上一节以WordCount分析了MapReduce的基本执行流程,但并没有从框架上进行分析,这一部分工作在后续慢慢补充。这一节,先剖析一下作业提交过程。
在分析之前,我们先进行一下粗略的思考,如果要我们自己设计分布式计算,应该怎么设计呢?假定有100个任务要并发执行,每个任务分别针对一块数据,这些数据本身是分布在多个机器上的,主要面临哪些问题?
1、数据如何分布是首先面临的问题,可能也是影响分布式计算性能的最关键问题。一个超大文件,按照哪种方式切割开来,分别丢到不同的机器?Hadoop的答案是按照64MB或者128MB等长切割,如果切的太小,要记录的元数据信息太多,如果切得太大,负载均衡可能比较差。如果按照某种方式切割开来后,怎么丢到多个机器?我觉得一种最简单的方案就是哪台机器剩余空间越多,就往哪台机器上丢。这样在存储空间上可以保持差不多。而且,不太会存在热点问题。这个以后分析HDFS的时候再看;
2、假如已经分布好了,那么任务的计算就在数据所在机器执行。哪个机器拥有什么数据,哪个机器就负责对自己拥有那块数据进行处理。任务的划分就取决于数据的划分,比如一个机器拥有了5个64MB,那就给他分配5个任务,各自处理一块,这种符合直觉的思维也是Hadoop采用的。当然,实际上没这么简单,比如有的机器可能数据分布就是多了些,那么岂不是这台机器会成为短板,整个作业的执行时间依赖于最慢这台机器执行的时间。在Hadoop里,为了解决这个问题,会把一个任务可能丢到两个机器上执行,谁先处理完,另一个就停了它。不管怎样,只要涉及到任务分配,是不是至少有一台机器负责这个分配过程吧?所以MapReduce有一个主控节点。不过理论上看也未必,假如大家按照某种同样的算法就能知道什么样的任务该到哪台机器上算,整个分布式计算集群也可以是P2P的。
3、关键的问题来了,如果数据之间存在关联怎么办?比如一个任务的执行需要依赖于另一个任务执行完毕才能开始,这种同步等待是并行计算的大忌,有可能大部分时间会花在等待上,甚至还不如串行执行?Hadoop里面假设的就是任务可以完全并行,如果需要关联,那么,就在这些并行任务之后,再启动一个任务去关联,后面的这种任务就是Reduce,不过天底下不一定都能这么理想地分,所以我觉得Hadoop还是有一定先天缺陷的,模型还是简单了点。
下面开始分析。
MapReduce集群包含一个JobTracker和多个TaskTracker,这里先不考虑YARN,仍然依据1版本进行分析。
一个MapReduce作业在Hadoop中称为Job,而JobTracker顾名思义就是对Job进行管理的节点,一个Job包含多个Map和Reduce任务,在Hadoop里Map和Reduce任务称为Task,而Job指的是Map-Reduce流程的称呼。一个Job包含多个Map Task和Reduce Task,在看作业提交代码之前,需要有一些基本的认识:
1、Job所需要的输入数据、资源(数据分布信息、参数配置等等)都存放于HDFS之上,其中资源信息需要Job客户端先提交至HDFS之上,这些资源信息并不传输至JobTracker,因为JobTracker本身也能随便访问HDFS,所以JobTracker是去HDFS中获得相应信息后再进行Map和Reduce Task分配;
2、JobClient和JobTracker可以看作CS结构,JobClient往HDFS中存入资源后,会朝JobTracker提交作业,至于到底传输给JobTracker些什么内容,实际上只是一个Job ID以及Job所在的HDFS文件目录等基本信息,需要注意的是,他们之间并不直接传递任何计算数据和资源数据,因为他们都是HDFS的客户端,都可以访问HDFS系统。
3、JobTracker的主要任务就是分配作业,所谓分配作业,说白了,就是将一个Job分为多个Map和Reduce任务,然后指定这些任务到底由哪些机器执行,执行任务的机器即为TaskTracker,作业到底分为多少个任务,这在传统的MPI编程中是由程序员指定的,分好任务后,任务到底在哪些机器上执行,这也是需要程序员指定的;MapReduce的不同在于,这个作业切分的过程,以及任务在哪些机器上执行的问题,是由Hadoop自己搞定的,程序员需要做的就是先将要计算的数据放到HDFS上,把Map和Reduce任务执行的(1份!)代码编写好,然后启动即可,数据到底放在了哪些机器,程序员可以不关心(查看HDFS管理信息才知道),编写的代码到底在哪些机器上(被自动拷贝多份!)执行,程序员也不关心(当然,非要去查看也是可以看到的)。
4、JobTracker分配好任务后,并不是直接通知TaskTracker,而是等着TaskTracker自己来取,这种设计可能是考虑MapReduce作业一般执行时间较长,比如几十分钟以上;而且JobTracker的压力不宜过大,趁着心跳时一起把任务信息获取了,否则单点容易形成瓶颈。JobTracker和TaskTracker之间存在心跳机制,可以配置,比如5秒(心跳频繁又会带来集群单点瓶颈难以扩展的问题,因为大家都跟JobTracker心跳,压力山大啊),因此,在JobClient向HDFS提交资源信息,并向JobTracker提交作业后Job进入作业队列,JobTracker从队列中取出Job并分配好Map/Reduce任务后的几秒后,TaskTracker可能才知道自己应该执行任务。这一作业启动过程时间一般都要几秒,延时较大,无法支持实时处理,这一点经常被Spark拿来鄙视,但Spark集群规模扩展后难道不存在单点瓶颈?但凡是单点分配任务的集群,不可避免都会遇到这个问题。除非分配任务的节点也可以扩展。
5、Map Task和Reduce Task最终运行于TaskTracker之上,TaskTracker一般是一台安装了JAVA虚拟机的Linux服务器,启动Map Task和Reduce Task时会启动JAVA虚拟机,执行Map或Reduce任务(因此Map、Reduce都是一个个JAVA进程),JAVA虚拟机启动的速度本身还是比较快,运行完毕后通知JobTracker,关闭JAVA虚拟机。一个TaskTracker可以启动很多个JAVA进程执行很多Map和Reduce任务,在YARN(Hadoop 2.0的分布式资源管理系统)中,可以指定一个Map、Reduce任务需要多少CPU核和内存,目前PC服务器一般有几十个核,和64GB以上内存,所以执行几十个Map/Reduce任务也是正常的;在YARN之前,可以配置一台服务器可以执行多少个Map/Reduce任务,但并不考虑各个Map/Reduce任务消耗资源的区别。
5、JobClient利用RPC机制请求JobTracker的服务,比如分配Job ID、启动作业、停止作业、查看Job进展等等。RPC机制是Hadoop里面一个很核心的部分,理解RPC机制是理解Hadoop的前提。JobTracker是MapReduce中最重要的一个类,实现了很多接口:
public class JobTracker implements MRConstants, InterTrackerProtocol, JobSubmissionProtocol, TaskTrackerManager, RefreshUserMappingsProtocol, RefreshAuthorizationPolicyProtocol, AdminOperationsProtocol, JobTrackerMXBean { 。。。。。。
其中,JobSubmissionProtocol就是JobClient和JobTracker之间RPC的服务接口。这个接口的实现类就是JobTracker,包含的功能主要有:
interface JobSubmissionProtocol extends VersionedProtocol { public JobID getNewJobId() throws IOException; public JobStatus submitJob(JobID jobName, String jobSubmitDir, Credentials ts) throws IOException; public ClusterStatus getClusterStatus(boolean detailed) throws IOException; public void killJob(JobID jobid) throws IOException; public void setJobPriority(JobID jobid, String priority) throws IOException; public boolean killTask(TaskAttemptID taskId, boolean shouldFail) throws IOException; public JobProfile getJobProfile(JobID jobid) throws IOException; public JobStatus getJobStatus(JobID jobid) throws IOException; public Counters getJobCounters(JobID jobid) throws IOException; public TaskReport[] getMapTaskReports(JobID jobid) throws IOException; public TaskReport[] getReduceTaskReports(JobID jobid) throws IOException; public TaskReport[] getCleanupTaskReports(JobID jobid) throws IOException; public TaskReport[] getSetupTaskReports(JobID jobid) throws IOException; ........ }
在JobClient这一端,使用动态代理机制(至于什么是动态代理,参考JAVA Proxy、InvocationHandler相关类),在调用JobSubmissionProtocol的下面方法(这个方法在Job客户端并没有具体实现)时:
public JobID getNewJobId() throws IOException;
进入代理类相关方法(invoke),以RPC机制往JobTracker发送相应请求(方法+参数),JobTracker接收到请求后,处理后返回结果。
下面进入代码分析。上一节结尾时分析到Job的作业提交方法:
/** * Submit the job to the cluster and return immediately. * @throws IOException */ public void submit() throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException { ensureState(JobState.DEFINE); setUseNewAPI(); // Connect to the JobTracker and submit the job connect(); info = jobClient.submitJobInternal(conf); super.setJobID(info.getID()); state = JobState.RUNNING; }
先来看connect()方法,掌握RPC机制,再分析submitJobInternal的作业提交过程:
0、JobClient与JobTracker之间的RPC机制
private void connect() throws IOException, InterruptedException { ugi.doAs(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>() { public Object run() throws IOException { jobClient = new JobClient((JobConf) getConfiguration()); return null; } }); }
在该方法中创建了一个JobClient对象,在其构造函数中调用init方法创建一个代理类:
public JobClient(JobConf conf) throws IOException { setConf(conf); init(conf); } public void init(JobConf conf) throws IOException { String tracker = conf.get("mapred.job.tracker", "local"); tasklogtimeout = conf.getInt( TASKLOG_PULL_TIMEOUT_KEY, DEFAULT_TASKLOG_TIMEOUT); this.ugi = UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser(); if ("local".equals(tracker)) { conf.setNumMapTasks(1); this.jobSubmitClient = new LocalJobRunner(conf); } else { this.rpcJobSubmitClient = createRPCProxy(JobTracker.getAddress(conf), conf); this.jobSubmitClient = createProxy(this.rpcJobSubmitClient, conf); } }
rpcJobSubmitClient 是一个JobSubmissionProtocol 对象,而JobSubmissionProtocol 是一个与JobTracker服务相关的RPC接口,提供了一些服务访问方法。
private JobSubmissionProtocol rpcJobSubmitClient;
在createRPCProxy方法中,调用了Hadoop RPC的创建代理的方法RPC.getProxy:
private static JobSubmissionProtocol createRPCProxy(InetSocketAddress addr, Configuration conf) throws IOException { JobSubmissionProtocol rpcJobSubmitClient = (JobSubmissionProtocol)RPC.getProxy( JobSubmissionProtocol.class, JobSubmissionProtocol.versionID, addr, UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser(), conf, NetUtils.getSocketFactory(conf, JobSubmissionProtocol.class), 0, RetryUtils.getMultipleLinearRandomRetry( conf, MAPREDUCE_CLIENT_RETRY_POLICY_ENABLED_KEY, MAPREDUCE_CLIENT_RETRY_POLICY_ENABLED_DEFAULT, MAPREDUCE_CLIENT_RETRY_POLICY_SPEC_KEY, MAPREDUCE_CLIENT_RETRY_POLICY_SPEC_DEFAULT ), false); return rpcJobSubmitClient; }
这个方法里面核心的是创建一个Invoker对象:
/** Construct a client-side proxy object that implements the named protocol, * talking to a server at the named address. */ public static VersionedProtocol getProxy( Class<? extends VersionedProtocol> protocol, long clientVersion, InetSocketAddress addr, UserGroupInformation ticket, Configuration conf, SocketFactory factory, int rpcTimeout, RetryPolicy connectionRetryPolicy, boolean checkVersion) throws IOException { if (UserGroupInformation.isSecurityEnabled()) { SaslRpcServer.init(conf); } final Invoker invoker = new Invoker(protocol, addr, ticket, conf, factory, rpcTimeout, connectionRetryPolicy); VersionedProtocol proxy = (VersionedProtocol)Proxy.newProxyInstance( protocol.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{protocol}, invoker); if (checkVersion) { checkVersion(protocol, clientVersion, proxy); } return proxy; }
而Invoker是一个实现了java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler的类,负责代理JobSubmissionProtocol的各种服务,当JobClient调用JobSubmissionProtocol的方法(比如JobID getNewJobId() )时,会进入Invoker的invoke方法,而在该方法中,会将调用的方法信息打包送至JobTracker执行:
private static class Invoker implements InvocationHandler { private Client.ConnectionId remoteId; private Client client; private boolean isClosed = false; ....... public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { ...... ObjectWritable value = (ObjectWritable) client.call(new Invocation(method, args), remoteId); .....return value.get(); }
client是RPC客户端,其call方法会创建一个Invocation对象,该对象封装了要调用的方法信息:
private static class Invocation implements Writable, Configurable { private String methodName; private Class[] parameterClasses; private Object[] parameters; private Configuration conf; .......
然后在call方法中,将这一信息序列化(Invocation 是一个可序列化对象)后送出去:
/** Make a call, passing <code>param</code>, to the IPC server defined by * <code>remoteId</code>, returning the value. * Throws exceptions if there are network problems or if the remote code * threw an exception. */ public Writable call(Writable param, ConnectionId remoteId) throws InterruptedException, IOException { Call call = new Call(param); Connection connection = getConnection(remoteId, call); connection.sendParam(call); // send the parameter boolean interrupted = false; synchronized (call) { while (!call.done) { try { call.wait(); // wait for the result } catch (InterruptedException ie) { // save the fact that we were interrupted interrupted = true; } } 。。。。。。 } }
sendParam(call)这一方法就是发送出去的代码:
/** Initiates a call by sending the parameter to the remote server. * Note: this is not called from the Connection thread, but by other * threads. */ public void sendParam(Call call) { if (shouldCloseConnection.get()) { return; } DataOutputBuffer d=null; try { synchronized (this.out) { if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) LOG.debug(getName() + " sending #" + call.id); //for serializing the //data to be written d = new DataOutputBuffer(); d.writeInt(call.id); call.param.write(d); byte[] data = d.getData(); int dataLength = d.getLength(); out.writeInt(dataLength); //first put the data length out.write(data, 0, dataLength);//write the data out.flush(); } } catch(IOException e) { markClosed(e); } finally { //the buffer is just an in-memory buffer, but it is still polite to // close early IOUtils.closeStream(d); } }
理解了上面的RPC机制,再来看作业提交函数submitJobInternal的执行。
submitJobInternal函数是JobClient向JobTracker提交作业的核心方法:
/** * Internal method for submitting jobs to the system. * @param job the configuration to submit * @return a proxy object for the running job * @throws FileNotFoundException * @throws ClassNotFoundException * @throws InterruptedException * @throws IOException */ public RunningJob submitJobInternal(final JobConf job ) throws FileNotFoundException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException, IOException { /* * configure the command line options correctly on the submitting dfs */ return ugi.doAs(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<RunningJob>() { public RunningJob run() throws FileNotFoundException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException, IOException{ JobConf jobCopy = job; Path jobStagingArea = JobSubmissionFiles.getStagingDir(JobClient.this, jobCopy); JobID jobId = jobSubmitClient.getNewJobId(); Path submitJobDir = new Path(jobStagingArea, jobId.toString()); jobCopy.set("mapreduce.job.dir", submitJobDir.toString()); JobStatus status = null; try { populateTokenCache(jobCopy, jobCopy.getCredentials()); copyAndConfigureFiles(jobCopy, submitJobDir); // get delegation token for the dir TokenCache.obtainTokensForNamenodes(jobCopy.getCredentials(), new Path [] {submitJobDir}, jobCopy); Path submitJobFile = JobSubmissionFiles.getJobConfPath(submitJobDir); int reduces = jobCopy.getNumReduceTasks(); InetAddress ip = InetAddress.getLocalHost(); if (ip != null) { job.setJobSubmitHostAddress(ip.getHostAddress()); job.setJobSubmitHostName(ip.getHostName()); } JobContext context = new JobContext(jobCopy, jobId); // Check the output specification if (reduces == 0 ? jobCopy.getUseNewMapper() : jobCopy.getUseNewReducer()) { org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.OutputFormat<?,?> output = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(context.getOutputFormatClass(), jobCopy); output.checkOutputSpecs(context); } else { jobCopy.getOutputFormat().checkOutputSpecs(fs, jobCopy); } jobCopy = (JobConf)context.getConfiguration(); // Create the splits for the job FileSystem fs = submitJobDir.getFileSystem(jobCopy); LOG.debug("Creating splits at " + fs.makeQualified(submitJobDir)); int maps = writeSplits(context, submitJobDir); jobCopy.setNumMapTasks(maps); // write "queue admins of the queue to which job is being submitted" // to job file. String queue = jobCopy.getQueueName(); AccessControlList acl = jobSubmitClient.getQueueAdmins(queue); jobCopy.set(QueueManager.toFullPropertyName(queue, QueueACL.ADMINISTER_JOBS.getAclName()), acl.getACLString()); // Write job file to JobTracker's fs FSDataOutputStream out = FileSystem.create(fs, submitJobFile, new FsPermission(JobSubmissionFiles.JOB_FILE_PERMISSION)); // removing jobtoken referrals before copying the jobconf to HDFS // as the tasks don't need this setting, actually they may break // because of it if present as the referral will point to a // different job. TokenCache.cleanUpTokenReferral(jobCopy); try { jobCopy.writeXml(out); } finally { out.close(); } // // Now, actually submit the job (using the submit name) // printTokens(jobId, jobCopy.getCredentials()); status = jobSubmitClient.submitJob( jobId, submitJobDir.toString(), jobCopy.getCredentials()); JobProfile prof = jobSubmitClient.getJobProfile(jobId); if (status != null && prof != null) { return new NetworkedJob(status, prof, jobSubmitClient); } else { throw new IOException("Could not launch job"); } } finally { if (status == null) { LOG.info("Cleaning up the staging area " + submitJobDir); if (fs != null && submitJobDir != null) fs.delete(submitJobDir, true); } } } }); }
该方法比较复杂,主要分为几个步骤,我们对其分解后逐一分析:
1、获取Job所在HDFS中的根目录
Path jobStagingArea = JobSubmissionFiles.getStagingDir(JobClient.this,jobCopy);
在MapReduce中,所有Job的信息(不是输入数据)都会存放于某个根目录下,这个根目录称为staging目录,Staging在英文中含义是临时工作台、脚手架等,个人理解他的意思是要执行MapReduce作业的这些框架信息(比如数据分布信息,Job配置参数等等)存放在这里。由参数mapreduce.jobtracker.staging.root.dir配置,默认是“/tmp/hadoop/mapred/staging”
这可以由getStagingDir方法的内部看到,JobClient里的这个方法最终会调用JobSubmissionFiles的getStagingDir方法:
public static Path getStagingDir(JobClient client, Configuration conf) throws IOException, InterruptedException { Path stagingArea = client.getStagingAreaDir(); FileSystem fs = stagingArea.getFileSystem(conf); 。。。。 return stagingArea; }
可见,调用了client的getStagingAreaDir方法:
public Path getStagingAreaDir() throws IOException { if (stagingAreaDir == null) { stagingAreaDir = new Path(jobSubmitClient.getStagingAreaDir()); } return stagingAreaDir; }
最终,调用jobSubmitClient的getStagingAreaDir方法,jobSubmitClient是一个JobSubmissionProtocol接口对象,通过动态代理,调用了位于服务端JobTracker的同名方法:
public String getStagingAreaDir() throws IOException { // Check for safe-mode checkSafeMode(); try{ final String user = UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser().getShortUserName(); return getMROwner().doAs(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<String>() { @Override public String run() throws Exception { return getStagingAreaDirInternal(user); } }); } catch(InterruptedException ie) { throw new IOException(ie); } }
其中调用了getStagingAreaDirInternal方法:
private String getStagingAreaDirInternal(String user) throws IOException { final Path stagingRootDir = new Path(conf.get("mapreduce.jobtracker.staging.root.dir", "/tmp/hadoop/mapred/staging")); final FileSystem fs = stagingRootDir.getFileSystem(conf); return fs.makeQualified(new Path(stagingRootDir, user+"/.staging")).toString(); }
得到该目录后,通过RPC返回。user是用户名,比如esingchan,则目录为:
/tmp/hadoop/mapred/staging/esingchan/.staging/
2、获取Job ID和Job工作目录(但还没创建):
JobID jobId = jobSubmitClient.getNewJobId(); Path submitJobDir = new Path(jobStagingArea, jobId.toString()); jobCopy.set("mapreduce.job.dir", submitJobDir.toString());
getNewJobId这个方法也是通过RPC获得ID信息(job id从1开始递增),然后在HDFS中的staging目录下创建工作目录,将这个目录设置成mapreduce.job.dir的值,最终目录一般呈现类似这种形式:
/tmp/hadoop/mapred/staging/esingchan/.staging/job_201408161410_0001/
Job ID的生成一般由时间等组成,具体在JobTracker方法getNewJobId中:
public synchronized JobID getNewJobId() throws IOException { // Check for JobTracker operational state checkJobTrackerState(); return new JobID(getTrackerIdentifier(), nextJobId++); }
3、创建工作目录,向HDFS提交资源数据:
copyAndConfigureFiles(jobCopy, submitJobDir);
copyAndConfigureFiles这个方法是JobClient向HDFS提交资源数据的主要方法。其实现为:
private void copyAndConfigureFiles(JobConf job, Path jobSubmitDir) throws IOException, InterruptedException { short replication = (short)job.getInt("mapred.submit.replication", 10); copyAndConfigureFiles(job, jobSubmitDir, replication); // Set the working directory if (job.getWorkingDirectory() == null) { job.setWorkingDirectory(fs.getWorkingDirectory()); } } private void copyAndConfigureFiles(JobConf job, Path submitJobDir, short replication) throws IOException, InterruptedException { if (!(job.getBoolean("mapred.used.genericoptionsparser", false))) { LOG.warn("Use GenericOptionsParser for parsing the arguments. " + "Applications should implement Tool for the same."); } // Retrieve command line arguments placed into the JobConf // by GenericOptionsParser. String files = job.get("tmpfiles"); String libjars = job.get("tmpjars"); String archives = job.get("tmparchives"); // // Figure out what fs the JobTracker is using. Copy the // job to it, under a temporary name. This allows DFS to work, // and under the local fs also provides UNIX-like object loading // semantics. (that is, if the job file is deleted right after // submission, we can still run the submission to completion) // // Create a number of filenames in the JobTracker's fs namespace FileSystem fs = submitJobDir.getFileSystem(job); LOG.debug("default FileSystem: " + fs.getUri()); if (fs.exists(submitJobDir)) { throw new IOException("Not submitting job. Job directory " + submitJobDir +" already exists!! This is unexpected.Please check what's there in" + " that directory"); } submitJobDir = fs.makeQualified(submitJobDir); FsPermission mapredSysPerms = new FsPermission(JobSubmissionFiles.JOB_DIR_PERMISSION); FileSystem.mkdirs(fs, submitJobDir, mapredSysPerms); Path filesDir = JobSubmissionFiles.getJobDistCacheFiles(submitJobDir); Path archivesDir = JobSubmissionFiles.getJobDistCacheArchives(submitJobDir); Path libjarsDir = JobSubmissionFiles.getJobDistCacheLibjars(submitJobDir); // add all the command line files/ jars and archive // first copy them to jobtrackers filesystem if (files != null) { FileSystem.mkdirs(fs, filesDir, mapredSysPerms); String[] fileArr = files.split(","); for (String tmpFile: fileArr) { URI tmpURI; try { tmpURI = new URI(tmpFile); } catch (URISyntaxException e) { throw new IllegalArgumentException(e); } Path tmp = new Path(tmpURI); Path newPath = copyRemoteFiles(fs,filesDir, tmp, job, replication); try { URI pathURI = getPathURI(newPath, tmpURI.getFragment()); DistributedCache.addCacheFile(pathURI, job); } catch(URISyntaxException ue) { //should not throw a uri exception throw new IOException("Failed to create uri for " + tmpFile, ue); } DistributedCache.createSymlink(job); } } if (libjars != null) { FileSystem.mkdirs(fs, libjarsDir, mapredSysPerms); String[] libjarsArr = libjars.split(","); for (String tmpjars: libjarsArr) { Path tmp = new Path(tmpjars); Path newPath = copyRemoteFiles(fs, libjarsDir, tmp, job, replication); DistributedCache.addArchiveToClassPath (new Path(newPath.toUri().getPath()), job, fs); } } if (archives != null) { FileSystem.mkdirs(fs, archivesDir, mapredSysPerms); String[] archivesArr = archives.split(","); for (String tmpArchives: archivesArr) { URI tmpURI; try { tmpURI = new URI(tmpArchives); } catch (URISyntaxException e) { throw new IllegalArgumentException(e); } Path tmp = new Path(tmpURI); Path newPath = copyRemoteFiles(fs, archivesDir, tmp, job, replication); try { URI pathURI = getPathURI(newPath, tmpURI.getFragment()); DistributedCache.addCacheArchive(pathURI, job); } catch(URISyntaxException ue) { //should not throw an uri excpetion throw new IOException("Failed to create uri for " + tmpArchives, ue); } DistributedCache.createSymlink(job); } } // First we check whether the cached archives and files are legal. TrackerDistributedCacheManager.validate(job); // set the timestamps of the archives and files and set the // public/private visibility of the archives and files TrackerDistributedCacheManager.determineTimestampsAndCacheVisibilities(job); // get DelegationTokens for cache files TrackerDistributedCacheManager.getDelegationTokens(job, job.getCredentials()); String originalJarPath = job.getJar(); if (originalJarPath != null) { // copy jar to JobTracker's fs // use jar name if job is not named. if ("".equals(job.getJobName())){ job.setJobName(new Path(originalJarPath).getName()); } Path originalJarFile = new Path(originalJarPath); URI jobJarURI = originalJarFile.toUri(); // If the job jar is already in fs, we don't need to copy it from local fs if (jobJarURI.getScheme() == null || jobJarURI.getAuthority() == null || !(jobJarURI.getScheme().equals(fs.getUri().getScheme()) && jobJarURI.getAuthority().equals( fs.getUri().getAuthority()))) { Path submitJarFile = JobSubmissionFiles.getJobJar(submitJobDir); job.setJar(submitJarFile.toString()); fs.copyFromLocalFile(originalJarFile, submitJarFile); fs.setReplication(submitJarFile, replication); fs.setPermission(submitJarFile, new FsPermission(JobSubmissionFiles.JOB_FILE_PERMISSION)); } } else { LOG.warn("No job jar file set. User classes may not be found. "+ "See JobConf(Class) or JobConf#setJar(String)."); } }
其中:
short replication = (short)job.getInt("mapred.submit.replication", 10);
表示这部分资源数据可靠性要求很高,在HDFS中默认保留10份。
copyAndConfigureFiles中以下几行代码:
String files = job.get("tmpfiles");
String libjars = job.get("tmpjars");
String archives = job.get("tmparchives");
Path filesDir = JobSubmissionFiles.getJobDistCacheFiles(submitJobDir);
Path archivesDir = JobSubmissionFiles.getJobDistCacheArchives(submitJobDir);
Path libjarsDir = JobSubmissionFiles.getJobDistCacheLibjars(submitJobDir);
FileSystem.mkdirs(fs, filesDir, mapredSysPerms);
Path newPath = copyRemoteFiles(fs,filesDir, tmp, job, replication);
FileSystem.mkdirs(fs, archivesDir, mapredSysPerms);
Path newPath = copyRemoteFiles(fs, archivesDir, tmp, job, replication);
FileSystem.mkdirs(fs, libjarsDir, mapredSysPerms);
Path newPath = copyRemoteFiles(fs, libjarsDir, tmp, job, replication);
分别在submitJorDir的目录下创建临时文件、Jar包文件、归档文件的目录,根据JobSubmissionFiles可以看出其目录名:
public static Path getJobDistCacheFiles(Path jobSubmitDir) { return new Path(jobSubmitDir, "files"); } /** * Get the job distributed cache archives path. * @param jobSubmitDir */ public static Path getJobDistCacheArchives(Path jobSubmitDir) { return new Path(jobSubmitDir, "archives"); } /** * Get the job distributed cache libjars path. * @param jobSubmitDir */ public static Path getJobDistCacheLibjars(Path jobSubmitDir) { return new Path(jobSubmitDir, "libjars"); }
可见,创建后的目录示例:
/tmp/hadoop/mapred/staging/esingchan/.staging/job_201408161410_0001/files
/tmp/hadoop/mapred/staging/esingchan/.staging/job_201408161410_0001/archives
/tmp/hadoop/mapred/staging/esingchan/.staging/job_201408161410_0001/libjars
之后,将用户程序的Jar包从本地文件系统上传到HDFS中,见下面的copyFromLocalFile方法:
String originalJarPath = job.getJar(); if (originalJarPath != null) { // copy jar to JobTracker's fs // use jar name if job is not named. if ("".equals(job.getJobName())){ job.setJobName(new Path(originalJarPath).getName()); } Path originalJarFile = new Path(originalJarPath); URI jobJarURI = originalJarFile.toUri(); // If the job jar is already in fs, we don't need to copy it from local fs if (jobJarURI.getScheme() == null || jobJarURI.getAuthority() == null || !(jobJarURI.getScheme().equals(fs.getUri().getScheme()) && jobJarURI.getAuthority().equals( fs.getUri().getAuthority()))) { Path submitJarFile = JobSubmissionFiles.getJobJar(submitJobDir); job.setJar(submitJarFile.toString()); fs.copyFromLocalFile(originalJarFile, submitJarFile); fs.setReplication(submitJarFile, replication); fs.setPermission(submitJarFile, new FsPermission(JobSubmissionFiles.JOB_FILE_PERMISSION));
而jar包所在目录即Job根目录,其文件名为:
/tmp/hadoop/mapred/staging/esingchan/.staging/job_201408161410_0001/files/job.jar,其名字由下面的方法指定:
public static Path getJobJar(Path jobSubmitDir) { return new Path(jobSubmitDir, "job.jar"); }
在HDFS中创建好该文件后,将JobClient本地编译好的jar文件复制至该文件。注意,libjars里面的文件是需要的其它临时jar库文件。
上面创建好的目录里存放的内容分别为:
/tmp/hadoop/mapred/staging/esingchan/.staging/job_201408161410_0001/libjars
用于存储执行job.jar需要的其它jar库文件。
/tmp/hadoop/mapred/staging/esingchan/.staging/job_201408161410_0001/archives
用于存储任务需要归档的一些文件(执行耗时完成时间啊等等各种归档信息)
/tmp/hadoop/mapred/staging/esingchan/.staging/job_201408161410_0001/files
用于存储执行程序所需的一些输入文件,注意不是计算的数据,而是其它一些文件。
到这一步后,实际上还没有完毕,还有两个文件需要上传,job.split和job.xml,分别代表job的文件分割信息和运行参数配置信息,但这两部分需要客户端解析分析才能得到,所以放在后面介绍。
4、创建Job配置文件
上面的目录为作业执行提供了数据基础,但关于任务数量等等任务配置信息还没有创建。任务配置信息不完全是用户直接指定的,而是需要进行一些分析获得。所有配置信息最终会由客户端JobClient生成后创建于HDFS的Staging目录下,即job.xml文件,主要包含任务参数,记录如Reduce数量等:
Path submitJobFile = JobSubmissionFiles.getJobConfPath(submitJobDir); public static Path getJobConfPath(Path jobSubmitDir) { return new Path(jobSubmitDir, "job.xml"); }
其过程中从用户指定的配置文件(其实也是xml文件,但是位于本地Linux文件系统)中获取一些参数,分析得到作业所需参数。主要获取的参数有:
获取Reduce数量:
int reduces = jobCopy.getNumReduceTasks();
获取客户端IP信息:
InetAddress ip = InetAddress.getLocalHost(); if (ip != null) { job.setJobSubmitHostAddress(ip.getHostAddress()); job.setJobSubmitHostName(ip.getHostName()); }
获取Map任务数量,这一信息是分析得到的,并不是直接获取到,获得的分片信息会以文件名job.split上传至HDFS:
创建Job参数,这些参数太多,使用JobContext类表示:
JobContext context = new JobContext(jobCopy, jobId);
注意,一般而言,Context中文含义是上下文,在Hadoop里一般用于记录参数,这里就是记录Job相关的参数,比如Map的实现类名等等,其声明为:
public class JobContext { // Put all of the attribute names in here so that Job and JobContext are // consistent. protected static final String INPUT_FORMAT_CLASS_ATTR = "mapreduce.inputformat.class"; protected static final String MAP_CLASS_ATTR = "mapreduce.map.class"; protected static final String COMBINE_CLASS_ATTR = "mapreduce.combine.class"; protected static final String REDUCE_CLASS_ATTR = "mapreduce.reduce.class"; protected static final String OUTPUT_FORMAT_CLASS_ATTR = "mapreduce.outputformat.class"; protected static final String PARTITIONER_CLASS_ATTR = "mapreduce.partitioner.class"; protected final org.apache.hadoop.mapred.JobConf conf; protected final Credentials credentials; private JobID jobId; public static final String JOB_NAMENODES = "mapreduce.job.hdfs-servers"; public static final String JOB_ACL_VIEW_JOB = "mapreduce.job.acl-view-job"; public static final String JOB_ACL_MODIFY_JOB = "mapreduce.job.acl-modify-job"; public static final String CACHE_FILE_VISIBILITIES = "mapreduce.job.cache.files.visibilities"; public static final String CACHE_ARCHIVES_VISIBILITIES = "mapreduce.job.cache.archives.visibilities"; public static final String JOB_CANCEL_DELEGATION_TOKEN = "mapreduce.job.complete.cancel.delegation.tokens"; public static final String USER_LOG_RETAIN_HOURS = "mapred.userlog.retain.hours"; /** * The UserGroupInformation object that has a reference to the current user */ protected UserGroupInformation ugi; 。。。。。。
实际上,JobContext就是封装了JobConf的一个类,JobConf相当于客户端最初本地的配置文件信息,被解析后封装为JobConf对象,而JobContext则可以查询JobConf得到相应信息,比如返回客户端的Mapper实现类:
public Class<? extends Mapper<?,?,?,?>> getMapperClass() throws ClassNotFoundException { return (Class<? extends Mapper<?,?,?,?>>) conf.getClass(MAP_CLASS_ATTR, Mapper.class); }
创建了JobContext后,用于检查输出目录的有效性:
// Check the output specification if (reduces == 0 ? jobCopy.getUseNewMapper() : jobCopy.getUseNewReducer()) { org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.OutputFormat<?,?> output = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(context.getOutputFormatClass(), jobCopy); output.checkOutputSpecs(context); } else { jobCopy.getOutputFormat().checkOutputSpecs(fs, jobCopy); }
之后,分析输入数据的Split分割信息,用于产生Map的数量:
// Create the splits for the job FileSystem fs = submitJobDir.getFileSystem(jobCopy); LOG.debug("Creating splits at " + fs.makeQualified(submitJobDir)); int maps = writeSplits(context, submitJobDir); jobCopy.setNumMapTasks(maps);
注意,对输入数据进行Split,也就决定了Map的数量,可以说,Map的数量是JobClient根据SplitSize产生的,Reduce的数量是用户指定的,但Map和Reduce具体运行在哪些机器由JobTracker分配。
在上面的代码中,获得的分片信息会以文件名job.split上传至HDFS:
/tmp/hadoop/mapred/staging/esingchan/.staging/job_201408161410_0001/files/job.split
这一部分的逻辑也有些复杂,我们暂时认为已经产生了job.split文件,在第6节进行详细分析。
在得到上述信息后,准备将信息写入Job配置文件Job.xml:
// Write job file to JobTracker's fs FSDataOutputStream out = FileSystem.create(fs, submitJobFile, new FsPermission(JobSubmissionFiles.JOB_FILE_PERMISSION)); // removing jobtoken referrals before copying the jobconf to HDFS // as the tasks don't need this setting, actually they may break // because of it if present as the referral will point to a // different job. TokenCache.cleanUpTokenReferral(jobCopy); try { jobCopy.writeXml(out); } finally { out.close(); }
submitJobFile即:
/tmp/hadoop/mapred/staging/esingchan/.staging/job_201408161410_0001/files/job.xml
5、向JobTracker真正提交Job
真正提交Job的代码为:
status = jobSubmitClient.submitJob(
jobId, submitJobDir.toString(), jobCopy.getCredentials());
JobProfile prof = jobSubmitClient.getJobProfile(jobId);
jobSubmitClient调用的这个方法同样利用RPC传递到JobTracker执行同名方法,可以看到,JobClient和JobTracker两者传递的内容实际上主要有两个,一个是Job ID,另一个是该Job在HDFS中的根目录,具体的资源数据等等实际上全部由JobClient预先放在HDFS中。其代码为:
JobStatus submitJob(JobID jobId, String jobSubmitDir, UserGroupInformation ugi, Credentials ts, boolean recovered) throws IOException { // Check for safe-mode checkSafeMode(); JobInfo jobInfo = null; if (ugi == null) { ugi = UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser(); } synchronized (this) { if (jobs.containsKey(jobId)) { // job already running, don't start twice return jobs.get(jobId).getStatus(); } jobInfo = new JobInfo(jobId, new Text(ugi.getShortUserName()), new Path(jobSubmitDir)); } // Store the job-info in a file so that the job can be recovered // later (if at all) // Note: jobDir & jobInfo are owned by JT user since we are using // his fs object if (!recovered) { Path jobDir = getSystemDirectoryForJob(jobId); FileSystem.mkdirs(fs, jobDir, new FsPermission(SYSTEM_DIR_PERMISSION)); FSDataOutputStream out = fs.create(getSystemFileForJob(jobId)); jobInfo.write(out); out.close(); } // Create the JobInProgress, do not lock the JobTracker since // we are about to copy job.xml from HDFS and write jobToken file to HDFS JobInProgress job = null; try { if (ts == null) { ts = new Credentials(); } generateAndStoreJobTokens(jobId, ts); job = new JobInProgress(this, this.conf, jobInfo, 0, ts); } catch (Exception e) { throw new IOException(e); } if (recovered && !job.getJobConf().getBoolean( JobConf.MAPREDUCE_RECOVER_JOB, JobConf.DEFAULT_MAPREDUCE_RECOVER_JOB)) { LOG.info("Job "+ jobId.toString() + " is not enable for recovery, cleaning up job files"); job.cleanupJob(); return null; } synchronized (this) { // check if queue is RUNNING String queue = job.getProfile().getQueueName(); if (!queueManager.isRunning(queue)) { throw new IOException("Queue \"" + queue + "\" is not running"); } try { aclsManager.checkAccess(job, ugi, Operation.SUBMIT_JOB); } catch (IOException ioe) { LOG.warn("Access denied for user " + job.getJobConf().getUser() + ". Ignoring job " + jobId, ioe); job.fail(); throw ioe; } // Check the job if it cannot run in the cluster because of invalid memory // requirements. try { checkMemoryRequirements(job); } catch (IOException ioe) { throw ioe; } try { this.taskScheduler.checkJobSubmission(job); } catch (IOException ioe){ LOG.error("Problem in submitting job " + jobId, ioe); throw ioe; } // Submit the job JobStatus status; try { status = addJob(jobId, job); } catch (IOException ioe) { LOG.info("Job " + jobId + " submission failed!", ioe); status = job.getStatus(); status.setFailureInfo(StringUtils.stringifyException(ioe)); failJob(job); throw ioe; } return status; } }
主要分为几个步骤:
5.1 创建JobInProgress对象,该对象是JobTracker用来记录Job信息的类。其声明为:
public class JobInProgress { JobProfile profile; JobStatus status; String jobFile = null; Path localJobFile = null; final QueueMetrics queueMetrics; TaskInProgress maps[] = new TaskInProgress[0]; TaskInProgress reduces[] = new TaskInProgress[0]; TaskInProgress cleanup[] = new TaskInProgress[0]; TaskInProgress setup[] = new TaskInProgress[0]; int numMapTasks = 0; int numReduceTasks = 0; final long memoryPerMap; final long memoryPerReduce; volatile int numSlotsPerMap = 1; volatile int numSlotsPerReduce = 1; final int maxTaskFailuresPerTracker; // Counters to track currently running/finished/failed Map/Reduce task-attempts int runningMapTasks = 0; int runningReduceTasks = 0; int finishedMapTasks = 0; int finishedReduceTasks = 0; int failedMapTasks = 0; int failedReduceTasks = 0; private static long DEFAULT_REDUCE_INPUT_LIMIT = -1L; long reduce_input_limit = -1L; private static float DEFAULT_COMPLETED_MAPS_PERCENT_FOR_REDUCE_SLOWSTART = 0.05f; int completedMapsForReduceSlowstart = 0; // runningMapTasks include speculative tasks, so we need to capture // speculative tasks separately int speculativeMapTasks = 0; int speculativeReduceTasks = 0; final int mapFailuresPercent; final int reduceFailuresPercent; int failedMapTIPs = 0; int failedReduceTIPs = 0; private volatile boolean launchedCleanup = false; private volatile boolean launchedSetup = false; private volatile boolean jobKilled = false; private volatile boolean jobFailed = false; JobPriority priority = JobPriority.NORMAL; final JobTracker jobtracker; protected Credentials tokenStorage; // NetworkTopology Node to the set of TIPs Map<Node, List<TaskInProgress>> nonRunningMapCache; // Map of NetworkTopology Node to set of running TIPs Map<Node, Set<TaskInProgress>> runningMapCache; // A list of non-local, non-running maps final List<TaskInProgress> nonLocalMaps; // Set of failed, non-running maps sorted by #failures final SortedSet<TaskInProgress> failedMaps; // A set of non-local running maps Set<TaskInProgress> nonLocalRunningMaps; // A list of non-running reduce TIPs Set<TaskInProgress> nonRunningReduces; // A set of running reduce TIPs Set<TaskInProgress> runningReduces; // A list of cleanup tasks for the map task attempts, to be launched List<TaskAttemptID> mapCleanupTasks = new LinkedList<TaskAttemptID>(); // A list of cleanup tasks for the reduce task attempts, to be launched List<TaskAttemptID> reduceCleanupTasks = new LinkedList<TaskAttemptID>(); 。。。。。。。
创建JobInProgress对象,对该任务进行初始化:
JobInProgress(JobTracker jobtracker, final JobConf default_conf, JobInfo jobInfo, int rCount, Credentials ts) throws IOException, InterruptedException { try { this.restartCount = rCount; this.jobId = JobID.downgrade(jobInfo.getJobID()); String url = "http://" + jobtracker.getJobTrackerMachine() + ":" + jobtracker.getInfoPort() + "/jobdetails.jsp?jobid=" + jobId; this.jobtracker = jobtracker; this.status = new JobStatus(jobId, 0.0f, 0.0f, JobStatus.PREP); this.status.setUsername(jobInfo.getUser().toString()); this.jobtracker.getInstrumentation().addPrepJob(conf, jobId); // Add the queue-level metric below (after the profile has been initialized) this.startTime = jobtracker.getClock().getTime(); status.setStartTime(startTime); this.localFs = jobtracker.getLocalFileSystem(); this.tokenStorage = ts; // use the user supplied token to add user credentials to the conf jobSubmitDir = jobInfo.getJobSubmitDir(); user = jobInfo.getUser().toString(); userUGI = UserGroupInformation.createRemoteUser(user); if (ts != null) { for (Token<? extends TokenIdentifier> token : ts.getAllTokens()) { userUGI.addToken(token); } } fs = userUGI.doAs(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<FileSystem>() { public FileSystem run() throws IOException { return jobSubmitDir.getFileSystem(default_conf); }}); /** check for the size of jobconf **/ Path submitJobFile = JobSubmissionFiles.getJobConfPath(jobSubmitDir); FileStatus fstatus = fs.getFileStatus(submitJobFile); if (fstatus.getLen() > jobtracker.MAX_JOBCONF_SIZE) { throw new IOException("Exceeded max jobconf size: " + fstatus.getLen() + " limit: " + jobtracker.MAX_JOBCONF_SIZE); } this.localJobFile = default_conf.getLocalPath(JobTracker.SUBDIR +"/"+jobId + ".xml"); Path jobFilePath = JobSubmissionFiles.getJobConfPath(jobSubmitDir); jobFile = jobFilePath.toString(); fs.copyToLocalFile(jobFilePath, localJobFile); conf = new JobConf(localJobFile); if (conf.getUser() == null) { this.conf.setUser(user); } if (!conf.getUser().equals(user)) { String desc = "The username " + conf.getUser() + " obtained from the " + "conf doesn't match the username " + user + " the user " + "authenticated as"; AuditLogger.logFailure(user, Operation.SUBMIT_JOB.name(), conf.getUser(), jobId.toString(), desc); throw new IOException(desc); } this.priority = conf.getJobPriority(); this.status.setJobPriority(this.priority); String queueName = conf.getQueueName(); this.profile = new JobProfile(user, jobId, jobFile, url, conf.getJobName(), queueName); Queue queue = this.jobtracker.getQueueManager().getQueue(queueName); if (queue == null) { throw new IOException("Queue \"" + queueName + "\" does not exist"); } this.queueMetrics = queue.getMetrics(); this.queueMetrics.addPrepJob(conf, jobId); this.submitHostName = conf.getJobSubmitHostName(); this.submitHostAddress = conf.getJobSubmitHostAddress(); this.numMapTasks = conf.getNumMapTasks(); this.numReduceTasks = conf.getNumReduceTasks(); this.memoryPerMap = conf.getMemoryForMapTask(); this.memoryPerReduce = conf.getMemoryForReduceTask(); this.taskCompletionEvents = new ArrayList<TaskCompletionEvent> (numMapTasks + numReduceTasks + 10); // Construct the jobACLs status.setJobACLs(jobtracker.getJobACLsManager().constructJobACLs(conf)); this.mapFailuresPercent = conf.getMaxMapTaskFailuresPercent(); this.reduceFailuresPercent = conf.getMaxReduceTaskFailuresPercent(); this.maxTaskFailuresPerTracker = conf.getMaxTaskFailuresPerTracker(); hasSpeculativeMaps = conf.getMapSpeculativeExecution(); hasSpeculativeReduces = conf.getReduceSpeculativeExecution(); // a limit on the input size of the reduce. // we check to see if the estimated input size of // of each reduce is less than this value. If not // we fail the job. A value of -1 just means there is no // limit set. reduce_input_limit = -1L; this.maxLevel = jobtracker.getNumTaskCacheLevels(); this.anyCacheLevel = this.maxLevel+1; this.nonLocalMaps = new LinkedList<TaskInProgress>(); this.failedMaps = new TreeSet<TaskInProgress>(failComparator); this.nonLocalRunningMaps = new LinkedHashSet<TaskInProgress>(); this.runningMapCache = new IdentityHashMap<Node, Set<TaskInProgress>>(); this.nonRunningReduces = new TreeSet<TaskInProgress>(failComparator); this.runningReduces = new LinkedHashSet<TaskInProgress>(); this.resourceEstimator = new ResourceEstimator(this); this.reduce_input_limit = conf.getLong("mapreduce.reduce.input.limit", DEFAULT_REDUCE_INPUT_LIMIT); // register job's tokens for renewal DelegationTokenRenewal.registerDelegationTokensForRenewal( jobInfo.getJobID(), ts, jobtracker.getConf()); // Check task limits checkTaskLimits(); } finally { //close all FileSystems that was created above for the current user //At this point, this constructor is called in the context of an RPC, and //hence the "current user" is actually referring to the kerberos //authenticated user (if security is ON). FileSystem.closeAllForUGI(UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser()); } }
5.2 将创建好的对象丢至任务队列中:
// Submit the job JobStatus status; try { status = addJob(jobId, job); } catch (IOException ioe) { LOG.info("Job " + jobId + " submission failed!", ioe); status = job.getStatus(); status.setFailureInfo(StringUtils.stringifyException(ioe)); failJob(job); throw ioe; } return status; } }
addJob是JobTracker的一个方法:
private synchronized JobStatus addJob(JobID jobId, JobInProgress job) throws IOException { totalSubmissions++; synchronized (jobs) { synchronized (taskScheduler) { jobs.put(job.getProfile().getJobID(), job); for (JobInProgressListener listener : jobInProgressListeners) { listener.jobAdded(job); } } } myInstrumentation.submitJob(job.getJobConf(), jobId); job.getQueueMetrics().submitJob(job.getJobConf(), jobId); LOG.info("Job " + jobId + " added successfully for user '" + job.getJobConf().getUser() + "' to queue '" + job.getJobConf().getQueueName() + "'"); AuditLogger.logSuccess(job.getUser(), Operation.SUBMIT_JOB.name(), jobId.toString()); return job.getStatus(); }
核心部分就是下面的代码:
synchronized (jobs) { synchronized (taskScheduler) { jobs.put(job.getProfile().getJobID(), job); for (JobInProgressListener listener : jobInProgressListeners) { listener.jobAdded(job); } } }
jobs记录了JobTracker目前所有的作业:
// All the known jobs. (jobid->JobInProgress) Map<JobID, JobInProgress> jobs = Collections.synchronizedMap(new TreeMap<JobID, JobInProgress>());
但这个对象并不是作业队列,真正的队列是jobInProgressListeners,该对象是一个JobInProgressListener的队列:
private final List<JobInProgressListener> jobInProgressListeners = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<JobInProgressListener>();
而JobInProgressListener是一个抽象类 ,其实现有很多个,如JobQueueJobInProgressListener用于监控job的运行状态,EagerTaskInitializationListener用于对Job进行初始化,JobTracker的JobInProgressListener队列里包含了多个这种类,新到的Job都被加入到各个JobInProgressListener中,以EagerTaskInitializationListener为例:
/** * We add the JIP to the jobInitQueue, which is processed * asynchronously to handle split-computation and build up * the right TaskTracker/Block mapping. */ @Override public void jobAdded(JobInProgress job) { synchronized (jobInitQueue) { jobInitQueue.add(job); resortInitQueue(); jobInitQueue.notifyAll(); } }
可见,Job被加入到队列中,jobInitQueue是一个List对象:
private List<JobInProgress> jobInitQueue = new ArrayList<JobInProgress>();
resortInitQueue()方法根据优先级等对队列里面的作业进行重新排列:
/** * Sort jobs by priority and then by start time. */ private synchronized void resortInitQueue() { Comparator<JobInProgress> comp = new Comparator<JobInProgress>() { public int compare(JobInProgress o1, JobInProgress o2) { int res = o1.getPriority().compareTo(o2.getPriority()); if(res == 0) { if(o1.getStartTime() < o2.getStartTime()) res = -1; else res = (o1.getStartTime()==o2.getStartTime() ? 0 : 1); } return res; } }; synchronized (jobInitQueue) { Collections.sort(jobInitQueue, comp); } }
因此,后加入队列的作业可能会因为优先级而被调整到前面执行。
jobInitQueue.notifyAll()这一行是通知其它线程,实际上是起到唤醒Job处理线程的作用,因为Job处理线程在没有Job的时候会wait,这可以从下面代码中看出:
class JobInitManager implements Runnable { public void run() { JobInProgress job = null; while (true) { try { synchronized (jobInitQueue) { while (jobInitQueue.isEmpty()) { jobInitQueue.wait(); } job = jobInitQueue.remove(0); } threadPool.execute(new InitJob(job)); } catch (InterruptedException t) { LOG.info("JobInitManagerThread interrupted."); break; } } LOG.info("Shutting down thread pool"); threadPool.shutdownNow(); } }
当被唤醒后,会执行 job = jobInitQueue.remove(0)获得队列中第一个Job,并调用线程池,threadPool用JAVA中标准的线程池类java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService实现。
5.3 Job任务执行
从Job队列中取出Job任务后,创建了InitJob对象,丢入线程池执行时,则执行run方法:
class InitJob implements Runnable { private JobInProgress job; public InitJob(JobInProgress job) { this.job = job; } public void run() { ttm.initJob(job); } }
于是,进入ttm的intiJob方法,ttm是TaskTrackerManager对象,而TaskTrackerManager是一个接口,实现类只有JobTracker,因此实际上进入JobTracker的initJob方法执行:
public void initJob(JobInProgress job) { 。。。。。。。try { JobStatus prevStatus = (JobStatus)job.getStatus().clone(); LOG.info("Initializing " + job.getJobID()); job.initTasks(); // Inform the listeners if the job state has changed JobStatus newStatus = (JobStatus)job.getStatus().clone(); if (prevStatus.getRunState() != newStatus.getRunState()) { JobStatusChangeEvent event = new JobStatusChangeEvent(job, EventType.RUN_STATE_CHANGED, prevStatus, newStatus); synchronized (JobTracker.this) { updateJobInProgressListeners(event); } } } } 。。。。。。 }
之后,进入JobInProgress的initTasks方法执行作业的初始化。至此为止,JobClient作业提交、JobTracker将作业丢入队列、额外线程从队列中取出作业并丢到线程池中执行作业初始化的基本代码解析完毕。关于Job如何进行初始化,以及任务如何分配等等内容,我们留作后续博文中研究。
另外,上面我们遗留了一个问题,即Map任务的数量的确定。
6、Map数量的确定
在前面JobClient进行作业提交时,涉及到向配置文件job.xml中写入Map数量的代码:
// Create the splits for the job FileSystem fs = submitJobDir.getFileSystem(jobCopy); LOG.debug("Creating splits at " + fs.makeQualified(submitJobDir)); int maps = writeSplits(context, submitJobDir); jobCopy.setNumMapTasks(maps);
writeSplits调用writeNewSplits,该方法最核心的是input.getSplits方法:
private int writeSplits(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.JobContext job, Path jobSubmitDir) throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException { JobConf jConf = (JobConf)job.getConfiguration(); int maps; if (jConf.getUseNewMapper()) { maps = writeNewSplits(job, jobSubmitDir); } else { maps = writeOldSplits(jConf, jobSubmitDir); } return maps; } private <T extends InputSplit> int writeNewSplits(JobContext job, Path jobSubmitDir) throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException { Configuration conf = job.getConfiguration(); InputFormat<?, ?> input = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(job.getInputFormatClass(), conf); List<InputSplit> splits = input.getSplits(job); T[] array = (T[]) splits.toArray(new InputSplit[splits.size()]); // sort the splits into order based on size, so that the biggest // go first Arrays.sort(array, new SplitComparator()); JobSplitWriter.createSplitFiles(jobSubmitDir, conf, jobSubmitDir.getFileSystem(conf), array); return array.length; }
createSplitFiles方法会生成两个文件:job.split和job.splitmetainfo:
public static <T extends InputSplit> void createSplitFiles(Path jobSubmitDir, Configuration conf, FileSystem fs, T[] splits) throws IOException, InterruptedException { FSDataOutputStream out = createFile(fs, JobSubmissionFiles.getJobSplitFile(jobSubmitDir), conf); SplitMetaInfo[] info = writeNewSplits(conf, splits, out); out.close(); writeJobSplitMetaInfo(fs,JobSubmissionFiles.getJobSplitMetaFile(jobSubmitDir), new FsPermission(JobSubmissionFiles.JOB_FILE_PERMISSION), splitVersion, info); } public static Path getJobSplitFile(Path jobSubmissionDir) { return new Path(jobSubmissionDir, "job.split"); } public static Path getJobSplitMetaFile(Path jobSubmissionDir) { return new Path(jobSubmissionDir, "job.splitmetainfo"); }
在理解上述代码时,需要理解Split。
Split代表了对输入数据的一种逻辑分割,对于每一个分割,最终都会有一个Map任务进行计算,而Reduce的数量是用户指定的,因此Split决定了MapReduce的计算任务数量。
在所有的InputSplit里,最重要的是FileSplit,代表了对输入HDFS文件的分割:
public class FileSplit extends InputSplit implements Writable { private Path file; private long start; private long length; private String[] hosts; .......
从FileSplit的定义来看,主要记录了Split块所属文件、在文件中的起始位置,长度等。比如一个100T的大文件,分割成100个FileSplit,每个1T。只有确定了文件的分割方式,才能确定Map的数量。
因为输入数据可能是文件、HBase表等等,所以针对不同的输入数据格式,有不同的类实现这一Split分割功能。这里只从文件来看,由FileInputFormat实现分割。其核心方法为getSplits:
/** * Generate the list of files and make them into FileSplits. */ public List<InputSplit> getSplits(JobContext job ) throws IOException { long minSize = Math.max(getFormatMinSplitSize(), getMinSplitSize(job)); long maxSize = getMaxSplitSize(job); // generate splits List<InputSplit> splits = new ArrayList<InputSplit>(); List<FileStatus>files = listStatus(job); for (FileStatus file: files) { Path path = file.getPath(); FileSystem fs = path.getFileSystem(job.getConfiguration()); long length = file.getLen(); BlockLocation[] blkLocations = fs.getFileBlockLocations(file, 0, length); if ((length != 0) && isSplitable(job, path)) { long blockSize = file.getBlockSize(); long splitSize = computeSplitSize(blockSize, minSize, maxSize); long bytesRemaining = length; while (((double) bytesRemaining)/splitSize > SPLIT_SLOP) { int blkIndex = getBlockIndex(blkLocations, length-bytesRemaining); splits.add(new FileSplit(path, length-bytesRemaining, splitSize, blkLocations[blkIndex].getHosts())); bytesRemaining -= splitSize; } if (bytesRemaining != 0) { splits.add(new FileSplit(path, length-bytesRemaining, bytesRemaining, blkLocations[blkLocations.length-1].getHosts())); } } else if (length != 0) { splits.add(new FileSplit(path, 0, length, blkLocations[0].getHosts())); } else { //Create empty hosts array for zero length files splits.add(new FileSplit(path, 0, length, new String[0])); } } // Save the number of input files in the job-conf job.getConfiguration().setLong(NUM_INPUT_FILES, files.size()); LOG.debug("Total # of splits: " + splits.size()); return splits; }
上面的获取Split的方法中,核心步骤是:
long minSize = Math.max(getFormatMinSplitSize(), getMinSplitSize(job)); long maxSize = getMaxSplitSize(job);
minSize为最小的Split大小,getFormatMinSplitSize的值是1,getMinSplitSize则来自于配置文件:
/** * Get the lower bound on split size imposed by the format. * @return the number of bytes of the minimal split for this format */ protected long getFormatMinSplitSize() { return 1; } /** * Get the minimum split size * @param job the job * @return the minimum number of bytes that can be in a split */ public static long getMinSplitSize(JobContext job) { return job.getConfiguration().getLong("mapred.min.split.size", 1L); }
getMaxSplitSize同样来自于配置文件,默认是Long的最大值:
/** * Get the maximum split size. * @param context the job to look at. * @return the maximum number of bytes a split can include */ public static long getMaxSplitSize(JobContext context) { return context.getConfiguration().getLong("mapred.max.split.size", Long.MAX_VALUE); }
之后,获取文件信息:
long length = file.getLen(); BlockLocation[] blkLocations = fs.getFileBlockLocations(file, 0, length);
获得文件的长度,并获取文件块所在的位置。BlockLocation记录了一个块在哪些DataNode机器上,其定义为:
public class BlockLocation implements Writable { private String[] hosts; //hostnames of datanodes private String[] names; //hostname:portNumber of datanodes private String[] topologyPaths; // full path name in network topology private long offset; //offset of the of the block in the file private long length; 。。。。。。。
long blockSize = file.getBlockSize(); long splitSize = computeSplitSize(blockSize, minSize, maxSize);
BlockSize为HDFS的块大小,默认64MB或128MB,splitSize则为Split的大小,computeSplitSize的实现为:
protected long computeSplitSize(long blockSize, long minSize, long maxSize) { return Math.max(minSize, Math.min(maxSize, blockSize)); }
可见,就是几个值选择一个。默认的,Split的大小就是blockSize,是一个Block的大小,也就是64MB等,当然,也可以设置为其它值。但无论如何设置,从下面的代码可以看出,Split的大小是一样的,除了最后一个FileSplit。而由于SPLIT_SLOP = 1.1,最后一个FileSplit是有可能大于一个Block大小的(<1.1个BlockSize即可,默认情况)。
long bytesRemaining = length; while (((double) bytesRemaining)/splitSize > SPLIT_SLOP) { int blkIndex = getBlockIndex(blkLocations, length-bytesRemaining); splits.add(new FileSplit(path, length-bytesRemaining, splitSize, blkLocations[blkIndex].getHosts())); bytesRemaining -= splitSize; } //最后一个块 if (bytesRemaining != 0) { splits.add(new FileSplit(path, length-bytesRemaining, bytesRemaining, blkLocations[blkLocations.length-1].getHosts())); }
每个FileSplit创建时,其大小都为splitSize,而这个值是通过前面代码获取的。从上面的代码中,blkInde表示某一个Block,而 blkLocations[blkIndex].getHosts()表示该Block所在的机器,这些机器作为FileSplit的参数,因此,应该是暗指Split的大小最好不要过大,比如假定一个Split是2个Block大小,而这个2个Block如果位于两个服务器上,那么在构造FileSplit时,则最终分配的Map任务只会位于一台服务器上,另一个Block则需要通过网络传输至Map所在机器,这说明,SPlit不宜大,最好保持就默认为一个Block。
从其构造函数来看:
public FileSplit(Path file, long start, long length, String[] hosts) { this.file = file; this.start = start; this.length = length; this.hosts = hosts; }
假如length很大,跨越了很多个Block,则可能跨越多台服务器,但hosts只是记录了某一个Block所处的服务器。从下面的方法可以看出,给Split分配的服务器就是Split的起始位置所在Block的所在机器(当然按照3份备份来说,至少有3台)。
protected int getBlockIndex(BlockLocation[] blkLocations, long offset) { for (int i = 0 ; i < blkLocations.length; i++) { // is the offset inside this block? if ((blkLocations[i].getOffset() <= offset) && (offset < blkLocations[i].getOffset() + blkLocations[i].getLength())){ return i; } } BlockLocation last = blkLocations[blkLocations.length -1]; long fileLength = last.getOffset() + last.getLength() -1; throw new IllegalArgumentException("Offset " + offset + " is outside of file (0.." + fileLength + ")"); }
FileInputFormat用于获取输入数据的分割,该类继承于基类InputFormat<K, V>,其定义为:
public abstract class InputFormat<K, V> { /** * Logically split the set of input files for the job. * * <p>Each {@link InputSplit} is then assigned to an individual {@link Mapper} * for processing.</p> * * <p><i>Note</i>: The split is a <i>logical</i> split of the inputs and the * input files are not physically split into chunks. For e.g. a split could * be <i><input-file-path, start, offset></i> tuple. The InputFormat * also creates the {@link RecordReader} to read the {@link InputSplit}. * * @param context job configuration. * @return an array of {@link InputSplit}s for the job. */ public abstract List<InputSplit> getSplits(JobContext context ) throws IOException, InterruptedException; /** * Create a record reader for a given split. The framework will call * {@link RecordReader#initialize(InputSplit, TaskAttemptContext)} before * the split is used. * @param split the split to be read * @param context the information about the task * @return a new record reader * @throws IOException * @throws InterruptedException */ public abstract RecordReader<K,V> createRecordReader(InputSplit split, TaskAttemptContext context ) throws IOException, InterruptedException; }
里面必须实现两个方法:getSplits、createRecordReader。因此,getSplits获得对输入数据的分割方式,createRecordReader则返回一个可以读取记录的类。
从前面可以看出,如果采用默认形式,则Map数量等于Block的数量,一般情况下,Split尺寸就等于Block。这里可能就会有个疑问,某些记录较长(比如一行文本),可能会跨越多个Block,那么,也就会跨越多个Split,而Map和Split是一一对应关系,跨越边界的记录被哪个Map执行呢?这个问题由RecordReader保证,在处理文本文件时,Hadoop提供了一些基本实现,典型的有TextInputFormat,这个类继承于FileInputFormat<LongWritable, Text> ,其声明为:
public class TextInputFormat extends FileInputFormat<LongWritable, Text> { @Override public RecordReader<LongWritable, Text> createRecordReader(InputSplit split, TaskAttemptContext context) { return new LineRecordReader(); } @Override protected boolean isSplitable(JobContext context, Path file) { CompressionCodec codec = new CompressionCodecFactory(context.getConfiguration()).getCodec(file); if (null == codec) { return true; } return codec instanceof SplittableCompressionCodec; } }
可见,其实现了LineRecordReader,读取整行记录。如果一行文本跨越了多个Split,则LineRecordReader不会关心SPlit,而会保证跨越的那个文本行由前一个Map任务执行,其代码为:
public boolean nextKeyValue() throws IOException { if (key == null) { key = new LongWritable(); } key.set(pos); if (value == null) { value = new Text(); } int newSize = 0; // We always read one extra line, which lies outside the upper // split limit i.e. (end - 1) while (getFilePosition() <= end) { newSize = in.readLine(value, maxLineLength, Math.max(maxBytesToConsume(pos), maxLineLength)); if (newSize == 0) { break; } pos += newSize; if (newSize < maxLineLength) { break; } // line too long. try again LOG.info("Skipped line of size " + newSize + " at pos " + (pos - newSize)); } if (newSize == 0) { key = null; value = null; return false; } else { return true; } }
其readLine方法会读取一整行,因为这是针对HDFS操作的,所以不管这一行是否跨越了多个Split,都会把记录全部读进来处理。
而在LineRecordReader的initialize方法中,有以下关键代码:
public void initialize(InputSplit genericSplit, TaskAttemptContext context) throws IOException { FileSplit split = (FileSplit) genericSplit; Configuration job = context.getConfiguration(); this.maxLineLength = job.getInt("mapred.linerecordreader.maxlength", Integer.MAX_VALUE); start = split.getStart(); end = start + split.getLength(); final Path file = split.getPath(); .....
start和end记录了该Split在整个文件中的起始位置和结束位置。并跳到Split的起始位置:
fileIn.seek(start); in = new LineReader(fileIn, job); filePosition = fileIn;
之后,如果start不为0,表明这不是第一个Split块,则会直接读取一行,而并不进行处理:
// If this is not the first split, we always throw away first record // because we always (except the last split) read one extra line in // next() method. if (start != 0) { start += in.readLine(new Text(), 0, maxBytesToConsume(start)); } this.pos = start;
这样就相当于忽略了跨越Split边界第一行,因为这一行已经被上一个Split对应的Map任务处理了。
总的来说,Map任务数量决定于Split数量,一般等于HDFS Block的整数倍,会存在一条记录跨越多个Split的情况,记录读取由RecordReader的实现类决定,在这个类中,会处理好边界问题。
后记:
Job提交的过程基本剖析完毕,从官网摘出其流程图:
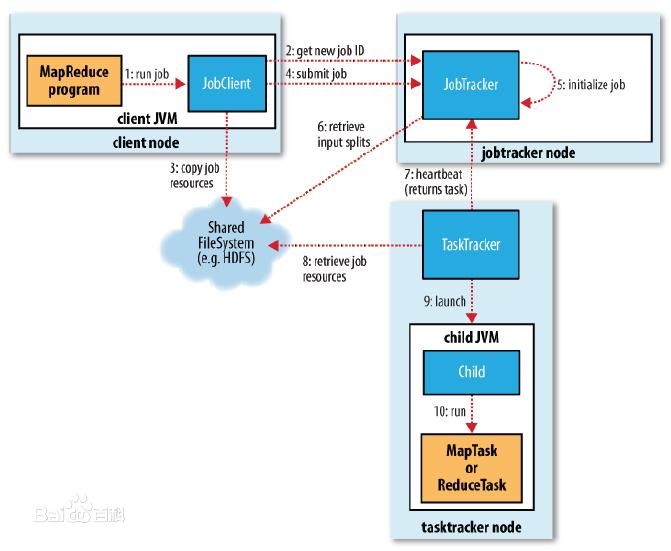
可以看出,一共有10个基本步骤:
1、创建JobClient对象,实现与JobTracker的RPC访问;
2、获取Job ID;
3、向HDFS上传所需数据文件(不是HDFS文件数据)、资源文件;这些文件属于Job相关文件,Map任务数量由JobClient负责统计得到,生成后写入HDFS的job.split文件中;
4、提交Job至JobTracker的队列;
5、初始化,即从Job队列中取出来进行初始化操作;
6、获取job.split等文件,进行任务分配等操作;
7、TaskTracker通过心跳机制,获取Job;
8、TaskTracker从HDFS中获取所需jar包、参数等资源信息;
9、启动虚拟机;
10、Map、Reduce Task在虚拟机中执行。
在本博文中,对1-4的过程进行了分析,关于JobTracker如何取出Job,以及Job如何分配,TaskTracker如何获取Map/Reduce Task的细节在后续博文中进行分析。
上面过程若有不对之处,敬请指正。