iOS常用的设计模式有:单例模式、委托模式、观察者模式和MVC模式。下面分别简单介绍。
一:单例模式
我们常用的UIApplication、NSUserdefaults、NSNotificationCenter这些类都是单例类。
单例模式的作用是解决应用中只有一个实例的一类问题,例如
UIAPPlication,这个实例代表了整个应用程序对象,它只能是一个实例,来实现应用程序中一些共享资源的访问和状态的保持等。我们常使用
[[UIApplication sharedApplication] openURL:[NSURL URLWithString:@"tel://110"]];
来调用系统拨打电话;
NSUserDefaults,这个实例可以方便的保存应用程序的一些设置,持久化保存一些需要的数据。例如我们使用
[[NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults] setObject:@"张三" forKey:@"name"]; NSString *name = [[NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults] objectForKey:@"name"]; NSLog(@"存储的名字是%@",name);
将“张三”这个名字存储在NSUserDefaults实例中,下次我们再次打开应用程序时依然能从这个实例中取出“张三”。
当需要的时候,我们也可以通过下面的方法自己来创建一个实例。假如我们现在需要一个Person的实例
Person.h
@interface Person : NSObject @property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *name; + (Person *)sharedPerson; @end
Person.m
#import "Person.h" @implementation Person static Person *personManager = nil; + (Person *)sharedPerson { //该函数由GCD实现,能确保在整个应用程序生命周期中只执行一次代码块 static dispatch_once_t onceToken; dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{ personManager = [[self alloc] init]; }); return personManager; } @end
我们可以通过方法+ (Person *)sharedPerson调用Person实例。
[[Person sharedPerson] setName:@"张三"]; NSLog(@"person的名字是%@",[[Person sharedPerson] name]);
二:委托模式
委托是为了降低一个对象的复杂度和耦合度,使其能够更具通用性而将其中一些处理至于委托对象中的编码方式。
比如小明是一个超人,但是他也要做饭、洗衣服、扫地等等,如果这些全部都有他亲自来做,那么小明就会变得特别繁忙,就没空去拯救地球了。
这时候,小明可以将做饭委托给电饭煲;将洗衣服委托给洗衣机;将扫地委托给机器人等等。
具体的实现类似如下:
小明.h
@protocol 小明的Delegate<NSObject> - (void)做饭; @end @interface 小明 : UIView @property(nonatomic,strong)id <小明的代理>delegate; @end
小明.m
- (void)小明发送指令 { [self.delegate 做饭]; }
电饭煲.m
- (void)viewDidLoad { [super viewDidLoad]; xiaoming = [[小明 alloc]init]; xiaoming.delegate = self(电饭煲); } - (void)做饭 { NSLog("我开始做饭了~") }
在小明的.h中,小明有一个委托就是“做饭”,并且先假想已经有一个委托人delegate了,在.m中当发送指令之后让委托人直接执行“做饭”。
在电饭煲的.m中,电饭煲通过“xiaoming.delegate = self”,主动担当起了小明的委托人,这个时候电饭煲就必须尽到委托人的职责,当小明发送指令时(比如按下某个按钮的事件),电饭煲就自动开始做饭了。
iOS开发中委托模式是经常使用的,例如UIAlertView,它有一个委托方法- (void)alertView:(UIAlertView *)alertView clickedButtonAtIndex:(NSInteger)buttonIndex,当按钮被点击时自动执行。
@protocol UIAlertViewDelegate <NSObject> // Called when a button is clicked. The view will be automatically dismissed after this call returns - (void)alertView:(UIAlertView *)alertView clickedButtonAtIndex:(NSInteger)buttonIndex @end
我们将ViewController作为委托人,实现UIAlertView的委托
@interface ViewController ()<UIAlertViewDelegate> @end @implementation ViewController - (void)viewDidLoad { [super viewDidLoad]; UIAlertView *alert = [[UIAlertView alloc] initWithTitle:@"提醒" message:@"我是超人么" delegate:self cancelButtonTitle:@"不是" otherButtonTitles:@"是", nil]; [alert show]; } - (void)alertView:(UIAlertView *)alertView clickedButtonAtIndex:(NSInteger)buttonIndex { if (buttonIndex == 0) { NSLog(@"我不是超人"); } else { NSLog(@"我是超人"); } }
在我之前的一篇博客里已经写过怎么写自定义代理,感兴趣的可以移步过去看看。
三、观察者模式
观察者模式也可以叫做订阅/发布模式,类似于我们现在订阅微信公众号。
观察者模式的具体应用有两个:通知机制(Notification)和KVO机制(Key-Value Observing)。
I 、通知机制

①注册通知使用方法- (void)addObserver:(id)observer selector:(SEL)aSelector name:(nullable NSString *)aName object:(nullable id)anObject;
解除通知使用方法- (void)removeObserver:(id)observer name:(nullable NSString *)aName object:(nullable id)anObject;
②投送通知有三种方法,根据是否需要传参等情况选择使用
- (void)postNotification:(NSNotification *)notification;
- (void)postNotificationName:(NSString *)aName object:(nullable id)anObject;
- (void)postNotificationName:(NSString *)aName object:(nullable id)anObject userInfo:(nullable NSDictionary *)aUserInfo;
③投送者投送通知之后会自动发送通知,这时接收者接收通知,在注册通知时会指定接收方法(SEL)aSelector,接收到通知之后会执行该方法。
系统中有很多地方都有用到通知机制,例如键盘的出现和消失,都会给通知中心投送通知,只要注册了该通知,就能监听到键盘的出现和消失事件。
下面我们写一个简单的例子,将present出来的test视图中输入的字符串回传给ViewController,简单演示下什么是通知机制。在例子中,有注册监听键盘出现消失的演示。
ViewController.m
#import "ViewController.h" #import "TestViewController.h" @interface ViewController ()<UIAlertViewDelegate> { UILabel *myLabel; } @end @implementation ViewController - (void)viewDidLoad { [super viewDidLoad]; UIButton *redButton = [[UIButton alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(50, 50, 100, 100)]; redButton.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor]; [redButton setTitle:@"跳转" forState:UIControlStateNormal]; [redButton addTarget:self action:@selector(clickedRedButton) forControlEvents:UIControlEventTouchUpInside]; [self.view addSubview:redButton]; myLabel = [[UILabel alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(50, 200, 200, 40)]; myLabel.textColor = [UIColor blackColor]; myLabel.backgroundColor = [UIColor yellowColor]; [self.view addSubview:myLabel]; //注册通知 [[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] addObserver:self selector:@selector(displayText:) name:@"testViewDismiss" object:nil]; } //接收到通知之后执行相应方法 - (void)displayText:(NSNotification *)notification { NSDictionary *dic = [notification userInfo]; myLabel.text = dic[@"text"]; } - (void)clickedRedButton { TestViewController *testVC = [[TestViewController alloc] init]; [self presentViewController:testVC animated:YES completion:^{ }]; } @end
TestViewController.m
#import "TestViewController.h" @interface TestViewController () { UITextField *textField; } @end @implementation TestViewController - (void)viewDidLoad { [super viewDidLoad]; self.view.backgroundColor = [UIColor whiteColor]; UIButton *blueButton = [[UIButton alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(50, 50, 100, 100)]; blueButton.backgroundColor = [UIColor blueColor]; [blueButton setTitle:@"消失" forState:UIControlStateNormal]; [blueButton addTarget:self action:@selector(clickedRedButton) forControlEvents:UIControlEventTouchUpInside]; [self.view addSubview:blueButton]; textField = [[UITextField alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(50, 200, 200, 40)]; textField.borderStyle = UITextBorderStyleRoundedRect; [self.view addSubview:textField]; //注册键盘出现的通知 [[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] addObserver:self selector:@selector(keyboardWasShown:) name:UIKeyboardWillShowNotification object:nil]; //注册键盘消失的通知 [[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] addObserver:self selector:@selector(keyboardWillBeHidden:) name:UIKeyboardWillHideNotification object:nil]; } - (void)clickedRedButton { [self dismissViewControllerAnimated:YES completion:^{ NSDictionary *dic = @{ @"text":textField.text }; //投送通知 [[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] postNotificationName:@"testViewDismiss" object:nil userInfo:dic]; }]; } - (void)keyboardWasShown:(NSNotification*)aNotification { NSLog(@"键盘出现"); } -(void)keyboardWillBeHidden:(NSNotification*)aNotification { NSLog(@"键盘消失"); } @end
运行效果如下:
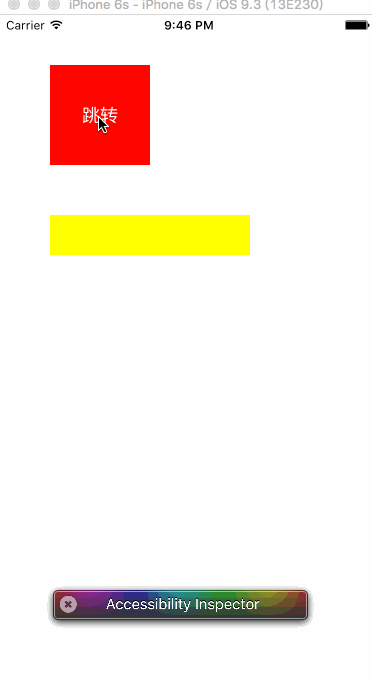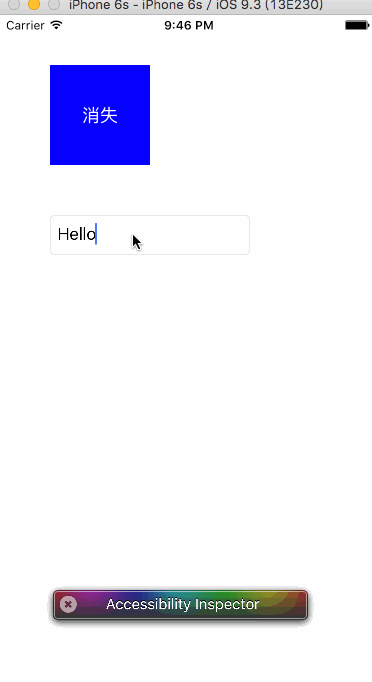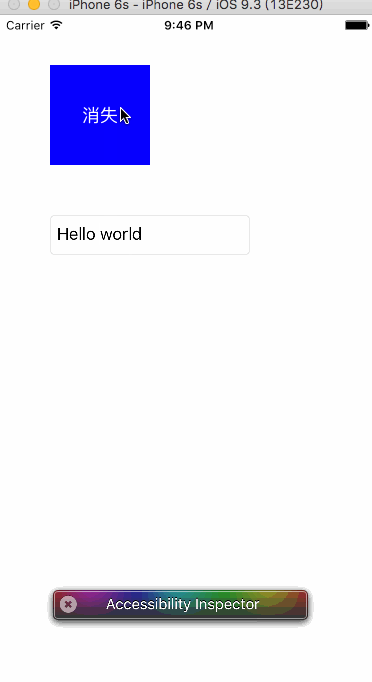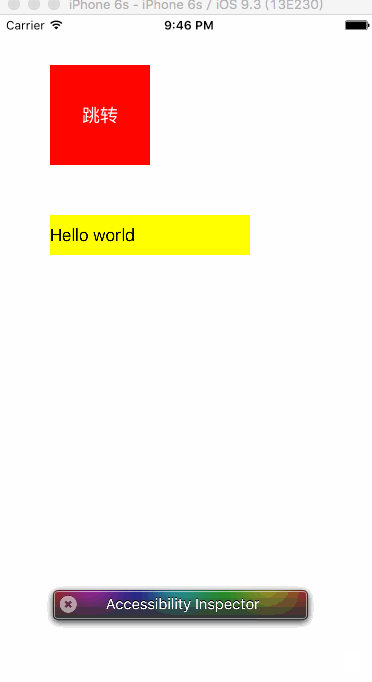
注意:接收者注册的通知name和投送者投送的通知name一定要一致。
通知机制可以让我们很方便的监听某些事件的发生,并传递一些我们需要的值。
II、KVO机制
KVO即键(key)-值(value)观察,之前看到过一篇博文,讲得非常透彻,自己目前的水平还不足以写的更好,大家可以点击下面链接查看。
四、MVC模式
Model即数据模型,通常用来处理应用业务逻辑,将数据传输给控制器。
View即视图,通过控制器传来的数据更新展示信息界面。
Controller即控制器,接收用户请求,根据请求更新模型,继而更新视图以响应用户的请求。控制器是视图和模型的媒介,可以降低视图和数据模型的耦合度。

MVC在开发中比较常用,一般小项目都可以按照这种大模式来开发。
在我之前写的一篇介绍UICollectionView的博文里,就是用了MVC模式,放在这里作为一个例子,大家可以移步过去看一下。
至此,iOS开发中常用的四种模式就介绍完了,灵活的使用可以使我们的开发更加高效。