2018-2019-1 20165311《信息安全系统设计基础》实验三 并发程序
实验三-并发程序-1
任务详情
- 学习使用Linux命令wc(1)
- 基于Linux Socket程序设计实现wc(1)服务器(端口号是你学号的后6位)和客户端
- 客户端传一个文本文件给服务器
- 服务器返加文本文件中的单词数
- 上方提交代码
-
附件提交测试截图,至少要测试附件中的两个文件
学习使用Linux命令wc(1)
-
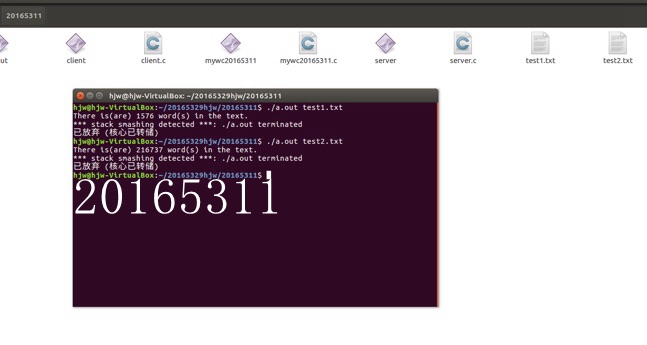
基于Linux Socket程序设计实现wc(1)服务器(端口号是你学号的后6位)和客户端
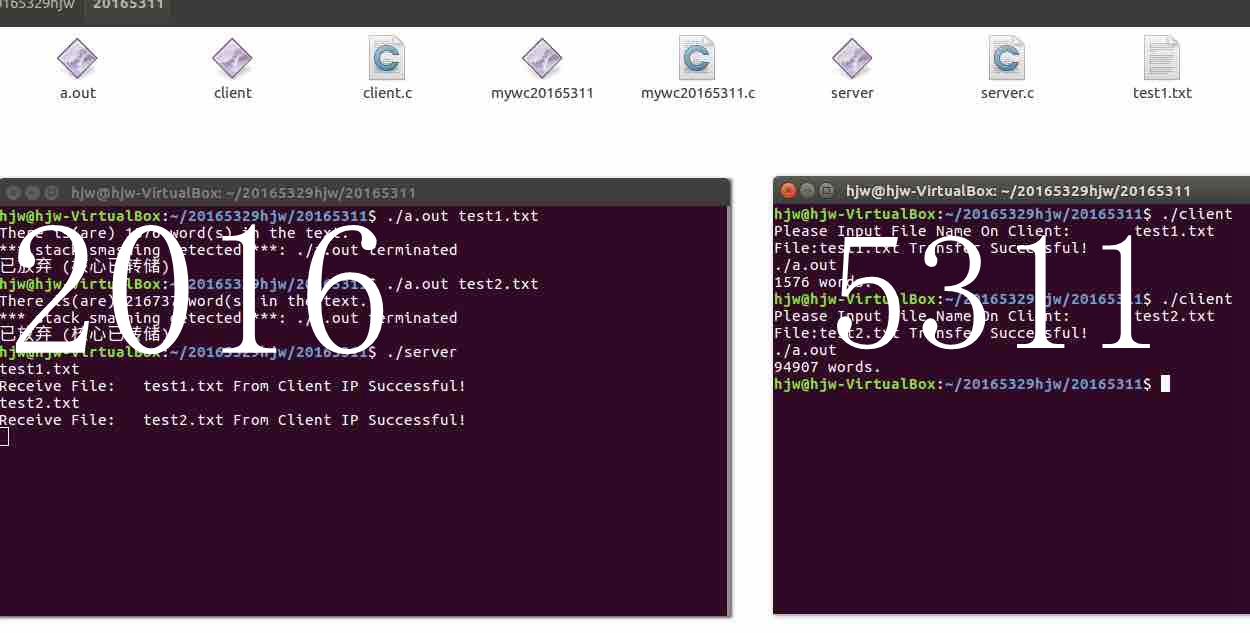
-
客户端传一个文本文件给服务器;服务器返加文本文件中的单词数
实验三-并发程序-2
任务详情
使用多线程实现wc服务器并使用同步互斥机制保证计数正确
上方提交代码
下方提交测试
对比单线程版本的性能,并分析原因
server.c: #include<stdlib.h> #include<pthread.h> #include<sys/socket.h> #include<sys/types.h> //pthread_t , pthread_attr_t and so on. #include<stdio.h> #include<netinet/in.h> //structure sockaddr_in #include<arpa/inet.h> //Func : htonl; htons; ntohl; ntohs #include<assert.h> //Func :assert #include<string.h> //Func :memset bzero #include<unistd.h> //Func :close,write,read #define SOCK_PORT 165329 #define BUFFER_LENGTH 1024 #define MAX_CONN_LIMIT 512 //MAX connection limit static void Data_handle(void * sock_fd); //Only can be seen in the file int CountWordsOfEuropeanTxtFile(char *szFileName); int CountWordsInOneLine(const char *szLine); int main() { int sockfd_server; int sockfd; int fd_temp; struct sockaddr_in s_addr_in; struct sockaddr_in s_addr_client; int client_length; sockfd_server = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0); //ipv4,TCP assert(sockfd_server != -1); //before bind(), set the attr of structure sockaddr. memset(&s_addr_in,0,sizeof(s_addr_in)); s_addr_in.sin_family = AF_INET; s_addr_in.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY); //trans addr from uint32_t host byte order to network byte order. s_addr_in.sin_port = htons(SOCK_PORT); //trans port from uint16_t host byte order to network byte order. fd_temp = bind(sockfd_server,(const struct sockaddr *)(&s_addr_in),sizeof(s_addr_in)); if(fd_temp == -1) { fprintf(stderr,"bind error! "); exit(1); } fd_temp = listen(sockfd_server,MAX_CONN_LIMIT); if(fd_temp == -1) { fprintf(stderr,"listen error! "); exit(1); } while(1) { printf("waiting for new connection... "); pthread_t thread_id; client_length = sizeof(s_addr_client); //Block here. Until server accpets a new connection. sockfd = accept(sockfd_server,(struct sockaddr * restrict)(&s_addr_client),(socklen_t *)(&client_length)); if(sockfd == -1) { fprintf(stderr,"Accept error! "); continue; //ignore current socket ,continue while loop. } printf("A new connection occurs! "); if(pthread_create(&thread_id,NULL,(void *)(&Data_handle),(void *)(&sockfd)) == -1) { fprintf(stderr,"pthread_create error! "); break; //break while loop } } //Clear int ret = shutdown(sockfd_server,SHUT_WR); //shut down the all or part of a full-duplex connection. assert(ret != -1); printf("Server shuts down "); return 0; } static void Data_handle(void * sock_fd) { int fd = *((int *)sock_fd); int i_recvBytes; char data_recv[BUFFER_LENGTH]; const char * data_send = "Server has received your request! "; while(1) { printf("waiting for file_name... "); //Reset data. memset(data_recv,0,BUFFER_LENGTH); i_recvBytes = read(fd,data_recv,BUFFER_LENGTH); if(i_recvBytes == 0) { printf("Maybe the client has closed "); break; } if(i_recvBytes == -1) { fprintf(stderr,"read error! "); break; } if(strcmp(data_recv,"quit")==0) { printf("Quit command! "); break; //Break the while loop. } printf("read from client : %s ",data_recv); char buffer[BUFFER_LENGTH]; int count=0; bzero(buffer, BUFFER_LENGTH); count = CountWordsOfEuropeanTxtFile(data_recv); sprintf(buffer,"%d", count); send(fd, buffer, sizeof(buffer), 0); if(write(fd,data_send,strlen(data_send)) == -1) { break; } } //Clear printf("terminating current client_connection... "); close(fd); //close a file descriptor. pthread_exit(NULL); //terminate calling thread! } int CountWordsOfEuropeanTxtFile(char *szFileName) { int nWords = 0;//词计数变量,初始值为0 FILE *fp; //文件指针 char carrBuffer[1024];//每行字符缓冲,每行最多1024个字符 //打开文件 if ((fp = fopen(szFileName, "r")) == NULL) { return -1; //文件打开不成功是返回-1 } while (!feof(fp))//如果没有读到文件末尾 { //从文件中读一行 if (fgets(carrBuffer, sizeof(carrBuffer),fp) != NULL) //统计每行词数 nWords += CountWordsInOneLine(carrBuffer); } //关闭文件 fclose(fp); return nWords; } int CountWordsInOneLine(const char *szLine) { int nWords = 0; int i=0; for (;i<strlen(szLine);i++) { if (*(szLine+i)!=' ') { nWords++; while ((*(szLine+i)!=' ')&&(*(szLine+i)!='�')) { i++; } } } //printf("%d ",nWords); return nWords; } client.c #include<stdlib.h> #include<sys/socket.h> #include<sys/types.h> //pthread_t , pthread_attr_t and so on. #include<stdio.h> #include<netinet/in.h> //structure sockaddr_in #include<arpa/inet.h> //Func : htonl; htons; ntohl; ntohs #include<assert.h> //Func :assert #include<string.h> //Func :memset bzero #include<unistd.h> //Func :close,write,read #define SOCK_PORT 165329 #define BUFFER_LENGTH 1024 int main() { int sockfd; int tempfd; struct sockaddr_in s_addr_in; char data_send[BUFFER_LENGTH]; char data_recv[BUFFER_LENGTH]; memset(data_send,0,BUFFER_LENGTH); memset(data_recv,0,BUFFER_LENGTH); sockfd = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0); //ipv4,TCP if(sockfd == -1) { fprintf(stderr,"socket error! "); exit(1); } //before func connect, set the attr of structure sockaddr. memset(&s_addr_in,0,sizeof(s_addr_in)); s_addr_in.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("127.0.0.1"); //trans char * to in_addr_t s_addr_in.sin_family = AF_INET; s_addr_in.sin_port = htons(SOCK_PORT); tempfd = connect(sockfd,(struct sockaddr *)(&s_addr_in),sizeof(s_addr_in)); if(tempfd == -1) { fprintf(stderr,"Connect error! "); exit(1); } while(1) { printf("Please Input File Name On Server(input "quit" to quit): "); scanf("%s", data_send); //gets(data_send); //scanf("%[^ ]",data_send); //or you can also use this tempfd = write(sockfd,data_send,BUFFER_LENGTH); if(tempfd == -1) { fprintf(stderr,"write error "); exit(0); } if(strcmp(data_send,"quit") == 0) //quit,write the quit request and shutdown client { break; } else { tempfd = read(sockfd,data_recv,BUFFER_LENGTH); assert(tempfd != -1); printf("%s ",data_recv); memset(data_send,0,BUFFER_LENGTH); memset(data_recv,0,BUFFER_LENGTH); } char buffer[BUFFER_LENGTH]; int length=0; bzero(buffer, BUFFER_LENGTH); length = recv(sockfd, buffer, BUFFER_LENGTH, 0); buffer[length] = '�'; printf("count=%s ", buffer); bzero(buffer, BUFFER_LENGTH); } int ret = shutdown(sockfd,SHUT_WR); //or you can use func close()--<unistd.h> to close the fd assert(ret != -1); return 0; }

-
对比单线程版本的性能,并分析原因
- 线程本身由于创建和切换的开销,采用多线程不会提高程序的执行速度,反而会降低速度,但是对于频繁IO操作的程序,多线程可以有效的并发。
- 单线程比较稳定易于实现,运行稳定。而多线程由于创建和切换的开销,采用多线程可能不会提高程序的执行速度,反而会降低速度,但是对于频繁IO操作的程序,多线程可以有效的并发。
- 对于包含不同任务的程序,可以考虑每个任务使用一个线程。这样的程序在设计上相对于单线程做所有事的程序来说,更为清晰明了,比如生产、消费者问题。
- 在实际的开发中对于性能优化的问题需要考虑到具体的场景来考虑是否使用多线程技术。