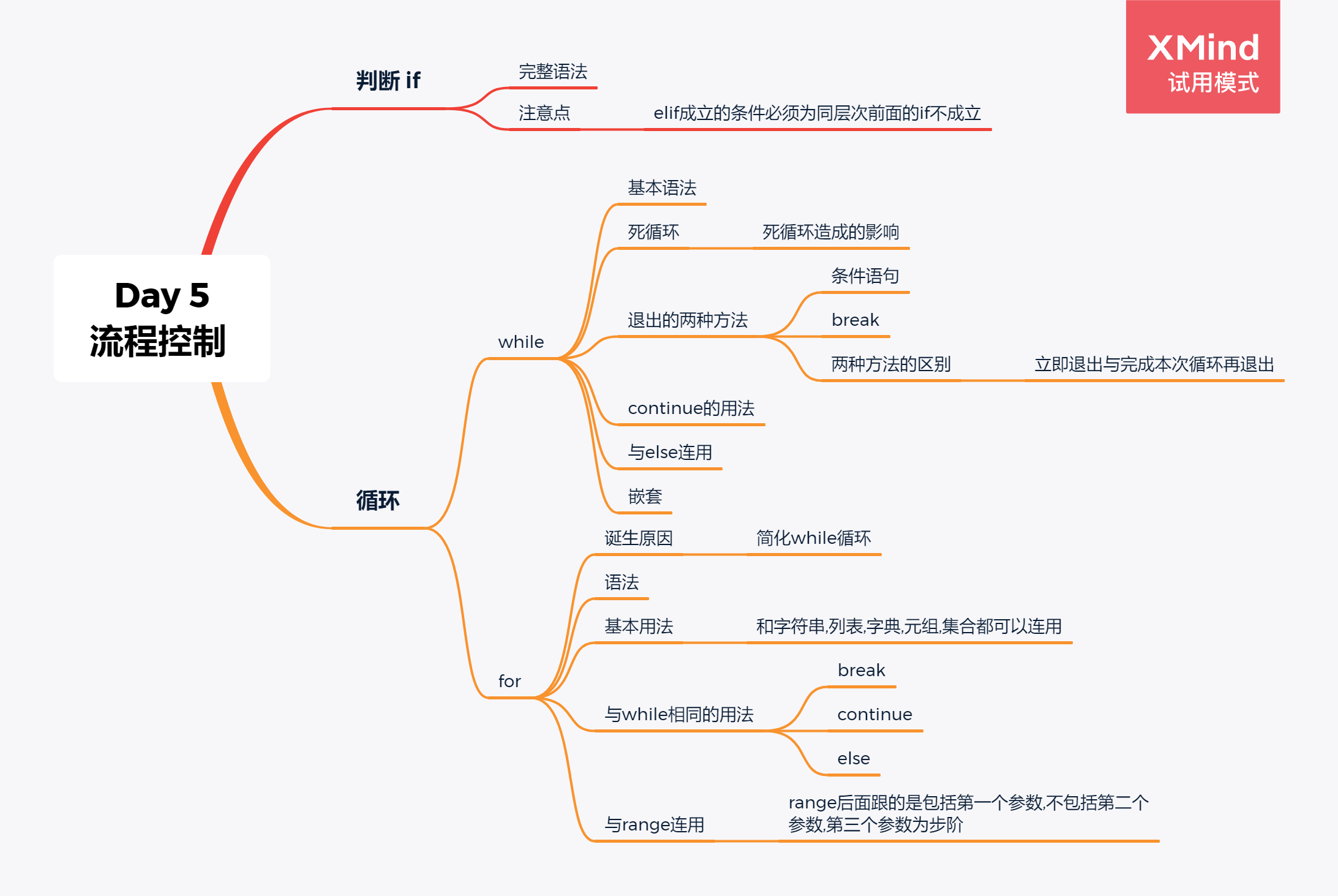
复习 if判断 If...else...
1.基本用法
完整语法
if condition:
statements1
elif condition:
statements2
else:
statements3
2.注意点
elif条件成立的前提一定是同层次前一句if不成立
一 while循环 while loops
Python has two primitive loop commands:
-
while loops
-
for loops
With the while loop we can execute a set of statements as long as a condition is true.
1.基本用法
语法
while condition:
statements
The while loop requires relevant variables to be ready, in this example we need to define an indexing variable, i, which we set to 1.
例1:打印0~5的整数
方法一:
i = 0
tag=True
while tag:
if i==5:
tag=False
print(i)
i += 1
方法二(另一种逻辑):
i = 0
tag=True
while tag:
print(i)
i += 1
if i==6:
tag=False
方法三(精简):
i = 0
while i <= 5:
print(i)
i += 1
2.死循环
永远不会结束的循环
死循环本身没有问题,但是如果死循环中没有I/O,只有纯运算,会消耗大量CPU
3.结束while循环的两种方式
方法一:条件给为false,见例1代码
特点:不会马上退出循环
方法二:使用break语句
特点:马上就退出循环,不会执行本层循环余下的语句
With the break statement we can stop the loop even if the while condition is true:
i = 0
while True:
if i==6:
break
print(i)
i += 1
例2:登陆接口(实现输错3次结束)
count = 0
while count < 3:
inp_username = input("请输入用户名:")
inp_passwd = input("请输入密码:")
if inp_username == "egon" and inp_passwd == "666":
print("登陆成功")
break
else:
print("登陆失败")
count += 1
登陆接口进阶版
count = 0
while count < 3:
inp_username = input("请输入用户名:")
inp_passwd = input("请输入密码:")
if inp_username == "egon" and inp_passwd == "666":
print("登陆成功")
while True:
print("""
1 取款
2 存款
3 转账
0 退出
""")
choice = input("请输入您的命令编号:")
if choice == "0":
break
elif choice == "1":
print("正在取款")
elif choice == "2":
print("正在存款")
elif choice == "3":
print("正在转账")
break
else:
print("登陆失败")
count += 1
4.continue的用法
用于结束本次循环
注意点:continue同级别之后千万不能写代码,写了也不会运行
With the continue statement we can stop the current iteration, and continue with the next:
例3:打印0,1,3,,5
逻辑1:(by Egon)
i = 0
while i < 6:
if i == 2 or i == 4:
i += 1
continue
print(i)
i += 1
逻辑2:(by myself)
i = -1
while i < 5:
i += 1
if i == 2 or i == 4:
continue
print(i)
5.while和else连用
With the else statement we can run a block of code once when the condition no longer is true:
用途:例,用于登录验证,多个用户和文件中的比对
二 for循环 for loops
A for loop is used for iterating over a sequence (that is either a list, a tuple, a dictionary, a set, or a string)
This is less like the for keyword in other programming languages, and works more like an iterator method as found in other object-orientated programming languages.
With the for loop we can execute a set of statements, once for each item in a list, tuple, set etc.
1.诞生原因
简化while循环
例4:打印列表中的内容
方法一:使用while循环
name = ["a", "b", "c", "d", "e"]
i = 0
while i < len(name):
print(name[i])
i += 1
方法二:使用for循环
name=["a","b","c","d","e"]
for i in name:
print(i)
2.语法
for iterating_var in sequence:
statements(s)
和字符串,列表,字典,元组,集合都可以连用
3.基本用法
例5:打印列表中的内容
dict = {"k1": "111", "k2": "222", "k3": "333"}
for x in dict:
print(x, dict[x])
4.与while相同用法
-
for+break
-
for+continue
-
for+else
5.range(a,b,c)用法
range后面跟的是包括第一个参数,不包括第二个参数,第三个参数为步阶
To loop through a set of code a specified number of times, we can use the range() function,
The range() function returns a sequence of numbers, starting from 0 by default, and increments by 1 (by default), and ends at a specified number.
The range() function defaults to increment the sequence by 1, however it is possible to specify the increment value by adding a third parameter: range(2, 30, 3):
补充:
IO密集型与计算密集型
涉及到网络运行有交互的,例如qq,微信,王者荣耀的基本为IO密集型
视频转码,挖比特币等大量涉及计算操作的为计算密集型
二手东
https://www.zhihu.com/question/28486591