一.SpringMVC 简介
1.SpringMVC 中重要组件
1.1 DispatcherServlet : 前端控制器,接收所有请求(如果配置/不包含 jsp)
1.2 HandlerMapping: 解析请求格式的.判断希望要执行哪个具体的方法.
1.3 HandlerAdapter: 负责调用具体的方法.
1.4 ViewResovler:视图解析器.解析结果,准备跳转到具体的物理视图
2.SpringMVC 运行原理图
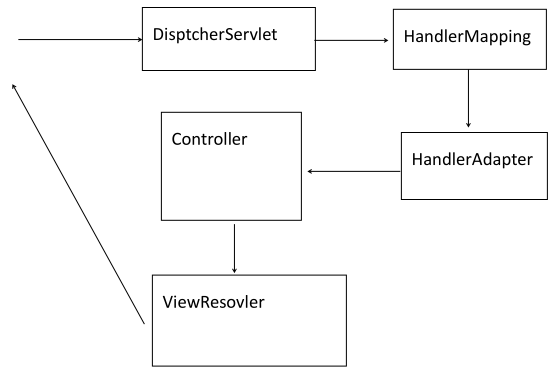
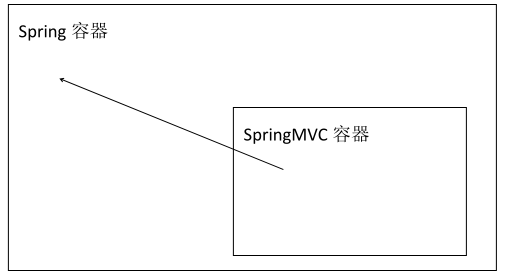
3.Spring 容器和 SpringMVC 容器的关系
3.1 代码

3.2 Spring 容器和 SpringMVC 容器是父子容器.
3.2.1 SpringMVC 容器中能够调用 Spring 容器的所有内容.
3.2.2 图示
二.SpringMVC 环境搭建
1. 导入 jar

2. 在 web.xml 中配置前端控制器 DispatcherServlet
2.1 如 果 不 配 置 <init-param> 会 在/WEB-INF/<servlet-name>-servlet.xml
<servlet> <servlet-name>jqk</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>jqk</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
3. 在 src 下新建 springmvc.xml
3.1 引入 xmlns:mvc 命名空间
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd"> <!-- 扫描注解 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.bjsxt.controller"></context:component-scan> <!-- 注解驱动 --> <!-- org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandler Mapping --> <!-- org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerA dapter --> <mvc:annotation-driven></mvc:annotation-driven> <!-- 静态资源 --> <mvc:resources location="/js/" mapping="/js/**"></mvc:resources> <mvc:resources location="/css/" mapping="/css/**"></mvc:resources> <mvc:resources location="/images/" mapping="/images/**"></mvc:resources> </beans>
4. 编写控制器类
@Controller public class DemoController { @RequestMapping("demo") public String demo(){ System.out.println("执行 demo"); return "main.jsp"; } @RequestMapping("demo2") public String demo2(){ System.out.println("demo2"); return "main1.jsp"; } }
三. 字符编码过滤器
1.在 web.xml 中配置 Filter
<!-- 字符编码过滤器 --> <filter> <filter-name>encoding</filter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class> <init-param> <param-name>encoding</param-name> <param-value>utf-8</param-value> </init-param> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>encoding</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping>
四.传参
1. 把内容写到方法(HandlerMethod)参数中,SpringMVC 只要有这个内容,注入内容.
2. 基本数据类型参数
2.1 默认保证参数名称和请求中传递的参数名相同
@Controller public class DemoController { @RequestMapping("demo") public String demo(String name,int age){ System.out.println("执行 demo"+" "+name+""+age); return "main.jsp"; } }
2.2 如果请求参数名和方法参数名不对应使用@RequestParam()赋值
@RequestMapping("demo")
public String demo(@RequestParam(value="name1") String name,@RequestParam(value="age1")int age){
System.out.println("执行 demo"+" "+name+""+age);
return "main.jsp";
}
2.3 如果方法参数是基本数据类型(不是封装类)可以通过@RequestParam 设置默认值.
2.3.1 防止没有参数时 500
@RequestMapping("page")
public String page(@RequestParam(defaultValue="2") int pageSize,@RequestParam(defaultValue="1") int pageNumber){
System.out.println(pageSize+" "+pageNumber);
return "main.jsp";
}
2.4 如果强制要求必须有某个参数
@RequestMapping("demo2")
public String demo2(@RequestParam(required=true) String name){
System.out.println("name 是 SQL 的查询条件,必须要传递 name 参数"+name);
return "main.jsp";
}
3. HandlerMethod 中参数是对象类型
3.1 请求参数名和对象中属性名对应(get/set 方法)
@RequestMapping("demo4")
public String demo4(People peo){
return "main.jsp";
}
4. 请求参数中包含多个同名参数的获取方式
4.1 复选框传递的参数就是多个同名参数
@RequestMapping("demo5")
public String demo5(String name,int age,@RequestParam("hover")List<String> abc){
System.out.println(name+" "+age+" "+abc);
return "main.jsp";
}
5. 请求参数中对象.属性格式
5.1 jsp 中代码
<input type="text" name="peo.name"/> <input type="text" name="peo.age"/>
5.2 新建一个类
5.2.1 对象名和参数中点前面名称对应
public class Demo {
private People peo;
5.3 控制器
@RequestMapping("demo6")
public String demo6(Demo demo){
System.out.println(demo);
return "main.jsp";
}
6. 在请求参数中传递集合对象类型参数
6.1 jsp 中格式
<input type="text" name="peo[0].name"/> <input type="text" name="peo[0].age"/> <input type="text" name="peo[1].name"/> <input type="text" name="peo[1].age"/>
6.2 新建类
public class Demo { private List<People> peo;
6.3 控制器
@RequestMapping("demo6")
public String demo6(Demo demo){
System.out.println(demo);
return "main.jsp";
}
7. restful 传值方式.
7.1 简化 jsp 中参数编写格式
7.2 在 jsp 中设定特定的格式
<a href="demo8/123/abc">跳转</a>
7.3 在控制器中
7.3.1 在@RequestMapping 中一定要和请求格式对应
7.3.2 {名称} 中名称自定义名称
7.3.3 @PathVariable 获取@RequestMapping 中内容,默认按照方法参数名称去寻找.
@RequestMapping("demo8/{id1}/{name}")
public String demo8(@PathVariable String name,@PathVariable("id1") int age){
System.out.println(name +" "+age);
return "/main.jsp";
}
五. 跳转方式
1. 默认跳转方式请求转发.
2. 设置返回值字符串内容
2.1 添加 redirect:资源路径 重定向
2.2 添加 forward:资源路径 或省略 forward: 转发
六. 视图解析器
1. SpringMVC 会提供默认视图解析器.
2. 程序员自定义视图解析器
<bean id="viewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"> <property name="prefix" value="/"></property> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp"></property> </bean>
3. 如果希望不执行自定义视图解析器,在方法返回值前面添加forward:或 redirect:
七.@ResponseBody
1. 在方法上只有@RequestMapping 时,无论方法返回值是什么认为需要跳转
2. 在方法上添加@ResponseBody(恒不跳转)
2.1 如果返回值满足 key-value 形式(对象或 map)
2.1.1 把响应头设置为 application/json;charset=utf-8
2.1.2 把转换后的内容输出流的形式响应给客户端.
2.2 如果返回值不满足 key-value,例如返回值为 String
2.2.1 把相应头设置为 text/html
2.2.2 把方法返回值以流的形式直接输出.
2.2.3 如果返回值包含中文,出现中文乱码
2.2.3.1 produces 表示响应头中 Content-Type 取值.
@RequestMapping(value="demo12",produces="text/html;charset=utf-8") @ResponseBody public String demo12() throws IOException{ People p = new People(); p.setAge(12); p.setName("张三"); return "中文"; }
3. 底层使用Jackson进行json转换,在项目中一定要导入jackson的jar
3.1 spring4.1.6 对 jackson 不支持较高版本,jackson 2.7 无效.
七.JSP 九大内置对象和四大作用域复习
1.九大内置对象
| 名称 | 类型 | 含义 | 获取方式 |
| request | HttpSevletRequest | 封装所有请求信息 | 方法参数 |
| response | HttpServletResponse |
封装所有响应信息 |
方法参数 |
| session | HttpSession | 封装所有会话信息 | req.getSession() |
| application | ServletContext | 所有信息 |
getServletContext(); request.getServletContext(); |
| out | PrintWriter | 输出对象 |
response.getWriter() |
| exception | Exception | 异常对象 | |
| page | Object | 当前页面对象 | |
| pageContext | PageContext | 获取其他对象 | |
| config | ServletConfig | 配置信息 |
2.四大作用域
2.1 page
2.1.1 在当前页面不会重新实例化.
2.2 request
2.2.1 在一次请求中同一个对象,下次请求重新实例化一个request 对象.
2.3 session
2.3.1 一次会话.
2.3.2 只要客户端 Cookie 中传递的 Jsessionid 不变,Session 不会重新实力会(不超过默认时间.)
2.3.3 实际有效时间:
2.3.3.1 浏览器关闭.Cookie 失效.
2.3.3.2 默认时间.在时间范围内无任何交互.在 tomcat 的web.xml 中配置
<session-config> <session-timeout>30</session-timeout> </session-config>
2.4 application
2.4.1 只有在 tomcat 启动项目时菜实例化.关闭 tomcat 时销毁application
八.SpringMVC 作用域传值的几种方式
1. 使用原生 Servlet
1.1 在 HanlderMethod 参数中添加作用域对象
@RequestMapping("demo1")
public String demo1(HttpServletRequest abc,HttpSession sessionParam){
//request 作用域
abc.setAttribute("req", "req 的值");
//session 作用域
HttpSession session = abc.getSession();
session.setAttribute("session", "session 的值");
sessionParam.setAttribute("sessionParam","sessionParam 的值");
//appliaction 作用域
ServletContext application = abc.getServletContext();
application.setAttribute("application","application 的值");
return "/index.jsp";
}
2. 使用 Map 集合
2.1 把 map 中内容放在 request 作用域中
2.2 spring 会对 map 集合通过 BindingAwareModelMap 进行实例化
@RequestMapping("demo2")
public String demo2(Map<String,Object> map){
System.out.println(map.getClass());
map.put("map","map 的值");
return "/index.jsp";
}
3. 使用 SpringMVC 中 Model 接口
3.1 把内容最终放入到 request 作用域中.
@RequestMapping("demo3")
public String demo3(Model model){
model.addAttribute("model", "model 的值");
return "/index.jsp";
}
4.使用 SpringMVC 中 ModelAndView 类
@RequestMapping("demo4")
public ModelAndView demo4(){
//参数,跳转视图
ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView("/index.jsp");
mav.addObject("mav", "mav 的值");
return mav;
}
九. 文件下载
1.访问资源时相应头如果没有设置 Content-Disposition,浏览器默认按照 inline 值进行处理
1.1 inline 能显示就显示,不能显示就下载.
2.只需要修改相应头中 Context-Disposition=”attachment;filename=文件名”
2.1 attachment 下载,以附件形式下载.
2.2 filename=值就是下载时显示的下载文件名
3.实现步骤
3.1 导入 apatch 的两个 jar
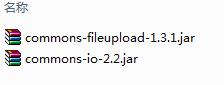
3.2 在 jsp 中添加超链接,设置要下载文件
3.2.1 在 springmvc 中放行静态资源 files 文件夹
<a href="download?fileName=a.rar">下载</a>
3.3 编写控制器方法
@RequestMapping("download")
public void download(String fileName,HttpServletResponse res,HttpServletRequest req) throws IOException{
//设置响应流中文件进行下载
res.setHeader("Content-Disposition","attachment;filename="+fileName);
//把二进制流放入到响应体中.
ServletOutputStream os = res.getOutputStream();
String path =req.getServletContext().getRealPath("files");
System.out.println(path);
File file = new File(path, fileName);
byte[] bytes =FileUtils.readFileToByteArray(file);
os.write(bytes);
os.flush();
os.close();
}
十. 文件上传
1. 基于 apache 的 commons-fileupload.jar 完成文件上传.
2. MultipartResovler 作用:
2.1 把客户端上传的文件流转换成 MutipartFile 封装类.
2.2 通过 MutipartFile 封装类获取到文件流
3. 表单数据类型分类
3.1 在<form>的 enctype 属性控制表单类型
3.2 默认值 application/x-www-form-urlencoded,普通表单数据.(少量文字信息)
3.3 text/plain 大文字量时使用的类型.邮件,论文
3.4 multipart/form-data 表单中包含二进制文件内容.
4. 实现步骤:
4.1 导入 springmvc 包和 apache 文件上传 commons-fileupload 和commons-io 两个 jar
4.2 编写 JSP 页面
<form action="upload" enctype="multipart/form-data" method="post"> 姓名:<input type="text" name="name"/><br/> 文件:<input type="file" name="file"/><br/> <input type="submit" value=" 提交 "/> </form>
4.3 配置 springmvc.xml
<!-- MultipartResovler 解析器 --> <bean id="multipartResolver" class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver"> <property name="maxUploadSize" value="50"></property> </bean> <!-- 异常解析器 --> <bean id="exceptionResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleMappingExceptionResolver"> <property name="exceptionMappings"> <props> <prop key="org.springframework.web.multipart.MaxUploadSizeExceededException">/error.jsp</prop> </props> </property> </bean>
4.4 编写控制器类
4.4.1 MultipartFile 对象名必须和<input type=”file”/>的 name 属性值相同
@RequestMapping("upload")
public String upload(MultipartFile file,String name) throws IOException{
String fileName = file.getOriginalFilename();
String suffix =fileName.substring(fileName.lastIndexOf("."));
//判断上传文件类型
if(suffix.equalsIgnoreCase(".png")){
String uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
FileUtils.copyInputStreamToFile(file.getInputStream(), new File("E:/"+uuid+suffix));
return "/index.jsp";
}else{
return "error.jsp";
}
}
十一. 自定义拦截器
1.跟过滤器比较像的技术.
2.发送 请求时被拦截器拦截,在控制器的前后添加额外功能.
2.1 跟 AOP 区分开.AOP 在特定方法前后扩充(对 ServiceImpl)
2.2 拦截器,请求的拦截.针对点是控制器方法.(对 Controller)
3.SpringMVC 拦截器和 Filter 的区别
3.1 拦截器只能拦截器 Controller
3.2 Filter 可以拦截任何请求.
4.实现自定义拦截器的步骤:
4.1 新建类实现 HandlerInterceptor
public class DemoInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor { //在进入控制器之前执行 //如果返回值为 false,阻止进入控制器 //控制代码 @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest arg0,HttpServletResponse arg1, Object arg2) throws Exception { System.out.println("arg2:"+arg2); System.out.println("preHandle"); return true; } //控制器执行完成,进入到 jsp 之前执行. //日志记录. //敏感词语过滤 @Override public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest arg0,HttpServletResponse arg1, Object arg2, ModelAndView arg3) throws Exception { System.out.println("往"+arg3.getViewName()+"跳转"); System.out.println("model 的值"+arg3.getModel().get("model")); String word =arg3.getModel().get("model").toString(); String newWord = word.replace("祖国", "**"); arg3.getModel().put("model", newWord); // arg3.getModel().put("model", "修改后的内容"); System.out.println("postHandle"); } //jsp 执行完成后执行 //记录执行过程中出现的异常. //可以把异常记录到日志中 @Override public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest arg0,HttpServletResponse arg1, Object arg2, Exception arg3) throws Exception { System.out.println("afterCompletion"+arg3.getMessage()); } }
4.2 在 springmvc.xml 配置拦截器需要拦截哪些控制器
4.2.1 拦截所有控制器
<mvc:interceptors> <bean class="com.bjsxt.interceptor.DemoInterceptor"></bean> </mvc:interceptors>
4.2.2 拦截特定的的 url
<mvc:interceptors> <mvc:interceptor> <mvc:mapping path="/demo"/> <mvc:mapping path="/demo1"/> <mvc:mapping path="/demo2"/> <bean class="com.bjsxt.interceptor.DemoInterceptor"></bean> </mvc:interceptor> </mvc:interceptors>
十二. 拦截器栈
1. 多个拦截器同时生效时,组成了拦截器栈
2. 顺序:先进后出.
3. 执行顺序和在 springmvc.xml 中配置顺序有关
4. 设置先配置拦截器 A 在配置拦截器 B 执行顺序为
preHandle(A) --> preHandle(B) --> 控制器方法 --> postHandle(B)
--> postHanle(A) --> JSP --> afterCompletion(B) --> afterCompletion(A)
十三.SpringMVC 运行原理
1. 文字解释
如果在 web.xml 中设置 DispatcherServlet 的<url-pattern>为/时,当用户发 起 请 求 , 请 求 一 个 控 制 器 , 首 先 会 执 行 DispatcherServlet. 由
DispatcherServlet 调 用 HandlerMapping 的DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping 解 析 URL, 解 析 后 调 用HandlerAdatper 组 件 的 AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter 调 用
Controller 中的 HandlerMethod.当 HandlerMethod 执行完成后会返回View,会被 ViewResovler 进行视图解析,解析后调用 jsp 对应的.class 文件并运行,最终把运行.class 文件的结果响应给客户端.以上就是 springmvc 运行原理