之前在网上看过许多关于拆箱和装箱的说法,看多了更糊涂了。今天看了《CLR VIA C#》第三版,突然感觉豁然开朗。
这篇博客之所以起名为新解,只是我看到的关于装箱拆箱操作的嘴让人透彻明白的解释。
废话就不说了,我们还是来看看吧!先来看例子:
下面是一段代码的三中不同写法,还有他们的反编译后的il,请问每种方法中装箱的次数???
-----------------------------------程序一------------------------------------ static void Main(string[] args) { Int32 v = 5; object o = v; v = 123; Console.WriteLine(v.ToString()+","+(int32)o); Console.ReadKey(); } .method private hidebysig static void Main(string[] args) cil managed { .entrypoint // 代码大小 53 (0x35) .maxstack 3 .locals init ([0] int32 v, [1] object o) IL_0000: nop IL_0001: ldc.i4.5 IL_0002: stloc.0 IL_0003: ldloc.0 IL_0004: box [mscorlib]System.Int32 IL_0009: stloc.1 IL_000a: ldc.i4.s 123 IL_000c: stloc.0 IL_000d: ldloc.0 IL_000e: box [mscorlib]System.Int32 IL_0013: ldstr "," IL_0018: ldloc.1 IL_0019: unbox.any [mscorlib]System.Int32 IL_001e: box [mscorlib]System.Int32 IL_0023: call string [mscorlib]System.String::Concat(object, object, object) IL_0028: call void [mscorlib]System.Console::WriteLine(string) IL_002d: nop IL_002e: call valuetype [mscorlib]System.ConsoleKeyInfo [mscorlib]System.Console::ReadKey() IL_0033: pop IL_0034: ret } // end of method Program::Main -----------------------------------------程序二-------------------------------- static void Main(string[] args) { Int32 v = 5; object o = v; v = 123; Console.WriteLine(v+","+o); Console.ReadKey(); } .method private hidebysig static void Main(string[] args) cil managed { .entrypoint // 代码大小 43 (0x2b) .maxstack 3 .locals init ([0] int32 v, [1] object o) IL_0000: nop IL_0001: ldc.i4.5 IL_0002: stloc.0 IL_0003: ldloc.0 IL_0004: box [mscorlib]System.Int32 IL_0009: stloc.1 IL_000a: ldc.i4.s 123 IL_000c: stloc.0 IL_000d: ldloc.0 IL_000e: box [mscorlib]System.Int32 IL_0013: ldstr "," IL_0018: ldloc.1 IL_0019: call string [mscorlib]System.String::Concat(object, object, object) IL_001e: call void [mscorlib]System.Console::WriteLine(string) IL_0023: nop IL_0024: call valuetype [mscorlib]System.ConsoleKeyInfo [mscorlib]System.Console::ReadKey() IL_0029: pop IL_002a: ret } // end of method Program::Main ---------------------------程序三------------------------------------------- static void Main(string[] args) { Int32 v = 5; object o = v; v = 123; Console.WriteLine(v.ToString()+","+o); Console.ReadKey(); } .method private hidebysig static void Main(string[] args) cil managed { .entrypoint // 代码大小 44 (0x2c) .maxstack 3 .locals init ([0] int32 v, [1] object o) IL_0000: nop IL_0001: ldc.i4.5 IL_0002: stloc.0 IL_0003: ldloc.0 IL_0004: box [mscorlib]System.Int32 IL_0009: stloc.1 IL_000a: ldc.i4.s 123 IL_000c: stloc.0 IL_000d: ldloca.s v IL_000f: call instance string [mscorlib]System.Int32::ToString() IL_0014: ldstr "," IL_0019: ldloc.1 IL_001a: call string [mscorlib]System.String::Concat(object, object, object) IL_001f: call void [mscorlib]System.Console::WriteLine(string) IL_0024: nop IL_0025: call valuetype [mscorlib]System.ConsoleKeyInfo [mscorlib]System.Console::ReadKey() IL_002a: pop IL_002b: ret } // end of method Program::Main
程序1中:3次 程序2:2次 程序3:1次
why??当然我们可以根据il代码中box出现的次数就可以判断出为什么是3,2,1,但是当我们没有il代码,或者在决断我们改怎样编写代码避免不比较的装箱拆箱操作呢??
《CLR Via C#》给了我们很详尽的解答:
我们先来认识一下装箱和拆箱的背景:
一.值类型和引用类型
CLR 支持两种类型,值类型和引用类型。
1.引用类型总是从托管堆上非配,C#的new关键词或放回对象的内存地址--也就是指向对象数据的内存地址;
2.引用类型对象是存放在栈上,而对象的引用实在堆上。
3.值类型一般就是在堆栈上非配的
4.值类型的复制是在堆栈中再开辟一个空间,将字节一个一个的复制过来,前后两个变量没有任何的联系
5.引用的类型复制,是在堆栈中声明一个对象,有别于待复制的对象,但其指向的引用都是堆中相同的一块地址。所以该变一个对象,另一个对象也会改变(如下图)
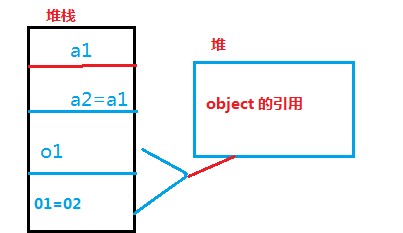
对应程序:
static void Main(string[] args) {
pointStrcut a1=new pointStrcut (); a1.x = "a1"; pointStrcut a2=a1; a2.x = "a2"; Console.WriteLine("a1 is " + a1.x + " a2 is "+a2.x); pointClass o1= new pointClass(); o1.x ="nihao"; pointClass o2= o1; o2.x = "buhao"; Console.WriteLine("a1.x is "+o1.x+" a2.x is "+o2.x)
}
internal class pointClass { public string x; public string y; } internal struct pointStrcut { public string x; public string y; }
结果:
strcutBox1 is strcutBox1 strcutBox2 is st
pclass1.x is buhao pclass2.x is buhao
在上例子中,class pointClass是引用类型,而struct PointStruct 是值类型
对已值类型,只在栈中开辟内存,复制是是整个copy。所以a1和a2 是完全没有联系的只是值相同的两个变量。a2的变化不会导致a1的变化
对引用类型,栈中保存对象,堆中保存对象的引用。copy是,栈中的对象不一样,但是所对应的引用地址是一样的,所以,o2的改变实际上市堆中内存块发生了改变,所以o1也随着改变。
那么值类型和引用类型有哪些?
值类型:直接派生于System.Valuetype 包括结构,枚举。枚举继承自system.enum,但是system.enum也继承自system.valueType 。
引用类型:类
一.何为装箱,拆箱
简单点装箱就是将值类型转化为引用类型,拆箱反之;
我们再看一段代码
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Point p = new Point(1, 1);
Console.WriteLine(p);
p.Change(2, 2);
Console.WriteLine(p); //1,1
object o = p;
Console.WriteLine(o); //2,2
((Point)o).Change(3, 3);
Console.WriteLine(o); //只改变了栈中的临时Point值(下式中显示写出临时变量o2) 2,2
Point o2 = (Point)o;
o2.Change(3, 3);
Console.WriteLine(o2); //2,2
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
internal struct Point
{
private Int32 x, y;
public Point(Int32 x, Int32 y)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public void Change(Int32 x, Int32 y)
{
this.x = x; this.y = y;
}
public override string ToString()
{
return "(" + x + "," + y + ")";
}
}
internal class pointClass
{
public string x;
public string y;
}
Console.WriteLine(o);的执行结果为什么是(2,2)??
仔细研究一下这一句:((Point)o).Change(3, 3);
o是一个object类型,时刻记住引用类型:栈上面保存对象,堆上面保存对象的引用。
那上面一句话干了什么?
将一个引用类型转化为值类型(拆箱),再调用change方法。 注意拆箱过程:拆箱会在栈上新建一个临时变量,并将堆中的所有数据全部复制到这个临时变量中!
也就是说o还是o,没有变化!我们用下面的方法显示拆箱过程
Point o2 = (Point)o;
o2.Change(3, 3);
Console.WriteLine(o2); //2,2
那如果我们要改变引用类型的变量改怎么办?看下面代码:(代码中有注释,一看便知)
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Point p = new Point(1, 1);
Console.WriteLine(p);
p.Change(2, 2);
Console.WriteLine(p); //1,1
object o = p;
Console.WriteLine(o); //2,2
((Point)o).Change(3, 3);
Console.WriteLine(o); //只改变了栈中的临时Point值(下式中显示写出临时变量o2) 2,2
Point o2 = (Point)o;
o2.Change(3, 3);
Console.WriteLine(o2); //2,2
((IChangeBoxedPoint)p).Change(4, 4); //同样 p先装箱生成临时变量,在堆中改变值,
Console.WriteLine(p); //依旧显示的是栈中的值 2,2
// IChangeBoxedPoint ipoint = (IChangeBoxedPoint)p;
// ipoint.Change(4,4);
// Console.WriteLine(ipoint);
((IChangeBoxedPoint)o).Change(5, 5); //o已经是引用类型,无需装箱
Console.WriteLine(o); //显示的是堆中的数据 5,5
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
internal interface IChangeBoxedPoint {
void Change(Int32 x,Int32 y);
}
internal struct Point : IChangeBoxedPoint
{
private Int32 x, y;
public Point(Int32 x, Int32 y)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public void Change(Int32 x, Int32 y)
{
this.x = x; this.y = y;
}
public override string ToString()
{
return "(" + x + "," + y + ")";
}
}
internal class pointClass
{
public string x;
public string y;
}
}
总结:在装箱和拆箱的过程中,无时无刻记住
1.装箱是值类型转化为引用类型
2.转化都有新的变量生成,装箱生成在栈中的对象和堆中的引用,拆箱生成栈中的数据变量