Kd-树是K-dimension tree的缩写,是对数据点在k维空间(如二维(x,y),三维(x,y,z),k维(x1,y,z..))中划分的一种数据结构,主要应用于多维空间关键数据的搜索(如:范围搜索和最近邻搜索)。本质上说,Kd-树就是一种平衡二叉树。
首先介绍一下基本的原理:
假设有6个二维数据点{(2,3),(5,4),(9,6),(4,7),(8,1),(7,2)},数据点位于二维空间内,如下图所示。为了能有效的找到最近邻,k-d树采用分而治之的思想,即将整个空间划分为几个小部分,首先,粗黑线将空间一分为二,然后在两个子空间中,细黑直线又将整个空间划分为四部分,最后虚黑直线将这四部分进一步划分。
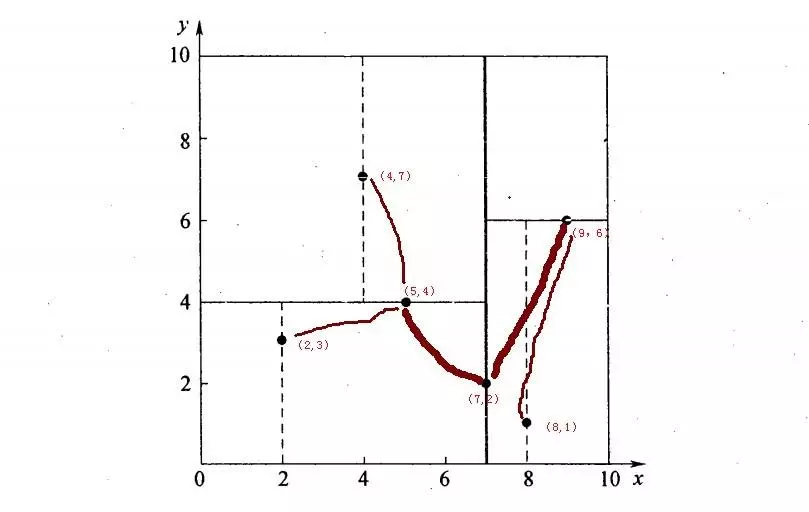
6个二维数据点{(2,3),(5,4),(9,6),(4,7),(8,1),(7,2)}构建kd树的具体步骤为:
- 确定:split域=x。具体是:6个数据点在x,y维度上的数据方差分别为39,28.63,所以在x轴上方差更大,故split域值为x;
- 确定:Node-data = (7,2)。具体是:根据x维上的值将数据排序,6个数据的中值(所谓中值,即中间大小的值)为7(注:2,4,5,7,8,9在数学中的中值为(5 + 7)/2=6,但因该算法的中值需在点集合之内,所以本文中值计算用的是len(points)//2=3, points[3]=(7,2),数组中以位置0开始),所以Node-data域位数据点(7,2)。这样,该节点的分割超平面就是通过(7,2)并垂直于:split=x轴的直线x=7;
- 确定:左子空间和右子空间。具体是:分割超平面x=7将整个空间分为两部分:x<=7的部分为左子空间,包含3个节点={(2,3),(5,4),(4,7)};另一部分为右子空间,包含2个节点={(9,6),(8,1)};
- 如上算法所述,kd树的构建是一个递归过程,我们对左子空间和右子空间内的数据重复根节点的过程就可以得到一级子节点(5,4)和(9,6),同时将空间和数据集进一步细分,如此往复直到空间中只包含一个数据点。
过对上面所示的空间划分之后,我们可以看出,点(7,2)可以为根结点,从根结点出发的两条红粗斜线指向的(5,4)和(9,6)则为根结点的左右子结点,而(2,3),(4,7)则为(5,4)的左右孩子(通过两条细红斜线相连),最后,(8,1)为(9,6)的左孩子(通过细红斜线相连)。如此,便形成了下面这样一棵k-d树:

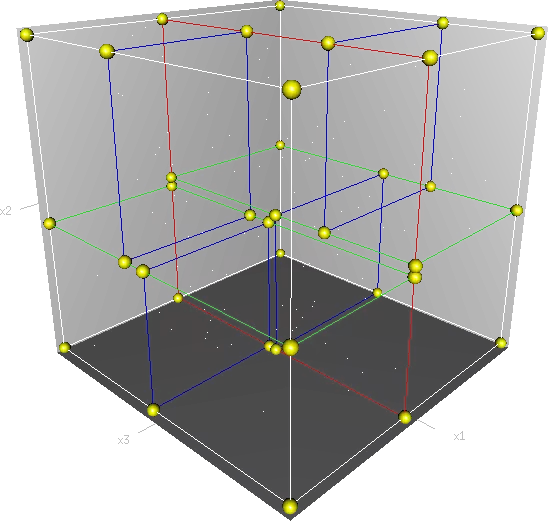
首先,边框为红色的竖直平面将整个空间划分为两部分,此两部分又分别被边框为绿色的水平平面划分为上下两部分。最后此4个子空间又分别被边框为蓝色的竖直平面分割为两部分,变为8个子空间,此8个子空间即为叶子节点。
//kdtree.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
#include <cmath>
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
struct KdTree
{
public:
vector<double> root;
KdTree* parent;
KdTree* leftChild;
KdTree* rightChild;
//默认构造函数
KdTree() { parent = leftChild = rightChild = NULL; }
~KdTree() {};
//判断kd树是否为空
bool isEmpty()
{
return root.empty();
}
//判断kd树是否只是一个叶子结点
bool isLeaf()
{
return (!root.empty()) &&
rightChild == NULL && leftChild == NULL;
}
//判断是否是树的根结点
bool isRoot()
{
return (!isEmpty()) && parent == NULL;
}
//判断该子kd树的根结点是否是其父kd树的左结点
bool isLeft()
{
return parent->leftChild->root == root;
}
//判断该子kd树的根结点是否是其父kd树的右结点
bool isRight()
{
return parent->rightChild->root == root;
}
};
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
#include "kdtree.h"
template<typename T>
vector<vector<T> > Transpose(vector<vector<T> > Matrix)
{
unsigned row = Matrix.size();
unsigned col = Matrix[0].size();
vector<vector<T> > Trans(col, vector<T>(row, 0));
for (unsigned i = 0; i < col; ++i)
{
for (unsigned j = 0; j < row; ++j)
{
Trans[i][j] = Matrix[j][i];
}
}
return Trans;
}
template <typename T>
T findMiddleValue(vector<T> vec)
{
sort(vec.begin(), vec.end());
auto pos = vec.size() / 2;
return vec[pos];
}
//构建kd树
void buildKdTree(KdTree* tree, vector<vector<double> > data, unsigned depth)
{
//样本的数量
unsigned samplesNum = data.size();
//终止条件
if (samplesNum == 0)
{
return;
}
if (samplesNum == 1)
{
tree->root = data[0];
return;
}
//样本的维度
unsigned k = data[0].size();
vector<vector<double> > transData = Transpose(data);
//选择切分属性
unsigned splitAttribute = depth % k;
vector<double> splitAttributeValues = transData[splitAttribute];
//选择切分值
double splitValue = findMiddleValue(splitAttributeValues);
//cout << "splitValue" << splitValue << endl;
// 根据选定的切分属性和切分值,将数据集分为两个子集
vector<vector<double> > subset1;
vector<vector<double> > subset2;
for (unsigned i = 0; i < samplesNum; ++i)
{
if (splitAttributeValues[i] == splitValue && tree->root.empty())
tree->root = data[i];
else
{
if (splitAttributeValues[i] < splitValue)
subset1.push_back(data[i]);
else
subset2.push_back(data[i]);
}
}
//子集递归调用buildKdTree函数
tree->leftChild = new KdTree;
tree->leftChild->parent = tree;
tree->rightChild = new KdTree;
tree->rightChild->parent = tree;
buildKdTree(tree->leftChild, subset1, depth + 1);
buildKdTree(tree->rightChild, subset2, depth + 1);
}
//逐层打印kd树
void printKdTree(KdTree *tree, unsigned depth)
{
for (unsigned i = 0; i < depth; ++i)
cout << " ";
for (vector<double>::size_type j = 0; j < tree->root.size(); ++j)
cout << tree->root[j] << ",";
cout << endl;
if (tree->leftChild == NULL && tree->rightChild == NULL)//叶子节点
return;
else //非叶子节点
{
if (tree->leftChild != NULL)
{
for (unsigned i = 0; i < depth + 1; ++i)
cout << " ";
cout << " left:";
printKdTree(tree->leftChild, depth + 1);
}
cout << endl;
if (tree->rightChild != NULL)
{
for (unsigned i = 0; i < depth + 1; ++i)
cout << " ";
cout << "right:";
printKdTree(tree->rightChild, depth + 1);
}
cout << endl;
}
}
//计算空间中两个点的距离
double measureDistance(vector<double> point1, vector<double> point2, unsigned method)
{
if (point1.size() != point2.size())
{
cerr << "Dimensions don't match!!";
exit(1);
}
switch (method)
{
case 0://欧氏距离
{
double res = 0;
for (vector<double>::size_type i = 0; i < point1.size(); ++i)
{
res += pow((point1[i] - point2[i]), 2);
}
return sqrt(res);
}
case 1://曼哈顿距离
{
double res = 0;
for (vector<double>::size_type i = 0; i < point1.size(); ++i)
{
res += abs(point1[i] - point2[i]);
}
return res;
}
default:
{
cerr << "Invalid method!!" << endl;
return -1;
}
}
}
//在kd树tree中搜索目标点goal的最近邻
//输入:目标点;已构造的kd树
//输出:目标点的最近邻
vector<double> searchNearestNeighbor(vector<double> goal, KdTree *tree)
{
/*第一步:在kd树中找出包含目标点的叶子结点:从根结点出发,
递归的向下访问kd树,若目标点的当前维的坐标小于切分点的
坐标,则移动到左子结点,否则移动到右子结点,直到子结点为
叶结点为止,以此叶子结点为“当前最近点”
*/
unsigned k = tree->root.size();//计算出数据的维数
unsigned d = 0;//维度初始化为0,即从第1维开始
KdTree* currentTree = tree;
vector<double> currentNearest = currentTree->root;
while (!currentTree->isLeaf())
{
unsigned index = d % k;//计算当前维
if (currentTree->rightChild->isEmpty() || goal[index] < currentNearest[index])
{
currentTree = currentTree->leftChild;
}
else
{
currentTree = currentTree->rightChild;
}
++d;
}
currentNearest = currentTree->root;
/*第二步:递归地向上回退, 在每个结点进行如下操作:
(a)如果该结点保存的实例比当前最近点距离目标点更近,则以该例点为“当前最近点”
(b)当前最近点一定存在于某结点一个子结点对应的区域,检查该子结点的父结点的另
一子结点对应区域是否有更近的点(即检查另一子结点对应的区域是否与以目标点为球
心、以目标点与“当前最近点”间的距离为半径的球体相交);如果相交,可能在另一
个子结点对应的区域内存在距目标点更近的点,移动到另一个子结点,接着递归进行最
近邻搜索;如果不相交,向上回退*/
//当前最近邻与目标点的距离
double currentDistance = measureDistance(goal, currentNearest, 0);
//如果当前子kd树的根结点是其父结点的左孩子,则搜索其父结点的右孩子结点所代表
//的区域,反之亦反
KdTree* searchDistrict;
if (currentTree->isLeft())
{
if (currentTree->parent->rightChild == NULL)
searchDistrict = currentTree;
else
searchDistrict = currentTree->parent->rightChild;
}
else
{
searchDistrict = currentTree->parent->leftChild;
}
//如果搜索区域对应的子kd树的根结点不是整个kd树的根结点,继续回退搜索
while (searchDistrict->parent != NULL)
{
//搜索区域与目标点的最近距离
double districtDistance = abs(goal[(d + 1) % k] - searchDistrict->parent->root[(d + 1) % k]);
//如果“搜索区域与目标点的最近距离”比“当前最近邻与目标点的距离”短,表明搜索
//区域内可能存在距离目标点更近的点
if (districtDistance < currentDistance)//&& !searchDistrict->isEmpty()
{
double parentDistance = measureDistance(goal, searchDistrict->parent->root, 0);
if (parentDistance < currentDistance)
{
currentDistance = parentDistance;
currentTree = searchDistrict->parent;
currentNearest = currentTree->root;
}
if (!searchDistrict->isEmpty())
{
double rootDistance = measureDistance(goal, searchDistrict->root, 0);
if (rootDistance < currentDistance)
{
currentDistance = rootDistance;
currentTree = searchDistrict;
currentNearest = currentTree->root;
}
}
if (searchDistrict->leftChild != NULL)
{
double leftDistance = measureDistance(goal, searchDistrict->leftChild->root, 0);
if (leftDistance < currentDistance)
{
currentDistance = leftDistance;
currentTree = searchDistrict;
currentNearest = currentTree->root;
}
}
if (searchDistrict->rightChild != NULL)
{
double rightDistance = measureDistance(goal, searchDistrict->rightChild->root, 0);
if (rightDistance < currentDistance)
{
currentDistance = rightDistance;
currentTree = searchDistrict;
currentNearest = currentTree->root;
}
}
}//end if
if (searchDistrict->parent->parent != NULL)
{
searchDistrict = searchDistrict->parent->isLeft() ?
searchDistrict->parent->parent->rightChild :
searchDistrict->parent->parent->leftChild;
}
else
{
searchDistrict = searchDistrict->parent;
}
++d;
}//end while
return currentNearest;
}
int main()
{
int data[6][2] = { { 2,3 },{ 5,4 },{ 9,6 },{ 4,7 },{ 8,1 },{ 7,2 } };
vector<vector<double> > train(6, vector<double>(2, 0));
for (unsigned i = 0; i < 6; ++i)
for (unsigned j = 0; j < 2; ++j)
train[i][j] = data[i][j];
KdTree* kdTree = new KdTree;
buildKdTree(kdTree, train, 0);
printKdTree(kdTree, 0);
vector<double> goal;
goal.push_back(3);
goal.push_back(4.5);
vector<double> nearestNeighbor = searchNearestNeighbor(goal, kdTree);
vector<double>::iterator beg = nearestNeighbor.begin();
cout << "The nearest neighbor is: ";
while (beg != nearestNeighbor.end()) cout << *beg++ << ",";
cout << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
给定点p,查询数据集中与其距离最近点的过程即为最近邻搜索。
如在上文构建好的k-d tree上搜索(3,5)的最近邻时,本文结合如下左右两图对二维空间的最近邻搜索过程作分析。
a)首先从根节点(7,2)出发,将当前最近邻设为(7,2),对该k-d tree作深度优先遍历。以(3,5)为圆心,其到(7,2)的距离为半径画圆(多维空间为超球面),可以看出(8,1)右侧的区域与该圆不相交,所以(8,1)的右子树全部忽略。
b)接着走到(7,2)左子树根节点(5,4),与原最近邻对比距离后,更新当前最近邻为(5,4)。以(3,5)为圆心,其到(5,4)的距离为半径画圆,发现(7,2)右侧的区域与该圆不相交,忽略该侧所有节点,这样(7,2)的整个右子树被标记为已忽略。
c)遍历完(5,4)的左右叶子节点,发现与当前最优距离相等,不更新最近邻。所以(3,5)的最近邻为(5,4)。
 |
 |
