1、查看数据库及表属性:
1)查看所有数据库
SHOW DATABASES;
2)选择使用的数据库
USE <DATABASE_NAME>
3)查看当前数据库下面的表
SHOW TABLES;
4)选择使用的表
USE <TABLE_NAME>
5)查看表结构
DESC <TABLE_NAME>
6)查看数据库编码
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'CHARACTER_SET_DATABASE'
7)查看表编码
SHOW CREATE TABLE <TABLE_NAME>
8)查看表属性
SHOW TABLE STATUS FROM <table_name>
2、用户操作:
1)创建用户
create user 'test'@'localhost(127.0.0.1)' identified by '12345678'; 本地使用
create user 'test'@'%' identified by '12345678'; 任意IP使用
2)删除用户
drop uesr 'test'@'IP地址'
3)赋予权限
grant insert, create, update on db.test to 'test'@'IP地址';
grant all on *.* to 'test'@'ip地址 // 赋予除了grant 外的所有权限
4)查看权限
show grants for 'test'@'IP地址''
5)取消权限
revoke all on *.* from 'test'@'ip地址'
3、数据库操作
1)修改数据库密码
set password for root@localhost='12345678'
2)创建/删除数据库并制定编码
CREATE DATABASE <数据库名> character set utf8
drop database <数据库名>
3)修改数据库编码
ALTER DATABASE <database_name> DEFAULT CHARACTER SET UTF8 COLLATE utf8_bin
4、表操作
1)创建表并制定编码
create table <table name>(name varchar(50) not null comment '姓名', price double not null) ENGINE=InnoDB default charset=utf8
create table test(id int(5) not null auto_increment, dt date default null comment '日期', hour tinyint(2) default 0 comment '小时', primary key(id), unique key dt_hour(dt, hour)) engine=InnoDB auto_increment=1 default charset=utf8 comment='测试数据'
InnoDB支持事物,原子性操作。即在同一个事物中操作数据库,要么全成功,要么全失败。
2)修改表编码
ALTER TABLE <table_name> DEFAULT CHARACTER SET UTF8 COLLATE utf8_bin
3)修改表名
ALTER TABLE <table_name> RENAME <new_name>
4)复制表
复制表结构:
create table table1 like <tablename>
create table tb1 select * from tb2 where 1=2
复制表数据
insert into table1 select * from <tablename>
5、字段操作
1)添加列
ALTER TABLE <table_name> ADD COLUMN <column_name> <column_type>
alter table test add name varchar(30) not null, add age(3) int not null default(23);
alter table test add gender enum("male", "female") default "female" first;
2)修改列类型
ALTER TABLE <table_name> change<column_name> <column_type>
3)修改列名
ALTER TABLE <table_name> CHANGE COLUMN <column_name> <new_column_name> <new_column_type>
4)删除字段
alter table test drop gender;
5)添加外键
ALTER TABLE<表名> add constraint <外键名> foreign key <字段名> reference <外表表明>(<字段名>) ON DELETE CASECADE ON UPDATE CASECADE
ON DELETE CASECADE ON UPDATE CASECADE:它告诉数据库在主表记录删除时,该怎么做
CASECADE:主表和从表保证一致性,删除主表记录,从表记录自动删除
SET NULL:将删除有关的记录设置为NULL值
RESTRICT:不允许删除(这是默认设置,也是最安全的设置)
NO ACTION:啥也不做
6)删除外键
ALTER TABLE <表名> DROP FOREIGN KEY<外键名>
这里要注意,外键名,不是字段名,所以删除的时候,不能用数据库中的字段名作为删除时候的外键名,否则或报错
7)修改已有字段为联合主键
alter table test add primary key(id,name);
8)删除主键
alter table test drop primaty key;
9)数据库自增
create table test1(name varchar(20) not null, id int not null auto_increment primary key)
create table test2(nid int not null auto_increment, name varchar(20), index(nid)) engine=InnoDB auto_increment=2 default charset=utf8
对于自增列,必须是索引(含主键)
10)修改自增起始值
alter table test auto_increment =10
如果当前自增值已经大于了我们设置的这个值,那么这个值会被忽略。
11)联合主键
create table tb1(id int not null, name varchar(30) not null, primary key(id, varchar))
insert into tb1(id, name) select 1,'jone' union select 1, 'marry';
12)修改主键
alter table test modify id int not null primary key aotu_increment
13)删除主键
alter table test modify id int not null;
14)删除表/数据
drop table tb1 删除表数据及表结构,不支持事物回滚
delete from table 删除表中所有数据,每删除一行就会写入日志,所以是支持事物回滚的。
truncate table 删除速度快于delete,也是删除全部数据,但是不支持事务回滚
速度 drop>truncate>delete
6、数据查询
1)条件查询
select name,age from tb1 where age (not) between 20 and 25;
select name,age as p_age from tb1 where gender="male" and age>20;
2)NULL查询
select * from tb1 where name is (not) NULL
3)ifnull
select ifnull(name, '你猜') as name, age from tb1
当name为null的时候,ifnull函数会取下标为1的值
3)IN 查询
select * from tb1 where age=20 or age=30 or age=40 or age=50;
= select * from tb1 where age in (20,30,40,50);
4)模糊查询(like)
select * from tb1 where name like 'han%'
select * from tb1 where name like 'han_'
select * from tb1 where name like "%/_%" escape '/'
这里用到了三种通配符:
%:匹配任意多个字符
_:匹配任意一个字符(包括中文)
escape '/':'/' 斜线后面的那一个通配符作为不同字符使用,不再作为通配符。其他地方的通配符 仍旧作为通配符使用。
5)分页查询
select * from tb1 limit 10 // 取10条数据
select * from tb1 limit start, num // 从第start条开始取,向后取num条
select * from tb1 limit 10 offset 20 // 从第20条数据开始取,向后取10条
6)结果集排序
select * from tb1 order by id desc, age asc // desc:从大到小 asc:从小到大
select * from tb1 order by id desc limit 10 // 取后10条数据
7)分组查询 group by
分组函数规则:
1)select [聚合函数] 字段名 from <tablename>
[where 查询条件]
[group by 查询条件]
[having过滤条件]
2)出现在select子句中的单独列必须出现在group by子句中作为分组列
3)分组列中可以不出现在select子句中
4)分组列可以出现在select子句中的一个复合表达式中
5)如果group by后面是一个复合表达式,那么在select子句中,它必须整体作为一个表达式的部分才能使用
select year(d) as '年', month(d) as '月', day(d) as '日', date(d) as '日期', count(to_days(d)=to_days(now())) from tb2 group by tb2

8)group_concat()
返回的是一个组的所有值以逗号隔开的字符串
select year(d) as '年', group_concat(d) from tb2 group by year(d)
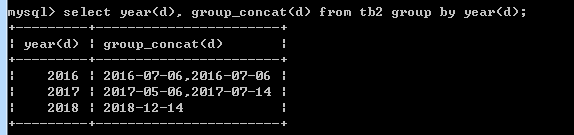
9)having 子句:对分组结果进行过滤
与where子句的区别:
where子句在分组前过滤; having在分组后过滤
不能在where子句中使用组函数,原因就是组函数只能在分组函数执行完成之后执行
having子句可以单独使用,不用和group by组合
如果有group by函数,则having子句中的列必须出现在group by函数中,或者是select子句的聚合函数。
10)去重复查询 distinct
select distinct * from tb1
7、数据插入
insert into tb1(字段1,字段2...) values(值1,值2...) , (值1,值2...), (值1, 值2)
insert into tb1(字段1,字段2...) select 字段1,字段2 from tb1
insert into tb1(字段1,字段2...) select 值1,值2 union select 值1,值2 union select 值1,值2;
时间插入 now()
create table tb2(d date, t time, dt datetime)
insert into tb2 values(now(), now(), now())
select * from tb2;

8、数据删除
delete from tb1 where ...
9、修改数据
update tb1 set 字段1='值1', 字段2='值2' where ...
10、聚合函数
常用的聚合函数有 count(), sum(), max(), min(), avg()
count():求个数
select count(*) from tb1 //求tb1表行数
select count(name) from tb1 // 求tb1表中name为非null 的行数 (为空的也算一个)
sum():求和
max():求最大值
min():求最小值
avg():求平均值
select sum(price), max(price) as '最贵', min(price) as '最便宜', avg(price) from tb1

11、多表相关查询
1)union:用于合并两个或多个select语句的结果集
使用union的各select语句必须拥有相同数量的列,且列的类型要相同。
union默认是去重的,如果要显示所有数据,需要用union all
union结果集中列名,总是使用第一个select语句的列名
2)JOIN:实现多表联合查询,默认是inner join
多表查询的时候,要注意多变之间的关联,否则会容易引起笛卡尔乘积现象
语法:
select 查询类别
from 表1 别名
join(连接类型) 表2 别名
on 连接条件
【where 筛选条件】
【group 分组】
【having 帅选条件】
【order by 排序列表】
内连接:inner join和等值连接效果是一样的。
join(inner join):返回匹配条件的数据项;连接条件放在on后面,筛选条件放在where后面。
select * from tb1 join tb2 on tb1.t_id = tb2.id
外连接:主要用于查询一个表中有,另一个表中没有的记录。
外连接查询的结果=内连接的结果+主表中有而从表中没有的记录。
如果从表中有和主表匹配的记录,则返回匹配的值
如果从表中没有和主表匹配的记录,则显示null
left join:左边是主表。返回join左侧的所有数据,join后边的表中如果没有匹配的数据,值设为为null
right join:右边是主表。返回join右侧的所有数据,join左侧的表中如果没有匹配的数据,值设为null
如查询没有学生的学校的名字
select sc.name from school sc left join student st on st.school_id = sc.id where st.school_id is null;
3)多表查询规则:
a)烦是可以使用table表名的地方,都可以使用一个(括号)括起来的join语句
select * from ((A join B on A.b_id=B.id) join C on B.id = C.b_id) on A.c_id=C.id
4)直接连表操作
select * from tb1, tb2 where tb1.tid = tb2.id
12、起别名 as或者空格
select s.name '学生名字',s1.name '学校名字' from student s, schools1 where s.school_id=s1.id;

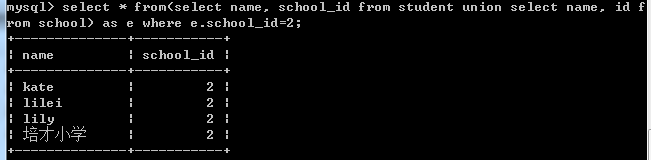
select * from (select name, school_id from student union select name, id from school) as e where e.school_id=2;
13、mysql 运算符
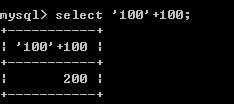
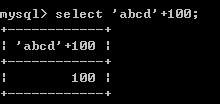
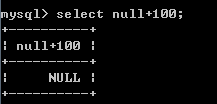
+-*/:数学运算 加 100+100-->200 '100'+100--->200 'abcd'+100--->100 null+100--->null
1)尝试将不是数字的字符串转化为数字
2)转化不了为数字的字符串为0
3)只要有一方为null,则结果为null

14、字符串连接 concat

说明:
char是定长字符串,varchar是变长字符串,char更快,varchar更节省空间,但是对于本身就是定长的如IP等,使用char就会比使用varchar好
创建数据库或者优化的时候,也应该把char放到前面,这样效率更高
参考资源:
https://blog.csdn.net/longting_/article/details/80658105
https://www.cnblogs.com/Jeffding/p/7535192.html
http://www.runoob.com/mysql/mysql-administration.html