本节重点思维导图
Java程序结构
public class 类名 { public static void main(String[] args){ //……语句 } }
一门语言是由以下各种元素组成:
- 关键字
- 数据类型
- 变量
- 运算符
- 表达式
- 语句
- 流程控制语句
关键字
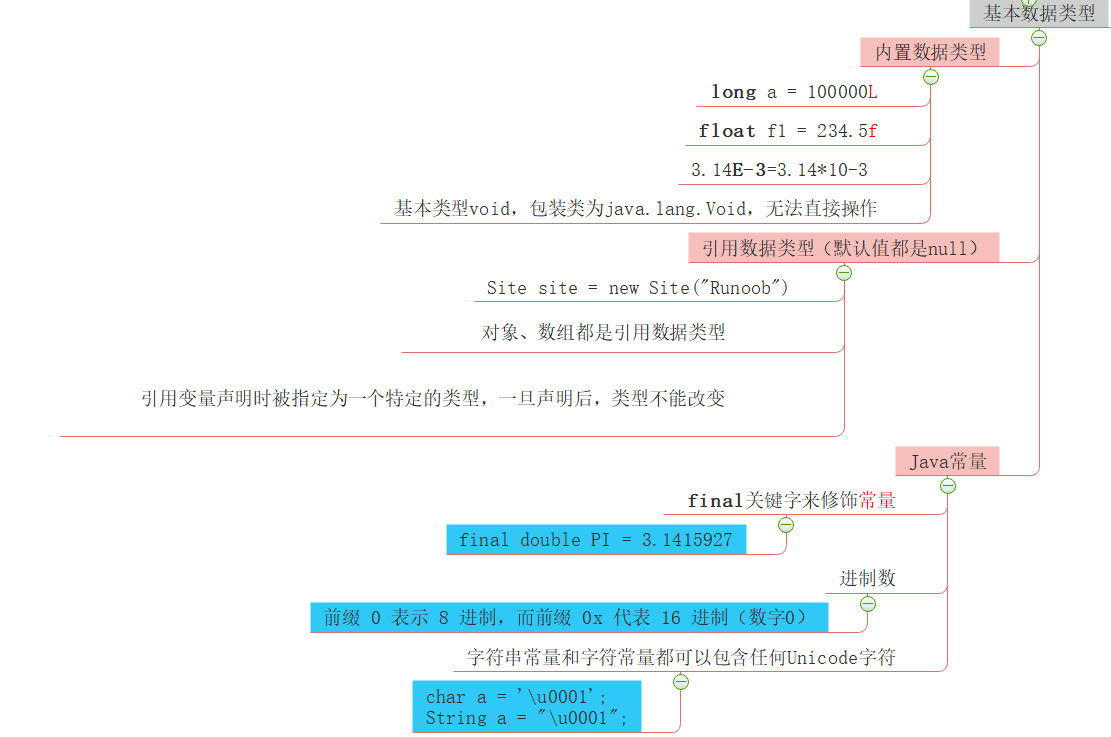
数据类型
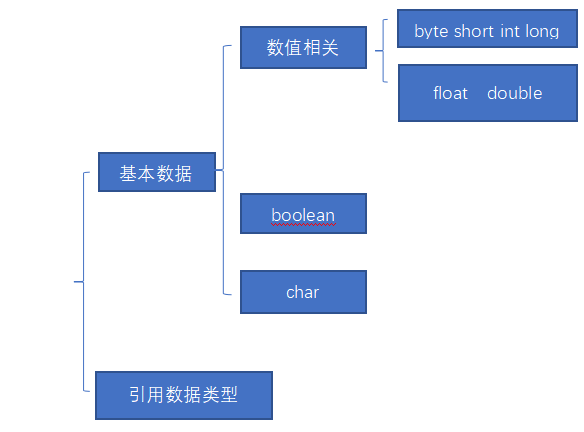
基本数据类型:boolean char byte short int long float double
引用数据类型:除了8种基本数据类型之外,其它的全部是引用数据类型
- 在Java中,引用类型的变量非常类似于C/C++的指针。
- 引用类型指向一个对象,指向对象的变量是引用变量。这些变量在声明时被指定为一个特定的类型。变量一旦声明后,类型就不能被改变了。
- 对象、数组都是引用数据类型。
- 所有引用类型的默认值都是null。
- 一个引用变量可以用来引用任何与之兼容的类型。
- 例子:Site site = new Site("Runoob")。
1bit(位) 1byte(字节)=8bit 1kb=1024byte 1M=1024kb 1G = 1024M 1T = 1024G 1pb=1024T
基本数据类型表
|
类型名称 |
长度(占计算机空间) |
表示数值的范围 |
举例 |
|
|
布尔型 |
boolean |
1bit |
true false |
|
|
整型数值 |
byte |
1个字节 |
-27 ~ 27-1 |
|
|
short |
2byte |
-215 ~ 215-1 |
||
|
int |
4byte |
-231~ 231-1 |
||
|
long |
8byte |
-263 ~ 263-1 |
||
|
浮点数值 |
float |
4byte |
有自己的算法,远远大于2N |
|
|
double |
8byte |
|||
|
字符型 |
char |
2byte |
0 ~ 216-1 一对单引号括起来的单个字符 |
都是正数 |

变量

变量的定义
数据类型 变量名;
变量的赋值
数据类型 变量名 = 值;
或
数据类型 变量名;
变量名 = 值;
变量命名规范

变量定义&赋值代码演示

public class Demo{ public static void main(String[] args) { boolean b1 = true; boolean b2 = false; int i1 = 0; int i2 = 8888; int i3; i3 = 9999; i3 = 99999999; i3 = 2147483647; i3 = -2147483648; byte byte1 = 0; // byte byte11 = (byte)0; //强制类型转换 byte byte2 = 127; byte byte3 = -128; short s1 = 789; short s2 = 32767; short s3 = -32768; long abc1 = 34; long abc2 = 2147483649L; long abc3 = -2147483648; long abc4 = -214748364889L; double d1 = 0; double d2 = 0.0; double d3 = 3271947123498321741239847321984712.0; double d4 = -3271947123498321741239847321984712.0; float f1 = 888; float f2 = 0.0f; float f3 = 0.0F; float f4 = 2147483648L; char c1= ' '; char c2 = 'a'; //char c3 = 'abc'; char c4 = 0; System.out.println("----------char c4 = 0 ----------"); System.out.println(c4); System.out.println("--------------------"); char c5 = '0'; System.out.println("----------char c4 = '0 '----------"); System.out.println(c5); System.out.println("--------------------"); char c6 = 65535; System.out.println("----------char c6 = 65535----------"); System.out.println(c6); System.out.println("--------------------"); System.out.println("-----int i7 = 'a' --------"); int i7 = 'a'; System.out.println(i7); int i8 = '?'; System.out.println("-----int i8 = '?' --------"); System.out.println(i8); } }
尤其:
public class Demo{ public static void main(String[] args) { char dddd= 97; System.out.println(dddd); int eeee = 'a'; System.out.println(eeee); } }
即:
常量
- 程序运行时不能被修改
- 使用 final 关键字来修饰常量
- 通常大写字母
final double PI = 3.1415927;
byte、int、long、和short都可以用十进制、16进制以及8进制来表示
前缀 0 表示 8 进制,而前缀 0x 代表 16 进制
int decimal = 100; int octal = 0144; int hexa = 0x64;
字符串常量和字符常量 可以包含任何Unicode字符
char a = 'u0001'; String a = "u0001";
补充
1. Float类型的数据同理
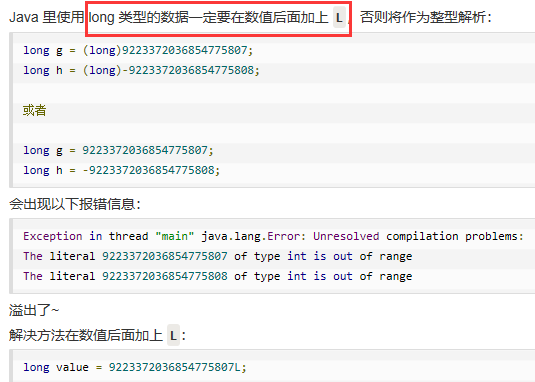
2.

3.

4.
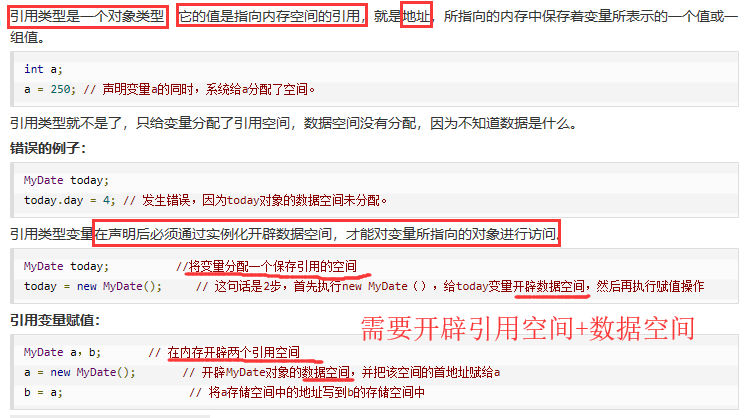
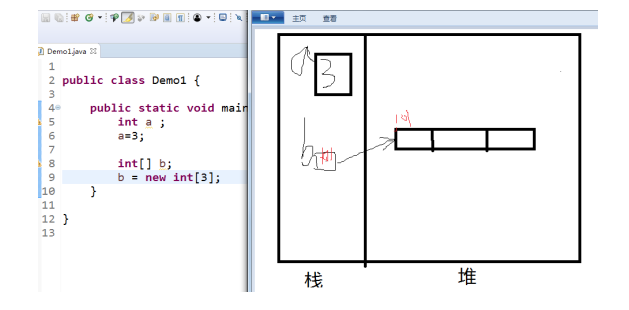
引用数据类型与基本数据类型的区别:
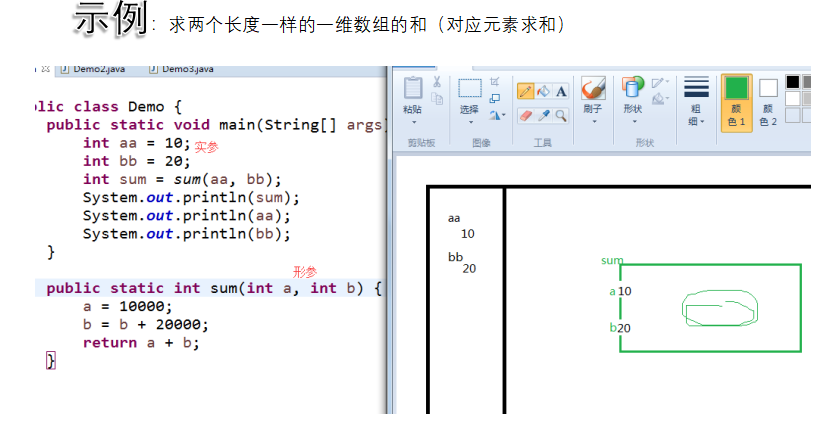
基本数据类型作为方法的参数,传递的是数据,对原来的参数没有影响
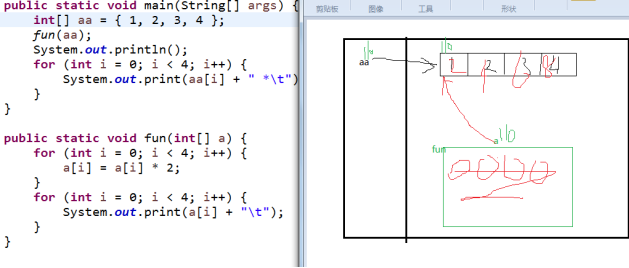
引用类型作为方法的参数时,传递的是地址,而不是字面值,String类型除外。
例【1】:
public class Demo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] aa = { 1, 2, 3, 4 }; int[] bb = { 5, 6, 7, 8 }; sum(aa, bb); for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { System.out.print(aa[i] + " "); } System.out.println(); for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { System.out.print(bb[i] + " "); } } public static void sum(int[] a, int[] b) { for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { int temp = a[i] + b[i]; System.out.println(temp); } } }
例【2】:
public class Demo5 { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "hello"; int[] aa = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, }; fun(str, aa); System.out.println(str); } public static void fun(String abc, int[] a) {// 可变长度的数组 for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { a[i] = a[i] * 2; } abc = abc + "world"; System.out.print(abc + " "); for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { System.out.print(a[i] + " "); } } }
