我们知道Logstash的架构如下:
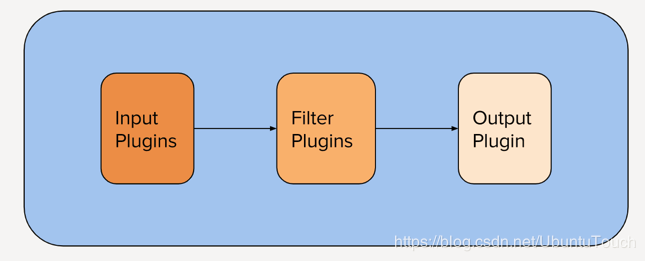
它的整个pipleline分为三个部分:
input插件:提取数据。 这可以来自日志文件,TCP或UDP侦听器,若干协议特定插件(如syslog或IRC)之一,甚至是排队系统(如Redis,AQMP或Kafka)。 此阶段使用围绕事件来源的元数据标记传入事件。
filter 插件:插件转换并丰富数据
output插件: 将已处理的事件加载到其他内容中,例如ElasticSearch或其他文档数据库,或排队系统,如Redis,AQMP或Kafka。 它还可以配置为与API通信。 也可以将像PagerDuty这样的东西连接到Logstash输出。
这里的input可以支持多个input,同时多个worker可以处理filter及output:

在今天的介绍中,我们来介绍一下如何使用多个input。
应用文件
为了说明问题的方便,我把所需要用到的文件都传到github地址https://github.com/liu-xiao-guo/logstash_multi-input。我们可以通过如下的方式来下载这些文件:
git clone https://github.com/liu-xiao-guo/logstash_multi-input
Logstash配置文件
Logstash的配置文件如下:
multi-input.conf
input { file { path => "/Users/liuxg/data/multi-input/apache.log" start_position => "beginning" sincedb_path => "/dev/null" # ignore_older => 100000 type => "apache" } } input { file { path => "/Users/liuxg/data/multi-input/apache-daily-access.log" start_position => "beginning" sincedb_path => "/dev/null" type => "daily" } } filter { grok { match => { "message" => '%{IPORHOST:clientip} %{USER:ident} %{USER:auth} [%{HTTPDATE:timestamp}] "%{WORD:verb} %{DATA:request} HTTP/%{NUMBER:httpversion}" %{NUMBER:response:int} (?:-|%{NUMBER:bytes:int}) %{QS:referrer} %{QS:agent}' } } if[type] == "apache" { mutate { add_tag => ["apache"] } } if [type] == "daily" { mutate { add_tag => ["daily"] } } } output { stdout { codec => rubydebug } if "apache" in [tags] { elasticsearch { index => "apache_log" template => "/Users/liuxg/data/apache_template.json" template_name => "apache_elastic_example" template_overwrite => true } } if "daily" in [tags] { elasticsearch { index => "apache_daily" template => "/Users/liuxg/data/apache_template.json" template_name => "apache_elastic_example" template_overwrite => true } } }
为了说明问题的方便,我们使用了两个input。它们分别对应不同的log文件。对于这两个input,我们也使用了不同的type来表示:apache和daily。尽管它们的格式是一样的,它们共同使用同样的一个grok filter,但是我们还是想分别对它们进行处理。为此,我们添加了一个tag。我们也可以添加一个field来进行区别。在output的部分,我们根据在filter部分设置的tag来对它们输出到不同的index里。
运行Logstash
$ pwd /Users/liuxg/elastic/logstash-7.3.0 bogon:logstash-7.3.0 liuxg$ sudo ./bin/logstash -f ~/data/multi-input/multi-input.conf
当你们运行这个例子的时候,你们需要根据自己存放multi-input.conf文件的位置改变而改变上面的命令。
运行的结果如下:

根据显示的结果可以看出来daily的事件最早被处理及输出。接着apache的数据才开始处理。在实际的应用中,我们可能有不同的数据源,比如来自其它beats的监听某个端口的数据。
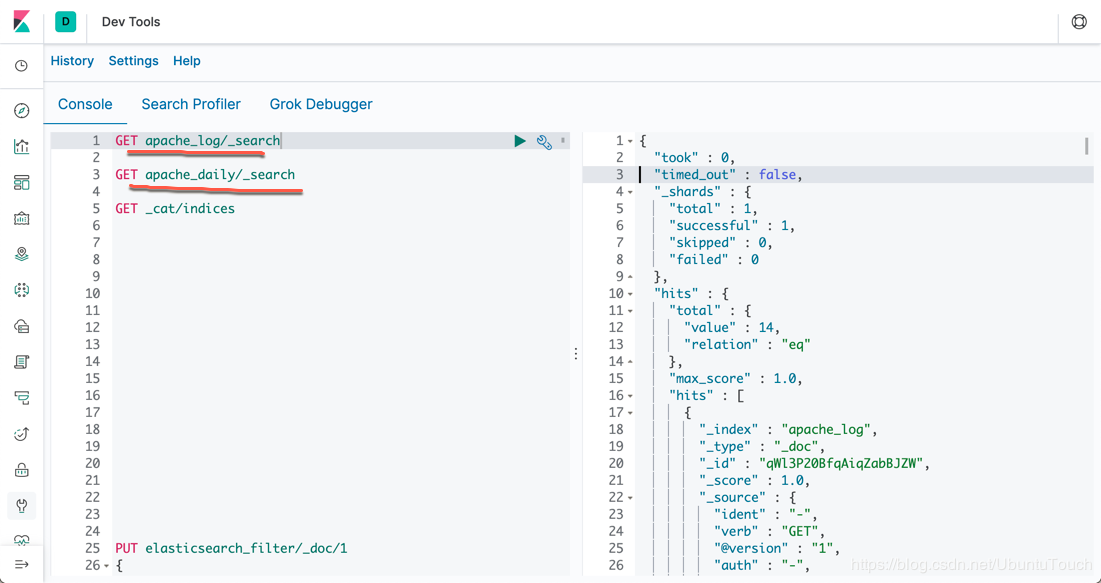
我们可以在Kibana中看到我们最终的index数据:
转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/UbuntuTouch/java/article/details/100980709