1.创建RandomWalk()类
from random import choice class RandomWalk(): """A class to generate random walks.""" def __init__(self, num_points=5000): """Initialize attributes of a walk.""" self.num_points = num_points # All walks start at (0, 0). self.x_values = [0] self.y_values = [0] def fill_walk(self): """Calculate all the points in the walk.""" # Keep taking steps until the walk reaches the desired length. while len(self.x_values) < self.num_points: # Decide which direction to go, and how far to go in that direction. x_direction = choice([1, -1]) x_distance = choice([0, 1, 2, 3, 4]) x_step = x_direction * x_distance y_direction = choice([1, -1]) y_distance = choice([0, 1, 2, 3, 4]) y_step = y_direction * y_distance # Reject moves that go nowhere. if x_step == 0 and y_step == 0: continue # Calculate the next x and y values. next_x = self.x_values[-1] + x_step next_y = self.y_values[-1] + y_step self.x_values.append(next_x) self.y_values.append(next_y)
2.绘制随机漫步图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from random_walk import RandomWalk rw=RandomWalk() rw.fill_walk() plt.scatter(rw.x_values,rw.y_values,s=15) plt.show()

3.设置随机漫步图的样式
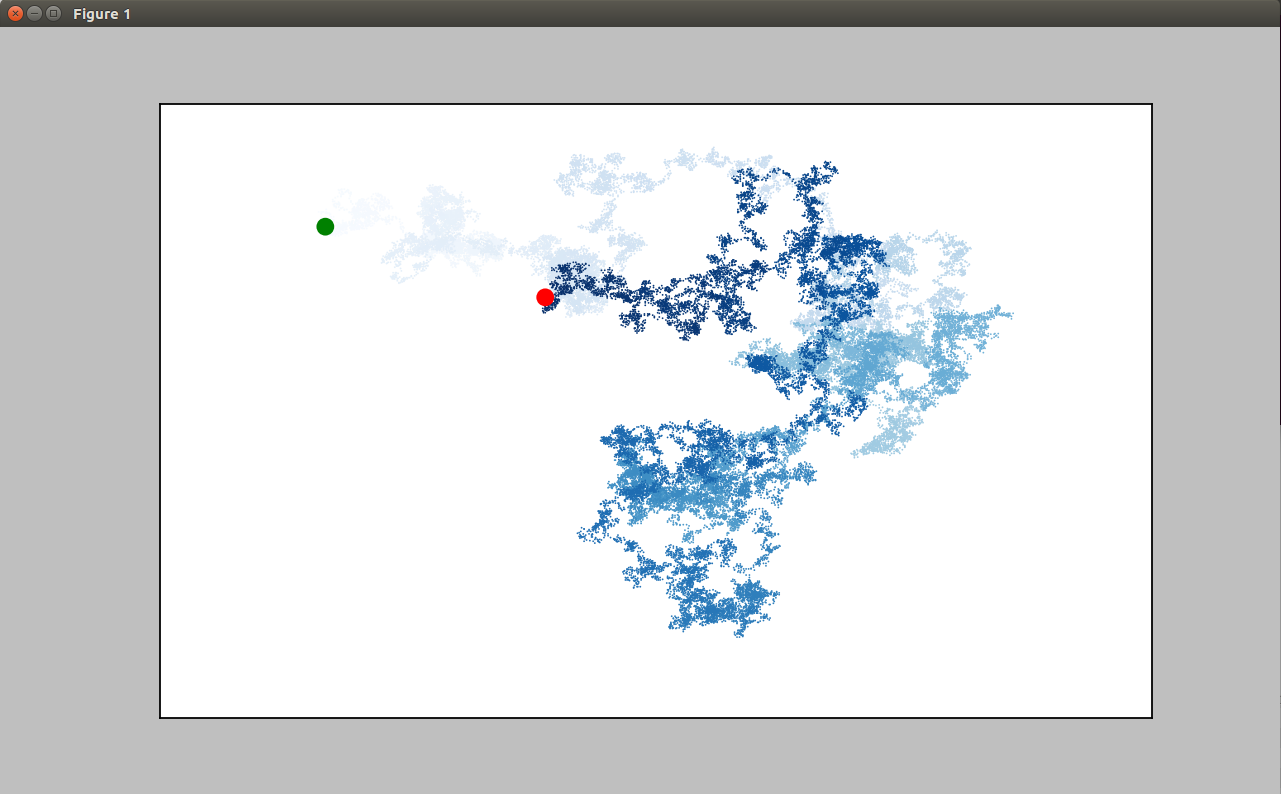
使用颜色映射来指出漫步中各点的先后顺序,并删除每个点的黑色轮廓。
point_numbers=list(range(rw.num_points)) plt.scatter(rw.x_values,rw.y_values,c=point_numbers,cmap=plt.cm.Blues,edgecolor='none',s=15)

4.重新绘制起点和终点&隐藏坐标轴
plt.scatter(0,0,c='green',edgecolor='none',s=100) plt.scatter(rw.x_values[-1],rw.y_values[-1],c='red',edgecolor='none',s=100) plt.axes().get_xaxis().set_visible(False) plt.axes().get_yaxis().set_visible(False)

5.增加点数&绘制窗口尺寸
首先修改随机漫步类的定义:
def __init__(self, num_points=50000):
以下给出rw_visual.py的完整代码:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from random_walk import RandomWalk rw=RandomWalk() rw.fill_walk() plt.figure(dpi=128,figsize=(10,6)) point_numbers=list(range(rw.num_points)) plt.scatter(rw.x_values,rw.y_values,c=point_numbers,cmap=plt.cm.Blues,edgecolor='none',s=1) plt.scatter(0,0,c='green',edgecolor='none',s=100) plt.scatter(rw.x_values[-1],rw.y_values[-1],c='red',edgecolor='none',s=100) plt.axes().get_xaxis().set_visible(False) plt.axes().get_yaxis().set_visible(False) plt.show()