//本次的作业为
/******************************************************* * Finds and prints n prime integers * Jeff Offutt, Spring 2003 ******************************************************/ public static void printPrimes (int n) { int curPrime; // Value currently considered for primeness int numPrimes; // Number of primes found so far. boolean isPrime; // Is curPrime prime? int [] primes = new int [MAXPRIMES]; // The list of prime numbers. // Initialize 2 into the list of primes. primes [0] = 2; numPrimes = 1; curPrime = 2; while (numPrimes < n) { curPrime++; // next number to consider ... isPrime = true; for (int i = 0; i <= numPrimes-1; i++) { // for each previous prime. if (curPrime%primes[i]==0) { // Found a divisor, curPrime is not prime. isPrime = false; break; // out of loop through primes. } } if (isPrime) { // save it! primes[numPrimes] = curPrime; numPrimes++; } } // End while // Print all the primes out. for (int i = 0; i <= numPrimes-1; i++) { System.out.println ("Prime: " + primes[i]); } } // end printPrimes
一、画出控制流图
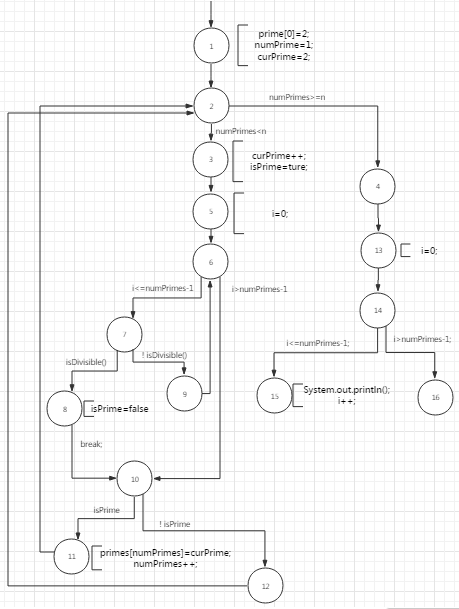
二、设计一个t2=(n=5)比t1=(n=3)容易发现发现的错误
数组越界的错误。
三、写一个测试用例,使相应的测试路径访问连接while语句开始到fot语句得边,而不用通过while的循环体
t:n=1
四、例举每个节点覆盖,边覆盖和主路径覆盖的TR
节点覆盖需求:{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16}
边覆盖需求:{(1,2),(2,3),(3,5),(5,6),(6,7),(7,8),(7,9),(9,6),(8,10),(6,10),(10,11),(10,12),(11,2),(12,2),(2,4),(4,13),(13,14),(14,15),(14,16)}
主路径覆盖需求:
{(1,2,3,4,5,6,7),
(1,2,3,4,5,6,8,9,10,11),
(1,2,3,4,5,6,8,9,11),
(1,2,3,4,5,9,10,11),
(1,2,3,4,5,9,11),
(1,2,12,13,14,15),
(1,2,12,16),
(3,4,5,6,8,9,10,11,2,12,13,14,15),
(3,4,5,6,8,9,11,2,12,13,14,15),
(3,4,5,6,8,9,10,11,2,12,13,16),
(3,4,5,6,8,9,11,2,12,13,16),
(3,4,5,9,10,11,2,12,13,14,15),
(3,4,5,9,11,2,12,13,14,15),
(3,4,5,9,10,11,2,12,13,16),
(3,4,5,9,11,2,12,13,16),
(6,7,5,9,10,11,2,12,13,14,15),
(6,7,5,9,11,2,12,13,14,15),
(6,7,5,9,10,11,2,12,13,16),
(6,7,5,9,11,2,12,13,16),
(14,15,13,16),
(13,14,15,13),
(5,6,7,5),
(2,3,4,5,6,8,9,10,11,2),
(2,3,4,5,6,8,9,11,2),
(2,3,4,5,9,10,11,2),
(2,3,4,5,9,11,2),
}
五、实现一个主路径覆盖的测试
package example; /** * Created by Ev_Eraser on 2016/3/18. */ public class Myclass { public String triangle(int a,int b,int c) { if(a + b < c || a + c < b || b+ c < a) return "notTriangle"; if(a == b && b == c) return "isosceles"; if(a == b || b == c || a == c) return "equilateral"; else return "scalene"; } }
测试类用例:
package example; import org.junit.After; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.junit.runners.Parameterized; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collection; import static org.junit.Assert.*; @RunWith(Parameterized.class) public class MyclassTest { private Myclass myClass; private int input1; private int input2; private int input3; private String expected; public MyclassTest(int input1, int input2,int input3,String expected){ this.input1 = input1; this.input2 = input2; this.input3 = input3; this.expected = expected; } @Before public void setUp() throws Exception { myClass = new Myclass(); } @Parameterized.Parameters public static Collection<Object[]> getData(){ return Arrays.asList(new Object[][]{ {2,2,2,"isosceles"}, {2,2,3,"equilateral"}, {2,4,3,"scalene"}, {2,9,2,"notTriangle"} }); } // @After // public void tearDown() throws Exception { // // } @Test public void testTriangle() throws Exception { assertEquals(this.expected, myClass.triangle(input1,input2,input3)); } }
