SGU 222:
很明显答案是(C_n^k*A_n^k)
Code
#define B cout << "BreakPoint" << endl;
#define O(x) cout << #x << " " << x << endl;
#define O_(x) cout << #x << " " << x << " ";
#define Msz(x) cout << "Sizeof " << #x << " " << sizeof(x)/1024/1024 << " MB" << endl;
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#define LL long long
const int inf = 1e9 + 9;
const int N = 2e5 + 5;
using namespace std;
inline int read() {
int s = 0,w = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
if(ch == '-')
w = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
s = s * 10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return s * w;
}
int n,k;
LL ans[N];
void pre(){
ans[1] = 1,ans[0] = 1;
for(int i = 2;i < 20;i++) ans[i] = ans[i - 1] * i;
}
void init(){
n = read(),k = read();
if(n < k) printf("0
");
else printf("%lld
",ans[k] * (ans[n] / ans[k] / ans[n - k]) * (ans[n] / ans[k] / ans[n - k]));
}
int main(){
pre();
init();
}
SGU223:
这个题是统计方案,依然是逐行转移,如果某个格子((i,j))放置了国王,那么上一行(j,j-1,j+1),这三个格子都是他的攻击范围,因此这三个格子是不能够放国王的,由于我们需要的答案是恰好放置(k)个国王的方案数,所以方程还需要加一维,记录放置的国王数。先预处理出一行的合法状态(用(s)数组记录)以及放置((sum)数组记录)的国王个数方程表示为:(dp[i][a][k]+=dp[i-1][b][k-sum[a]](s[a]&s[b]==0))
Code
#define B cout << "BreakPoint" << endl;
#define O(x) cout << #x << " " << x << endl;
#define O_(x) cout << #x << " " << x << " ";
#define Msz(x) cout << "Sizeof " << #x << " " << sizeof(x)/1024/1024 << " MB" << endl;
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#define LL long long
const int inf = 1e9 + 9;
const int N = 2e5 + 5;
using namespace std;
inline int read() {
int s = 0,w = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
if(ch == '-')
w = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
s = s * 10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return s * w;
}
const int maxn = 15, maxk = 105, sz = 10;
struct Trans{
int a,b,ch1;
Trans(int a = 0,int b = 0,int ch1 = 0):a(a),b(b),ch1(ch1){}
};
int n,k;
Trans ts[1<<(sz<<1)]; int tl;
LL f[maxn][maxk][1<<sz], ans;
void DFS(int u,int lst,int now,int cnt){
if(u == n) ts[++tl] = Trans(lst,now,cnt);
else{
DFS(u + 1, lst, now, cnt);
if(!u||(!(lst & (1<<(u - 1))) && !(now & (1<<(u - 1))))){
DFS(u + 1,lst|(1 << u),now,cnt);
DFS(u + 1,lst,now|(1 << u),cnt + 1);
}
}
}
int main(){
n = read(),k = read();
f[0][0][0] = 1;
DFS(0,0,0,0);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) for(int j = 0; j <= k; j++) for(int p = 1; p <= tl; p++) if(j - ts[p].ch1 >= 0) f[i][j][ts[p].b] += f[i - 1][j-ts[p].ch1][ts[p].a];
for(int i = 0; i < (1<<n); i++) ans += f[n][k][i];
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
poj 1321:
看到的第一眼,觉得和n皇后问题很像,再仔细一看,就是很像啊,方法相同,只是本题只要判断不在一行或者一列,规定了棋子放置位置,故要增加判断条件,dfs就可。
Code
#define B cout << "BreakPoint" << endl;
#define O(x) cout << #x << " " << x << endl;
#define O_(x) cout << #x << " " << x << " ";
#define Msz(x) cout << "Sizeof " << #x << " " << sizeof(x)/1024/1024 << " MB" << endl;
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#define LL long long
const int inf = 1e9 + 9;
const int N = 2e5 + 5;
using namespace std;
inline int read() {
int s = 0,w = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
if(ch == '-')
w = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
s = s * 10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return s * w;
}
char a[10][10];
int vis[10],n,k,tot,m;
void DFS(int cur){
if(k == m){
tot++;
return ;
}
if(cur >= n) return ;
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
if(vis[j] == 0 && a[cur][j] == '#'){
vis[j] = 1,m++;
DFS(cur + 1),vis[j] = 0;
m--;
}
DFS(cur + 1);
}
int main(){
while((n = read(),k = read()) && n != -1 && k != -1){
tot = 0,m = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) scanf("%s",&a[i]);
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
DFS(0);
printf("%d
",tot);
}
return 0;
}
poj 1185:
由于当前行和前两行有关系,所以得用3维矩阵来保存一个状态下最多的炮兵个数,用(dp[i][curst][prest])表示当前第(i)行状态对(curst),前一行状态为(prest)的最大炮兵数。
转移方程为(dp[i][curst][prest]=max left{dp[i-1][prest][preprest] ight}),这样求到最后一行之后,答案就是最后一行所有状态中最大的那个。程序初始化的时候需要对第一行进行预处理,设置(dp[0][st][0]=st)合法(&st)中(1)的个数。这样进行下面的计算的时候,由于0状态肯定是和所有状态兼容的,所以就不会影响计算结果。
Code
#define B cout << "BreakPoint" << endl;
#define O(x) cout << #x << " " << x << endl;
#define O_(x) cout << #x << " " << x << " ";
#define Msz(x) cout << "Sizeof " << #x << " " << sizeof(x)/1024/1024 << " MB" << endl;
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#define LL long long
#define me(a) memset(a,0,sizeof(a))
const int inf = 1e9 + 9;
const int N = 2e5 + 5;
using namespace std;
inline int read() {
int s = 0,w = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
if(ch == '-')
w = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
s = s * 10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return s * w;
}
int f[115][70][70],a[105],g[70],num[70],m,n,len;
char str[111];
int main(){
while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)){
me(f),me(num);
me(a),me(g);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
scanf("%s", str);
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++) if(str[j] == 'H') a[i] += (1<<j);
}
len = 1;
for(int i = 0;i < (1<<m); i++){
if(!(i&(i<<1)) && !(i&(i<<2))){
int k = i, sum = 0;
while(k){
if(k&1) sum++;
k >>= 1;
}
num[len] = sum;
g[len++] = i;
}
}
for(int i = 1; i < len; i++) if(!(a[1]&g[i])) f[1][i][1] = num[i];
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = 1; j < len; j++){
if(g[j]&a[i]) continue;
for(int k = 1; k < len; k++){
if(g[j] & g[k]) continue;
if(g[k] & a[i-1]) continue;
for(int t = 1; t < len; t++){
if(g[t] & g[j]) continue;
if(g[t] & g[k]) continue;
if(g[t] & a[i - 2]) continue;
f[i][j][k] = max(f[i][j][k], f[i-1][k][t] + num[j]);
}
}
}
}
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 1;i < len; i++) for(int j = 1;j < len; j++) ans = max(ans, f[n][i][j]);
printf("%d
", ans);
}
return 0;
}
hdu 2640:
状态是每个物体的第三行...
由于第二行的特殊性,加上不能重叠,可以知道第三行状态很少一共有:
00000000 , 01001000
01000000 , 01000100
00100000 , 01000010
00010000 , 00100100
00001000 , 00100010
00000100 , 00010010
00000010
13种.
所以我们求出所有合法状态就可了。
Code
#define B cout << "BreakPoint" << endl;
#define O(x) cout << #x << " " << x << endl;
#define O_(x) cout << #x << " " << x << " ";
#define Msz(x) cout << "Sizeof " << #x << " " << sizeof(x)/1024/1024 << " MB" << endl;
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#define LL long long
const int inf = 1e9 + 9;
const int N = 2e5 + 5;
using namespace std;
inline int read() {
int s = 0,w = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
if(ch == '-')
w = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
s = s * 10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return s * w;
}
int t,n,m,f[2][13][13],num,vis[13],cnt[13];
char map[105][10];
void init(){
vis[0] = cnt[0] = 0;
num = 1;
for(int i = 1;i + 1 < m;i++){
vis[num] = (1 << i),cnt[num] = 1,num++;
for(int j = i + 3;j + 1 < m;j++) vis[num] = (1 << i) + (1 << j),cnt[num] = 2,num++;
}
}
bool ch1(int st,int i){
for(int j = 0;j < m;j++) if(st & (1<<j)) if(map[i][j]=='#' || map[i-1][j]=='#' || map[i-1][j-1]=='#' || map[i-1][j+1]=='#' || map[i-2][j]=='#') return 0;
return 1;
}
bool ch2(int x,int y){
int a[3][8];
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
for(int i = 0;i < 8;i++){
if(x&(1<<i)) a[0][i]++,a[1][i]++,a[1][i-1]++,a[1][i+1]++,a[2][i]++;
if(y&(1<<i)) a[1][i]++,a[2][i]++,a[2][i-1]++,a[2][i+1]++;
}
for(int i = 0;i < 8;i++) if(a[0][i] > 1 || a[1][i] > 1 || a[2][i] > 1) return 0;
return 1;
}
bool ck3(int x,int y){
for(int i = 0;i < m;i++) if(x & (1<<i)) if(y & (1<<i)) return 0;
return 1;
}
void solve(){
init();
int now = 0;
memset(f[now],0,sizeof(f[now]));
for(int i = 2;i < n;i++){
now ^= 1;
memset(f[now],0,sizeof(f[now]));
for(int j = 0;j < num;j++){
int x = vis[j];
for(int k = 0;k < num;k++){
int y = vis[k];
for(int r = 0;r < num;r++){
int z = vis[r];
if(!ch1(z,i)) continue;
if(!ch2(z,x)) continue;
if(!ck3(z,y)) continue;
f[now][r][j] = max(f[now][r][j],f[1-now][j][k]+cnt[r]);
}
}
}
}
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < num;i++) for(int j = 0;j < num;j++) ans = max(ans,f[now][i][j]);
printf("%d
",ans);
}
int main(){
t = read();
while(t--){
n = read(),m = read();
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) scanf("%s",map[i]);
if(n <= 2||m <= 2 ) puts("0");
else solve();
}
return 0;
}
poj 2411:
1.(h*w)若为奇数,则无解。
2.按行处理。处理第(i)行时,保证前(i-1)行全部覆盖,当前行的状态为(state)。
以(f[i][state])表示处理到第(i)行,第(i)行的状态为(state),且前(i-1)行全部填满的方案数。
(f[i][state]=∑f[i-1][state2])
需要统计有哪些(state2)可以转移到(state),可以用(dfs)来预处理出来。
Code
#define B cout << "BreakPoint" << endl;
#define O(x) cout << #x << " " << x << endl;
#define O_(x) cout << #x << " " << x << " ";
#define Msz(x) cout << "Sizeof " << #x << " " << sizeof(x)/1024/1024 << " MB" << endl;
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#define LL long long
const int inf = 1e9 + 9;
const int N = 2e3 + 5;
using namespace std;
inline int read() {
int s = 0,w = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
if(ch == '-')
w = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
s = s * 10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return s * w;
}
const int maxm = 12;
LL f[15][1 << maxm],num;
int n,m,maxx,ans;
void updata(int i , int opt, int pos ){
if (pos == m){
f[i][opt] += num;
return;
}
updata(i,opt,pos + 1);
if(pos < m && !(1 << pos - 1 & opt) && !(1 << pos & opt)) updata( i , opt | (1 << pos - 1) | (1 << pos) , pos + 1);
}
void solve(){
memset(f , 0 , sizeof(f));
num = 1;
maxx = (1 << m) - 1;
updata(1 , 0 , 1);
for(int i = 2; i <= n; ++i)
for(int opt = 0; opt < 1 << m; ++opt){
if (f[i - 1][opt]) num = f[i - 1][opt];
else continue;
updata(i , ~ opt & maxx , 1 );
}
printf("%lld
",f[n][maxx]);
}
int main(){
n = read(),m = read();
while (n && m){
if (n < m) swap(n,m);
solve();
n = read(),m = read();
}
}
hdu 2280:
我们可以用(dp[i][num][state])表示能否达到在第(1)~(i-1)行填满的情况下,用了(num)个(1*1),第i行状态为(state)的状态。我们遍历每一行,每种(num),每种状态,通过(dfs)来尝试放各种棋子,要判断好每种棋子能不能放
Code
#define B cout << "BreakPoint" << endl;
#define O(x) cout << #x << " " << x << endl;
#define O_(x) cout << #x << " " << x << " ";
#define Msz(x) cout << "Sizeof " << #x << " " << sizeof(x)/1024/1024 << " MB" << endl;
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#define LL long long
const int inf = 1e9 + 9;
const int N = 2e3 + 5;
using namespace std;
inline int read() {
int s = 0,w = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
if(ch == '-')
w = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
s = s * 10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return s * w;
}
int g[N],n,m,f[N][1<<6];
void dfs(int i,int k,int state1,int state2,int v){
if(k > 5){
f[i][state2] = max(f[i][state2] , v);
return;
}
if(k <= 4){
if(!(state1&(1 << k - 1)) && !(state2 & (3 << k - 1))) dfs(i,k + 1,state1 | (1 << k - 1),state2 | (3 << k - 1),v + 3);
if(!(state1&(1 << k)) && !(state2 & (3 << k - 1))) dfs(i,k + 1,state1 | (1 << k),state2 | (3 << k - 1),v + 3);
if(!(state1&(3 << k - 1)) && !(state2 & (1 << k - 1))) dfs(i,k + 1,state1 | (3 << k - 1),state2 | (1 << k - 1),v + 3);
if(!(state1&(3 << k - 1)) && !(state2 & (1 << k))) dfs(i,k + 1,state1 | (3 << k - 1),state2 | (1 << k),v + 3);
if(!(state2&(3 << k - 1))) dfs(i,k + 1,state1,state2 | (3 << k - 1),v + 2);
}
else if(!(state1&(1 << k - 1)) && !(state2 & (1 << k - 1))) dfs(i,k + 1,state1|(1 << k - 1),state2|(1 << k - 1),v + 2);
dfs(i,k + 1,state1,state2,v);
}
void dfs2(int k,int sta,int v){
if(k > 5){
f[1][sta] = max(f[1][sta] , v);
return;
}
if(k <= 4) if(!(sta & (3<<k - 1))) dfs2(k+1 , sta | (3<<k-1) , v+2);
dfs2(k + 1,sta,v);
}
int main(){
char a;
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m) != EOF){
memset(g,0,sizeof(g));
int all = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n ; i++)
for(int j = 1; j <= 5 ; j++){
cin>>a;
if(a == '1') g[i] |= (1<<j-1);
else all++;
}
memset(f , -1 , sizeof(f));
f[1][g[1]] = 0;
dfs2(1,g[1],0);
for(int i = 2;i <= n;i++) for(int j = 0; j < (1 << 5) ; j++) if(f[i - 1][j] >= 0) dfs(i,1,j,g[i],f[i - 1][j]);
int maxn = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < (1 << 5);i++) maxn = max(maxn , f[n][i]);
int remain = all - maxn;
if(remain <= m) puts("YES");
else puts("NO");
}
return 0;
}
poj 1038:
乱搞就行了
(Dfs)优化状压(dp) (O(我不知道,反正过不了,需要再优化))(理论上80%)
再剩下的,卡常数+卡常数+一个小优化(有可能被卡一个点)
以上属于乱搞,正解在下面
(O(3^{10}*N)),我们知道,设,我们更新第(i)行的状态,那么如果第(i-1)行的第(j)个位置不能被选取,则第(i-2)行的第(j)个位置同样不可以被选取,那么(4^N)状态转化为(3^N),理论时间复杂度可能会超时(这个大概是60-70%的样子),所以需要用到(Dfs)优化(这个大概70-100%,有的人就能,反正我没有),之后同样,用链式前向星优化一下,就可以过了,当然,还可以继续优化。
下面是乱搞的代码
Code
#define B cout << "BreakPoint" << endl;
#define O(x) cout << #x << " " << x << endl;
#define O_(x) cout << #x << " " << x << " ";
#define Msz(x) cout << "Sizeof " << #x << " " << sizeof(x)/1024/1024 << " MB" << endl;
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#define LL long long
const int inf = 1e9 + 9;
const int N = 155;
const int M = 205;
using namespace std;
inline int read() {
int s = 0,w = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
if(ch == '-')
w = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
s = s * 10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return s * w;
}
int f[3][M][M],cur[N],n,m,K,can[M],p[1 << 15],cnt2,head[M][M];
int to[M * M * 30],to2[M * M * 30],to3[M * M * 30],cnt[M * M * 30],nxt[M * M * 30];
int a,b,ans,cnt4;
void dfs(int f1,int f2,int step,int f3,int cnt1){
if(to[cnt4] != f1 || to3[cnt4] != f2){
to[++cnt4] = f1;
to2[cnt4] = f3;
to3[cnt4] =f2;
cnt[cnt4] = cnt1;
nxt[cnt4] = head[a][b];
head[a][b] = cnt4;
}
if(step >= m)return ;
if(step < m - 1 && !(f1 & (3 << step)) && !(f2 & (3 << step))) dfs(f1|(3<<step),f2|(3<<step),step+2,f3|(3<<step),cnt1+1);
if(step < m - 2 && !(f1 & (7<<(step)))) dfs(f1 | (7 << step),f2,step + 3,f3 | (7 << step),cnt1 + 1);
if(step < m - 2&& !(f1 & (7<<step)) && !(f2 & (7 << step))) dfs(f1|(7<<step),f2|(7 << step),step + 3,f3,cnt1 + 1);
dfs(f1,f2,step + 1,f3,cnt1);
return ;
}
void init(){
memset(cur,0,sizeof(cur));
memset(head,0,sizeof(head));
cnt4 = 0;
}
int main(){
int T = read();
while(T--){
init();
n = read(),m = read(),K = read();
int mask = (1 << m) - 1;
for(int i = 1;i <= K;i++){
int x = read(),y = read();
cur[x] |= (1 << (y - 1));
}
cur[0] = cur[n + 1] = mask;
ans = 0,cnt2 = 0;
for(int j = 0;j <= mask;j++){
int s = j;
if(((s & 3) == 1) || (s != 0 && ((((~s)) & ((~s) << 2)) && (((((~s)) & ((((~s))) << 2)) >> 1) & s))))continue;
can[++cnt2] = j;
p[j] = cnt2;
}
for(int i = 1;i <= cnt2;i++){
for(int j = 1;j <= cnt2;j++){
if((can[i] & can[j]) != can[i]) continue;
a = i,b = j;
dfs(can[i],can[j],0,0,0);
}
}
memset(f[1],0,sizeof(f[1]));
for(int i = 1;i < n;i++){
memset(f[(i + 1) & 1],0,sizeof(f[(i+1)&1]));
for(int j = 1;j <= cnt2;j++){
if(can[j] & cur[i])continue;
for(int k = j;k <= cnt2;k++){
if((can[k] & cur[i - 1]))continue;
if((can[k] & can[j]) != can[j])continue;
for(int l = head[j][k];l;l = nxt[l]){
if((to[l] & cur[i])||(to3[l] & cur[i - 1]) || (to2[l] & cur[i + 1]))continue;
f[(i ^ 1) & 1][p[to2[l]]][p[to[l]|to2[l]]] = max(f[(i ^ 1) & 1][p[to2[l]]][p[to[l]|to2[l]]],f[i & 1][j][k]+cnt[l]);
}
if(i==1)break;
}
}
for(int j = 1;j <= cnt2;j++) for(int k = 1;k <= cnt2;k++) ans = max(ans,f[(i + 1) & 1][j][k]);
}
printf("%d
",ans);
}
return 0;
}
hdu 2442:
状态就是 占有这块 和 不占有这块
$dp[ i ][ j ][ k ] $代表 前 (i) 行 第$ i (行状态为) j (第) i-1 (行状态为) k $的最大面积
可以首先用 (dfs) 初始化出 (i=2) 的状态
再来统计答案即可。
Code
#define B cout << "BreakPoint" << endl;
#define O(x) cout << #x << " " << x << endl;
#define O_(x) cout << #x << " " << x << " ";
#define Msz(x) cout << "Sizeof " << #x << " " << sizeof(x)/1024/1024 << " MB" << endl;
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
typedef long long LL;
const int maxn = 1e2 + 5;
const int sz = 1<<6;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int inf = 2e9 + 7;
using namespace std;
inline int read() {
int s = 0,w = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
if(ch == '-')
w = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
s = s * 10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return s * w;
}
int n,m,dp[maxn][sz][sz];
void dfs(int s,int u,int v,int num,int pos,int t){
if(pos>=m){
if(dp[t][s][u]<num) dp[t][s][u] = num;
return ;
}
if(pos > 0){
if(!(s & (1<<pos)) && !(u & (3<<pos-1)) && !(v & (1<<pos))) dfs(s|(1<<pos),u|(3<<pos-1),v|(1<<pos),num+4,pos+1,t);
if(!(s & (1<<pos)) && !(u & (1<<pos)) && !(v & (3<<pos-1))) dfs(s|(1<<pos),u|(1<<pos),v|(3<<pos-1),num+4,pos+1,t);
}
if(pos>1){
if(!(s & (1<<pos-1)) && !(u & (7<<pos-2)) && !(v&(1<<pos-1))) dfs(s|(1<<pos-1),u|(7<<pos-2),v|(1<<pos-1),num+5,pos+1,t);
if(!(s & (1<<pos-1)) && !(u & (7<<pos-2))) dfs(s|(1<<pos-1),u|(7<<pos-2),v,num+4,pos+1,t);
if(!(s & (1<<pos)) && !(u & (7<<pos-2))) dfs(s|(1<<pos),u|(7<<pos-2),v,num+4,pos+1,t);
}
dfs(s,u,v,num,pos + 1,t);
}
void dfs2(int s,int u,int num,int pos){
if(pos >= m){
if(dp[2][s][u]<num) dp[2][s][u] = num;
return ;
}
if(!(s & (1<<pos-1)) && !(u&(7<<pos-2))) dfs2(s|(1<<pos-1),u|(7<<pos-2),num +4 ,pos + 3);
if(!(s & (1<<pos)) && !(u&(7<<pos-2))) dfs2(s|(1<<pos),u|(7<<pos-2),num + 4,pos + 3);
dfs2(s,u,num,pos+1);
}
int main(){
while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)){
if(n==1||m==1) {puts("0"); continue;}
memset(dp,-1,sizeof dp);
dfs2(0,0,0,2);
int num = 1 << m;
for(int i = 3;i <= n;i++)
for(int j = 0;j < num;j++) for(int k = 0;k < num;k++) if(dp[i-1][j][k] >= 0) dfs(0,j,k,dp[i-1][j][k],1,i);
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < num;i++) for(int j = 0;j < num;j++) if(ans < dp[n][i][j]) ans = dp[n][i][j];
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
hdu 1755:
这道题直接暴力枚举复杂度为 (n!*m)
但是(k<100) , 所以我们可以通过取模用(dp[i][j]) 表示(k=i) 时,(-x)取模(k)为(j)的最小值
Code
#define B cout << "BreakPoint" << endl;
#define O(x) cout << #x << " " << x << endl;
#define O_(x) cout << #x << " " << x << " ";
#define Msz(x) cout << "Sizeof " << #x << " " << sizeof(x)/1024/1024 << " MB" << endl;
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#define LL long long
const int inf = 1e9 + 9;
const int N = 2e5 + 5;
using namespace std;
inline int read() {
int s = 0,w = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
if(ch == '-')
w = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
s = s * 10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return s * w;
}
int vis[10],n,m,x,k,num[10],dp[102][102];
void dfs(int t , int state){
if(t >= n){
for(int i = 1;i <= 100;i++) if(dp[i][state % i] > state) dp[i][state % i] = state;
return;
}
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
if(!vis[i]){
vis[i] = 1;
dfs(t + 1,state * 10 + num[i]);
vis[i] = 0;
}
}
}
int main(){
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)!=EOF){
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) num[i] = read();
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
for(int i = 0;i <= 100;i++) for(int j = 0;j <= 100;j++) dp[i][j] = inf;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
if(num[i]){
vis[i] = 1;
dfs(1,num[i]);
vis[i] = 0;
}
}
for(int i = 0;i < m;i++){
x = read(),k = read();
if(dp[k][(((-x) % k) + k) % k] < inf) printf("%d
",dp[k][(((-x)%k)+k)%k]);
else puts("None");
}
}
return 0;
}
hdu 1820:
象的攻击路线是斜的,所以我们可以将棋盘旋转45°,这样攻击路线就成了水平,象就变成了车
之后可以发现,如果将棋盘分为黑白格子,黑白棋子之间是无法互相攻击的,那我们就可以将他们分开考虑
把棋盘处理成2个下面的图形
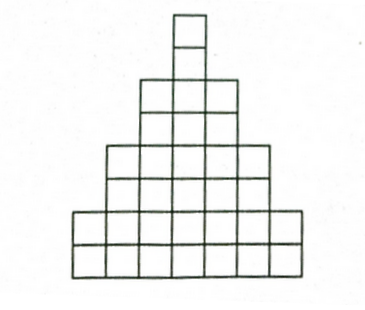
设(dp[i][j])表示前(i)行放了(j)个车的方法数,(c[i])表示第(i)行可以放置的棋子数量,那么转移方程为:
(dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + dp[i-1][j-1] * (c[i] - (j - 1)))
需要注意的是(c)数组应该是增序的,这样才能保证前面的(j-1)行放了车,对应这一行就有(j-1)个位
Code
#define B cout << "BreakPoint" << endl;
#define O(x) cout << #x << " " << x << endl;
#define O_(x) cout << #x << " " << x << " ";
#define Msz(x) cout << "Sizeof " << #x << " " << sizeof(x)/1024/1024 << " MB" << endl;
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#define LL long long
const int inf = 1e9 + 9;
const int N = 70;
using namespace std;
inline int read() {
int s = 0,w = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
if(ch == '-')
w = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
s = s * 10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return s * w;
}
int n,k,c1[N],c2[N],dp1[10][N],dp2[10][N];
void init(){
memset(c1,0,sizeof(c1));
memset(c2,0,sizeof(c2));
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) for(int j = 1;j <= n;j++)
if((i + j) & 1) c2[(i+j)>>1]++;
else c1[(i+j)>>1]++;
}
void solve(int dp[N][N],int c[N]){
for(int i = 0;i <= n;i++) dp[i][0] = 1;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) for(int j = 1;j <= c[i];j++) dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i - 1][j - 1] * (c[i] - j + 1);
}
int main(){
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&k)&&n+k){
init();
sort(c1 + 1,c1 + 1 + n),sort(c2 + 1,c2 + n);
memset(dp1,0,sizeof(dp1)),memset(dp2,0,sizeof(dp2));
solve(dp1,c1),solve(dp2,c2);
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0;i <= k;i++) ans += dp1[n][i] * dp2[n - 1][k - i];
printf("%d
",ans);
}
return 0;
}
hdu1668:
(dp[state][i][j])表示(state)状态下倒数第二个岛为(i),最后一个岛为(j)时的最优解,(g[state][i][j])为相应的路径数目,其中(state)的二进制表示的(i)位为(1)表示岛(i)被访问过,反之为(0)。
则显然当有边((i,j))存在时,有如下初值可赋:
(dp[(1<<i)+(1<<j)][i][j]=val[i]+val[j]+val[i]*val[j],g[(1<<i)+(1<<j)][i][j]=1)
如果状态((state,i,j))可达,检查岛(k),如果此时(k)没有被访问过并且有边((j,k))存在,则做如下操作:
1)设tmp为下一步访问岛k时获得的总利益,(r=state+(1<<k))。
2)如果(t,p>dp[r][j][k]),表示此时可以更新到更优解,则更新:
(dp[r][j][k]=q,g[r][j][k]=g[state][i][j]。)
3)如果(tmp==dp[r][j][k]),表示此时可以获得达到局部最优解的更多方式,则更新:
$ g[r][j][k]+=g[p][i][j]。(
最后检查所有的状态)((1<<n)-1,i,j)$,叠加可以得到最优解的道路数。
需要注意的是,题目约定一条路径的两种行走方式算作一种,所以最终结果要除(2)。
Code
#define B cout << "BreakPoint" << endl;
#define O(x) cout << #x << " " << x << endl;
#define O_(x) cout << #x << " " << x << " ";
#define Msz(x) cout << "Sizeof " << #x << " " << sizeof(x)/1024/1024 << " MB" << endl;
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#define LL long long
const int inf = 1e9 + 9;
const int N = 2e5 + 5;
using namespace std;
inline int read() {
int s = 0,w = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
if(ch == '-')
w = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
s = s * 10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return s * w;
}
int n,m,val[15],map[13][13],dp[1<<13][13][13];
LL g[1<<13][13][13];
int main(){
int t = read();
while(t--){
n = read(),m = read();
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) val[i] = read();
memset(map,0,sizeof(map));
while(m--){
int u = read()-1,v = read()-1;
map[u][v] = map[v][u] = 1;
}
if(n==1){
printf("%d 1
",val[0]);
continue;
}
memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp));
memset(g,0,sizeof(g));
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) for(int j = 0;j < n;j++) if(i != j && map[i][j]) dp[(1<<i)|(1<<j)][i][j] = val[i] + val[j] + val[i] * val[j],g[(1<<i)|(1<<j)][i][j] = 1;
for(int i = 0;i < (1<<n);i++)
for(int j = 0;j < n;j++)
if((i & (1<<j)) != 0)
for(int k = 0;k < n;k++)
if(map[j][k] && j!=k && (i&(1<<k))!=0 && dp[i][j][k]!=-1)
for(int x=0;x<n;x++)
if(map[k][x] && j!=x && k!=x && (i&(1<<x))==0){
int tmp = dp[i][j][k]+val[x]+val[k]*val[x];
if(map[j][x]) tmp+=val[j]*val[k]*val[x];
if(dp[i|(1<<x)][k][x]<tmp) dp[i|(1<<x)][k][x] = tmp,g[i|(1<<x)][k][x] = g[i][j][k];
else if(dp[i|(1<<x)][k][x] == tmp) g[i|(1<<x)][k][x] += g[i][j][k];
}
int ans1 =0;
LL ans2 = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) for(int j =0 ;j < n;j++)
if(i!=j && map[i][j]){
if(ans1 < dp[(1<<n) - 1][i][j]) ans1 = dp[(1<<n) - 1][i][j],ans2 = g[(1<<n) - 1][i][j];
else if(ans1 == dp[(1<<n) - 1][i][j]) ans2+=g[(1<<n) - 1][i][j];
}
cout<<ans1<<" "<<ans2 / 2<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
hdu 2518:
思路比较简单,不过代码量比较大。。
需要判断出每个图形有几种旋转方式。 建立矩阵,列数数72,60个小方格,外加12个图形限制,每个图形只能用一次。。
因为只有6中情况,所以要先用自己的代码跑出每组例子,然后直接输出结果就ok了。
若是直接把代码提交上去而不进行处理,肯定TLE,于是先用程序把所有答案跑出啦再打表输出。
Code
#define B cout << "BreakPoint" << endl;
#define O(x) cout << #x << " " << x << endl;
#define O_(x) cout << #x << " " << x << " ";
#define Msz(x) cout << "Sizeof " << #x << " " << sizeof(x)/1024/1024 << " MB" << endl;
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#define LL long long
const int inf = 1e9 + 9;
const int N = 2e5 + 5;
using namespace std;
inline int read() {
int s = 0,w = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
if(ch == '-')
w = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
s = s * 10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return s * w;
}
using namespace std;
int ans[]={0,0,0,2,368,1010,2339};
int main(){
int n,m;
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m) != -1){
if(n>m) swap(n,m);
printf("%d
",ans[n]);
}
return 0;
}