一、数组
数组(array)是多个相同数据类型按照一定顺序排列的集合,并使用一个名字命名,并通过编号的方式对这些数据进行统一管理
数组的相关概念:
- 数组名
- 元素
- 角标(下标、索引):数组的索引从0开始,到数组长度-1结束
- 长度
数组的特点:
- 数据是有序排列的
- 数组是引用类型变量。数组的元素可以是基本数据类型,也可以是引用数据类型
- 数据对象会在内存开辟一块连续的空间
- 数组的长度一旦确定,不能更改
数组的分类:
- 按照维数:一维数组、二维数组……
- 按照数组元素类型:基本数据类型元素的数组、引用数据类型元素的数组
一维数组的使用:
- 一维数组的声明和初始化
-
int[] ids; // 声明 ids = new int[]{1001, 1002, 1003, 1004}; // 静态初始化:数组的初始化和数组元素的赋值同时进行 String[] names = new String[5]; //动态初始化:数组的初始化和数组元素的赋值分开进行
-
- 如何调用数组指定位置的元素
-
names[0] = "小陈"; names[1] = "小吴"; names[2] = "小李"; names[3] = "老邓"; names[4] = "小王"; // names[5] = "小邓"; // 报错,java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
-
- 如何获取数组的长度
-
System.out.println(names.length); // 5
-
- 如何遍历数组
-
for (int i=0;i<names.length;i++){ System.out.println(names[i]); }
-
- 数组元素的默认初始化值
- 数组元素是整形:0
- 数组元素是浮点型:0.0
- 数组元素是char型:0或'u0000',而非'0'
- 数组元素是布尔值:false
- 数组元素是引用数据类型:null
-
String[] arr = new String[4]; for (int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){ System.out.print(arr[i] + " "); } // null null null null
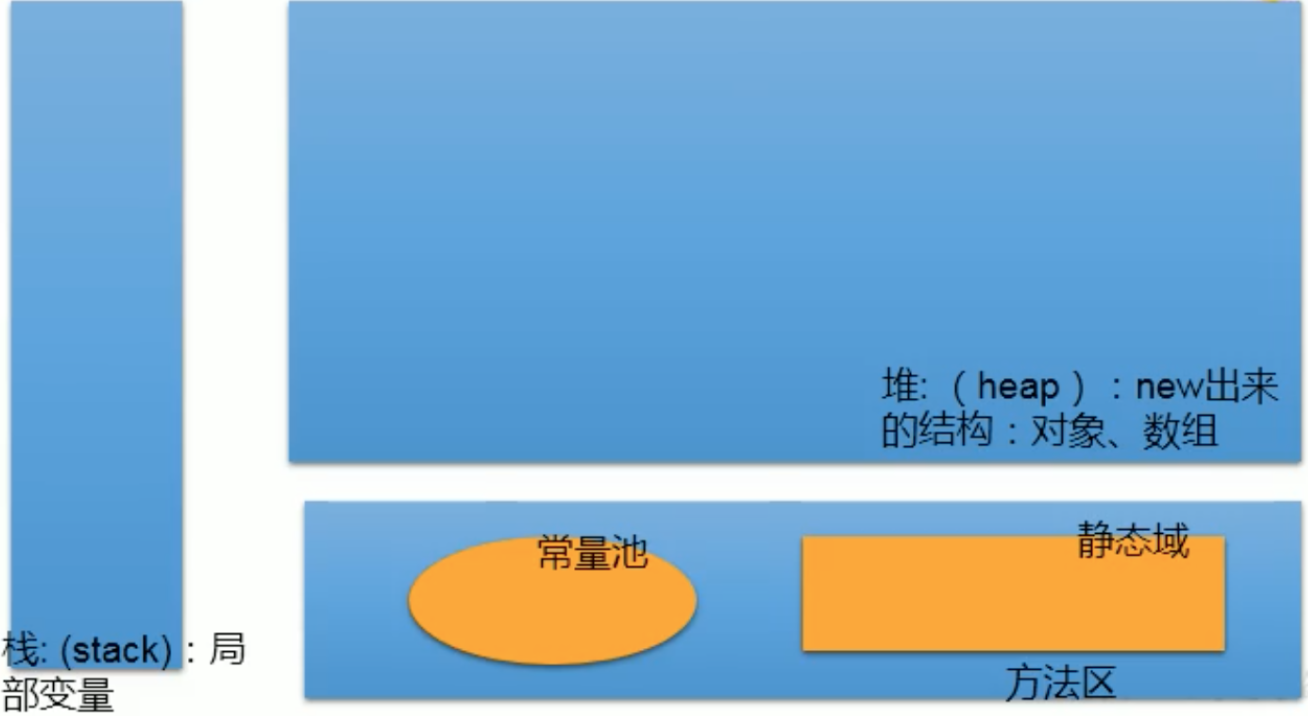
- 数组的内存解析
- 简化版内存结构
例题:UN公社单间短期出租4个月,1550元/月(水电煤公摊,网费35元/月),空调、卫生间、厨房齐全。屋内均是IT行业人员,喜欢安静。所以要求来租者最好是同行或者刚毕业的年轻人,爱干净。安静,联系方式:
public class TestDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = new int[]{8, 2, 1, 0, 3}; int[] index = new int[]{2, 0, 3, 2, 4, 0, 1, 3, 2, 3, 3}; String tel = ""; for (int i = 0; i < index.length; i++) { tel += arr[index[i]]; } System.out.println("联系方式:" + tel); } }
二维数组的使用
对于二维数组的理解,我们可以看成是以为数组array1又作为另一个一维数组array2的元素而存在。其实,从数组底层的运行机制来看,没有多维数组
- 二维数组的声明和初始化
-
public class TestDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { int[][] ids; // 声明 ids = new int[][]{{1,2,3},{4,5},{6,7,8,9}}; // 静态初始化:数组的初始化和数组元素的赋值同时进行 int[][] ids2= {{1,2,3},{4,5},{6,7,8,9}}; //类型推断,也是正确写法 String[][] names = new String[3][2]; //动态初始化1:数组的初始化和数组元素的赋值分开进行 String[][] names2 = new String[3][]; //动态初始化2:数组的初始化和数组元素的赋值分开进行 String[] names3[] = new String[3][]; //也是正确写法 } }
-
- 如何调用数组指定位置的元素
-
System.out.println(ids[0][1]); //2 System.out.println(names[1][1]); //null System.out.println(names2[1]); //null names2[1] = new String[4]; System.out.println(names2[1][1]); //null
-
- 如何获取数组的长度
-
System.out.println(names.length); //3 System.out.println(ids[2].length); //4
-
- 如何遍历数组
-
for(int i=0;i<ids.length;i++){ for(int j=0;j<ids[i].length;j++){ System.out.print(ids[i][j]+" "); } System.out.println(); } // 1 2 3 // 4 5 // 6 7 8 9
-
- 数组元素的默认初始化值
- 针对初始化方式一:比如:int[][] arr = new int[4][3];
- 外层元素的初始化值为:地址值
- 内层元素的初始化值为:与一位数组初始化值情况相同
- 针对初始化方式二:比如:int[][] arr = new int[4][];
- 外层元素的初始化值为:null
- 内层元素的初始化值为:不能调用,报空指针错误
- 数组的内存解析
例题:
1、打印杨辉三角
public class TestDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { // 杨辉三角 int[][] yangHui= new int[10][]; for(int i=0;i<yangHui.length;i++){ yangHui[i]=new int[i+1]; yangHui[i][0] = yangHui[i][i] = 1; // 首尾赋值为1 // 给中间位置赋值 for(int j=1;j<yangHui[i].length-1;j++){ yangHui[i][j]=yangHui[i-1][j-1]+yangHui[i-1][j]; } } // 遍历数组 for(int i=0;i<yangHui.length;i++){ for (int j=0;j<yangHui[i].length;j++){ System.out.print(yangHui[i][j]+" "); } System.out.println(); } } }
2、创建一个长度为6的int型数组,要求取值为1-30,同时元素值各不相同
public class TestDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建一个长度为6的int型数组,要求取值为1-30,同时元素值各不相同 int[] arr = new int[6]; for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { arr[i] = (int) (Math.random() * 30 + 1); for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) { if (arr[i] == arr[j]) { i--; break; } } } for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { System.out.print(arr[i] + " "); } } }
3、求数组中元素的最大值、最小值、平均数、总和
定义一个int型的一维数组,包含10个元素,分别赋一些随机数,然后求出所有元素的最大值、最小值、和值、平均数,并输出
要求:所有随机数都是两位数
public class TestDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { //定义一个int型的一维数组,包含10个元素,分别赋一些随机数,然后求出所有元素的最大值、最小值、和值、平均数,并输出 //要求:所有随机数都是两位数[10,99] int[] arr = new int[10]; for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { arr[i] = (int) (Math.random() * 88 + 10); //公式:[a,b]:(int) (Math.random() * (b-a+1) + a) System.out.print(arr[i] + " "); } System.out.println(); // 最大值 int maxValue = arr[0]; for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) { if (maxValue < arr[i]) { maxValue = arr[i]; } } System.out.println("最大值:" + maxValue); // 最小值 int minValue = arr[0]; for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) { if (minValue > arr[i]) { minValue = arr[i]; } } System.out.println("最小值:" + minValue); // 和值 int sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { sum += arr[i]; } System.out.println("总和值:" + sum); // 平均值 double avg = sum / arr.length; System.out.println("平均值:" + avg); } }
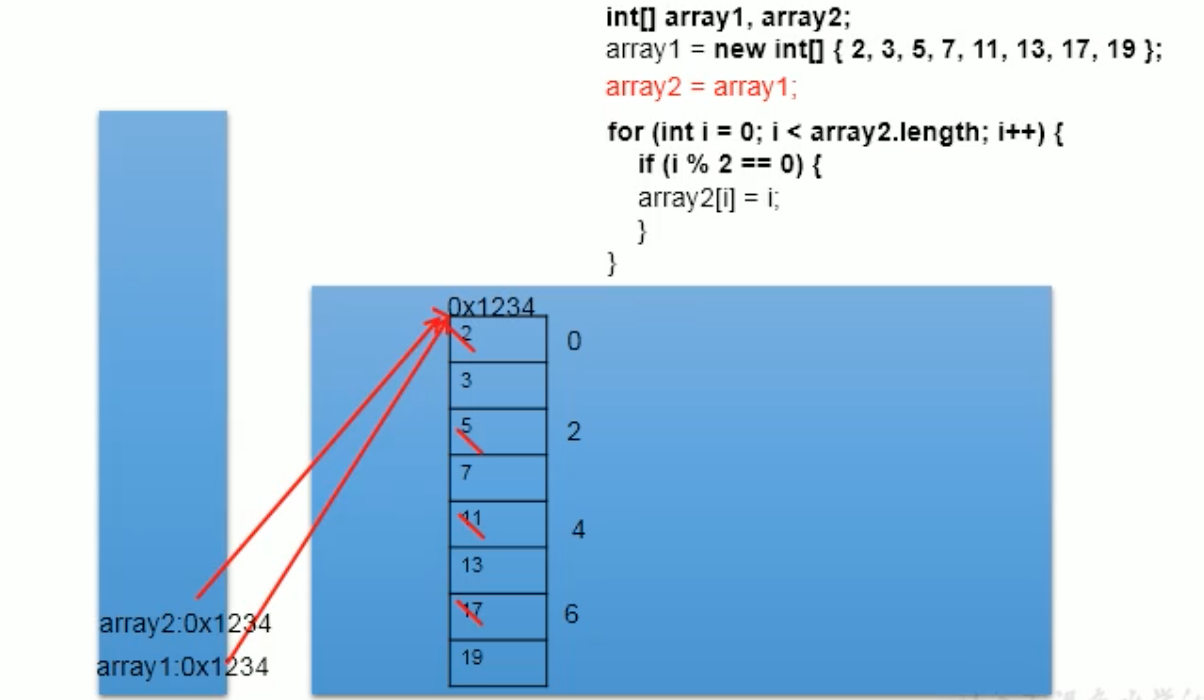
4、数组的引用
public class TestDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arry1,arry2; arry1=new int[]{8,9,65,32,56,23,7,5,43}; arry2=arry1; // arry2引用指向arry1,注意此时arry1与arry2是同一个数组,不是复制 // 此时修改arry1的值后,arry2的值会随之修改 for(int i=0;i<arry1.length;i++){ if(i%2==0){ arry1[i] = i; } } for(int i=0;i<arry2.length;i++){ System.out.print(arry2[i]+" "); // 0 9 2 32 4 23 6 5 8 } } }
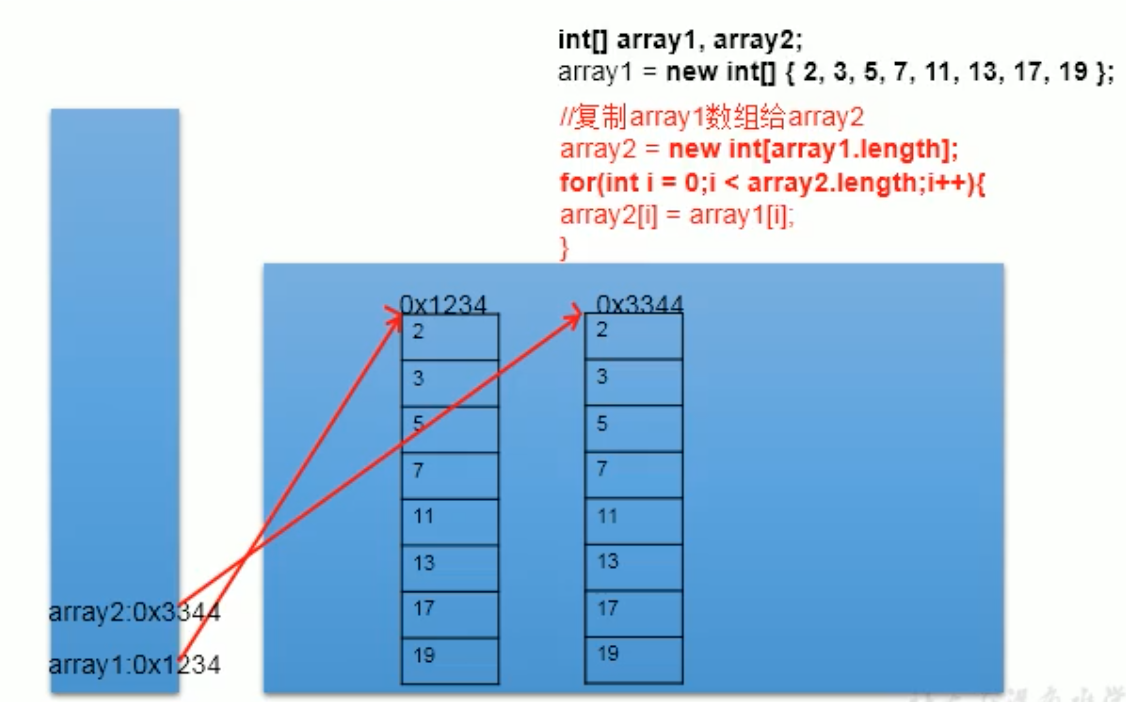
5、数组的复制
public class TestDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arry1,arry2; arry1=new int[]{8,9,65,32,56,23,7,5,43}; arry2=new int[9]; // 复制数组arry1 for(int i=0;i<arry1.length;i++){ arry2[i]=arry1[i]; } for(int i=0;i<arry1.length;i++){ if(i%2==0){ arry1[i] = i; //此时修改arry1后,arry2的值不变 } } for(int i=0;i<arry2.length;i++){ System.out.print(arry2[i]+" "); // 8 9 65 32 56 23 7 5 43 } } }
6、数组的反转
public class TestDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arry = new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}; // 数组的反转 // 方法一 // for (int i = 0; i < arry.length / 2; i++) { // int temp = arry[i]; // arry[i] = arry[arry.length - i - 1]; // arry[arry.length - i - 1] = temp; // } // 方法二 for (int i = 0, j = arry.length - 1; i < j; i++, j--) { int temp = arry[i]; arry[i] = arry[j]; arry[j] = temp; } for (int i = 0; i < arry.length; i++) { System.out.print(arry[i] + " "); // 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 } } }
7、数组的线性查找
public class TestDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { String[] arry = new String[]{"aa", "bb", "cc", "dd", "ee", "ff", "gg"}; // 数组的查找 //线性查找(地毯式搜索) String dest = "gg"; boolean isFlag = true; for (int i = 0; i < arry.length; i++) { if (dest.equals(arry[i])) { System.out.println("找到了指定元素的位置:" + i); isFlag = false; break; } } if (isFlag) { System.out.print("很遗憾,没有找到你要找的元素呢"); } } }
8、数组的二分查找
public class TestDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arry = new int[]{-55, -23, -5, 3, 9, 13, 35, 46, 56, 67}; //二分法查找 //前提:查找的数组必须有序 int dest = 56; // 要查找的元素 int head = 0;//初始起始索引 int end = arry.length - 1;//初始的末尾索引 boolean isFlag = true; while (head <= end) { int middle = (head + end) / 2; //中间值 if (dest == arry[middle]) { System.out.println("找到了你要查找的元素,位置为:" + middle); isFlag = false; break; } else if (dest < arry[middle]) { end = middle - 1; } else if (dest > arry[middle]) { head = middle + 1; } } if (isFlag) { System.out.print("很遗憾,没有找到你要找的元素呢"); } } }
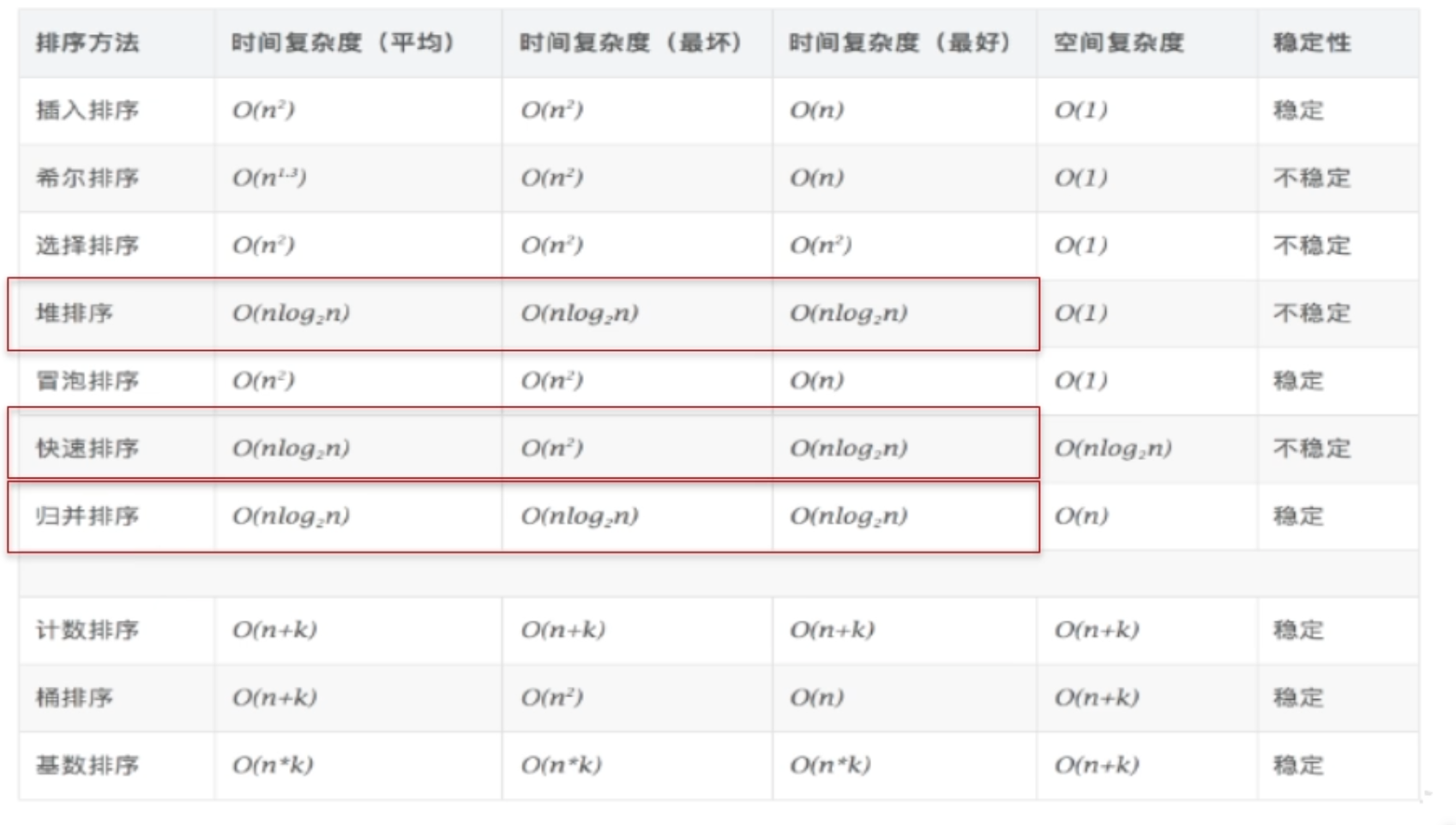
数组排序
- 选择排序
- 直接选择排序
- 堆排序
- 交换排序
- 冒泡排序
- 快速排序
- 插入排序
- 直接插入排序
- 折半插入排序
- Shell排序
- 归并排序
- 桶式排序
- 基数排序
冒泡排序举例
public class TestDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = new int[]{-55, -23, -5, 3, 9, 13, 35, 46, 56, 67}; // 冒泡排序 int temp; for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) { // 比较次数 for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - 1 - i; j++) { // 比较到的位置 if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) { temp = arr[j]; arr[j] = arr[j + 1]; arr[j + 1] = temp; } } } //遍历排序后的数组 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { System.out.print(arr[i] + " "); } } }
快速排序
原理:
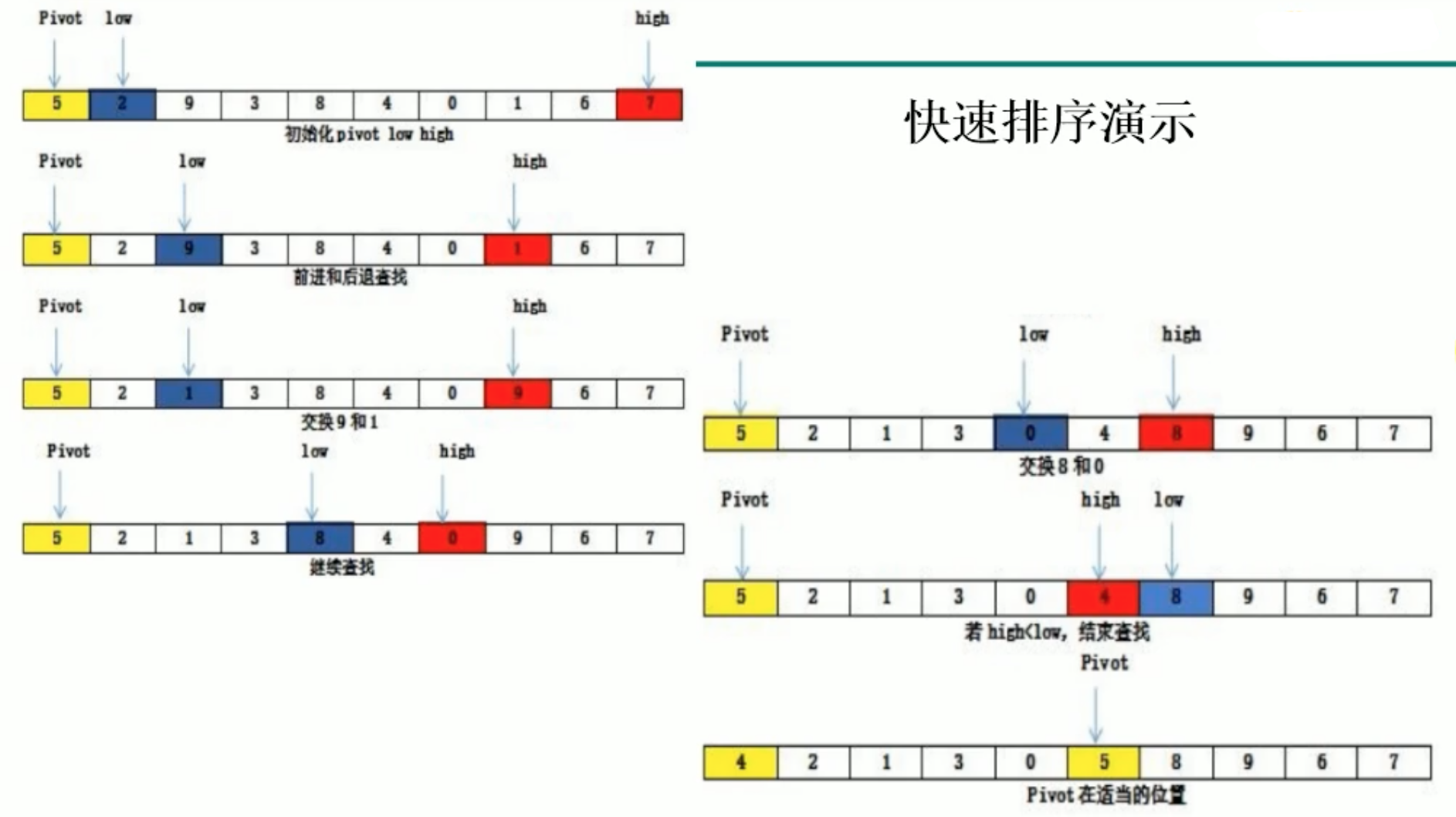
demo:

举例:
public class QuickSort { private static void swap(int[] data, int i, int j) { int temp = data[i]; data[i] = data[j]; data[j] = temp; } private static void subSort(int[] data, int start, int end) { if (start < end) { int base = data[start]; int low = start; int high = end + 1; while (true) { while (low < end && data[++low] - base <= 0) ; while (high > start && data[--high] - base >= 0) ; if (low < high) { swap(data, low, high); } else { break; } } swap(data, start, high); subSort(data, start, high - 1);//递归调用 subSort(data, high + 1, end); } } public static void quickSort(int[] data) { subSort(data, 0, data.length - 1); } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] data = {9, -16, 30, 23, -30, -49, 25, 21, 30}; System.out.println("排序之前: " + java.util.Arrays.toString(data)); quickSort(data); System.out.println("排序之后: " + java.util.Arrays.toString(data)); } }
排序算法性能对比