数据。
举个例子:
In [41]: cheese = pd.DataFrame({'first': ['John', 'Mary'],
....: 'last': ['Doe', 'Bo'],
....: 'height': [5.5, 6.0],
....: 'weight': [130, 150]})
....:
In [42]: cheese
Out[42]:
first last height weight
0 John Doe 5.5 130
1 Mary Bo 6.0 150
In [43]: cheese.melt(id_vars=['first', 'last'])
Out[43]:
first last variable value
0 John Doe height 5.5
1 Mary Bo height 6.0
2 John Doe weight 130.0
3 Mary Bo weight 150.0
In [44]: cheese.melt(id_vars=['first', 'last'], var_name='quantity')
Out[44]:
first last quantity value
0 John Doe height 5.5
1 Mary Bo height 6.0
2 John Doe weight 130.0
3 Mary Bo weight 150.0
使用Pivot tables
虽然Pivot可以进行DF的轴转置,Pandas还提供了 pivot_table() 在转置的同时可以进行数值的统计。
pivot_table() 接收下面的参数:
data: 一个df对象
values:一列或者多列待聚合的数据。
Index: index的分组对象
Columns: 列的分组对象
Aggfunc: 聚合的方法。
先创建一个df:
In [59]: import datetime
In [60]: df = pd.DataFrame({'A': ['one', 'one', 'two', 'three'] * 6,
....: 'B': ['A', 'B', 'C'] * 8,
....: 'C': ['foo', 'foo', 'foo', 'bar', 'bar', 'bar'] * 4,
....: 'D': np.random.randn(24),
....: 'E': np.random.randn(24),
....: 'F': [datetime.datetime(2013, i, 1) for i in range(1, 13)]
....: + [datetime.datetime(2013, i, 15) for i in range(1, 13)]})
....:
In [61]: df
Out[61]:
A B C D E F
0 one A foo 0.341734 -0.317441 2013-01-01
1 one B foo 0.959726 -1.236269 2013-02-01
2 two C foo -1.110336 0.896171 2013-03-01
3 three A bar -0.619976 -0.487602 2013-04-01
4 one B bar 0.149748 -0.082240 2013-05-01
.. ... .. ... ... ... ...
19 three B foo 0.690579 -2.213588 2013-08-15
20 one C foo 0.995761 1.063327 2013-09-15
21 one A bar 2.396780 1.266143 2013-10-15
22 two B bar 0.014871 0.299368 2013-11-15
23 three C bar 3.357427 -0.863838 2013-12-15
[24 rows x 6 columns]
下面是几个聚合的例子:
In [62]: pd.pivot_table(df, values='D', index=['A', 'B'], columns=['C'])
Out[62]:
C bar foo
A B
one A 1.120915 -0.514058
B -0.338421 0.002759
C -0.538846 0.699535
three A -1.181568 NaN
B NaN 0.433512
C 0.588783 NaN
two A NaN 1.000985
B 0.158248 NaN
C NaN 0.176180
In [63]: pd.pivot_table(df, values='D', index=['B'], columns=['A', 'C'], aggfunc=np.sum)
Out[63]:
A one three two
C bar foo bar foo bar foo
B
A 2.241830 -1.028115 -2.363137 NaN NaN 2.001971
B -0.676843 0.005518 NaN 0.867024 0.316495 NaN
C -1.077692 1.399070 1.177566 NaN NaN 0.352360
In [64]: pd.pivot_table(df, values=['D', 'E'], index=['B'], columns=['A', 'C'],
....: aggfunc=np.sum)
....:
Out[64]:
D E
A one three two one three two
C bar foo bar foo bar foo bar foo bar foo bar foo
B
A 2.241830 -1.028115 -2.363137 NaN NaN 2.001971 2.786113 -0.043211 1.922577 NaN NaN 0.128491
B -0.676843 0.005518 NaN 0.867024 0.316495 NaN 1.368280 -1.103384 NaN -2.128743 -0.194294 NaN
C -1.077692 1.399070 1.177566 NaN NaN 0.352360 -1.976883 1.495717 -0.263660 NaN NaN 0.872482
添加margins=True会添加一个All列,表示对所有的列进行聚合:
In [69]: df.pivot_table(index=['A', 'B'], columns='C', margins=True, aggfunc=np.std)
Out[69]:
D E
C bar foo All bar foo All
A B
one A 1.804346 1.210272 1.569879 0.179483 0.418374 0.858005
B 0.690376 1.353355 0.898998 1.083825 0.968138 1.101401
C 0.273641 0.418926 0.771139 1.689271 0.446140 1.422136
three A 0.794212 NaN 0.794212 2.049040 NaN 2.049040
B NaN 0.363548 0.363548 NaN 1.625237 1.625237
C 3.915454 NaN 3.915454 1.035215 NaN 1.035215
two A NaN 0.442998 0.442998 NaN 0.447104 0.447104
B 0.202765 NaN 0.202765 0.560757 NaN 0.560757
C NaN 1.819408 1.819408 NaN 0.650439 0.650439
All 1.556686 0.952552 1.246608 1.250924 0.899904 1.059389
使用crosstab
Crosstab 用来统计表格中元素的出现次数。
In [70]: foo, bar, dull, shiny, one, two = 'foo', 'bar', 'dull', 'shiny', 'one', 'two'
In [71]: a = np.array([foo, foo, bar, bar, foo, foo], dtype=object)
In [72]: b = np.array([one, one, two, one, two, one], dtype=object)
In [73]: c = np.array([dull, dull, shiny, dull, dull, shiny], dtype=object)
In [74]: pd.crosstab(a, [b, c], rownames=['a'], colnames=['b', 'c'])
Out[74]:
b one two
c dull shiny dull shiny
a
bar 1 0 0 1
foo 2 1 1 0
crosstab可以接收两个Series:
In [75]: df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2, 2, 2, 2], 'B': [3, 3, 4, 4, 4],
....: 'C': [1, 1, np.nan, 1, 1]})
....:
In [76]: df
Out[76]:
A B C
0 1 3 1.0
1 2 3 1.0
2 2 4 NaN
3 2 4 1.0
4 2 4 1.0
In [77]: pd.crosstab(df['A'], df['B'])
Out[77]:
B 3 4
A
1 1 0
2 1 3
还可以使用normalize来指定比例值:
In [82]: pd.crosstab(df['A'], df['B'], normalize=True)
Out[82]:
B 3 4
A
1 0.2 0.0
2 0.2 0.6
还可以normalize行或者列:
In [83]: pd.crosstab(df['A'], df['B'], normalize='columns')
Out[83]:
B 3 4
A
1 0.5 0.0
2 0.5 1.0
可以指定聚合方法:
In [84]: pd.crosstab(df['A'], df['B'], values=df['C'], aggfunc=np.sum)
Out[84]:
B 3 4
A
1 1.0 NaN
2 1.0 2.0
get_dummies
get_dummies可以将DF中的一列转换成为k列的0和1组合:
df = pd.DataFrame({'key': list('bbacab'), 'data1': range(6)})
df
Out[9]:
data1 key
0 0 b
1 1 b
2 2 a
3 3 c
4 4 a
5 5 b
pd.get_dummies(df['key'])
Out[10]:
a b c
0 0 1 0
1 0 1 0
2 1 0 0
3 0 0 1
4 1 0 0
5 0 1 0
get_dummies 和 cut 可以进行结合用来统计范围内的元素:
In [95]: values = np.random.randn(10)
In [96]: values
Out[96]:
array([ 0.4082, -1.0481, -0.0257, -0.9884, 0.0941, 1.2627, 1.29 ,
0.0824, -0.0558, 0.5366])
In [97]: bins = [0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1]
In [98]: pd.get_dummies(pd.cut(values, bins))
Out[98]:
(0.0, 0.2] (0.2, 0.4] (0.4, 0.6] (0.6, 0.8] (0.8, 1.0]
0 0 0 1 0 0
1 0 0 0 0 0
2 0 0 0 0 0
3 0 0 0 0 0
4 1 0 0 0 0
5 0 0 0 0 0
6 0 0 0 0 0
7 1 0 0 0 0
8 0 0 0 0 0
9 0 0 1 0 0
get_dummies还可以接受一个DF参数:
In [99]: df = pd.DataFrame({'A': ['a', 'b', 'a'], 'B': ['c', 'c', 'b'],
....: 'C': [1, 2, 3]})
....:
In [100]: pd.get_dummies(df)
Out[100]:
C A_a A_b B_b B_c
0 1 1 0 0 1
1 2 0 1 0 1
2 3 1 0 1 0
本文已收录于 http://www.flydean.com/05-python-pandas-reshaping-pivot/
最通俗的解读,最深刻的干货,最简洁的教程,众多你不知道的小技巧等你来发现!
欢迎关注我的公众号:「程序那些事」,懂技术,更懂你!