题目描述
在给定的网格中,每个单元格可以有以下三个值之一:
- 值 0 代表空单元格;
- 值 1 代表新鲜橘子;
- 值 2 代表腐烂的橘子。
每分钟,任何与腐烂的橘子(在 4 个正方向上)相邻的新鲜橘子都会腐烂。
返回直到单元格中没有新鲜橘子为止所必须经过的最小分钟数。如果不可能,返回 -1。
示例:
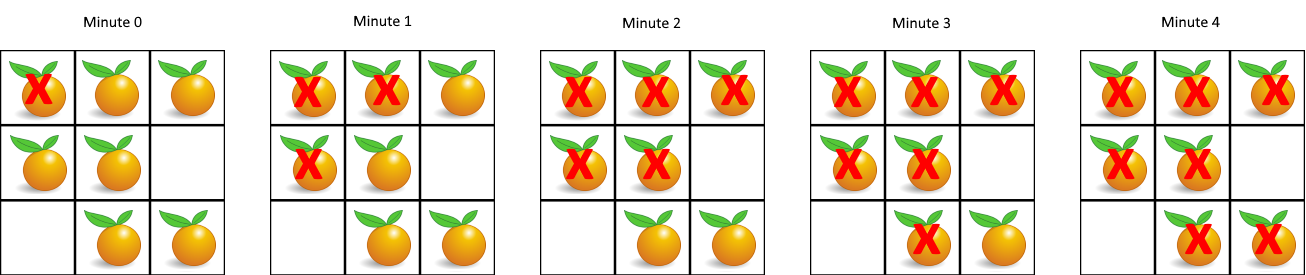
输入:[[2,1,1],[1,1,0],[0,1,1]]
输出:4
输入:[[2,1,1],[0,1,1],[1,0,1]]
输出:-1
解释:左下角的橘子(第 2 行, 第 0 列)永远不会腐烂,因为腐烂只会发生在 4 个正向上。
输入:[[0,2]]
输出:0
解释:因为 0 分钟时已经没有新鲜橘子了,所以答案就是 0 。
说明:
- 1 <= grid.length <= 10
- 1 <= grid[0].length <= 10
- grid[i][j] 仅为 0、1 或 2
思路
求没有新鲜橘子为止所必须经过的最小分钟数就是求从源点到目标点的最短路径,使用 bfs 来做。这个是多源 bfs,也就是 bfs 搜索的起点不止一个,这里 bfs 搜索的起点就是初始时所有已腐烂橘子的位置。我们首先将所有腐烂橘子的位置入队列,然后 bfs 搜索,就是层次遍历,记录一个变量 depth,代表遍历的深度,depth 初始化为 0 ,每遍历一层,depth 就更新为 depth+1。每遍历到一个新鲜的橘子,新鲜橘子的个数就减一。如果遍历结束,新鲜橘子的个数为 0,说明所有橘子都腐烂了,返回遍历的深度 depth;否则,说明有的新鲜橘子无法遍历到,这些橘子不会腐烂,返回 -1.
代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
int orangesRotting(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
if(grid.empty()) return -1;
int rows = grid.size();
int cols = grid[0].size();
int freshCnt = 0; // 新鲜橘子的个数
queue<pair<int, int>> q; // 存放腐烂橘子的位置<row, col>
for(int i=0; i<rows; i++){
for(int j=0; j<cols; j++){
if(grid[i][j]==1) freshCnt++;
else if(grid[i][j]==2){
q.push(make_pair(i, j));
}
}
}
int depth = 0; // 深度
int dirs[4][2] = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
while(freshCnt>0 && !q.empty()){
depth++;
int n = q.size();
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){ // 层次遍历
int row = q.front().first;
int col = q.front().second;
q.pop();
for(int j=0; j<4; j++){
int nextRow =row + dirs[j][0];
int nextCol = col + dirs[j][1];
if(nextRow>=0 && nextRow<rows && nextCol>=0 && nextCol<cols && grid[nextRow][nextCol]==1){
q.push(make_pair(nextRow, nextCol));
grid[nextRow][nextCol] = 2;
freshCnt--;
}
}
}
}
if(freshCnt>0) return -1;
else return depth;
}
};
- 时间复杂度:O(m*n)
m、n 分别为 grid 的行列数。 - 空间复杂度:O(m*n)