1 昨日回顾
工厂三兄弟
·简单的工厂模式
·工厂方法模式
·抽象工厂模式
简单工厂模式:
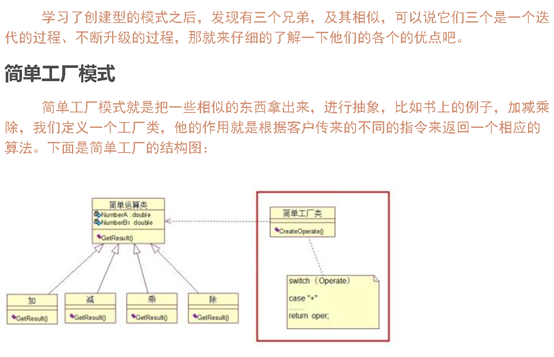

(不符合开闭原则)
工厂方法模式:


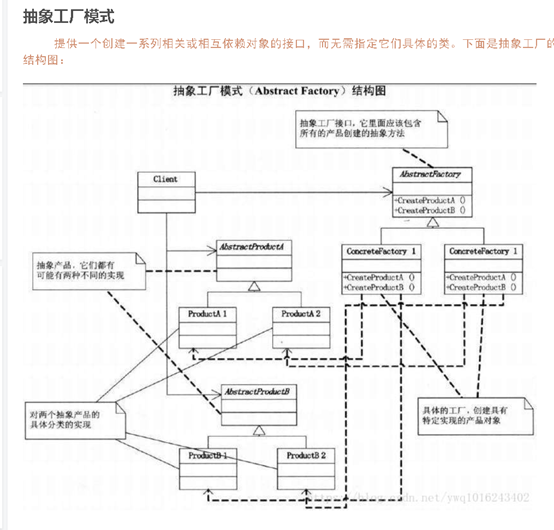
抽象工厂模式:

单例模式
代理模式
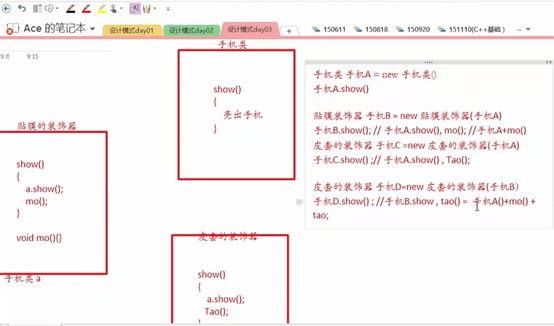
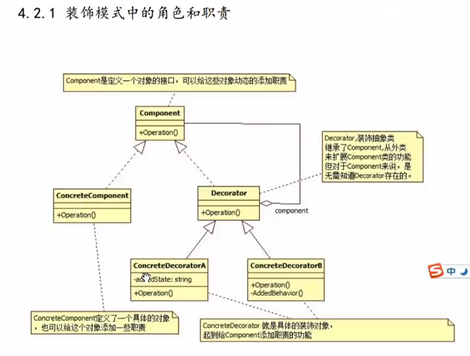
2 装饰器模式


#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 抽象的手机类
class Phone
{
public:
virtual void show() = 0;
};
class iPhone : public Phone
{
public:
virtual void show() {
cout << "秀出了iphone" << endl;
}
};
class Mi : public Phone
{
virtual void show() {
cout << "秀出了小米手机" << endl;
}
};
// 写一个抽象的装饰器
class Decorator :public Phone
{
public:
Decorator(Phone *phone)
{
this->phone = phone;
}
virtual void show() = 0;
protected:
Phone *phone; // 拥有一个 所有手机的父类指针
};
// 具体的手机贴膜装饰器
class MoDecorator :public Decorator
{
public:
// 构造函数初始化列表
MoDecorator(Phone *phone) :Decorator(phone) {}
virtual void show() {
this->phone->show(); // 保持原有的show方法
this->mo(); // 额外添加一个mo的方法
}
// 膜装饰器,可以修饰添加的方法
void mo() {
cout << "手机有了贴膜" << endl;
}
};
// 皮套的装饰器类
class TaoDecorator :public Decorator
{
public:
// 构造函数初始化列表
TaoDecorator(Phone *phone) : Decorator(phone) {}
virtual void show()
{
this->phone->show();
tao();
}
void tao() {
cout << "手机有了皮套" << endl;
}
};
int main(void)
{
Phone *phone = new iPhone;
phone->show();
cout << "-------" << endl;
Phone *moPhone = new MoDecorator(phone);
moPhone->show();
cout << "-------" << endl;
Phone *taoPhone = new TaoDecorator(phone);
taoPhone->show();
cout << "--------" << endl;
Phone *moTaoPhone = new TaoDecorator(moPhone);
moTaoPhone->show(); // moPhone.show() + tao() == phone.show() + mo() + tao()
system("pause");
return 0;
}
3 装饰器模式练习
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Hero
{
public:
virtual void status() = 0;
};
class Akali :public Hero
{
public:
virtual void status() {
cout << "HP:1000" << endl;
cout << "AP:500" << endl;
cout << "AD:50" << endl;
}
};
// 英雄的装饰器
class Decorator :public Hero
{
public:
Decorator(Hero *hero) {
this->hero = hero;
}
virtual void status() = 0;
protected:
Hero * hero;
};
// 日炎斗篷的装饰器
class RYDecorator :public Decorator
{
public:
RYDecorator(Hero * hero) :Decorator(hero) {}
virtual void status() {
this->hero->status(); // 先调用被装饰的 英雄的基本状态
cout << "HP + 10000" << endl;
}
};
// 深渊权杖装饰器
class SYQZDecorator : public Decorator
{
public:
SYQZDecorator(Hero *hero) :Decorator(hero) {}
virtual void status() {
this->hero->status();
cout << "AP + 50000" << endl;
}
};
int main(void)
{
Hero *akali = new Akali;
cout << "akali的初始状态" << endl;
akali->status();
cout << "通过日炎斗篷创建新的akali" << endl;
Hero *ryAkali = new RYDecorator(akali);
ryAkali->status();
cout << "再通过 深渊权杖的装备装饰器 修饰日炎akali" << endl;
Hero *syAkali = new SYQZDecorator(ryAkali);
syAkali->status();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
装饰器模式对比一下代理模式:
class Proxy: public BaseClass
{
public:
Proxy(BaseClass * obj)
{
this.obj = obj
}
virtual void ....
virtual void ....
private:
Baseclss * obj
}
class Decorator : public BaseClass
{
public:
Decorator(BaseClass *obj)
{
this->obj = obj
virtual void ... = 0
}
protected:
BaseClass *obj
}
class Decorator1 : public Decorator
{
public:
Decorator1(BaseClass * obj) : Decorator(obj) {}
virtual void ....{
this->obj->...
...
}
}
...
4 装饰器练习回顾
5 外观模式
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class SysA
{
public:
void operationA() {
cout << "sysA。。。" << endl;
}
private:
};
class SysB
{
public:
void operationB() {
cout << "sysB。。。" << endl;
}
private:
};
class SysC
{
public:
void operationC() {
cout << "sysC。。。" << endl;
}
private:
};
class SysD
{
public:
void operationD() {
cout << "sysD。。。" << endl;
}
private:
};
// 外观模式
class Facade
{
public:
void methodOne()
{
sysa.operationA();
sysb.operationB();
}
void methodTwo()
{
sysc.operationC();
sysd.operationD();
}
private:
SysA sysa;
SysB sysb;
SysC sysc;
SysD sysd;
};
int main(void)
{
/*
SysA sa;
SysB sb;
sa.operationA();
sb.operationB();
*/
// 外观
Facade fa;
//AB 方法组合
fa.methodOne();
// CD 组合
fa.methodTwo();
return 0;
}
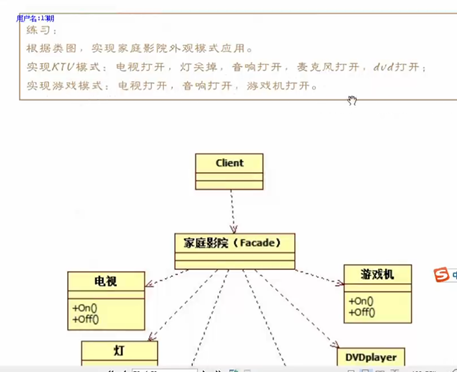
…

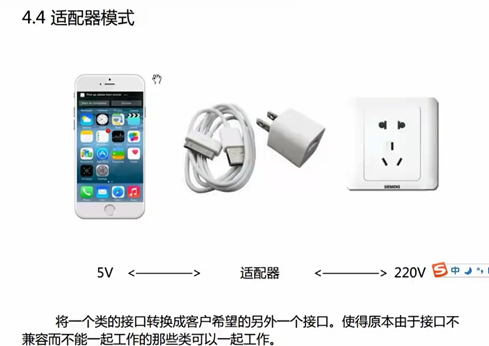
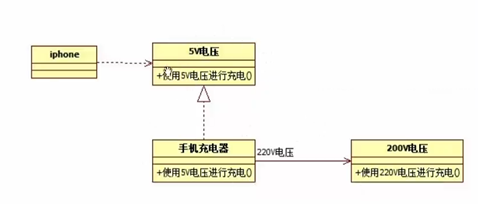
6 适配器模式
7 模板方法模式
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 5v电压的类
/*
class V5
{
public:
void useV5() {
cout << "使用了5v的点压" << endl;
}
};
*/
class V5
{
public:
// 虚函数
virtual void useV5() = 0;
};
// 目前只有v220的类 没有v5
class V220
{
public:
void useV220() {
cout << "使用了220v电压" << endl;
}
};
// 定义一个中间的适配器类
class Adapter :public V5 {
public:
Adapter(V220 *v220)
{
this->v220 = v220;
}
~Adapter() {
if (this->v220 != NULL)
{
delete this->v220;
}
}
virtual void useV5() {
// useV5函数实际使用的是V220
v220->useV220();
}
private:
V220 *v220;
};
// iPhone
class iPhone
{
public:
iPhone(V5 *v5)
{
this->v5 = v5;
}
~iPhone()
{
if (this->v5 != NULL)
{
delete this->v5;
}
}
// 充电的方法
void charge() {
cout << "iphone手机进行了充电" << endl;
v5->useV5();
}
private:
V5 *v5;
};
int main(void)
{
// iPhone只能使用V5的
iPhone * phone = new iPhone(new Adapter(new V220));
phone->charge();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
7 模板方法模式


模板方法:

模板方法、钩子的介绍
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 抽象的制作饮料方法
class MakeDrink
{
public:
// 1 把水煮开
void boil()
{
cout << "把水煮开" << endl;
}
// 2 冲某物
virtual void brew() = 0;
// 3 从大杯倒入小杯
void putInCup() {
cout << "把冲泡好的音量 从大杯倒入小杯" << endl;
}
// 4 加一些佐料
virtual void addThings() = 0;
// 钩子函数, hook 通过用户重写改变固定业务是否调用
virtual bool CustomWantAddThings() {
return true;
}
// 业务的逻辑的统一模板
void make() {
boil();
brew();
putInCup();
if (CustomWantAddThings() == true) {
addThings();
}
addThings();
}
};
// 制作咖啡
class MakeCoffee : public MakeDrink
{
public:
MakeCoffee(bool isAdd)
{
this->isAdd = isAdd;
};
// 2 冲某物
virtual void brew()
{
cout << "冲泡咖啡豆" << endl;
}
// 4 加一些佐料
virtual void addThings() {
cout << "添加糖和牛奶" << endl;
}
virtual bool CustomWantAddThings() {
return isAdd;
}
private:
bool isAdd;
};
// 冲泡茶叶
class MakeTea :public MakeDrink
{
public:
MakeTea(bool isAdd)
{
this->isAdd = isAdd;
}
// 2 冲某物
virtual void brew()
{
cout << "冲泡 茶叶" << endl;
}
// 4 加一些佐料
virtual void addThings() {
cout << "添加 柠檬 或者 菊花" << endl;
}
virtual bool CustomWantAddThings() {
return isAdd;
}
private:
bool isAdd;
};
int main(void)
{
MakeDrink *makeCoffee = new MakeCoffee(true);
makeCoffee->make();
cout << "-----------" << endl;
MakeDrink *makeTea = new MakeTea(false);
makeTea->make();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
8 命令模式

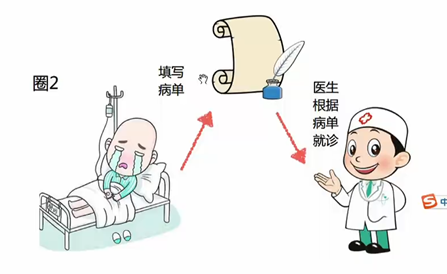
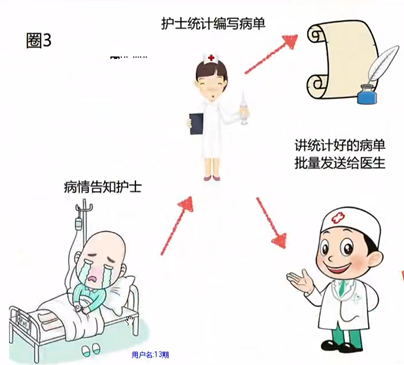
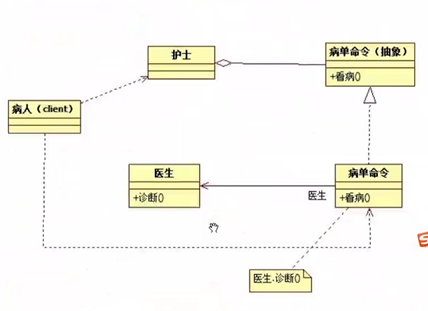
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
// 系统的一个核心类模块
class Doctor
{
public:
// 治疗眼睛的方法
void treatEyes() {
cout << "医生治疗了眼睛" << endl;
}
// 治疗鼻子的方法
void treatNose() {
cout << "医生治疗了鼻子" << endl;
}
};
// 定义一个抽象的病单
class Command
{
public:
Command(Doctor *doctor)
{
this->doctor = doctor;
}
~Command() {
if (this->doctor != NULL) {
delete doctor;
doctor = NULL;
}
}
virtual void treat() = 0;
protected:
Doctor * doctor;
};
// 治疗眼睛的病单
class CommandEyes :public Command
{
public:
CommandEyes(Doctor * doctor):Command(doctor){}
// 病单执行治疗的时候 实际上让医生治疗
void treat() {
doctor->treatEyes();
}
};
// 治疗鼻子的病单
class CommandNoses :public Command
{
public:
CommandNoses(Doctor *doctor) :Command(doctor) {}
void treat() {
doctor->treatNose();
}
};
// 护士长
class NurseBoss {
public:
NurseBoss()
{
m_list.clear();
}
~NurseBoss()
{
m_list.clear();
}
// 给护士长添加病单的方法
void setCmd(Command *cmd)
{
this->m_list.push_back(cmd);
}
// 下发手里所有订单的指令
void notify()
{
for (list <Command *>::iterator it = m_list.begin(); it != m_list.end(); it++)
{
(*it)->treat();
}
}
private:
list <Command*> m_list;
};
// 病人
int main(void)
{
NurseBoss *woman = new NurseBoss;
Command *cmd1 = new CommandEyes(new Doctor);
Command *cmd2 = new CommandNoses(new Doctor);
// 将所有指令都给护士长
woman->setCmd(cmd1);
woman->setCmd(cmd2);
woman->notify();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
9 中午回顾
10 命令模式烤串练习

#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
// 命令的执行者
class Cooker
{
public:
void makeChuaner() {
cout << "烤串师傅进行了烤串" << endl;
}
void makeChicken() {
cout << "烤串师傅进行了烤鸡翅" << endl;
}
};
// 命令
class Command
{
public:
Command(Cooker *cooker)
{
this->cooker = cooker;
}
~Command() {
if (this->cooker != NULL)
{
delete this->cooker;
this->cooker = NULL;
}
}
virtual void execute() = 0;
protected:
Cooker *cooker;
};
// 烤串命令
class CommandChuaner :public Command
{
public:
CommandChuaner(Cooker *cooker) : Command(cooker) {};
virtual void execute() {
this->cooker->makeChuaner();
}
};
// 烤鸡命令
class CommandChicken :public Command
{
public:
CommandChicken(Cooker *cooker) :Command(cooker) {};
virtual void execute() {
this->cooker->makeChicken();
}
};
// 管理命令的模块
class Waitress
{
public:
// 给服务员添加菜单的方法
void setCmd(Command *cmd) {
this->cmd_list.push_back(cmd);
}
void notify() {
list<Command *>::iterator it = cmd_list.begin();
for (; it != cmd_list.end(); it++)
{
(*it)->execute();
}
}
private:
list<Command *> cmd_list;
};
int main(void)
{
// 初始化一个管理命令的模块——服务员
Waitress * mm = new Waitress;
// 烤串命令
Command *chuaner = new CommandChuaner(new Cooker);
// 烤鸡命令
Command *chicken = new CommandChicken(new Cooker);
// 把订单给服务员
mm->setCmd(chuaner);
mm->setCmd(chicken);
// 让师傅干活
mm->notify();
delete mm;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
11 命令模式的优缺点

12 策略模式案例

#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 抽象的策略( 抽象的武器 )
class AbstractStrategy
{
public:
// 纯虚函数, 使用具体武器的策略
virtual void useWeapon() = 0;
private:
};
class KnifeStrategy : public AbstractStrategy
{
public:
virtual void useWeapon() {
cout << "使用匕首,进行近战攻击" << endl;
}
};
class AKStrategy :public AbstractStrategy
{
public:
virtual void useWeapon() {
cout << "使用ak,进行远程攻击" << endl;
}
};
class Hero
{
public:
Hero()
{
strategy = NULL;
}
void setStrategy(AbstractStrategy *strategy)
{
this->strategy = strategy;
}
// 攻击方法
void fight() {
cout << "英雄开始战斗了" << endl;
this->strategy->useWeapon();
}
private:
// 拥有一个 使用攻击策略的抽象成员
AbstractStrategy *strategy;
};
int main(void)
{
AbstractStrategy *knife = new KnifeStrategy;
AbstractStrategy *ak47 = new AKStrategy;
Hero *hero = new Hero;
cout << "远程兵来了,要更换远程攻击" << endl;
hero->setStrategy(ak47);
hero->fight();
cout << "近战兵来了 更换近战的攻击" << endl;
hero->setStrategy(knife);
hero->fight();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
12 策略模式案例
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 抽象策略 ( 抽象的武器 )
class AbstractStrategy
{
public:
// 纯虚函数, 使用具体武器的策略
virtual void useWeapon() = 0;
};
// 匕首策略
class KnifeStrategy: public AbstractStrategy
{
public:
virtual void useWeapon() {
cout << "使用匕首,进行近战攻击" << endl;
}
};
// ak策略
class AKStrategy : public AbstractStrategy
{
public:
virtual void useWeapon() {
cout << "使用ak 进行远程攻击" << endl;
}
};
class Hero
{
public:
Hero() {
strategy = NULL;
}
void setStrategy(AbstractStrategy *strategy)
{
this->strategy = strategy;
}
// 攻击方法
void fight() {
cout << "英雄开始战斗了" << endl;
this->strategy->useWeapon();
}
private:
// 拥有一个 抽象策略
AbstractStrategy *strategy;
};
int main(void)
{
// 初始化匕首策略
AbstractStrategy *knife = new KnifeStrategy;
// 初始化ak策略
AbstractStrategy *ak47 = new AKStrategy;
Hero *hero = new Hero;
cout << "远程兵来了, 要更换远程武器" << endl;
// 为英雄设置策略
hero->setStrategy(ak47);
hero->fight();
cout << "--------------------" << endl;
cout << "近战兵来了, 更换近战攻击" << endl;
// 为英雄设置策略
hero->setStrategy(knife);
hero->fight();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
13 策略模式练习和类图总结

#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
// 销售策略
class AbstractStrategy {
public:
// 商品具体的销售策略计算方式
virtual double getPrice(double price) = 0;
};
// 策略A 商品打八折
class StrategyA :public AbstractStrategy
{
public:
virtual double getPrice(double price) {
return price * 0.8;
}
};
// 策略B 如果商品超过200,减100
class StrategyB : public AbstractStrategy
{
public:
virtual double getPrice(double price)
{
if (price > 200) {
price = price - 100;
}
return price;
}
};
// 商品
class Item
{
public:
Item(string name, double price)
{
this->name = name;
this->price = price;
};
// 提供一个可以更换策略的方法
void setStrategy(AbstractStrategy *strategy)
{
this->strategy = strategy;
}
// 最终获得商品的价格的方法
double SellPrice(){
return this->strategy->getPrice(this->price);
}
private:
string name;
double price; // 商品的价格
// 销售的策略
AbstractStrategy *strategy;
};
int main(void)
{
Item it("nike鞋", 201);
AbstractStrategy *sA = new StrategyA;
AbstractStrategy *sB = new StrategyB;
it.setStrategy(sA);
cout << "nike鞋应该卖" << it.SellPrice() << endl;
cout << "-------" << endl;
it.setStrategy(sB);
cout << "nike鞋应该卖" << it.SellPrice() << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
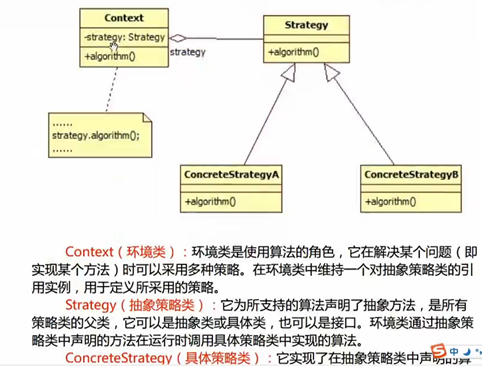

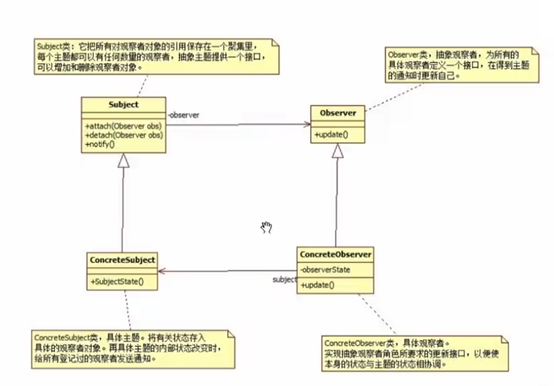
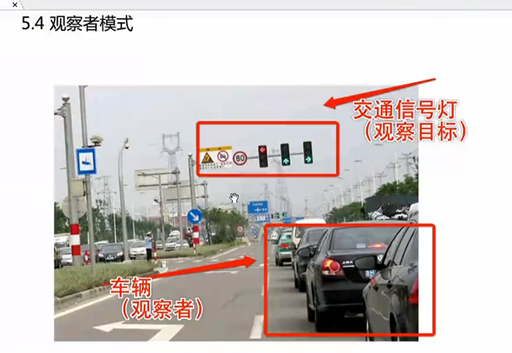
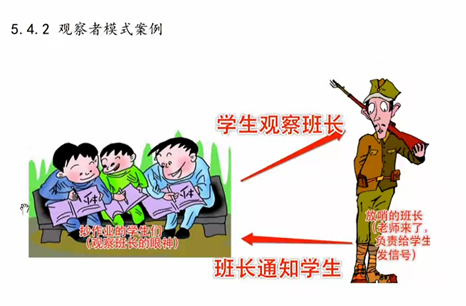
14 观察者模式
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
// 抽象的 订阅者
class Listener {
public:
// 纯虚函数
// 老师来了 该怎么办
virtual void onTeacherComing() = 0;
// 学生干坏事的方法
virtual void doBadThing() = 0;
};
// 抽象的 发布者
class Notifier
{
public:
// 添加观察者的方法
virtual void addListener(Listener * listner) = 0;
// 删除观察者的方法
virtual void delListener(Listener *listener) = 0;
// 通知所有观察者的方法
virtual void notify() = 0;
};
// 具体的订阅者
class Student : public Listener
{
public:
Student(string name, string badthing)
{
this->name = name;
this->badthing = badthing;
}
// 重写纯虚函数
virtual void onTeacherComing()
{
cout << " 学生" << name << "发现班长给我们释眼神了, 停止" << badthing << endl;
cout << " 改为写作业" << endl;
}
virtual void doBadThing()
{
cout << "学生" << name << "目前正在" << badthing << endl;
}
private:
string name;
string badthing;
};
// 具体的发布者
class Monitor : public Notifier
{
public:
// 添加订阅者的方法
virtual void addListener(Listener * listner)
{
this->l_list.push_back(listner);
}
// 删除订阅者的方法
virtual void delListener(Listener *listener)
{
this->l_list.remove(listener);
}
// 通知所有订阅者的方法
virtual void notify()
{
// 广播信息 让每一个订阅者都执行各自的重写的onTeacherComing方法
for (list <Listener *>::iterator it = l_list.begin();it!=l_list.end();it++) {
(*it)->onTeacherComing();
}
}
private:
list<Listener *> l_list; // 存放订阅者的容器
};
int main(void)
{
Listener *s1 = new Student("张三","抄作业");
Listener *s2 = new Student("李四", "打lol");
Listener *s3 = new Student("王五", "看李四玩lol");
// 发布者
Notifier *bossXu = new Monitor;
// 添加订阅者
bossXu->addListener(s1);
bossXu->addListener(s2);
bossXu->addListener(s3);
cout << "教室一片和谐,老师没有来" << endl;
s1->doBadThing();
s2->doBadThing();
s3->doBadThing();
cout << "班长突然发现老师来了,给学生们使了一个眼神" << endl;
// 广播消息
bossXu->notify();
system("pause");
return 0;
}