写Java程序时会经常从classpath下读取文件,是时候该整理一下了,并在不断深入的过程中,陆续补充上。
现在Java project 都以maven项目居多, 比如像下面这样的一个项目结构:
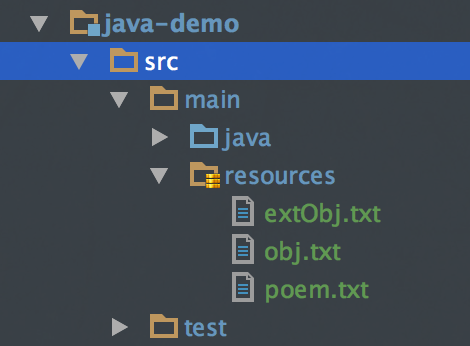
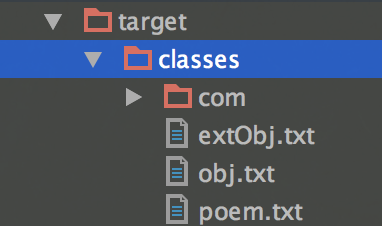
编译后的class文件都到了target目录,如下面的结构:
看代码:
import java.io.File; import java.net.URL; public class Poem { public static void main(String[] args) { Poem poem = new Poem(); poem.getFile("extObj.txt"); } private void getFile(String fileName) { ClassLoader classLoader = getClass().getClassLoader(); /** getResource()方法会去classpath下找这个文件,获取到url resource, 得到这个资源后,调用url.getFile获取到 文件 的绝对路径 */ URL url = classLoader.getResource(fileName); /** * url.getFile() 得到这个文件的绝对路径 */ System.out.println(url.getFile()); File file = new File(url.getFile()); System.out.println(file.exists()); } }
通过上面这种方式就可以获取到这个文件资源。
在一个static method 里可以直接通过类的ClassLoader对象获取文件资源。
URL url = Poem.class.getClassLoader().getResource("extObj.txt"); File file = new File(url.getFile());
// 直接获取到输入流 // fileName 就是resources里的文件名 InputStream in = Poem.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(fileName);
综上述,类里的getClassLoader去寻找fileName都是从classpath去找的,毕竟是ClassLoader嘛。
如果一个包里面有一个配置文件,那该怎么获取呢? 如图:

第一个dbconfig.properties在类package下,第二个dbconfig.properties在resources目录下,
那怎么获取到package下的dbconfig properties文件呢?
here goes code:
package com.getfilefromclasspath; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.util.Properties; public class ClassLoaderDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ClassLoaderDemo demo = new ClassLoaderDemo(); demo.loadProperties(); } public void loadProperties() throws IOException { InputStream input = null; try { /** /dbconfig.properties 绝对路径, 取到的文件是classpath下的 resources/dbconfig.properties 相对路径 获取文件流 */ // 获取到classpath下的文件 input = Class.forName(ClassLoaderDemo.class.getName()).getResourceAsStream("/dbconfig.properties"); // 获取到package下的文件 // input = Class.forName(ClassLoaderDemo.class.getName()).getResourceAsStream("resources/dbconfig.properties"); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } printProperties(input); } private void printProperties(InputStream input) throws IOException { Properties properties = new Properties(); properties.load(input); System.out.println(properties.getProperty("username")); } }
不使用Class.forName(), 通过具体对象获取到Class对象:
//also can be this way: input = this.getClass().getResourceAsStream("resources/dbconfig.properties"); // 对应package下的文件 input = this.getClass().getResourceAsStream("/dbconfig.properties"); // 对应resources下的文件
Class对象还有getResource() 的方法去获取文件资源,使用规则和上面的一样。
maven项目还要注意一点,maven 的compiler插件在编译时是不会将package下的文本文件给编译到target下的,
下图是我在用mybatis框架的时候将xml的mapper给放到package编译后的效果:
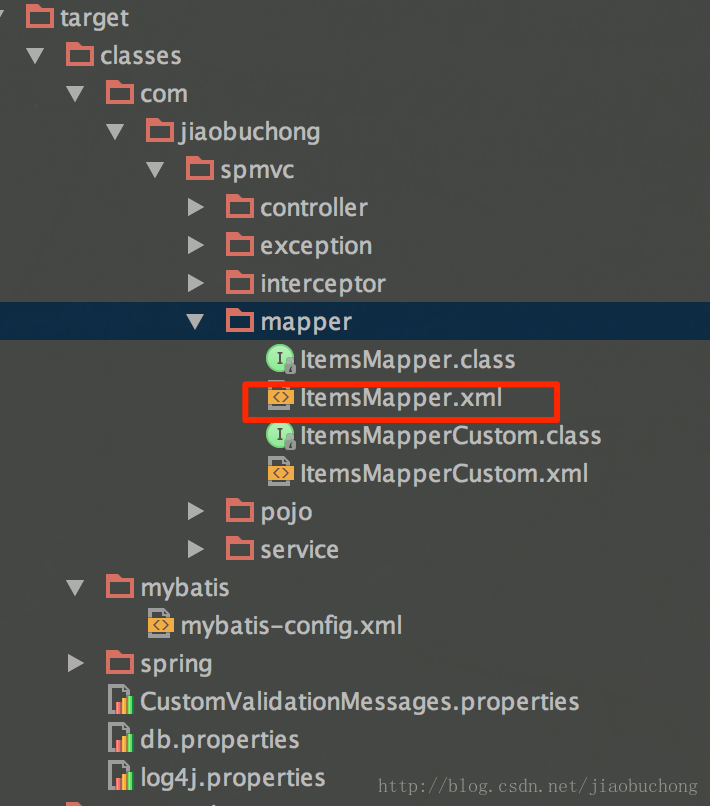
这个得在pom.xml加对应的配置(这是在使用mybatis时遇到的坑):
<build>
<finalName>java-io</finalName>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<!--properties的配置文件会和编译后的class文件放在一起-->
<include>**/*.properties</include>
</includes>
</resource>
<resource>
<!--加载配置的资源-->
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
</resource>
</resources>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>