常用的布局实现方式:线性布局,框架布局,表格布局,相对布局,绝对布局
1,线性布局
(1)线性布局是一种很重要的布局,也是经常用到的一种布局
(2)在线性布局中,所有的元素都按照水平竖直的顺序在界面上排序
如果水平排序,则每行包含一个界面元素
如果垂直排序,则每列只包含一个元素

(3)线性布局常用的常用属性:
android:orientation=“vertical”(该属性决定了他的子控件的布局方式)】
android:gravity=“center”(该属性决定了他的子类的xy位置)
常用到的几个属性值:
center_vertical:垂直(y轴)居中)
center_horizontal:水平(x轴)居中
centrer:水平垂直都居中
right:子类控件位于当前布局的右边
left:子类控件位于当前布局的左边
bottom:子类控件位于当前布局的下面
(4)代码操作过程
1)首先为了能完整的体验创建线性布局的过程,首先删除自动建立的res/layout/main.xml文件,然后建立用于显示垂直排列的线性布局的XML文件
2)右键--->xml--->LayoutXML File打开新文件建立向导
3)文件名为:main_vertical.xml
4)保存位置为res/layout
5)双击建立的
关键代码:
横向:
android:orientation="horizontal"
纵向:
android:orientation="vertical"
完整代码:
(1)纵向布局
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:stretchColumns="*" android:id="@+id/Tablelayout01"> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:textSize="40dp" android:text="hello"/> <Button android:id="@+id/btn" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="button1" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btn3" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="button2" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btn2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_x="150dp" android:layout_y="120dp" android:text="button3" /> </LinearLayout>
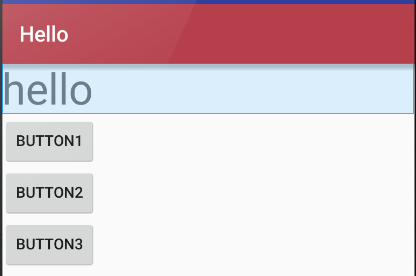
(2)横向布局
完整代码
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="horizontal" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:stretchColumns="*" android:id="@+id/Tablelayout01"> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:textSize="40dp" android:text="hello"/> <Button android:id="@+id/btn" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="button1" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btn3" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="button2" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btn2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_x="150dp" android:layout_y="120dp" android:text="button3" /> </LinearLayout>
效果:
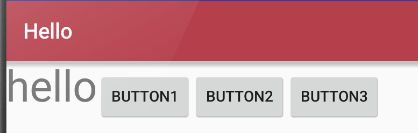
2,框架布局
http://www.cnblogs.com/excellencesy/p/9051441.html
3,表格布局
(1)表格布局也是一种常用的界面布局,它将屏幕划分网络,通过指定行和列可以将界面元素添加到网格中
1)网格的边界对用户是不可见的
2)表格布局还支持嵌套,可以将另一个表格布局放置在前一个表格布局的网格中,也可以在表格不居中添加其他的界面布局,例如:线性布局,相对布局等等
(2)表格布局的注意事项
1)向界面中添加一个表格布局,无需修改布局的属性值。其中,id属性为TableLayout01.layout Width 和Layout height属性都是wrap_content
2)向TableLayout中添加一个表格布局,无需修改布局的属相值。其中为
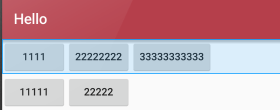
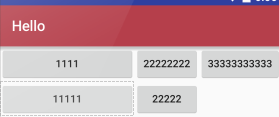
A隐藏从0 开始的索引列:
android:collapseColumns="0,1"
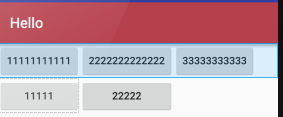

B收缩从零开始的索引列:
android:shrinkColumns="0,2,1"
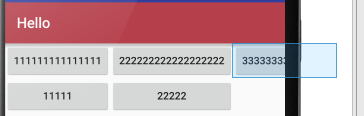
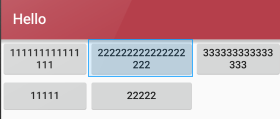
C拉伸从另开始的索引列:
android:stretchColumns="0"
(3) 实例
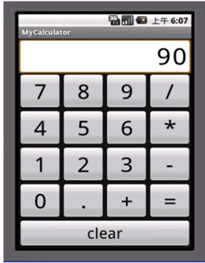
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:stretchColumns="*"
android:id="@+id/Tablelayout01">
<TextView android:id="@+id/tv"
android:text="90"
android:textSize="40dp"
android:gravity="right"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="50dp"/>
<TableRow android:id="@+id/tableroe01"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<Button android:id="@+id/bt1"
android:text="1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/bt2"
android:text="2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/bt3"
android:text="3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/bt4"
android:text="+"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</TableRow>
<TableRow android:id="@+id/tablerow02"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content">
<Button android:id="@+id/bt31"
android:text="4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/bt32"
android:text="5"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/bt33"
android:text="6"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/bt34"
android:text="-"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</TableRow>
<TableRow android:id="@+id/tablerow03"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content">
<Button android:id="@+id/bt41"
android:text="7"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/bt42"
android:text="8"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/bt43"
android:text="9"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/bt44"
android:text="*"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</TableRow>
<TableRow android:id="@+id/tablerow04"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content">
<Button android:id="@+id/bt21"
android:text="+"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/bt22"
android:text="-"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/bt23"
android:text="*"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/bt24"
android:text="/"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</TableRow>
<TableRow android:id="@+id/tablerow05"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="match_parent">
<Button android:id="@+id/bt51"
android:text="center"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_span="4" />
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>
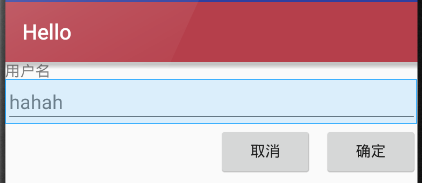
4,相对布局
(1)相对布局是一种非常灵活的布局方式,能够通过指定界面元素与其他元素的相对位置关系,确定所有元素的布局位置
(2)能够最大程度保证在各种屏幕类型的手机上正确的显示界面布局
(3)相对布局示例说明
1)添加TextView控件(“用户名”),相对布局会将TextView控件放置在屏幕的最上方
2)然后添加TextView控件,并声明该控件的位置在TextView控件的下面,相对布局会根据TextView的位置确定EditText控件的位置
3)之后添加的第一个Button控件,声明在EditText控件的下方,且在福控件的最右边
4)最后,添加第二个Button控件,声明该控件处于相同的水平位置
关键代码解读:
设置在哪个组件的下面:
android:layout_below="@id/label"
设置在相对布局组件的最右侧:
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
设置距离左边的组件的距离:
android:layout_marginLeft="10dip"
设置左边的组件是哪个:
android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/cancel"
设置在距离上面组件的距离:
android:layout_alignTop="@id/cancel“
完整代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:stretchColumns="*"
android:id="@+id/Tablelayout01">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="用户名"/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/tv"
android:hint="hahah"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_below="@id/et"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dip"
android:text="确定"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/btn"
android:layout_alignTop="@id/btn"
android:text="取消"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
5,绝对布局
(1)绝对布局能通过指定界面元素的坐标位置,来确定用户界面的整体布局
(2)绝对布局是一种不推荐使用的界面布局,因为通过X轴和Y轴确定界面元素的位置后,android紫铜不能根据不同的屏幕对界面元素的位置进行调整,降低了界面布局对不同的类型和尺寸屏幕的适应能力
(3)每一个界面控件都必须指定坐标(X,Y),例如“确认”按钮的坐标是(40,120),“取消”按钮的坐标是(120,120)。坐标原点(0,0),在屏幕的左上角
关键代码解读:
android:layout_x="40dp"
android:layout_y="120dp"
完整代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<AbsoluteLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:stretchColumns="*"
android:id="@+id/Tablelayout01">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_x="40dp"
android:layout_y="40dp"
android:text="用户名:"/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_x="40dp"
android:layout_y="60dp"
android:hint="hahah"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_x="40dp"
android:layout_y="120dp"
android:text="确定"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_x="150dp"
android:layout_y="120dp"
android:text="取消"
/>
</AbsoluteLayout>
显示结果:
