问题的提出:
我们在访问淘宝,京东这些商城系统的时候,我们可以随意的在文本框输入关键字就可以获取到所想要的信息或者相关的信息,那么我们到底是如何实现这个功能的呢,为什么可以随意的输入就可以显示相关的信息。
其实我们在进行搜索服务的时候,都是想好的关键字,而这些存储在数据库中的关键字已经被luncence进行了检索管理,比如一个商品描述的大文本,有很多文字,luncence已经将这些文字分片分离,所以我们在搜索的时候出发它的确不包含这些文字,否则一般都是可以搜索到相关内容的。
下面转载了一篇关于luncence的文章:
1. Solr 是什么?
Solr它是一种开放源码的、基于 Lucene Java 的搜索服务器,易于加入到 Web 应用程序中。Solr 提供了层面搜索(就是统计)、命中醒目显示并且支持多种输出格式(包括XML/XSLT 和JSON等格式)。它易于安装和配置,而且附带了一个基于HTTP 的管理界面。可以使用 Solr 的表现优异的基本搜索功能,也可以对它进行扩展从而满足企业的需要。Solr的特性包括:
- 高级的全文搜索功能
- 专为高通量的网络流量进行的优化
- 基于开放接口(XML和HTTP)的标准
- 综合的HTML管理界面
- 可伸缩性-能够有效地复制到另外一个Solr搜索服务器
- 使用XML配置达到灵活性和适配性
- 可扩展的插件体系
2. Lucene 是什么?
Lucene是一个基于Java的全文信息检索工具包,它不是一个完整的搜索应用程序,而是为你的应用程序提供索引和搜索功能。Lucene 目前是 Apache Jakarta(雅加达) 家族中的一个开源项目。也是目前最为流行的基于Java开源全文检索工具包。目前已经有很多应用程序的搜索功能是基于 Lucene ,比如Eclipse 帮助系统的搜索功能。Lucene能够为文本类型的数据建立索引,所以你只要把你要索引的数据格式转化的文本格式,Lucene 就能对你的文档进行索引和搜索。
3. Solr vs Lucene
Solr与Lucene 并不是竞争对立关系,恰恰相反Solr 依存于Lucene,因为Solr底层的核心技术是使用Lucene 来实现的,Solr和Lucene的本质区别有以下三点:搜索服务器,企业级和管理。Lucene本质上是搜索库,不是独立的应用程序,而Solr是。Lucene专注于搜索底层的建设,而Solr专注于企业应用。Lucene不负责支撑搜索服务所必须的管理,而Solr负责。所以说,一句话概括 Solr: Solr是Lucene面向企业搜索应用的扩展。
Solr与Lucene架构图:
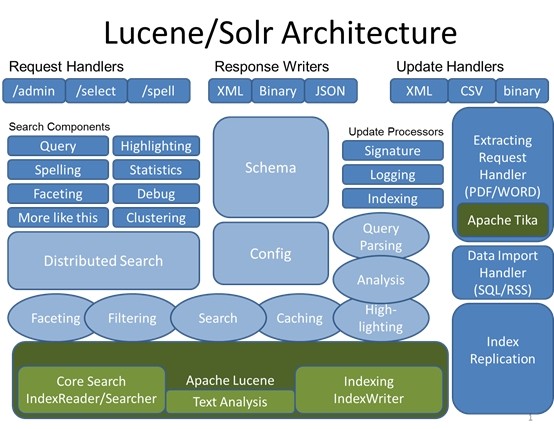
Solr使用Lucene并且扩展了它!
- 一个真正的拥有动态字段(Dynamic Field)和唯一键(Unique Key)的数据模式(Data Schema)
- 对Lucene查询语言的强大扩展!
- 支持对结果进行动态的分组和过滤
- 高级的,可配置的文本分析
- 高度可配置和可扩展的缓存机制
- 性能优化
- 支持通过XML进行外部配置
- 拥有一个管理界面
- 可监控的日志
- 支持高速增量式更新(Fast incremental Updates)和快照发布(Snapshot Distribution)
首先呢,学习任何一门新的亦或是旧的开源技术,百度其中一二是最简单的办法,先了解其中的大概,思想等等。这里就贡献一个讲解很到位的ppt。已经被我转成了PDF,便于搜藏。
其次,关于第一次编程初探,建议还是查看官方资料。百度到的资料,目前Lucene已经更新到4.9版本,这个版本需要1.7以上的JDK,所以如果还用1.6甚至是1.5的小盆友,请参考低版本,由于我用的1.6,因此在使用Lucene4.0。
这是Lucene4.0的官网文档:http://lucene.apache.org/core/4_0_0/core/overview-summary.html
这里非常佩服Lucene的开元贡献者,可以阅读Lucene in Action,作者最初想要写软件赚钱,最后贡献给了Apache,跑题了。
最后,提醒学习Lucene的小盆友们,这个开源软件的版本更新不慢,版本之间的编程风格亦是不同,所以如果百度到的帖子,可能这段代码,用了4.0或者3.6就会不好使。
比如,以前版本的申请IndexWriter时,是这样的:
IndexWriter indexWriter = new IndexWriter(indexDir,luceneAnalyzer, true );
但是4.0,我们需要配置一个conf,把配置内容放到这个对象中:
IndexWriterConfig config = new IndexWriterConfig(Version.LUCENE_CURRENT, analyzer);
IndexWriter iwriter = new IndexWriter(directory, config);
所以,请一定要参考官方文档的编程风格,进行代码的书写。
最后的最后,从官网上面下载下来的文件,已经上传至百度网盘,欢迎下载。

这是其中最常用的五个文件:
第一个,也是最重要的,Lucene-core-4.0.0.jar,其中包括了常用的文档,索引,搜索,存储等相关核心代码。
第二个,Lucene-analyzers-common-4.0.0.jar,这里面包含了各种语言的词法分析器,用于对文件内容进行关键字切分,提取。
第三个,Lucene-highlighter-4.0.0.jar,这个jar包主要用于搜索出的内容高亮显示。
第四个和第五个,Lucene-queryparser-4.0.0.jar,提供了搜索相关的代码,用于各种搜索,比如模糊搜索,范围搜索,等等。
废话说到这里,下面我们简单的讲解一下什么是全文检索。
比如,我们一个文件夹中,或者一个磁盘中有很多的文件,记事本、world、Excel、pdf,我们想根据其中的关键词搜索包含的文件。例如,我们输入Lucene,所有内容含有Lucene的文件就会被检查出来。这就是所谓的全文检索。
因此,很容易的我们想到,应该建立一个关键字与文件的相关映射,盗用ppt中的一张图,很明白的解释了这种映射如何实现。
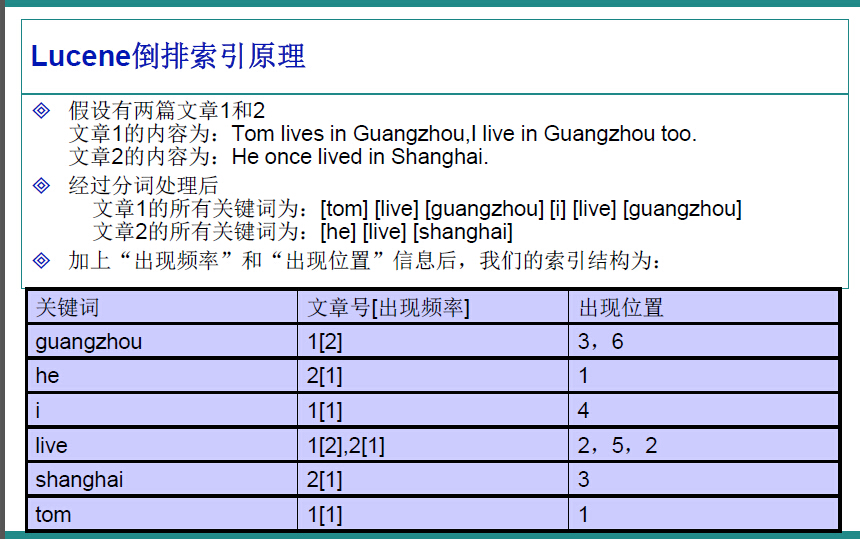
在Lucene中,就是使用这种“倒排索引”的技术,来实现相关映射。
有了这种映射关系,我们就来看看Lucene的架构设计。
下面是Lucene的资料必出现的一张图,但也是其精髓的概括。
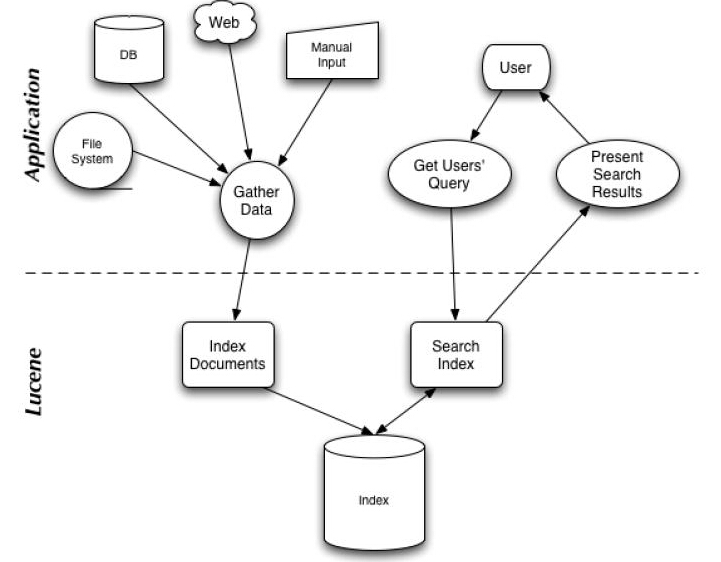
我们可以看到,Lucene的使用主要体现在两个步骤:
1 创建索引,通过IndexWriter对不同的文件进行索引的创建,并将其保存在索引相关文件存储的位置中。
2 通过索引查寻关键字相关文档。
下面针对官网上面给出的一个例子,进行分析:
1 Analyzer analyzer = new StandardAnalyzer(Version.LUCENE_CURRENT);
2
3 // Store the index in memory:
4 Directory directory = new RAMDirectory();
5 // To store an index on disk, use this instead:
6 //Directory directory = FSDirectory.open("/tmp/testindex");
7 IndexWriterConfig config = new IndexWriterConfig(Version.LUCENE_CURRENT, analyzer);
8 IndexWriter iwriter = new IndexWriter(directory, config);
9 Document doc = new Document();
10 String text = "This is the text to be indexed.";
11 doc.add(new Field("fieldname", text, TextField.TYPE_STORED));
12 iwriter.addDocument(doc);
13 iwriter.close();
14
15 // Now search the index:
16 DirectoryReader ireader = DirectoryReader.open(directory);
17 IndexSearcher isearcher = new IndexSearcher(ireader);
18 // Parse a simple query that searches for "text":
19 QueryParser parser = new QueryParser(Version.LUCENE_CURRENT, "fieldname", analyzer);
20 Query query = parser.parse("text");
21 ScoreDoc[] hits = isearcher.search(query, null, 1000).scoreDocs;
22 assertEquals(1, hits.length);
23 // Iterate through the results:
24 for (int i = 0; i < hits.length; i++) {
25 Document hitDoc = isearcher.doc(hits[i].doc);
26 assertEquals("This is the text to be indexed.", hitDoc.get("fieldname"));
27 }
28 ireader.close();
29 directory.close();
索引的创建
首先,我们需要定义一个词法分析器。
比如一句话,“我爱我们的中国!”,如何对他拆分,扣掉停顿词“的”,提取关键字“我”“我们”“中国”等等。这就要借助的词法分析器Analyzer来实现。这里面使用的是标准的词法分析器,如果专门针对汉语,还可以搭配paoding,进行使用。
1 Analyzer analyzer = new StandardAnalyzer(Version.LUCENE_CURRENT);
参数中的Version.LUCENE_CURRENT,代表使用当前的Lucene版本,本文环境中也可以写成Version.LUCENE_40。
第二步,确定索引文件存储的位置,Lucene提供给我们两种方式:
1 本地文件存储
Directory directory = FSDirectory.open("/tmp/testindex");
2 内存存储
Directory directory = new RAMDirectory();
可以根据自己的需要进行设定。
第三步,创建IndexWriter,进行索引文件的写入。
IndexWriterConfig config = new IndexWriterConfig(Version.LUCENE_CURRENT, analyzer); IndexWriter iwriter = new IndexWriter(directory, config);
这里的IndexWriterConfig,据官方文档介绍,是对indexWriter的配置,其中包含了两个参数,第一个是目前的版本,第二个是词法分析器Analyzer。
第四步,内容提取,进行索引的存储。
Document doc = new Document();
String text = "This is the text to be indexed.";
doc.add(new Field("fieldname", text, TextField.TYPE_STORED));
iwriter.addDocument(doc);
iwriter.close();
第一行,申请了一个document对象,这个类似于数据库中的表中的一行。
第二行,是我们即将索引的字符串。
第三行,把字符串存储起来(因为设置了TextField.TYPE_STORED,如果不想存储,可以使用其他参数,详情参考官方文档),并存储“表明”为"fieldname".
第四行,把doc对象加入到索引创建中。
第五行,关闭IndexWriter,提交创建内容。
这就是索引创建的过程。
关键字查询:
第一步,打开存储位置
DirectoryReader ireader = DirectoryReader.open(directory);
第二步,创建搜索器
IndexSearcher isearcher = new IndexSearcher(ireader);
第三步,类似SQL,进行关键字查询
QueryParser parser = new QueryParser(Version.LUCENE_CURRENT, "fieldname", analyzer);
Query query = parser.parse("text");
ScoreDoc[] hits = isearcher.search(query, null, 1000).scoreDocs;
assertEquals(1, hits.length);
for (int i = 0; i < hits.length; i++) {
Document hitDoc = isearcher.doc(hits[i].doc);
assertEquals("This is the text to be indexed.",hitDoc.get("fieldname"));
}
这里,我们创建了一个查询器,并设置其词法分析器,以及查询的“表名“为”fieldname“。查询结果会返回一个集合,类似SQL的ResultSet,我们可以提取其中存储的内容。
关于各种不同的查询方式,可以参考官方手册,或者推荐的PPT
第四步,关闭查询器等。
ireader.close(); directory.close();
最后,博猪自己写了个简单的例子,可以对一个文件夹内的内容进行索引的创建,并根据关键字筛选文件,并读取其中的内容。
创建索引:
/**
* 创建当前文件目录的索引
* @param path 当前文件目录
* @return 是否成功
*/
public static boolean createIndex(String path){
Date date1 = new Date();
List<File> fileList = getFileList(path);
for (File file : fileList) {
content = "";
//获取文件后缀
String type = file.getName().substring(file.getName().lastIndexOf(".")+1);
if("txt".equalsIgnoreCase(type)){
content += txt2String(file);
}else if("doc".equalsIgnoreCase(type)){
content += doc2String(file);
}else if("xls".equalsIgnoreCase(type)){
content += xls2String(file);
}
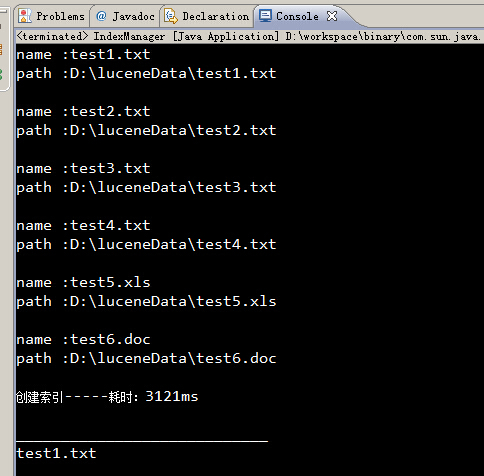
System.out.println("name :"+file.getName());
System.out.println("path :"+file.getPath());
// System.out.println("content :"+content);
System.out.println();
try{
analyzer = new StandardAnalyzer(Version.LUCENE_CURRENT);
directory = FSDirectory.open(new File(INDEX_DIR));
File indexFile = new File(INDEX_DIR);
if (!indexFile.exists()) {
indexFile.mkdirs();
}
IndexWriterConfig config = new IndexWriterConfig(Version.LUCENE_CURRENT, analyzer);
indexWriter = new IndexWriter(directory, config);
Document document = new Document();
document.add(new TextField("filename", file.getName(), Store.YES));
document.add(new TextField("content", content, Store.YES));
document.add(new TextField("path", file.getPath(), Store.YES));
indexWriter.addDocument(document);
indexWriter.commit();
closeWriter();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
content = "";
}
Date date2 = new Date();
System.out.println("创建索引-----耗时:" + (date2.getTime() - date1.getTime()) + "ms
");
return true;
}
进行查询:
/**
* 查找索引,返回符合条件的文件
* @param text 查找的字符串
* @return 符合条件的文件List
*/
public static void searchIndex(String text){
Date date1 = new Date();
try{
directory = FSDirectory.open(new File(INDEX_DIR));
analyzer = new StandardAnalyzer(Version.LUCENE_CURRENT);
DirectoryReader ireader = DirectoryReader.open(directory);
IndexSearcher isearcher = new IndexSearcher(ireader);
QueryParser parser = new QueryParser(Version.LUCENE_CURRENT, "content", analyzer);
Query query = parser.parse(text);
ScoreDoc[] hits = isearcher.search(query, null, 1000).scoreDocs;
for (int i = 0; i < hits.length; i++) {
Document hitDoc = isearcher.doc(hits[i].doc);
System.out.println("____________________________");
System.out.println(hitDoc.get("filename"));
System.out.println(hitDoc.get("content"));
System.out.println(hitDoc.get("path"));
System.out.println("____________________________");
}
ireader.close();
directory.close();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
Date date2 = new Date();
System.out.println("查看索引-----耗时:" + (date2.getTime() - date1.getTime()) + "ms
");
}
全部代码:
 View Code
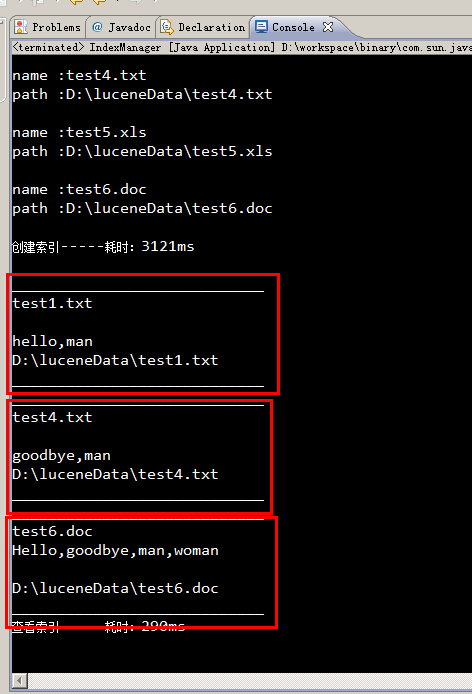
View Code运行结果:
所有包含man关键字的文件,都被筛选出来了。