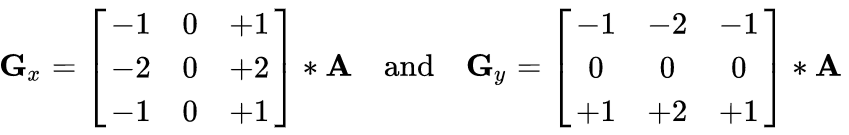一、图像梯度算法
1、图像梯度-Sobel算子
dst = cv2.Sobel(src, ddepth, dx, dy, ksize)
- ddepth:图像的深度
- dx和dy分别表示水平和竖直方向
- ksize是Sobel算子的大小
1 # *******************图像梯度算法**********************开始 2 import cv2 3 # import numpy as np 4 5 img = cv2.imread('pie.png',cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE) 6 cv2.imshow("img",img) 7 cv2.waitKey() 8 cv2.destroyAllWindows() 9 10 # 显示图像函数 11 def cv_show(img,name): 12 cv2.imshow(name,img) 13 cv2.waitKey() 14 cv2.destroyAllWindows() 15 16 # Sobel算子——x轴 17 sobelx = cv2.Sobel(img,cv2.CV_64F,1,0,ksize=3) # 计算水平的 18 cv_show(sobelx,'sobelx') 19 20 # 白到黑是正数,黑到白就是负数了,所有的负数会被截断成0,所以要取绝对值 21 sobelx = cv2.Sobel(img,cv2.CV_64F,1,0,ksize=3) 22 sobelx = cv2.convertScaleAbs(sobelx) # 取绝对值 23 cv_show(sobelx,'sobelx') 24 25 # Sobel算子——y轴 26 sobely = cv2.Sobel(img,cv2.CV_64F,0,1,ksize=3) 27 sobely = cv2.convertScaleAbs(sobely) # 取绝对值 28 cv_show(sobely,'sobely') 29 30 # 求和 31 sobelxy = cv2.addWeighted(sobelx,0.5,sobely,0.5,0) # 按权重计算 32 cv_show(sobelxy,'sobelxy') 33 34 # 也有直接计算xy轴的————不推荐使用 35 # sobelxy=cv2.Sobel(img,cv2.CV_64F,1,1,ksize=3) 36 # sobelxy = cv2.convertScaleAbs(sobelxy) 37 # cv_show(sobelxy,'sobelxy') 38 # *******************图像梯度算法**********************结束
用lena图像来实际操作一下:
1 # *******************图像梯度算法-实际操作**********************开始 2 import cv2 3 4 # 显示图像函数 5 def cv_show(img,name): 6 cv2.imshow(name,img) 7 cv2.waitKey() 8 cv2.destroyAllWindows() 9 10 img = cv2.imread('lena.jpg',cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE) 11 cv_show(img,'img') 12 13 # 分别计算x和y 14 img = cv2.imread('lena.jpg',cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE) 15 sobelx = cv2.Sobel(img,cv2.CV_64F,1,0,ksize=3) 16 sobelx = cv2.convertScaleAbs(sobelx) 17 sobely = cv2.Sobel(img,cv2.CV_64F,0,1,ksize=3) 18 sobely = cv2.convertScaleAbs(sobely) 19 sobelxy = cv2.addWeighted(sobelx,0.5,sobely,0.5,0) 20 cv_show(sobelxy,'sobelxy') 21 # *******************图像梯度算法-实际操作**********************结束


2、图像梯度-Scharr和Laplacian算子
(1)Scharr算子
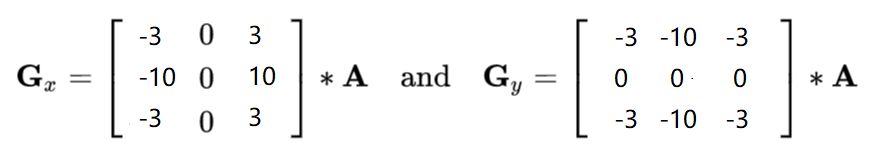
(2)Laplacian算子
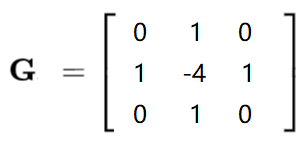
(3)不同算子之间的差距
1 # *******************图像梯度算子-Scharr+laplacian**********************开始 2 import cv2 3 import numpy as np 4 5 #不同算子的差异 6 img = cv2.imread('lena.jpg',cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE) 7 sobelx = cv2.Sobel(img,cv2.CV_64F,1,0,ksize=3) 8 sobely = cv2.Sobel(img,cv2.CV_64F,0,1,ksize=3) 9 sobelx = cv2.convertScaleAbs(sobelx) 10 sobely = cv2.convertScaleAbs(sobely) 11 sobelxy = cv2.addWeighted(sobelx,0.5,sobely,0.5,0) 12 13 scharrx = cv2.Scharr(img,cv2.CV_64F,1,0) 14 scharry = cv2.Scharr(img,cv2.CV_64F,0,1) 15 scharrx = cv2.convertScaleAbs(scharrx) 16 scharry = cv2.convertScaleAbs(scharry) 17 scharrxy = cv2.addWeighted(scharrx,0.5,scharry,0.5,0) 18 19 laplacian = cv2.Laplacian(img,cv2.CV_64F) 20 laplacian = cv2.convertScaleAbs(laplacian) 21 22 res = np.hstack((sobelxy,scharrxy,laplacian)) 23 24 # 显示图像函数 25 def cv_show(img,name): 26 cv2.imshow(name,img) 27 cv2.waitKey() 28 cv2.destroyAllWindows() 29 cv_show(res,'res') 30 # *******************图像梯度算子-Scharr+laplacian**********************结束
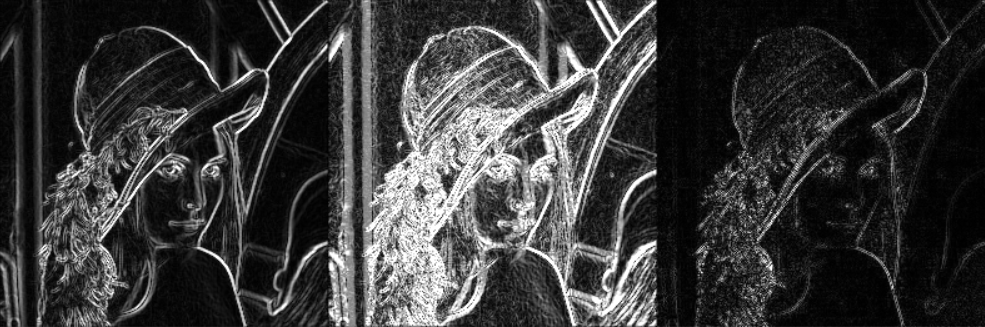
二、边缘检测
Canny边缘检测
-
1) 使用高斯滤波器,以平滑图像,滤除噪声。
-
2) 计算图像中每个像素点的梯度强度和方向。
-
3) 应用非极大值(Non-Maximum Suppression)抑制,以消除边缘检测带来的杂散响应。
-
4) 应用双阈值(Double-Threshold)检测来确定真实的和潜在的边缘。
-
5) 通过抑制孤立的弱边缘最终完成边缘检测。
1、高斯滤波器

2、梯度和方向
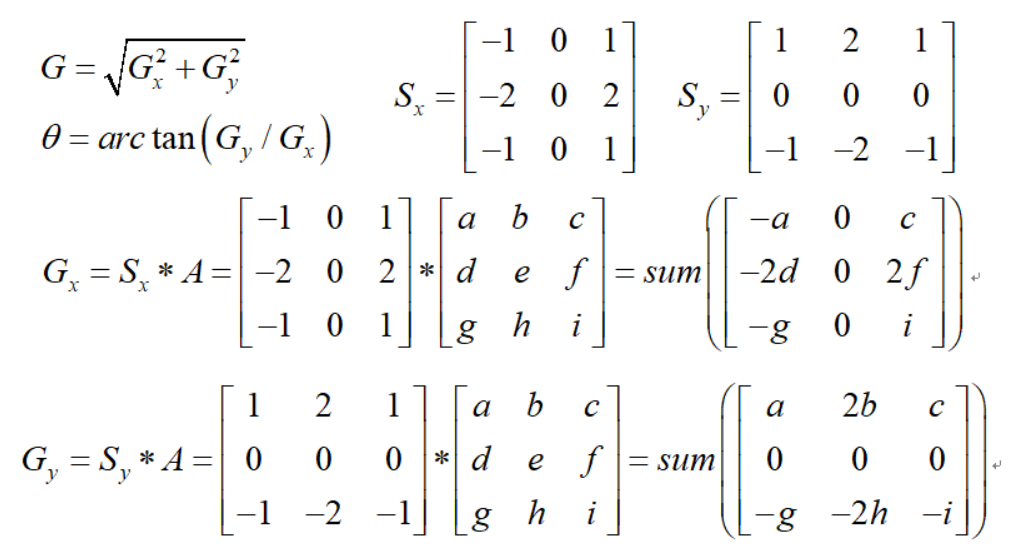
3、非极大值抑制


4、双阈值检测

1 # *******************边缘检测**********************开始 2 import cv2 3 import numpy as np 4 5 img=cv2.imread("lena.jpg",cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE) 6 7 v1=cv2.Canny(img,80,150) # 设置双阈值 最小和最大 8 v2=cv2.Canny(img,50,100) 9 10 res = np.hstack((v1,v2)) 11 12 # 显示图像函数 13 def cv_show(img,name): 14 cv2.imshow(name,img) 15 cv2.waitKey() 16 cv2.destroyAllWindows() 17 cv_show(res,'res') 18 # *******************边缘检测**********************结束

三、图像金字塔
1、高斯金字塔
(1)高斯金字塔:向下采样方法(缩小)

(2)高斯金字塔:向上采样方法(放大)
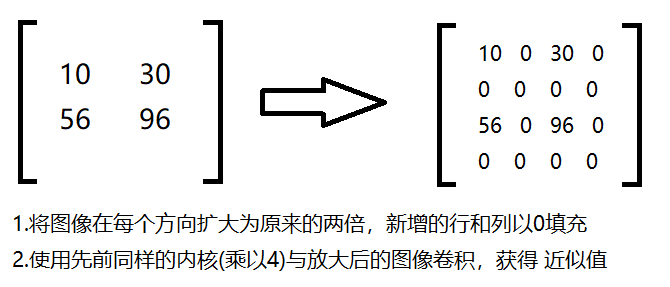
1 # *******************图像金字塔--高斯金字塔**********************开始 2 import cv2 3 import numpy as np 4 5 # 显示图像函数 6 def cv_show(img,name): 7 cv2.imshow(name,img) 8 cv2.waitKey() 9 cv2.destroyAllWindows() 10 11 img=cv2.imread("AM.png") 12 # cv_show(img,'img') 13 print (img.shape) 14 15 # 高斯金字塔-上采样 (可执行多次) 16 up=cv2.pyrUp(img) 17 # cv_show(up,'up') 18 print (up.shape) 19 20 # 高斯金字塔-下采样 (可执行多次) 21 down=cv2.pyrDown(img) 22 # cv_show(down,'down') 23 print (down.shape) 24 25 # 高斯金字塔-先上采样再下采样 (会损失信息-变模糊) 26 up=cv2.pyrUp(img) 27 up_down=cv2.pyrDown(up) 28 # cv_show(up_down,'up_down') 29 cv_show(np.hstack((img,up_down)),'up_down') 30 # *******************图像金字塔--高斯金字塔**********************结束

2、拉普拉斯金字塔
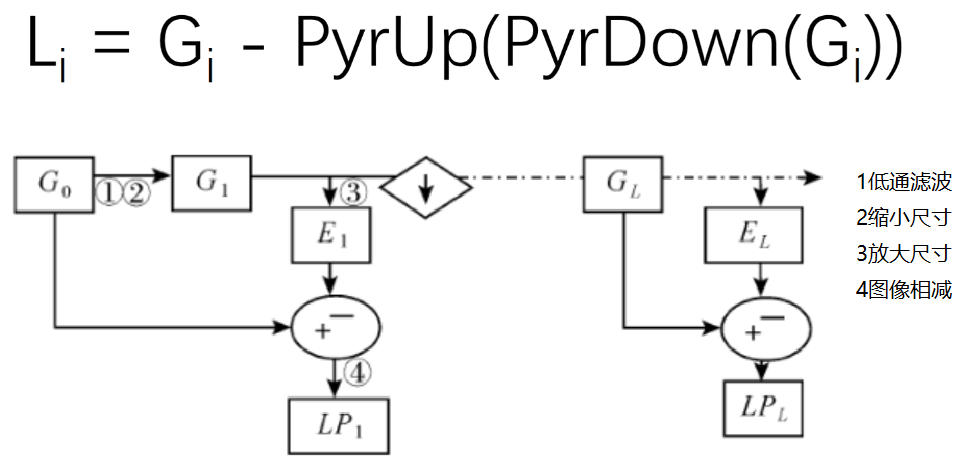
1 # *******************图像金字塔-拉普拉斯金字塔**********************开始 2 import cv2 3 import numpy as np 4 5 # 显示图像函数 6 def cv_show(img,name): 7 cv2.imshow(name,img) 8 cv2.waitKey() 9 cv2.destroyAllWindows() 10 11 img=cv2.imread("AM.png") 12 down=cv2.pyrDown(img) 13 down_up=cv2.pyrUp(down) 14 l_1=img-down_up 15 cv_show(l_1,'l_1') 16 # *******************图像金字塔-拉普拉斯金字塔**********************结束
四、图像轮廓
cv2.findContours(img,mode,method)
mode:轮廓检索模式
- RETR_EXTERNAL :只检索最外面的轮廓;
- RETR_LIST:检索所有的轮廓,并将其保存到一条链表当中;
- RETR_CCOMP:检索所有的轮廓,并将他们组织为两层:顶层是各部分的外部边界,第二层是空洞的边界;
- RETR_TREE:检索所有的轮廓,并重构嵌套轮廓的整个层次;
method:轮廓逼近方法
- CHAIN_APPROX_NONE:以Freeman链码的方式输出轮廓,所有其他方法输出多边形(顶点的序列)。
- CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE:压缩水平的、垂直的和斜的部分,也就是,函数只保留他们的终点部分。
为提高准确性,使用二值图像。
1、轮廓检测及绘制
1 # *******************图像轮廓**********************开始 2 import cv2 3 import numpy as np 4 5 # 读入图像转换为二值图像 6 img = cv2.imread('contours.png') 7 gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # 转换为灰度图 8 ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(gray, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) # 转换成二值图 9 10 # 显示图像函数 11 def cv_show(img,name): 12 cv2.imshow(name,img) 13 cv2.waitKey() 14 cv2.destroyAllWindows() 15 # cv_show(thresh,'thresh') 16 17 # 轮廓检测 第一个就是二值的结果 第二个是一堆轮廓点 第三个是层级 18 binary, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE) 19 20 # 绘制轮廓 21 draw_img = img.copy() # 注意需要copy,要不原图会变。。。 22 res = cv2.drawContours(draw_img, contours, -1, (0, 0, 255), 2) # 传入绘制图像,轮廓,轮廓索引(-1全部),颜色模式,线条厚度 23 # cv_show(res,'res') 24 25 draw_img = img.copy() 26 res = cv2.drawContours(draw_img, contours, 2, (0, 0, 255), 2) 27 cv_show(res,'res') 28 # *******************图像轮廓**********************结束

2、轮廓特征
1 import cv2 2 3 # 读入图像转换为二值图像 4 img = cv2.imread('contours.png') 5 gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # 转换为灰度图 6 ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(gray, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) # 转换成二值图 7 8 # 轮廓检测 第一个就是二值的结果 第二个是一堆轮廓点 第三个是层级 9 binary, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE) 10 11 # 绘制轮廓 12 draw_img = img.copy() 13 res = cv2.drawContours(draw_img, contours, 2, (0, 0, 255), 2) 14 15 # 轮廓特征 16 cnt = contours[0] # 获取轮廓 17 print(cv2.contourArea(cnt)) # 计算面积 18 print(cv2.arcLength(cnt, True)) # 计算周长,True表示闭合的
3、轮廓近似

1 import cv2 2 3 img = cv2.imread('contours2.png') 4 # 显示图像函数 5 def cv_show(img,name): 6 cv2.imshow(name,img) 7 cv2.waitKey() 8 cv2.destroyAllWindows() 9 10 # 二值+轮廓检测 11 gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) 12 ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(gray, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) 13 binary, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE) 14 cnt = contours[0] 15 # 轮廓绘制 16 draw_img = img.copy() 17 res = cv2.drawContours(draw_img, [cnt], -1, (0, 0, 255), 2) 18 # cv_show(res,'res') 19 20 # 轮廓近似 21 epsilon = 0.05*cv2.arcLength(cnt,True) 22 approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(cnt,epsilon,True) 23 24 draw_img = img.copy() 25 res = cv2.drawContours(draw_img, [approx], -1, (0, 0, 255), 2) 26 cv_show(res,'res')

(1)边界矩形
1 # *******************图像轮廓-边界矩形**********************开始 2 import cv2 3 4 # 显示图像函数 5 def cv_show(img,name): 6 cv2.imshow(name,img) 7 cv2.waitKey() 8 cv2.destroyAllWindows() 9 10 img = cv2.imread('contours.png') 11 12 gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) 13 ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(gray, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) 14 binary, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE) 15 cnt = contours[0] 16 17 # 边界矩形 18 x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(cnt) 19 img = cv2.rectangle(img,(x,y),(x+w,y+h),(0,255,0),2) 20 cv_show(img,'img') 21 # 轮廓面积与边界矩形比 22 area = cv2.contourArea(cnt) 23 x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(cnt) 24 rect_area = w * h 25 extent = float(area) / rect_area 26 print ('轮廓面积与边界矩形比',extent) 27 # *******************图像轮廓-边界矩形**********************结束
(2)外接圆
1 # 外接圆 2 (x,y),radius = cv2.minEnclosingCircle(cnt) 3 center = (int(x),int(y)) 4 radius = int(radius) 5 img = cv2.circle(img,center,radius,(0,255,0),2) 6 cv_show(img,'img')
五、傅里叶变换
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/19763358
1、傅里叶的作用
-
高频:变化剧烈的灰度分量,例如边界
-
低频:变化缓慢的灰度分量,例如一片大海
2、滤波
-
低通滤波器:只保留低频,会使得图像模糊
-
高通滤波器:只保留高频,会使得图像细节增强
opencv中主要就是cv2.dft()和cv2.idft(),输入图像需要先转换成np.float32 格式,得到的结果中频率为0的部分会在左上角,通常要转换到中心位置,通过shift变换。
3、傅里叶变换
1 # *******************傅里叶变换**********************开始 2 import numpy as np 3 import cv2 4 from matplotlib import pyplot as plt 5 6 img = cv2.imread('lena.jpg',0) 7 8 img_float32 = np.float32(img) 9 10 # 傅里叶变换 11 dft = cv2.dft(img_float32, flags = cv2.DFT_COMPLEX_OUTPUT) 12 dft_shift = np.fft.fftshift(dft) # 低频值移动到中间 13 14 # 对两通道进行转换——映射公式 15 magnitude_spectrum = 20*np.log(cv2.magnitude(dft_shift[:,:,0],dft_shift[:,:,1])) 16 17 plt.subplot(121),plt.imshow(img, cmap = 'gray') 18 plt.title('Input Image'), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([]) 19 plt.subplot(122),plt.imshow(magnitude_spectrum, cmap = 'gray') 20 plt.title('Magnitude Spectrum'), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([]) 21 plt.show() 22 # *******************傅里叶变换**********************结束

4、高通、低通滤波器
低通滤波器:
1 # *******************低通滤波器**********************开始 2 import numpy as np 3 import cv2 4 from matplotlib import pyplot as plt 5 6 img = cv2.imread('lena.jpg',0) 7 8 img_float32 = np.float32(img) 9 10 # 傅里叶变换 11 dft = cv2.dft(img_float32, flags = cv2.DFT_COMPLEX_OUTPUT) 12 dft_shift = np.fft.fftshift(dft) 13 14 rows, cols = img.shape 15 crow, ccol = int(rows/2) , int(cols/2) # 中心位置 16 17 # 低通滤波 18 mask = np.zeros((rows, cols, 2), np.uint8) # 掩码 19 mask[crow-30:crow+30, ccol-30:ccol+30] = 1 # 区域 20 21 # IDFT 22 fshift = dft_shift*mask # 掩码结合 23 f_ishift = np.fft.ifftshift(fshift) # 位置还原 24 img_back = cv2.idft(f_ishift) # 傅里叶逆变换 25 img_back = cv2.magnitude(img_back[:,:,0],img_back[:,:,1]) # 图像转换 26 27 plt.subplot(121),plt.imshow(img, cmap = 'gray') 28 plt.title('Input Image'), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([]) 29 plt.subplot(122),plt.imshow(img_back, cmap = 'gray') 30 plt.title('Result'), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([]) 31 32 plt.show() 33 # *******************低通滤波器**********************结束

高通滤波器:
1 # *******************高通滤波器**********************开始 2 import numpy as np 3 import cv2 4 from matplotlib import pyplot as plt 5 6 img = cv2.imread('lena.jpg',0) 7 8 img_float32 = np.float32(img) 9 10 dft = cv2.dft(img_float32, flags = cv2.DFT_COMPLEX_OUTPUT) 11 dft_shift = np.fft.fftshift(dft) 12 13 rows, cols = img.shape 14 crow, ccol = int(rows/2) , int(cols/2) # 中心位置 15 16 # 高通滤波 17 mask = np.ones((rows, cols, 2), np.uint8) # 掩码 18 mask[crow-30:crow+30, ccol-30:ccol+30] = 0 19 20 # IDFT 21 fshift = dft_shift*mask 22 f_ishift = np.fft.ifftshift(fshift) 23 img_back = cv2.idft(f_ishift) 24 img_back = cv2.magnitude(img_back[:,:,0],img_back[:,:,1]) 25 26 plt.subplot(121),plt.imshow(img, cmap = 'gray') 27 plt.title('Input Image'), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([]) 28 plt.subplot(122),plt.imshow(img_back, cmap = 'gray') 29 plt.title('Result'), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([]) 30 31 plt.show() 32 # *******************高通滤波器**********************结束