Given a set of distinct integers, S, return all possible subsets.
Note:
- Elements in a subset must be in non-descending order.
- The solution set must not contain duplicate subsets.
For example,
If S = [1,2,3], a solution is:
[ [3], [1], [2], [1,2,3], [1,3], [2,3], [1,2], [] ]
该题和Combinations很类似,只不过是k需要从0到size中取值。
class Solution { private: vector<vector<int>> res; vector<int> s; public: void tra(int k,int start,int dep,vector<int> temp) { if(dep==k){ res.push_back(temp); return; } for(int i=start;i<s.size();++i){ temp.push_back(s[i]); tra(k,i+1,dep+1,temp);//是i+1,而不是start+1 temp.erase(temp.end()-1); } } vector<vector<int>> subsets(vector<int> &S) { s=S; sort(s.begin(),s.end()); vector<int> temp; for(int k=0;k<=s.size();++k){ tra(k,0,0,temp); } return res; } };
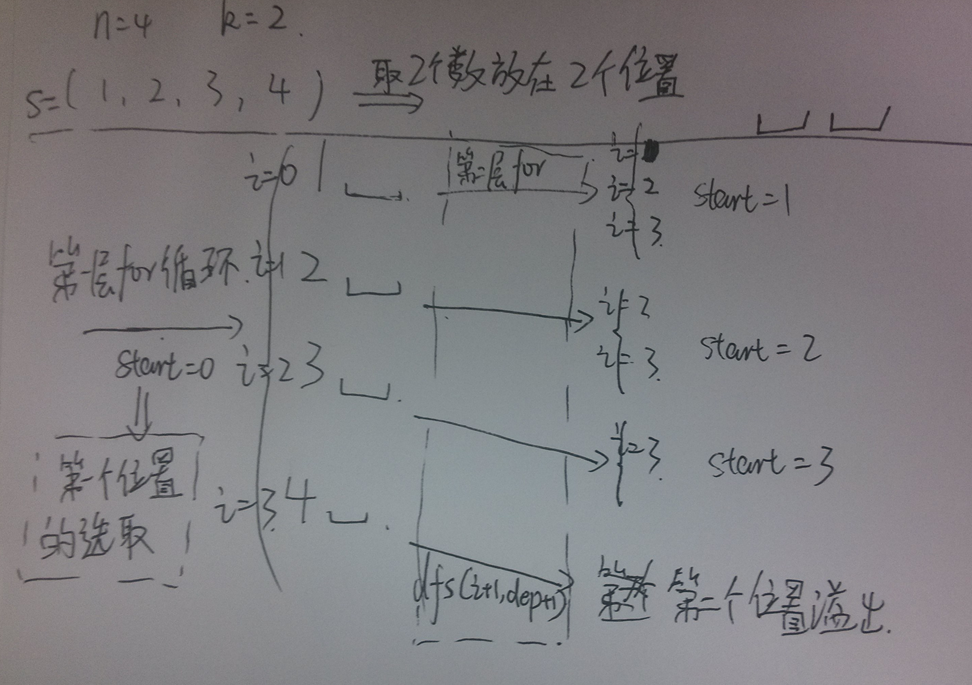
我的分析图:
Subsets 2
Given a collection of integers that might contain duplicates, S, return all possible subsets.
Note:
- Elements in a subset must be in non-descending order.
- The solution set must not contain duplicate subsets.
For example,
If S = [1,2,2], a solution is:
[ [2], [1], [1,2,2], [2,2], [1,2], [] ]
class Solution { private: vector<vector<int>> res; vector<int> s; public: void tra(int k,int start,int dep,vector<int> temp) { if(dep==k){ for (int i=0;i<res.size();++i) { if(res[i]==temp) return; } res.push_back(temp); return; } for(int i=start;i<s.size();++i){ temp.push_back(s[i]); tra(k,i+1,dep+1,temp); temp.erase(temp.end()-1); } } vector<vector<int>> subsetsWithDup(vector<int> &S) { s=S; sort(s.begin(),s.end()); vector<int> temp; res.push_back(temp); for(int k=1;k<=s.size();++k){ tra(k,0,0,temp); } return res; } };