一.三元表达式 Ternary operator
Ternary operators also known as conditional expressions are operators that evaluate something based on a condition being true or false. It was added to Python in version 2.5. It simply allows to test a condition in a single line replacing the multiline if-else making the code compact.
[on_true] if [expression] else [on_false]
二.生成式
列表生成式
[x for x in data if condition]
[exp1 if condition else exp2 for x in data]
字典生成式
#d = {key: value for (key, value) in iterable}
d1 = {‘x‘: 1, ‘y‘: 2, ‘z‘: 3}
d2 = {k: v for (k, v) in d1.items()}
print(d2)
集合生成式
s1={x for x in range(10)}
print(s1)
三.生成器 Generator
Generator functions are a special kind of function that return a lazy iterator. These are objects that you can loop over like a list. However, unlike lists, lazy iterators do not store their contents in memory.
Example 1: Reading Large Files
csv_gen = (row for row in open(file_name))
This is a more succinct way to create the list csv_gen. You’ll learn more about the Python yield statement soon. For now, just remember this key difference:
-
Using yield will result in a generator object.
-
Using return will result in the first line of the file only.
Example 2: Generating an Infinite Sequence
>>> gen = infinite_sequence()
>>> next(gen)
0
>>> next(gen)
1
>>> next(gen)
2
>>> next(gen)
3
Here, you have a generator called gen, which you manually iterate over by repeatedly calling next(). This works as a great sanity check to make sure your generators are producing the output you expect.
四.函数的递归调用 Recursive functions
What is recursion?
Recursion is the process of defining something in terms of itself.
A physical world example would be to place two parallel mirrors facing each other. Any object in between them would be reflected recursively.
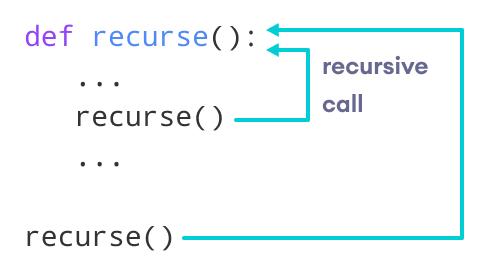
Python Recursive Function
In Python, we know that a function can call other functions. It is even possible for the function to call itself. These types of construct are termed as recursive functions.
The following image shows the working of a recursive function called recurse
Advantages of Recursion
Recursive functions make the code look clean and elegant. A complex task can be broken down into simpler sub-problems using recursion. Sequence generation is easier with recursion than using some nested iteration.
Disadvantages of Recursion
Sometimes the logic behind recursion is hard to follow through. Recursive calls are expensive (inefficient) as they take up a lot of memory and time. Recursive functions are hard to debug.
五 匿名函数 anonymous function
A lambda function is a small anonymous function.
A lambda function can take any number of arguments, but can only have one expression.
Syntax
lambda arguments : expression
Example:
x = lambda a, b, c: a + b + c
print(x(5, 6, 2))
Why Use Lambda Functions?
Why Use Lambda Functions? The power of lambda is better shown when you use them as an anonymous function inside another function.
def myfunc(n):
return lambda a : a * n
mydoubler = myfunc(5)
print(mydoubler(333))
Use lambda functions when an anonymous function is required for a short period of time.
六 面向过程的编程
POP 面向过程
POP, refers to Procedural Oriented Programming and its deals with programs and functions. Programs are divided into functions and data is global.
OOP 面向对象
OOP, refers to Object Oriented Programming and its deals with objects and their properties. Major concepts of OOPs are −
-
Class/objects 类/对象
-
Abstraction 抽象
-
Encapsulation /ɪnˌkæpsjuˈleɪʃn/ 封装
-
Polymorphism /,pɒlɪ'mɔːfɪzəm/ 多态
-
Inheritance 继承