自己一直学习计算机视觉方面的东西,现在想学习一下数据挖掘跟搜索引擎,自己基础也有点薄弱,看朱明的那本数据挖掘,只能片面的了解这个数据挖掘。不过最近有一本书 机器学习实战,于是乎通过实战的形式了解一下基本的算法的执行过程。
在算法当中,很多都是相通的,模式识别、机器学习、数据挖掘、自然语言处理等等这些算法归结起来其实差不了多少,题外话不多说了,好好学习。
k近邻算法
对于这个算法,我用自己的话来描述一下,就是把一个未知数与所有已有的数据样本求距离,对距离进行排序,取前k个数,这k这个数中,那个类别多,那这个未知数就属于哪个类别。
不用说,大家也知道这个k的选取还是很重要的。先用书上最简单的例子表述一下。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -* from numpy import * import operator def createDataSet(): group = array([[1.0,1.1],[1.0,1.0],[0,0],[0,0.1]]) labels = ['A','A','B','B'] return group, labels def classify0(inX, dataSet, labels, k): #行的个数也就是训练集的个数 dataSetSize = dataSet.shape[0] print ('dataSetSize:',dataSetSize) #tile表示将输入向量inX在行方向上重复dataSetSize次,在列的方向上重复1次,具体就是构建一个跟训练集对应的数组大小,相减就是为了求距离 diffMat = tile(inX,(dataSetSize,1)) - dataSet print('diffMat:',diffMat) sqDiffMat = diffMat**2 print('sqDiffMat:',sqDiffMat) #sum默认axis=0为普通相加,axis=1为矩阵的每一个行向量相加 sqDistances = sqDiffMat.sum(axis=1) print('sqDistances:',sqDistances) distances = sqDistances**0.5 print('distances:',distances) sortedDistIndicies = distances.argsort() print('sortedDistIndicies:',sortedDistIndicies) #定义一个词典 classCount={} #range(k) 为[0,1,2....k-1] print('labels:',labels) for i in range(k): voteIlabel = labels[sortedDistIndicies[i]]#获得最小的k个长度 #get 返回键值key对应的值;如果key没有在字典里,则返回default参数的值,这边default是0,功能计算每个标签类别的个数 classCount[voteIlabel] = classCount.get(voteIlabel,0) + 1 #sorted 排序是产生一个新的列表,sort是在原有基础上排序,key按第一个域进行排序,Ture为逆序 print('classCount:',classCount) sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.iteritems(),key=operator.itemgetter(1),reverse=True) print('sortedClassCount:',sortedClassCount) return sortedClassCount[0][0]
这边我已经将要解释的地方标识了。
下面就是运行,运行结果如下:
1: >>> import kNN
2: >>> group,labels = kNN.createDataSet()
3: >>> kNN.classify0([0,0],group,labels,3)
4: ('dataSetSize:', 4L)
5: ('diffMat:', array([[-1. , -1.1],
6: [-1. , -1. ],
7: [ 0. , 0. ],
8: [ 0. , -0.1]]))
9: ('sqDiffMat:', array([[ 1. , 1.21],
10: [ 1. , 1. ],
11: [ 0. , 0. ],
12: [ 0. , 0.01]]))
13: ('sqDistances:', array([ 2.21, 2. , 0. , 0.01]))
14: ('distances:', array([ 1.48660687, 1.41421356, 0. , 0.1 ]))
15: ('sortedDistIndicies:', array([2, 3, 1, 0], dtype=int64))
16: ('labels:', ['A', 'A', 'B', 'B'])
17: ('classCount:', {'A': 1, 'B': 2})
18: ('sortedClassCount:', [('B', 2), ('A', 1)])
19: 'B'
对照这个结果看上面的代码应该都能够看懂。
好,跟书上说得一样,这个例子没有实际的用处,于是书上给出了两个实际的例子。一个是使用k-近邻算法改进约会网站的配对效果。
算法过程,如书中:
这个例子给出了机器学习的一般过程
首先我们要知道我们要做什么,知道要做什么之后,我们要采集数据,数据采集完了之后,我们要将数据进行预处理。
1、因为我们采集过来的数据,可能面临杂乱、重复、不完整等等原因,常见处理方法有数据集成、数据清洗、数据变换、数据归约。
对于本例,认为数据是有效的,我们处理是数据变换,将数据变成分类器可以识别的格式。数据归约将数据同一化,不然数据值大的就相当于权重大了,对处理有影响。
定义一个函数将文本转换为数组
1: def file2matrix(filename):
2: fr = open(filename)
3: arrayOLines = fr.readlines()
4: numberOfLines = len(arrayOLines)
5: print('numberOfLines:',numberOfLines)
6: returnMat = zeros((numberOfLines,3))
7: print('returnMat:',returnMat)
8: classLabelVector = []
9: index = 0
10: for line in arrayOLines:
11: #没有传入参数时,是默认去除首尾空格
12: line = line.strip()
13: listFromLine = line.split(' ')
14: returnMat[index,:] = listFromLine[0:3]
15: classLabelVector.append(int(listFromLine[-1]))
16: index += 1
17: print('returnMat:',returnMat)
18: print('classLabelVector:',classLabelVector[0:20])
19: return returnMat,classLabelVector
20:
运行结果如下:
1: >>> reload(kNN)
2: <module 'kNN' from 'E:Machine Learningexercisech02kNN.py'>
3: >>> datingDataMat,datingLabels = kNN.file2matrix('datingTestSet.txt')
4: ('numberOfLines:', 1000)
5: ('returnMat:', array([[ 0., 0., 0.],
6: [ 0., 0., 0.],
7: [ 0., 0., 0.],
8: ...,
9: [ 0., 0., 0.],
10: [ 0., 0., 0.],
11: [ 0., 0., 0.]]))
12: ('returnMat:', array([[ 4.09200000e+04, 8.32697600e+00, 9.53952000e-01],
13: [ 1.44880000e+04, 7.15346900e+00, 1.67390400e+00],
14: [ 2.60520000e+04, 1.44187100e+00, 8.05124000e-01],
15: ...,
16: [ 2.65750000e+04, 1.06501020e+01, 8.66627000e-01],
17: [ 4.81110000e+04, 9.13452800e+00, 7.28045000e-01],
18: [ 4.37570000e+04, 7.88260100e+00, 1.33244600e+00]]))
19: ('classLabelVector:', [3, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 3, 3, 1, 3, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 3])
在我们进行模型选择的时候,我们可以通过图形化数据的方式,这样我们可以根据一定的经验就知道应该使用什么样的模型。
我们通过Matplotlib来显示图像,这个包的安装,直接下载这个包就可以了,如果提示你缺少什么包,补齐就好了。
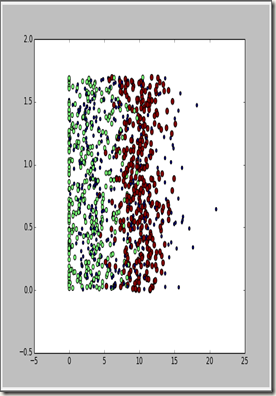
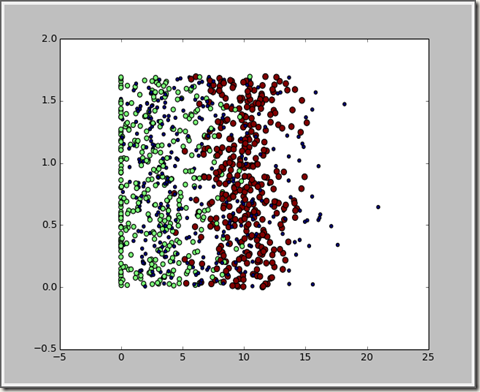
根据作者使用,我们画出玩视频游戏所消耗的时间百分比 与每周所消费的冰淇淋公升数
1: >>> import matplotlib
2: >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
3: >>> fig = plt.figure()
4: >>> ax = fig.add_subplot(111)//这边111表示把绘图区域分成1行*1列共1个区域,然后在区域1上创建一个轴对象
5: >>> ax.scatter(datingDataMat[:,1],datingDataMat[:,2])//scatter表示散点图
6: <matplotlib.collections.PathCollection object at 0x00000000064DD128>
7: >>> plt.show()
对于这个图很难看出有用的东西,用颜色进行标识,如下图:
1: ax.scatter(datingDataMat[:,1],datingDataMat[:,2],15.0*array(datingLabels),15.0*array(datingLabels))
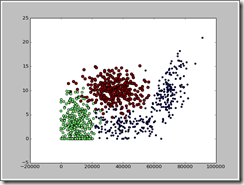
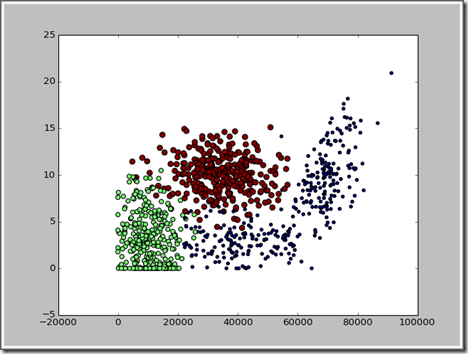
换一下属性,x轴用每年获取的飞行常客里程数表示,则三类分的就比较明显了。
下面就是归一化,不归一化,值大的相当于权重就大,而权重的大小是应该我们去添加的,不是由值的大小来
对于归一化,我们一般有三种处理方法。
1、[(原值-最小值)/(最大值-最小值)]*(新的最大值-新的最小值)+新的最小值。
2、(原值-均值)/标准差
3、小数的规范化,就是移动小数点位,归化到0-1之间
我们就采用的是第一种方式,这边我们新的最大值是1,最小值是0.我们的归一化就是:
[(原值-最小值)/(最大值-最小值)]
1: def autoNorm(dataSet):
2: minVals = dataSet.min(0)
3: maxVals = dataSet.max(0)
4: print('minVals:',minVals)
5: print('maxVals:',maxVals)
6: ranges = maxVals - minVals
7: normDataSet = zeros(shape(dataSet))
8: m = dataSet.shape[0]
9: print('m:',m)
10: normDataSet = dataSet - tile(minVals,(m,1))
11: normDataSet = normDataSet/tile(ranges,(m,1))
12: return normDataSet,ranges,minVals
13:
执行结果
1: >>> reload(kNN)
2: <module 'kNN' from 'E:Machine Learningexercisech02kNN.py'>
3: >>> normMat,ranges,minVals = kNN.autoNorm(datingDataMat)
4: ('minVals:', array([ 0. , 0. , 0.001156]))
5: ('maxVals:', array([ 9.12730000e+04, 2.09193490e+01, 1.69551700e+00]))
6: ('m:', 1000L)
7: >>> normMat
8: array([[ 0.44832535, 0.39805139, 0.56233353],
9: [ 0.15873259, 0.34195467, 0.98724416],
10: [ 0.28542943, 0.06892523, 0.47449629],
11: ...,
12: [ 0.29115949, 0.50910294, 0.51079493],
13: [ 0.52711097, 0.43665451, 0.4290048 ],
14: [ 0.47940793, 0.3768091 , 0.78571804]])
15: >>> ranges
16: array([ 9.12730000e+04, 2.09193490e+01, 1.69436100e+00])
17: >>> minVals
18: array([ 0. , 0. , 0.001156])
为了评估算法,我们将数据分成训练集和测试集,通常用70%的数据作为训练集,用剩下30%的数据作为测试集。很重要的一点是训练集和测试集均要含有各种类型的数据,通常我们要对数据进行“洗牌”,然后再分成训练集和测试集。
下面进行测试
1: def datingClassTest():
2: hoRatio = 0.10
3: datingDataMat,datingLabels = file2matrix('datingTestSet.txt')
4: normMat,ranges,minVals = autoNorm(datingDataMat)
5: m = normMat.shape[0]
6: numTestVecs = int(m*hoRatio)
7: errorCount = 0.0
8: for i in range(numTestVecs):
9: #这边的意思是拿前10%的数据作为测试,后90%的数据是训练样本
10: classifierResult = classify0(normMat[i,:],normMat[numTestVecs:m,:],datingLabels[numTestVecs:m],5)
11: print "the classifier came back with:%d,the real answer is: %d" %(classifierResult,datingLabels[i])
12: if(classifierResult !=datingLabels[i]):
13: errorCount +=1.0
14: print "the total error rate is :%f" %(errorCount/float(numTestVecs))
得到的结果
1: >>> import kNN
2: >>> kNN.datingClassTest()
3: the classifier came back with:3,the real answer is: 3
4: the classifier came back with:2,the real answer is: 2
5: the classifier came back with:1,the real answer is: 1
6: 。。。。。。
7: the classifier came back with:3,the real answer is: 3
8: the classifier came back with:3,the real answer is: 3
9: the classifier came back with:2,the real answer is: 2
10: the classifier came back with:2,the real answer is: 1
11: the classifier came back with:1,the real answer is: 1
12: the total error rate is :0.040000
这个结果还好,我这边设置的k为5,k的变化结果也会变化,所有怎么选择这个k也是值得研究的。
最后为了适合系统的使用变得直观一点,写下如下函数:
1: def classifyPerson():
2: resultList = ['not at all','in small doses','in large doses']
3: percentTats = float(raw_input("percentage of time spent playing video games?"))
4: ffMiles = float(raw_input("frequent flier miles earned per year?"))
5: iceCream = float(raw_input("liters of ice cream consumed per year?"))
6: datingDataMat,datingLabels = file2matrix('datingTestSet.txt')
7: normMat,ranges,minVals = autoNorm(datingDataMat)
8: inArr = array([ffMiles,percentTats,iceCream])
9: classifierResult = classify0((inArr-minVals)/ranges,normMat,datingLabels,3)
10: #这边减1是由于最后分类的数据是1,2,3对应到数组中是0,1,2
11: print "You will probably like this person: ",resultList[classifierResult -1]
运行结果如下:
1: >>> import kNN
2: >>> kNN.classifyPerson()
3: percentage of time spent playing video games?11
4: frequent flier miles earned per year?11111
5: liters of ice cream consumed per year?0.6
6: You will probably like this person: in large doses
7: >>> kNN.classifyPerson()
8: percentage of time spent playing video games?10
9: frequent flier miles earned per year?10000
10: liters of ice cream consumed per year?0.5
11: You will probably like this person: in small doses
下一个demo是手写识别系统,书中为了简化只设别0-9的数字。
作者这边是将图像数据转化成向量
写下如下函数:
1: #把图像文本数据存入returnVect
2: def img2vector(filename):
3: #图像像素是32*32
4: returnVect = zeros((1,1024))
5: fr = open(filename)
6: for i in range(32):
7: lineStr = fr.readline()
8: for j in range(32):
9: returnVect[0,32*i+j] = int(lineStr[j])
10: return returnVect
运行查看如下:
1: >>> import kNN
2: >>> kNN.img2vector('testDigits/0_13.txt')
3: array([[ 0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.]])
4: >>> testVector = kNN.img2vector('testDigits/0_13.txt')
5: >>> testVector[0,0:31]
6: array([ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.,
7: 0., 1., 1., 1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.,
8: 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.])
分类函数已经有,下面就是测试模型
1: def handwritingClassTest():
2: hwLabels = []
3: #获取文件目录
4: trainingFileList = listdir('trainingDigits')
5: m = len(trainingFileList)
6: trainingMat = zeros((m,1024))
7: for i in range(m):
8: fileNameStr = trainingFileList[i]
9: #得到数组如[0_12,txt],[0]是第一个数据0_12
10: fileStr = fileNameStr.split('.')[0]
11: #得到数组如[0,12]获得第一个数[0],从这边看出文件名还是有很大作用的。
12: classNumStr = int(fileStr.split('_')[0])
13: hwLabels.append(classNumStr)
14: trainingMat[i,:] = img2vector('trainingDigits/%s' % fileNameStr)
15: testFileList = listdir('testDigits')
16: errorCount = 0.0
17: mTest = len(testFileList)
18: for i in range(mTest):
19: fileNameStr = testFileList[i]
20: fileStr = fileNameStr.split('.')[0]
21: classNumStr = int(fileStr.split('_')[0])
22: vectorUnderTest = img2vector('testDigits/%s' % fileNameStr)
23: classifierResult = classify0(vectorUnderTest, trainingMat, hwLabels, 3)
24: print "the classifier came back with: %d, the real answer is: %d" % (classifierResult, classNumStr)
25: if (classifierResult != classNumStr): errorCount += 1.0
26: print " the total number of errors is: %d" % errorCount
27: print " the total error rate is: %f" % (errorCount/float(mTest))
最后得到的结果
1: >>> import kNN
2: >>> kNN.handwritingClassTest()
3: the classifier came back with: 0, the real answer is: 0
4: the classifier came back with: 0, the real answer is: 0
5: 。。。。。。
6: the classifier came back with: 9, the real answer is: 9
7: the classifier came back with: 9, the real answer is: 9
8: the classifier came back with: 9, the real answer is: 9
9: the classifier came back with: 9, the real answer is: 9
10:
11: the total number of errors is: 11
12:
13: the total error rate is: 0.011628
错误率还是很低的,这个模型是可行的。最后作者给出k近邻算法的不足。k近邻算法必须保存全部数据集,训练集大的话,占用存储空间大,由于要对每个数据计算距离是浮点型计算,计算量大。
另外相似性的判断是根据欧式距离来的,这样如果计算欧式距离的属性中如果有无关属性或者噪音数据比较多的话,那这个测量的距离就不是真正的距离,误差较大。解决办法有给重要属性的权重加大。
刚学习Python,主要以看代码,自己照着敲代码,思考了一下整个思路,了解了基本的Python语法。
下面继续学习决策树。