1. c++自动提供了以下的成员函数
默认构造函数,如果没有定义构造函数
默认析构函数,如果没有定义
复制构造函数,如果没有定义,java参见:https://blog.csdn.net/ShewMi/article/details/80788591
赋值运算符,如果没有定义
地址运算符,如果没有定义
移动构造函数
移动赋值运算符
a. 默认构造函数
编译器在没有提供构造函数时候,编译器将提供一个不接受任何参数,也不执行任何操作的构造函数
如果定义了构造函数,编译器将不提供任何默认构造函数,如果希望创建对象时不显示的对它进行初始化,则必须显示定义默认构造函数,这种构造函数没有任何参数,但是可以使用它来设置特定的值
b. 复制构造函数
复制构造函数用于将一个对象复制到一个新创建的对象中,也就是说,它用于初始化过程中,而不是常规的赋值过程中
调用的时机:
当函数的参数为类对象的时候
函数的返回值是类对象
对象需要另一个对象进行初始化
由于按值传递对象将调用赋值构造函数,因此应该使用按引用传递对象,这样可以节省调用构造函数的时间以及存储新对象的空间。
默认赋值构造函数的功能:逐个赋值非静态成员(成员赋值也称浅赋值),赋值的是成员的值,如果类中存在一个静态的对象计数变量,默认的复制构造函数不说明其行为,也不增加计数器的个数,但是析构函数会更新次数,解决方法是提供一个对计数进行更新的显示复制构造函数
如果对象中存在指针变量,默认的复制构造函数将不会为该指针分配空间,复制时候会将原对象和复制对象的指针指向同一个位置,析构两个对象会对同一个指针delete两次,从而会出现严重的问题。
警告:如果类中包含了使用new 初始化的指针成员,应当定义一个复制构造函数,以复制指向的数据,而不是指针,这称为深度复制。复制的另一种形式(成员复制或者浅复制)只是复制指针值,浅复制仅浅浅复制指针的信息,而不会深入挖掘以复制指针引用的结构
赋值构造函数本质是构造函数,所以可以按照下面方式显式调用:

c. 赋值运算符:
String knot;
String metoo = knot; // 调用的拷贝构造函数
String youtoo;
youtoo = knot; // 调用赋值运算符重载
默认的赋值运算符隐式实现也是对成员进行逐个赋值,如果成员本身就是类对象,则程序将使用这个类定义的赋值运算符来复制这个成员,静态数据成员不受影响。
注意:由于目标对象可能以及引用了以前分配的数据,所以函数应该使用delete[] 来释放这些数据
函数应当避免将对象赋值给自身,否则,在给对象重新赋值之前,释放内存操作可能会删除对象的内容。
函数返回一个指向调用对象的引用,通过返回一个对象,函数可以像赋值常规操作那样,连续进行赋值
d. 默认析构函数:
如果类中有使用new的指针成员变量,析构函数是必不可少的,此外,析构函数一般被定义为virtual,这是为了重载以后被重载的类也能够正常的释放内存
例:String类
#include <iostream> using namespace std; class String { private: char* str; int len; static int num_strings; static const int CINLIM = 80; // static 修饰的常量在类中初始化 public: // constructors and other methods String(); String(const char*); String(const String&); ~String(); int length() const { return len; } // overloaded operator methods String& operator=(const String &); String& operator=(const char *); char& operator[](int); const char& operator[](int) const; // overloaded operator friends friend bool operator<(const String&, const String&); friend bool operator>(const String&, const String&); friend bool operator==(const String&, const String&); friend ostream& operator<<(ostream&, const String&); friend istream& operator>>(istream&, String&); // static function static int howMany(); };
#include "String.h" #include <cstring> #include <iostream> using namespace std; #pragma warning(disable:4996) int String::num_strings = 0; int String::howMany() { return num_strings; } String::String(const char* s) { len = strlen(s); str = new char[len + 1]; strcpy(str, s); num_strings++; } String::String() { len = 0; str = new char[1]; str[0] = '�'; num_strings++; } String::String(const String& st) { num_strings++; len = st.len; str = new char[len + 1]; strcpy(str, st.str); } String::~String() { --num_strings; delete[] str; } String& String::operator=(const String& st) { if (this == &st) { return *this; } delete[] str; len = st.len; str = new char[len + 1]; strcpy(str, st.str); return *this; } String& String::operator=(const char* s) { delete[] str; len = strlen(s); str = new char[len + 1]; strcpy(str, s); return *this; } char& String::operator[](int i) { return str[i]; } const char& String::operator[](int i) const { return str[i]; } bool operator<(const String& str1, const String& str2) { return strcmp(str1.str, str2.str); } bool operator>(const String& str1, const String& str2) { return str2 < str1; } bool operator==(const String& str1, const String& str2) { return strcmp(str1.str, str2.str) == 0; } ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const String& st) { os << st.str; return os; } istream& operator>>(istream& is, String& st) { char temp[String::CINLIM]; is.get(temp, String::CINLIM); if (is) st = temp; while (is && is.get() != ' ') { continue; } return is; }
测试代码:
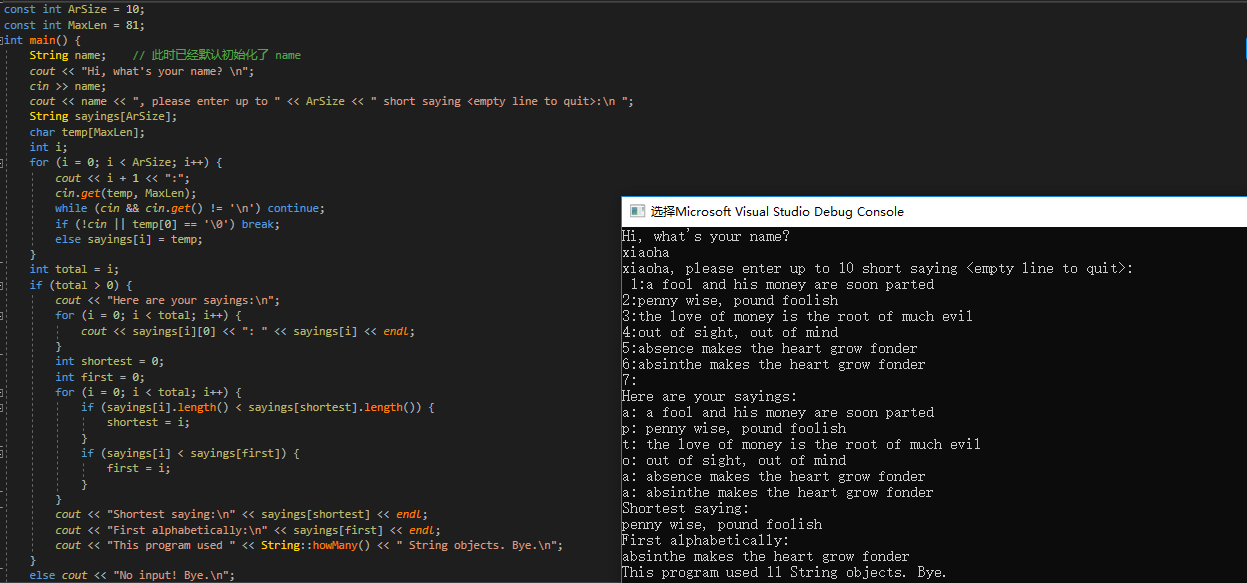
if(!cin || temp[0] == '0')
break;
较早的get(char*, int)在 读取到空行后,返回的值不为false,然而,对于这些版本来说,如果读取了一个空行,则字符串的第一个字符将会是一个空字符
if(!cin || temp[0] == '�')
break;
如果执行了最新的c++标准,则if语句中的第一个条件将检测到空行,第二个条件用于旧版本实现检测空行。
2. 在构造函数中使用new时候应当注意的事项
a. 如果在构造函数中使用new来初始化指针成员,则应当在析构函数中使用delete
b. new 和delete必须互相兼容,new对应delete,new[] 对应于delete[]
c. 如果有多个构造函数,则必须以相同的方式使用New,要么都带括号,要么都不带,因为只有一个析构函数,所有的构造函数必须与它兼容,然而可以在一个构造函数中使用new初始化指针,另一个构造函数中将指针初始化为空,这是因为delete(无论是带中括号还是不带中括号)可以用于空指针。
NULL,0,还是nullptr:以前空指针可以用于0或NULL来表示,C程序员通常使用NULL而不是0,以指出这是一个指针,就像使用'�'而不是0来表示空字符,以指出这是一个字符一样,然而C++传统上更喜欢使用简单的0,而不是等价的NULL,但C++11提供了关键字nullptr,这将是一种更好的选择。
d. 应当定义一个复制构造函数,通过深度复制将一个对象初始化为另一个对象。
e. 应当定义一个赋值运算符,通过深度复制将一个对象复制给另一个对象。
3. 返回对象的说明
a. 返回指向const对象的引用
使用const引用的常见原因是旨在提高效率,对于何时可以采用这种方法存在一些限制,如果函数返回传递给它的对象,可以通过返回引用来提高效率。
需要说明:返回对象调用复制构造函数,而返回引用不用。引用指向的对象应该在调用函数执行时存在,传递的对象是const,这样返回的类型必须是const,这样才匹配。
b. 返回指向非const对象的引用
两种常见的返回非const对象情形:重载复制运算符以及重载与cout一起使用的<<运算符,operator=返回值用于连续赋值,operator<<用于拼接输出
c. 返回对象:
如果返回的对象是被调用函数中的局部变量。
d. 返回const对象
4. 使用指向对象的指针
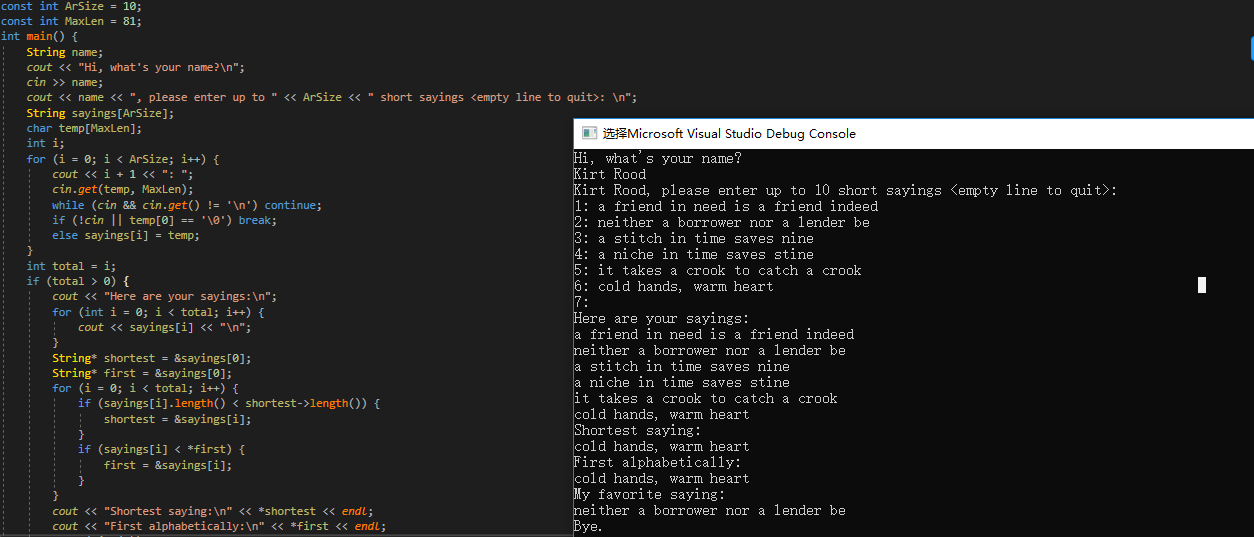

5. 队列模拟:
#include <cstdlib> class Customer { private: long arrive; int processtime; public: Customer() { arrive = processtime = 0; } void set(long when) { processtime = rand() % 3 + 1; arrive = when; } long when() const{ return arrive; } int ptime() const { return processtime; } };
#include "Customer.h" typedef Customer Item; class Queue { private: struct Node { Item item; Node* next; }; enum { Q_SIZE = 10 }; Node* front; Node* rear; int items; // current number of items in Queue const int qsize; // maximum number of items in Queue // 防止系统产生默认的拷贝构造函数 // 声明为私有后,调用Queue snick = nup; 以及 ss = nup系统将报错 Queue(const Queue& q) : qsize(10) {} // const修饰的非静态常量,必须使用初始化列表的方式初始化,同时也必须采用这种格式初始化引用数据成员 Queue& operator=(const Queue& q) { return *this; } public: Queue(int qs = Q_SIZE); ~Queue(); bool isEmpty() const; bool isFull() const; int queueCount() const; bool enqueue(const Item& item); // add item to end bool dequeue(Item& item); // remove item from front };
#include "Queue.h" Queue::Queue(int qs) : qsize(qs) { front = nullptr; rear = nullptr; items = 0; } Queue::~Queue() { Node* temp; while (front != nullptr) { temp = front; front = front->next; delete temp; } } int Queue::queueCount() const{ return items; } bool Queue::isEmpty() const { return items == 0; } bool Queue::isFull() const { return items == qsize; } bool Queue::enqueue(const Item& item) { if (isFull()) { return false; } Node* add = new Node; add->item = item; add->next = NULL; items++; if (front == nullptr) { front = add; } else { rear->next = add; } rear = add; return true; } bool Queue::dequeue(Item& item) { if (front == nullptr) { return false; } item = front->item; items--; Node* temp = front; front = front->next; delete temp; if (items == 0) { rear = nullptr; } return true; }
#include "Queue.h" const int MIN_PER_HR = 60; bool newcustomer(double x) { return (rand() * x / RAND_MAX) < 1; // rand(),RADN_MAX在cstdlib文件中 } int main() { srand(time(0)); // random initializing of rand() cout << "Case Study: Bank of Heather Automatic Teller "; cout << "Enter maxinm size of queue:"; int qs; cin >> qs; Queue line(qs); cout << "Enter the number of simulation hours: "; int hours; cin >> hours; long cyclelimit = MIN_PER_HR * hours; cout << "Enter the average of number of customer per hour: "; double perhour; cin >> perhour; double min_per_cust; min_per_cust = MIN_PER_HR; Item temp; long turnaways = 0; long customers = 0; long served = 0; long sum_line = 0; int wait_time = 0; long line_wait = 0; for (int cycle = 0; cycle < cyclelimit; cycle++) { if (newcustomer(min_per_cust)) { if (line.isFull()) { turnaways++; } else { customers++; temp.set(cycle); line.enqueue(temp); } } if (wait_time <= 0 && !line.isEmpty()) { line.dequeue(temp); wait_time = temp.ptime(); line_wait += cycle - temp.when(); served++; } if (wait_time > 0) { wait_time--; } sum_line += line.queueCount(); } if (customers > 0) { cout << "Customers accepted: " << customers << endl; cout << " custormer served: " << served << endl; cout << " turnaways: " << turnaways << endl; cout << "average queue size: "; cout.precision(2); cout.setf(ios_base::fixed, ios_base::floatfield); cout << (double) sum_line / cyclelimit << endl; cout << " average wait time: " << (double)line_wait / served << " minutes "; } else { cout << "No customers! "; } cout << "Done! "; return 0;