Comparing Methods
a.compareTo(b); //按字典顺序比较两个字符串,返回0: a=b, 返回正数: a > b, 返回负数: a < b
Sorting Methods
Arrays.sort(); //字母序优先于长度
Collections.sort();
Custom Comparator
- max heap,按频率排序,频率相同则字典序
PriorityQueue<String> heap = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> map.get(a) == map.get(b) ? b.compareTo(a) : (map.get(a) - map.get(b)));
HashMap, Heap... Related Sort
- Heap
PriorityQueue 默认小根堆(自动排序特性),不保证整个队列都有序,只保证队列头是最小的
PriorityQueue <Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<> (26, Collections.reverseOrder()); //大根堆
- TreeMap documents
treemap基于红黑树,检索时间是O(logn),默认按照key的自然大小排序(升序,从小到大)
- Map sort by value
List<Map.Entry<Integer, Integer>> list = new ArrayList<Map.Entry<Integer, Integer>>(map.entrySet()); Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Map.Entry<Integer, Integer>>() { public int compare(Entry<Integer, Integer> o1, Entry<Integer, Integer> o2) { return o1.getValue().compareTo(o2.getValue()); } }); // for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> mapping : list) { // System.out.println(mapping.getKey() + ":" + mapping.getValue()); // }
经典排序
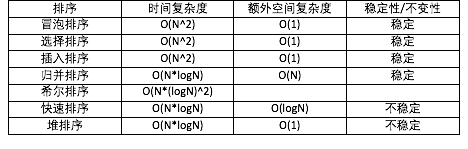
1. Selection Sort
public class Solution { public void sortIntegers(int[] A) { // write your code here for(int i = 0; i < A.length; i++) { int min_idx = i; for(int j = i + 1; j < A.length; j++) { if(A[j] < A[min_idx]) min_idx = j; } int tmp = A[i]; A[i] = A[min_idx]; A[min_idx] = tmp; } } }
2. Merge Sort
public class MergeSort { public static int[] mergeSort(int[] array) { // Write your solution here if(array == null || array.length == 0) return array; int[] helper = new int[array.length]; mergeSort(array, helper, 0, array.length - 1); return array; } private static void mergeSort(int[] array, int[] helper, int left, int right) { if(left >= right) return; int mid = left + (right - left) / 2; mergeSort(array, helper, left, mid); mergeSort(array, helper, mid + 1, right); merge(array, helper, left, mid, right); } private static void merge(int[] a, int[] helper, int left, int mid, int right) { for(int i = left; i <= right; i++) { helper[i] = a[i]; } int p1 = left, p2 = mid + 1, p = left; while(p1 <= mid && p2 <= right) { if(helper[p1] <= helper[p2]) a[p++] = helper[p1++]; else a[p++] = helper[p2++]; } while(p1 <= mid) { a[p++] = helper[p1++]; } while(p2 <= right) { a[p++] = helper[p2++]; } } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {3,1,5,7,9,8,4,2,0}; MergeSort solution = new MergeSort(); arr = solution.mergeSort(arr); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); } }
3. Quick Sort
public class QuickSort { public int[] quickSort(int[] array) { quickSort(array, 0, array.length - 1); return array; } public void quickSort(int[] array, int left, int right) { if(left >= right) return; Random r = new Random(); int pivot_idx = left + r.nextInt(right - left + 1); int pivot = array[pivot_idx]; swap(array, pivot_idx, right); int i = left, j = right - 1; while(i <= j) { if(array[i] < pivot) { i++; } else{ swap(array, i, j--); } } swap(array, i, right); quickSort(array, left, i - 1); quickSort(array, i + 1, right); } private void swap(int[] array, int i, int j) { int tmp = array[i]; array[i] = array[j]; array[j] = tmp; } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {3,1,5,7,9,8,4,2,0}; QuickSort solution = new QuickSort(); arr = solution.quickSort(arr); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); } }
to be continued...