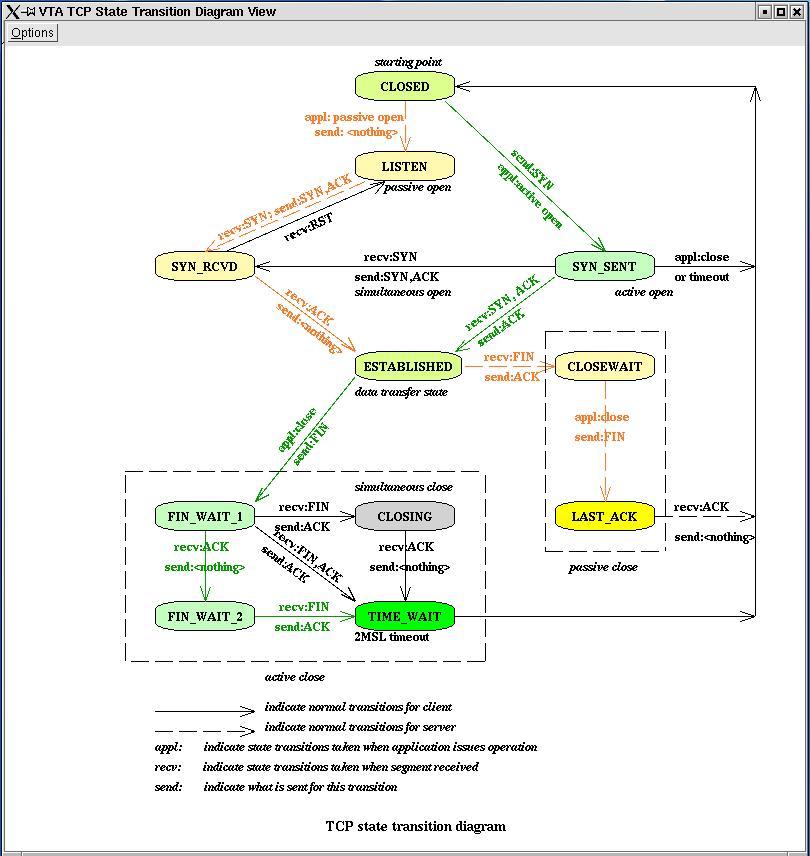
TCP States

code:
#include<winsock2.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#pragma comment(lib, "ws2_32.lib")
int main(int argc,char**argv)
{
WSADATA wsaData;
SOCKET SendingSocket;
SOCKADDR_IN ServerAddr;
unsigned int Port=80;
int RetCode;
//Initialize Winsock version 2.2
WSAStartup(MAKEWORD(2,2),&wsaData);
printf("Client:Winsock DLL status is %s.\n",wsaData.szSystemStatus);
//Create a new socket to make a client connection.
//AF_INET=2,The Internet Protocol version 4(IPv4)address family,TCP protocpl
SendingSocket=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,IPPROTO_TCP);
if(SendingSocket==INVALID_SOCKET)
{
printf("Client:socket()failed !Error code:%ld\n",WSAGetLastError());
WSACleanup();
return -1;
}
else
printf("Client:socket () is OK!\n");
//Set up a SOCKETADDR_IN structure that will be used to connect to a listening server on port 5150,For demonstration purposes ,let's assume our server IP address is 127.0.0.1 or localhost.
//IPv4
ServerAddr.sin_family=AF_INET;
//Port no.
ServerAddr.sin_port=htons(Port);
//The IPaddress
ServerAddr.sin_addr.S_un.S_addr=inet_addr("209.131.36.158");
RetCode=connect(SendingSocket,(SOCKADDR*)&ServerAddr,sizeof(ServerAddr));
if(RetCode!=0)
{
printf("Client:connect() failed!Error code :%ld\n",WSAGetLastError());
closesocket(SendingSocket);
WSACleanup();
return -1;
}
else
{
printf("Client connect() is OK,got connected ...\n");
printf("Client Ready for sending and receiving data..\n");
}
// At this point you can start sending or receiving data on
// the socket SendingSocket. We will describe sending and receiving data
// later in the chapter.
// When you are finished sending and receiving data on socket SendingSocket,
// you should close the socket using the closesocket API. We will
// describe socket closure later in the chapter.
if(closesocket(SendingSocket)!=0)
printf("Client :Cannot close \"Sending Socket .Error code:%ld\n",WSAGetLastError());
else
printf("Client :Closing \"SendingSocket\"socket..\n");
if(WSACleanup()!=0)
printf("Client: WSACleanup() failed!...\n");
else
printf("Client: WSACleanup() is OK...\n");
return 0;
}