PyTorch in Action: A Step by Step Tutorial
Installation Guide
Step 1, donwload the Miniconda and installing it on your computer.
The reason why explain installing conda is that some of classmates don`t have a conda environment on their computer.
https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/miniconda/
Step 2, create a conda virtual envriomment
In this ariticle, we assume that there is a CPU version of PyTorch is going to be installed. To specifically distinguish CPU version and GPU version, we`re going to create a virtual environment named "PyTorch-CPU".
In the Conda Prompt run the following commands:
conda create -n PyTorch-CPU pip
Step 3, install PyTorch
On the website of PyTorch(https://pytorch.org/), there is a guidance on the page. To chose the most appropriate options(e.g. as the follow figure).
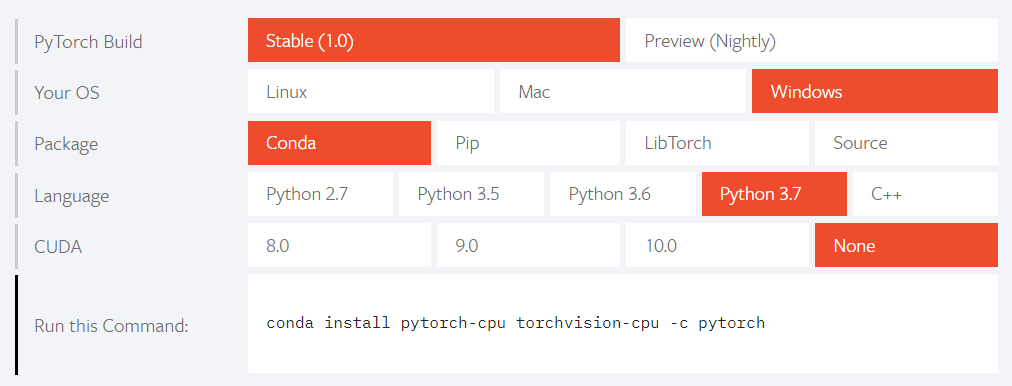
In the Conda Prompt run the following commands:
activate PyTorh-CPU
conda install pytorch-cpu torchvision-cpu -c pytorch
Congratulations, installation of PyTorch is complete!
Data Processing
Before we start ours building. We have to access the dataset and clean it.
Here we have accessed 西瓜数据集3.0. And we convert the character-described features to numeric.
# encoding:utf8
# 西瓜3.0 数据集
waterMelons = [
# 1
['青绿', '蜷缩', '浊响', '清晰', '凹陷', '硬滑', '好瓜'],
# 2
['乌黑', '蜷缩', '沉闷', '清晰', '凹陷', '硬滑', '好瓜'],
# 3
['乌黑', '蜷缩', '浊响', '清晰', '凹陷', '硬滑', '好瓜'],
# 4
['青绿', '蜷缩', '沉闷', '清晰', '凹陷', '硬滑', '好瓜'],
# 5
['浅白', '蜷缩', '浊响', '清晰', '凹陷', '硬滑', '好瓜'],
# 6
['青绿', '稍蜷', '浊响', '清晰', '稍凹', '软粘', '好瓜'],
# 7
['乌黑', '稍蜷', '浊响', '稍糊', '稍凹', '软粘', '好瓜'],
# 8
['乌黑', '稍蜷', '浊响', '清晰', '稍凹', '硬滑', '好瓜'],
# 9
['乌黑', '稍蜷', '沉闷', '稍糊', '稍凹', '硬滑', '坏瓜'],
# 10
['青绿', '硬挺', '清脆', '清晰', '平坦', '软粘', '坏瓜'],
# 11
['浅白', '硬挺', '清脆', '模糊', '平坦', '硬滑', '坏瓜'],
# 12
['浅白', '蜷缩', '浊响', '模糊', '平坦', '软粘', '坏瓜'],
# 13
['青绿', '稍蜷', '浊响', '稍糊', '凹陷', '硬滑', '坏瓜'],
# 14
['浅白', '稍蜷', '沉闷', '稍糊', '凹陷', '硬滑', '坏瓜'],
# 15
['乌黑', '稍蜷', '浊响', '清晰', '稍凹', '软粘', '坏瓜'],
# 16
['浅白', '蜷缩', '浊响', '模糊', '平坦', '硬滑', '坏瓜'],
# 17
['青绿', '蜷缩', '沉闷', '稍糊', '稍凹', '硬滑', '坏瓜']
]
features = list() # [[青绿, 乌黑, 浅白], [蜷缩, 硬挺...], ...]
def numeric(data):
l = list()
for i,s in enumerate(data):
val = features[i].index(s)
l.append(val)
return l
if __name__ == '__main__':
for melon in waterMelons:
for i, feature in enumerate(melon):
try:
if feature not in features[i]:
features[i].append(feature)
except IndexError:
features.append([feature])
f = open('data/WaterMelon.txt', encoding='utf8', mode='w')
for melon in waterMelons:
val = numeric(melon)
f.write("%s
" % val)
Your first Neural Network with PyTorch
Here we implement a neural network with input layer and log softmax layer.
There are 12 parameters need to be trained:
# encoding:utf8
import torch
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Model, self).__init__()
self.layer = torch.nn.Linear(6, 2)
self.softmax = torch.nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.layer(x)
out = self.softmax(out)
return out
if __name__ == '__main__':
x, y = list(), list()
with open('data/WaterMelon.txt', encoding='utf8') as f:
for line in f:
l = eval(line.strip())
x.append(l[:-1])
y.append(l[-1])
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=33)
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = torch.Tensor(x_train), torch.Tensor(x_test), torch.Tensor(y_train).long(), torch.Tensor(y_test).long()
model = Model()
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
criticism = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# train
for epoch in range(500):
out = model(x_train)
loss = criticism(out, y_train)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# test
y_pred = model(x_test)
_, predicted = torch.max(y_pred, 1)
acc = torch.sum(y_test == predicted ).numpy() / len(x_test)
print(acc)
We got the accuracy 0.8, sometimes we got 1.
LOL!