1. 引言
有向无环图(Directed Acyclic Graph, DAG)是有向图的一种,字面意思的理解就是图中没有环。常常被用来表示事件之间的驱动依赖关系,管理任务之间的调度。拓扑排序是对DAG的顶点进行排序,使得对每一条有向边(u, v),均有u(在排序记录中)比v先出现。亦可理解为对某点v而言,只有当v的所有源点均出现了,v才能出现。
下图给出有向无环图的拓扑排序:
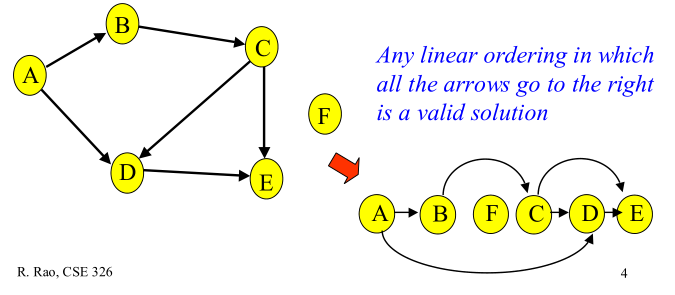
下图给出的顶点排序不是拓扑排序,因为顶点D的邻接点E比其先出现:

2. 算法原理与实现
拓扑排序的实现算法有两种:入度表、DFS,其时间复杂度均为(O(V+E))。
入度表
对于DAG的拓扑排序,显而易见的办法:
- 找出图中0入度的顶点;
- 依次在图中删除这些顶点,删除后再找出0入度的顶点;
- 然后再删除……再找出……
- 直至删除所有顶点,即完成拓扑排序
为了保存0入度的顶点,我们采用数据结构栈(亦可用队列);算法的可视化可参看这里。
图用邻接表(adjacency list)表示,用数组inDegreeArray[]记录结点的入度变化情况。C实现:
// get in-degree array
int *getInDegree(Graph *g) {
int *inDegreeArray = (int *) malloc(g->V * sizeof(int));
memset(inDegreeArray, 0, g->V * sizeof(int));
int i;
AdjListNode *pCrawl;
for(i = 0; i < g->V; i++) {
pCrawl = g->array[i].head;
while(pCrawl) {
inDegreeArray[pCrawl->dest]++;
pCrawl = pCrawl->next;
}
}
return inDegreeArray;
}
// topological sort function
void topologicalSort(Graph *g) {
int *inDegreeArray = getInDegree(g);
Stack *zeroInDegree = initStack();
int i;
for(i = 0; i < g->V; i++) {
if(inDegreeArray[i] == 0)
push(i, zeroInDegree);
}
printf("topological sorted order
");
AdjListNode *pCrawl;
while(!isEmpty(zeroInDegree)) {
i = pop(zeroInDegree);
printf("vertex %d
", i);
pCrawl = g->array[i].head;
while(pCrawl) {
inDegreeArray[pCrawl->dest]--;
if(inDegreeArray[pCrawl->dest] == 0)
push(pCrawl->dest, zeroInDegree);
pCrawl = pCrawl->next;
}
}
}
时间复杂度:得到inDegreeArray[]数组的复杂度为(O(V+E));顶点进栈出栈,其复杂度为(O(V));删除顶点后将邻接点的入度减1,其复杂度为(O(E));整个算法的复杂度为(O(V+E))。
DFS
在DFS中,依次打印所遍历到的顶点;而在拓扑排序时,顶点必须比其邻接点先出现。在下图中,顶点5比顶点0先出现,顶点4比顶点1先出现。
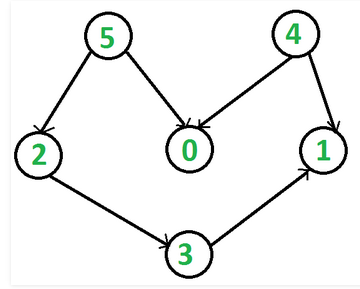
在DFS实现拓扑排序时,用栈来保存拓扑排序的顶点序列;并且保证在某顶点入栈前,其所有邻接点已入栈。DFS版拓扑排序的可视化参看这里。
C实现:
/* recursive DFS function to traverse the graph,
* the graph is represented by adjacency list
*/
void dfs(int u, Graph *g, int *visit, Stack *s) {
visit[u] = 1;
AdjListNode *pCrawl = g->array[u].head;
while(pCrawl) {
if(!visit[pCrawl->dest])
dfs(pCrawl->dest, g, visit, s);
pCrawl = pCrawl->next;
}
push(u, s);
}
// the topological sort function
void topologicalSort(Graph *g) {
int *visit = (int *) malloc(g->V * sizeof(int));
memset(visit, 0, g->V * sizeof(int));
Stack *s = initStack();
int i;
for(i = 0; i < g->V; i++) {
if(!visit[i]) dfs(i, g, visit, s);
}
// the order of stack element is the sorted order
while(!isEmpty(s)) {
printf("vertex %d
", pop(s));
}
}
时间复杂度:应与DFS相同,为(O(V+E))。
完整代码在Github。
3. 参考资料
[1] R. Rao, Lecture 20: Topo-Sort and Dijkstra’s Greedy Idea.
[2] GeeksforGeeks, Topological Sorting.
[3] GeeksforGeeks, Graph and its representations.