SpringApplicationRunListener:接口的作用主要就是在Spring Boot 启动初始化的过程中可以通过SpringApplicationRunListener接口回调来让用户在启动的各个流程中可以加入自己的逻辑
@SpringBootApplication annotation can be used to enable those three features, that is:
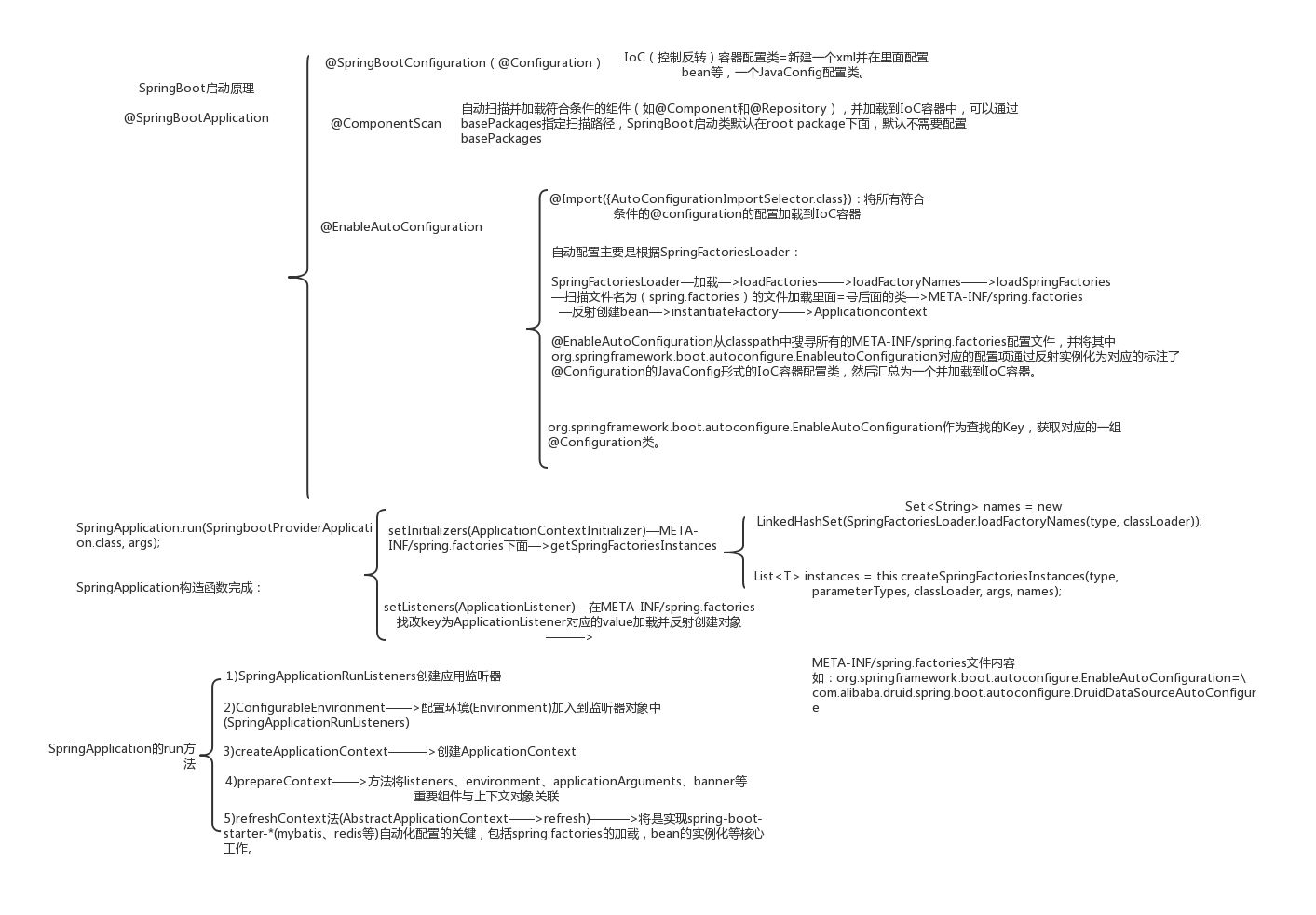
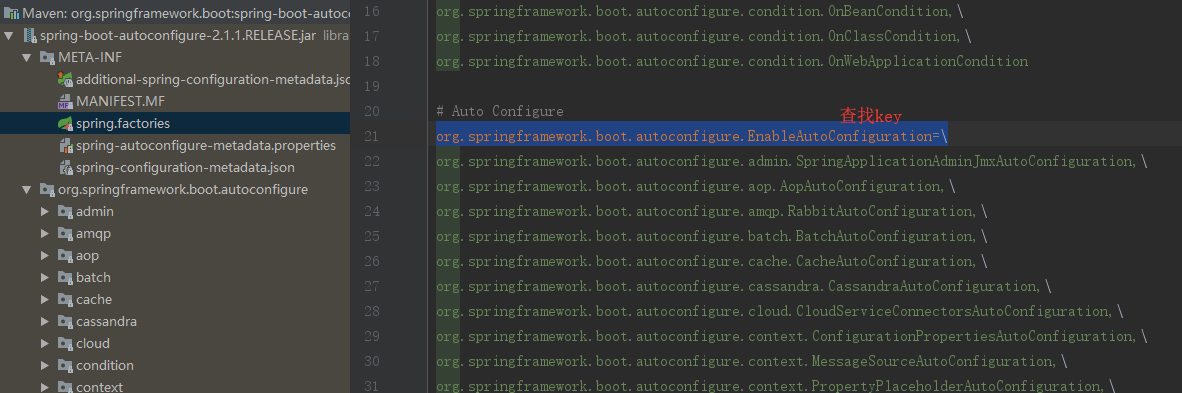
@EnableAutoConfiguration: enable Spring Boot’s auto-configuration mechanism(扫描“spring.factories”文件,实现自动注册)@ComponentScan: enable@Componentscan on the package where the application is located (see the best practices)等同于(<compan-scan/>扫描加上注解的类)@Configuration: allow to register extra beans in the context or import additional configuration classes等同于(spring中在spring.xml文件中 写一个<bean/>。bean注册及bean管理)
内置Tomcat
The @SpringBootApplication annotation is equivalent to using @Configuration, @EnableAutoConfiguration, and @ComponentScan with their default attributes, as shown in the following example:
SpringBoot自动配置模块
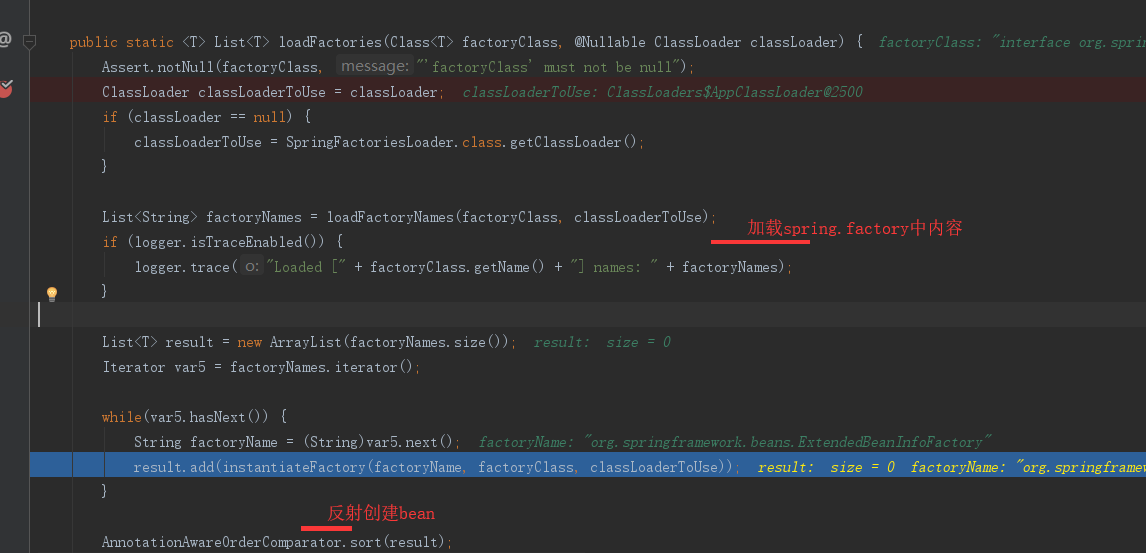
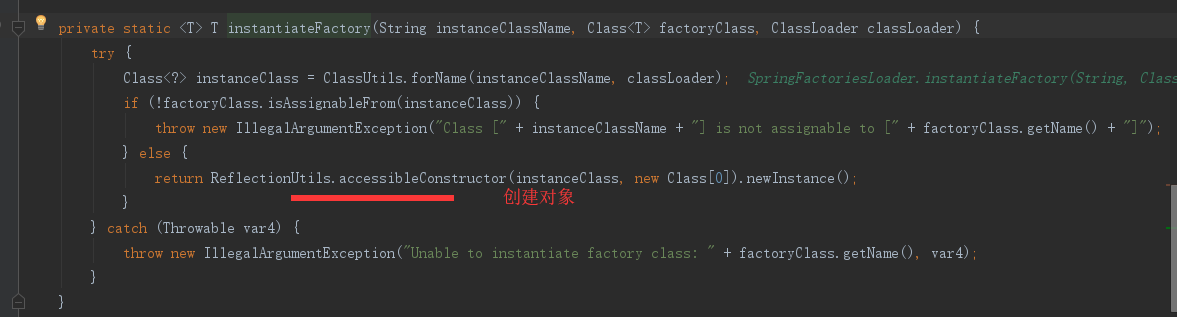
该配置模块的主要使用到了SpringFactoriesLoader,即Spring工厂加载器,该对象提供了loadFactoryNames方法,入参为factoryClass和classLoader,即需要传入工厂类名称和对应的类加载器,方法会根据指定的classLoader,加载该类加器搜索路径下的指定文件,即spring.factories文件,传入的工厂类为接口,而文件中对应的类则是接口的实现类,或最终作为实现类,所以文件中一般为如下图这种一对多的类名集合,获取到这些实现类的类名后,loadFactoryNames方法返回类名集合,方法调用方得到这些集合后,再通过反射获取这些类的类对象、构造方法,最终生成实例。
SpringBoot自动化配置关键组件关系图
mybatis-spring-boot-starter、spring-boot-starter-web等组件的META-INF文件下均含有spring.factories文件,自动配置模块中,SpringFactoriesLoader收集到文件中的类全名并返回一个类全名的数组,返回的类全名通过反射被实例化,就形成了具体的工厂实例,工厂实例来生成组件具体需要的bean。
之前我们提到了EnableAutoConfiguration注解,其类图如下:

可以发现其最终实现了ImportSelector(选择器)和BeanClassLoaderAware(bean类加载器中间件),重点关注一下AutoConfigurationImportSelector的selectImports方法。
MybatisAutoConfiguration
在上面的代码可以看到自动配置器会根据传入的factoryClass.getName()到项目系统路径下所有的spring.factories文件中找到相应的key,从而加载里面的类。我们就选取这个mybatis-spring-boot-autoconfigure下的spring.factories文件
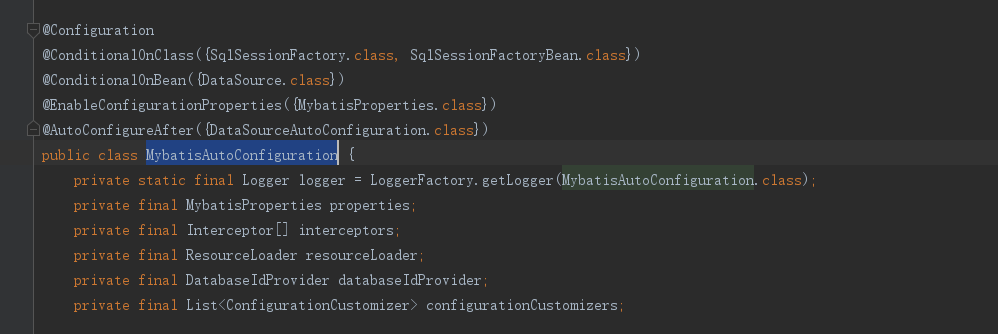
发现Spring的@Configuration,俨然是一个通过注解标注的springBean,继续向下看,
-
@ConditionalOnClass({ SqlSessionFactory.class, SqlSessionFactoryBean.class}):当存在SqlSessionFactory.class,SqlSessionFactoryBean.class这两个类时才解析MybatisAutoConfiguration配置类,否则不解析这一个配置类,make sence,我们需要mybatis为我们返回会话对象,就必须有会话工厂相关类。 -
@CondtionalOnBean(DataSource.class):只有处理已经被声明为bean的dataSource。 -
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(MapperFactoryBean.class)这个注解的意思是如果容器中不存在name指定的bean则创建bean注入,否则不执行(该类源码较长,篇幅限制不全粘贴)
以上配置可以保证sqlSessionFactory、sqlSessionTemplate、dataSource等mybatis所需的组件均可被自动配置,@Configuration注解已经提供了Spring的上下文环境,所以以上组件的配置方式与Spring启动时通过mybatis.xml文件进行配置起到一个效果。
通过分析我们可以发现,只要一个基于SpringBoot项目的类路径下存在SqlSessionFactory.class, SqlSessionFactoryBean.class,并且容器中已经注册了dataSourceBean,就可以触发自动化配置,意思说我们只要在maven的项目中加入了mybatis所需要的若干依赖,就可以触发自动配置,但引入mybatis原生依赖的话,每集成一个功能都要去修改其自动化配置类,那就得不到开箱即用的效果了。

这里是截取的mybatis-spring-boot-starter的源码中pom.xml文件中所有依赖:
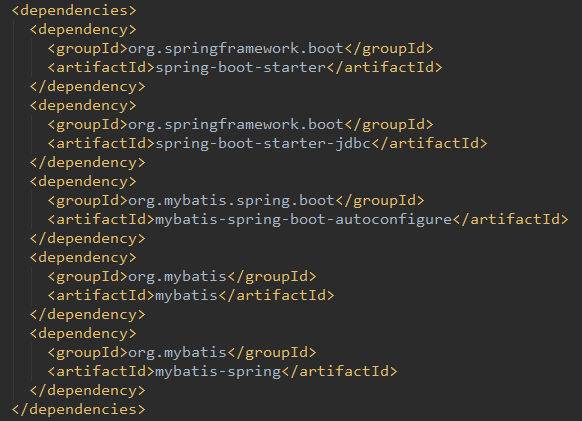
因为maven依赖的传递性,我们只要依赖starter就可以依赖到所有需要自动配置的类,实现开箱即用的功能。也体现出Springboot简化了Spring框架带来的大量XML配置以及复杂的依赖管理,让开发人员可以更加关注业务逻辑的开发。
SpringBoot 内置tomcat
@SpringBootApplication->,@EnableAutoConfiguration->@ComponentScan,@EnableAutoConfiguration->AutoConfigurationImportSelector:selectImports()
-getAutoConfigurationEntry()->getCandidateConfigurations():
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,
autoconfig.jar 下面 spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.1.1.RELEASE.jar->spring.factories
ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration(生产出一个servlet容器)):
EmbeddedTomcat->TomcatServletWebServerFactory->getWebServer
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
//等于创建了server 里面在添加Connector,host 等
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
File baseDir = this.baseDirectory != null ? this.baseDirectory : this.createTempDir("tomcat");
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
this.customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
this.configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
Iterator var5 = this.additionalTomcatConnectors.iterator();
while(var5.hasNext()) {
Connector additionalConnector = (Connector)var5.next();
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
this.prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
return this.getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
}
Tomcat 在什么时候被创建的?
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootProviderApplication.class, args)->refreshContext()->onRefresh->
ServletWebServerApplicationContext->createWebServer()->
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
this.createWebServer();
} catch (Throwable var2) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", var2);
}
}
private void createWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletContext();
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
//在加载的时候getWebServerFactory 已经加载了
ServletWebServerFactory factory = this.getWebServerFactory();
//创建webServer ServletWebServerFactory 有不同的实现类 如 tomcat ,jetty的
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(new ServletContextInitializer[]{this.getSelfInitializer()});
} else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
this.getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
} catch (ServletException var4) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context", var4);
}
}
this.initPropertySources();
}
SpringApplication.run()
Spring Context IOC 容器 (spring所有初始化的操作)
Listener
Filter
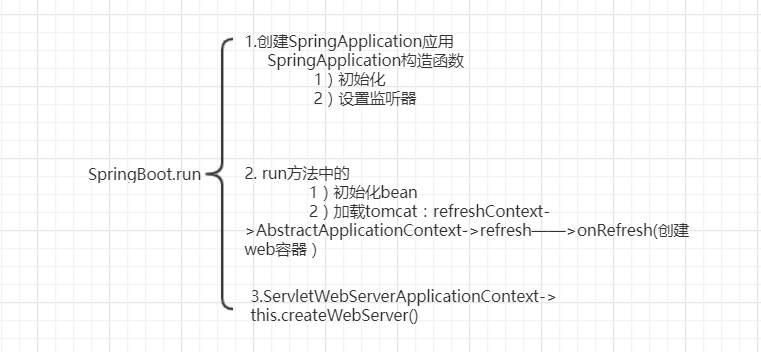
1.创建SpringApplication应用
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class... primarySources) { this.sources = new LinkedHashSet(); this.bannerMode = Mode.CONSOLE; this.logStartupInfo = true; this.addCommandLineProperties = true; this.addConversionService = true; this.headless = true; this.registerShutdownHook = true; this.additionalProfiles = new HashSet(); this.isCustomEnvironment = false; this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader; Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null"); this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
//判断web应用类型 this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
//初始化 this.setInitializers(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
//设计监听器 SpringFactories-> spring.factories文件 this.setListeners(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class)); this.mainApplicationClass = this.deduceMainApplicationClass(); }
# Application Listeners
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.BackgroundPreinitializer
# Auto Configuration Import Listeners
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportListener=
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionEvaluationReportAutoConfigurationImportListener
2.run (以下源码删除了部分代码)
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) { ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null; Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList(); this.configureHeadlessProperty(); Collection exceptionReporters; try { ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args); ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this.prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments); this.configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
//打印banner Banner printedBanner = this.printBanner(environment);
// spring上下文 context = this.createApplicationContext(); exceptionReporters = this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class, new Class[]{ConfigurableApplicationContext.class}, context); this.prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
// 在该方法中加载tomcat :AbstractApplicationContext->refresh——>onRefresh(创建web容器) this.refreshContext(context); this.afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments); if (this.logStartupInfo) { (new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)).logStarted(this.getApplicationLog(), stopWatch); } listeners.started(context); this.callRunners(context, applicationArguments); } catch (Throwable var10) { this.handleRunFailure(context, var10, exceptionReporters, listeners); throw new IllegalStateException(var10); } try { listeners.running(context); return context; } catch (Throwable var9) { this.handleRunFailure(context, var9, exceptionReporters, (SpringApplicationRunListeners)null); throw new IllegalStateException(var9); } }
创建web容器即Tomcat
protected void onRefresh() { super.onRefresh(); try { this.createWebServer(); } catch (Throwable var2) { throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", var2); } }