Bootstrap#start()
daemon = bootstrap, 所以调用的还是 org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap#start()
public void start() throws Exception { if (catalinaDaemon == null) { init(); } Method method = catalinaDaemon.getClass().getMethod("start", (Class[]) null); // 反射调用 Catalina#start() method.invoke(catalinaDaemon, (Object[]) null); }
反射调用了 Catalina#start() 方法, 进行启动工作.
Catalina#start()
public void start() { if (getServer() == null) { load(); } if (getServer() == null) { log.fatal("Cannot start server. Server instance is not configured."); return; } //获取当前纳秒值 long t1 = System.nanoTime(); // Start the new server try { //StandardServer#start(), 最终调用的是 StandardServer#startInternal() getServer().start(); } catch (LifecycleException e) { log.fatal(sm.getString("catalina.serverStartFail"), e); try { getServer().destroy(); } catch (LifecycleException e1) { log.debug("destroy() failed for failed Server ", e1); } return; } //再次获取当前纳秒值, 计算启动花了多长时间 long t2 = System.nanoTime(); if(log.isInfoEnabled()) { log.info("Server startup in " + ((t2 - t1) / 1000000) + " ms"); } // Register shutdown hook // 注册回调方法, 用于安全关闭服务 if (useShutdownHook) { if (shutdownHook == null) { shutdownHook = new CatalinaShutdownHook(); } Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(shutdownHook); // If JULI is being used, disable JULI's shutdown hook since // shutdown hooks run in parallel and log messages may be lost // if JULI's hook completes before the CatalinaShutdownHook() LogManager logManager = LogManager.getLogManager(); if (logManager instanceof ClassLoaderLogManager) { ((ClassLoaderLogManager) logManager).setUseShutdownHook( false); } } // Bootstrap中会设置await为true,其目的在于让tomcat在shutdown端口阻塞监听关闭命令 if (await) { await(); stop(); } }
这里继续调用了 Server 的 start 方法. 实际调用的是 org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase#start(),
然后此方法中调用了抽象方法 startInternal(), 也就是 StandardServer#startInternal()
StandardServer#startInternal()
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException { // 事件通知 CONFIGURE_START_EVENT -> configure_start fireLifecycleEvent(CONFIGURE_START_EVENT, null); // 修改tomcat状态为 STARTING, 这一步也会进行事件通知 START_EVENT -> start setState(LifecycleState.STARTING); //NamingResourcesImpl#startInternal() 全局资源 //在server.xml中配置了该变量, pathname="conf/tomcat-users.xml" globalNamingResources.start(); // Start our defined Services synchronized (servicesLock) { for (Service service : services) { // StandardService.startInternal() service.start(); } } }
service.start() 最终调用的是 StandardService.startInternal()
StandardService.startInternal()
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException { if(log.isInfoEnabled()) log.info(sm.getString("standardService.start.name", this.name)); setState(LifecycleState.STARTING); // Start our defined Container first if (engine != null) { synchronized (engine) { //StandardEngine#start() 最终调用 StandardEngine#startInternal() //这一句代码, 就将 Host, Context, Wrapper 的 start 执行到了 //host是通过 server.xml 解析得到 //context是通过扫描文件的方式解析得到, 有三种方式: xml配置方式, war包方式, 文件夹方式 //wrapper也是通过扫描jar包的方式得到 engine.start(); } } // 启动Executor线程池, 默认情况下, 是空, 通过修改 server.xml中的tomcatThreadPool来改变 synchronized (executors) { for (Executor executor: executors) { executor.start(); } } // 启动 MapperListener, 进行注册功能 // 最终会调用 MapperListener#startInternal() 方法 //* 这个方法主要干了两件事情 //* 1. 将 MapperListener 注册到容器和子容器(Host, Context, Wrapper)的 listeners 和 lifecycleListeners 中 //* 2. 注册 host, context, wrapper mapperListener.start(); // Start our defined Connectors second synchronized (connectorsLock) { for (Connector connector: connectors) { try { // If it has already failed, don't try and start it if (connector.getState() != LifecycleState.FAILED) { //最终调用 Connector.startInternal() connector.start(); } } catch (Exception e) { log.error(sm.getString( "standardService.connector.startFailed", connector), e); } } } }
这里和初始化的时候很像, 初始化的时候, 是对他们分别初始化, 而这里, 是对他们分别启动
1. engine.start() : 启动 engine, 里面会启动 Host, Context, Wrapper. 最终会调用 StandardEngine#startInternal()
2. executor.start() : 启动线程池, 默认情况下, 这个线程池为空.
3. mapperListener.start() : 将MapperListener注册到 Host,Context,Wrapper 的监听器中, 然后对 Host, Context, Wrapper 进行映射
4. connector.start() : 启动连接器
StandardEngine#startInternal()
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException { // Log our server identification information if(log.isInfoEnabled()) log.info( "Starting Servlet Engine: " + ServerInfo.getServerInfo()); // Standard container startup //通过解析 server.xml 文件, 可以拿到 engine下面有一个 host, 也就是说, StandardEngine.children有一个host super.startInternal(); }
super.startInternal() 调用的是父类 org.apache.catalina.core.ContainerBase#startInternal() 方法:
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException { // Start our subordinate components, if any logger = null; getLogger(); //集群客户端 Cluster cluster = getClusterInternal(); if (cluster instanceof Lifecycle) { //如果有集群的话, 则会启动集群 ((Lifecycle) cluster).start(); } //域 Realm realm = getRealmInternal(); if (realm instanceof Lifecycle) { ((Lifecycle) realm).start(); } // Start our child containers, if any // 把子容器的启动步骤放在线程中处理,默认情况下线程池只有一个线程处理任务队列 //StandardEngine 调用的时候, 这里拿到的 children 有一个值: StandardHost[localhost] // <Engine name="Catalina" defaultHost="localhost"> // <Host name="localhost" appBase="webapps" unpackWARs="true" autoDeploy="true" startStopThreads="1"> // </engine> Container children[] = findChildren(); List<Future<Void>> results = new ArrayList<>(); for (Container child : children) { //StartChild 的 call方法, 调用的是 child.start() 方法, 最终会调用 StandardHost.startInternal results.add(startStopExecutor.submit(new StartChild(child))); } MultiThrowable multiThrowable = null; // 阻塞当前线程,直到子容器start完成 for (Future<Void> result : results) { try { result.get(); } catch (Throwable e) { log.error(sm.getString("containerBase.threadedStartFailed"), e); if (multiThrowable == null) { multiThrowable = new MultiThrowable(); } multiThrowable.add(e); } } if (multiThrowable != null) { throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("containerBase.threadedStartFailed"), multiThrowable.getThrowable()); } // Start the Valves in our pipeline (including the basic), if any // 启用 Pipeline --> StandardPipeline#startInternal() if (pipeline instanceof Lifecycle) { ((Lifecycle) pipeline).start(); } //StandardHost调用时, 激发 STARTING 监听器 HostConfig,最终会调用 HostConfig#start() 方法 - 这一步很关键 setState(LifecycleState.STARTING); // Start our thread // 开启ContainerBackgroundProcessor线程用于调用子容器的backgroundProcess方法, // 默认情况下backgroundProcessorDelay=-1,不会启用该线程 threadStart(); }
1. 通过Future框架异步调用 StandardHost#startInternal() 方法, 并阻塞等待所有当前 engine 下所有的 Host 启动完成
2. setState() 时, 会激发监听器 HostConfig. 这个HostConfig 是在 解析 Server.xml 的时候, 创建并绑定的.
StandardHost#startInternal()
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException { // Set error report valve // errorValve默认使用 ErrorReportValve String errorValve = getErrorReportValveClass(); if ((errorValve != null) && (!errorValve.equals(""))) { try { boolean found = false; // 如果所有的阀门中已经存在这个实例,则不进行处理,否则添加到 Pipeline 中 Valve[] valves = getPipeline().getValves(); for (Valve valve : valves) { if (errorValve.equals(valve.getClass().getName())) { found = true; break; } } // 如果未找到则添加到 Pipeline 中,注意是添加到 basic valve 的前面 // 默认情况下,first valve 是 AccessLogValve,basic 是 StandardHostValve if(!found) { Valve valve = (Valve) Class.forName(errorValve).getConstructor().newInstance(); getPipeline().addValve(valve); } } catch (Throwable t) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t); log.error(sm.getString( "standardHost.invalidErrorReportValveClass", errorValve), t); } } // 调用父类 ContainerBase,完成统一的启动动作 super.startInternal(); }
这里的 startInternal() 就是上面的 org.apache.catalina.core.ContainerBase#startInternal() 方法.
但是此时, host 的 children 是空的, 所以里面并没有能够调用 StandardContext#startInternal()
HostConfig#lifecycleEvent()
HostConfig 实现了 LifecycleListener 接口. 所以实际上, 他是一个监听器.
setState() 的时候, 会激发 HostConfig的监听器方法 lifecycleEvent(),
public void lifecycleEvent(LifecycleEvent event) { // Identify the host we are associated with try { host = (Host) event.getLifecycle(); if (host instanceof StandardHost) { setCopyXML(((StandardHost) host).isCopyXML()); setDeployXML(((StandardHost) host).isDeployXML()); setUnpackWARs(((StandardHost) host).isUnpackWARs()); setContextClass(((StandardHost) host).getContextClass()); } } catch (ClassCastException e) { log.error(sm.getString("hostConfig.cce", event.getLifecycle()), e); return; } // Process the event that has occurred //判断事件是否由 Host 发出,并且为 HostConfig 设置属性 if (event.getType().equals(Lifecycle.PERIODIC_EVENT)) { check(); } else if (event.getType().equals(Lifecycle.BEFORE_START_EVENT)) { beforeStart(); } else if (event.getType().equals(Lifecycle.START_EVENT)) { start(); } else if (event.getType().equals(Lifecycle.STOP_EVENT)) { stop(); } }
根据当前事件的状态, 会调用这里的 start() 方法. 此start 方法中, 会执行 部署 webapp 的方法 : org.apache.catalina.startup.HostConfig#deployApps()
protected void deployApps() { File appBase = host.getAppBaseFile(); File configBase = host.getConfigBaseFile(); // 过滤出 webapp 要部署应用的目录 String[] filteredAppPaths = filterAppPaths(appBase.list()); // Deploy XML descriptors from configBase // 1. xml部署 - 不推荐这么使用 // <host><context docBase="D://abc/eee" path="sdm" reloadable="true"></context></host> // 部署 xml 描述文件 deployDescriptors(configBase, configBase.list()); // Deploy WARs // 2. war包部署 // 解压 war 包,但是这里还不会去启动应用 deployWARs(appBase, filteredAppPaths); // Deploy expanded folders // 3. 目录部署 // 处理已经存在的目录,前面解压的 war 包不会再行处理 deployDirectories(appBase, filteredAppPaths); }
源码里面放的几个 Context , 都是目录结构的, 所以会走 deployDirectories() 方法
protected void deployDirectories(File appBase, String[] files) { if (files == null) return; ExecutorService es = host.getStartStopExecutor(); List<Future<?>> results = new ArrayList<>(); for (String file : files) { if (file.equalsIgnoreCase("META-INF")) continue; if (file.equalsIgnoreCase("WEB-INF")) continue; File dir = new File(appBase, file); if (dir.isDirectory()) { ContextName cn = new ContextName(file, false); if (isServiced(cn.getName()) || deploymentExists(cn.getName())) continue; results.add(es.submit(new DeployDirectory(this, cn, dir))); } } for (Future<?> result : results) { try { result.get(); } catch (Exception e) { log.error(sm.getString( "hostConfig.deployDir.threaded.error"), e); } } }
1. 通过调试, 能看到:
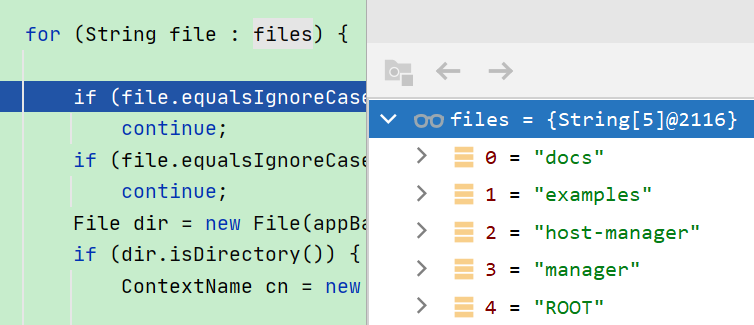
这里的每一个文件夹, 转换之后, 就是一个 Context .
2. 这里又出现了 Future . 这次提交的是 DeployDirectory, 是 HostConfig 的一个内部类. 看一下他的 run 方法:
private static class DeployDirectory implements Runnable { private HostConfig config; private ContextName cn; private File dir; public DeployDirectory(HostConfig config, ContextName cn, File dir) { this.config = config; this.cn = cn; this.dir = dir; } @Override public void run() { config.deployDirectory(cn, dir); } }
实际调用的, 还是 HostConfig 的方法:
protected void deployDirectory(ContextName cn, File dir) { long startTime = 0; // Deploy the application in this directory if( log.isInfoEnabled() ) { startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); log.info(sm.getString("hostConfig.deployDir", dir.getAbsolutePath())); } Context context = null; File xml = new File(dir, Constants.ApplicationContextXml); File xmlCopy = new File(host.getConfigBaseFile(), cn.getBaseName() + ".xml"); DeployedApplication deployedApp; boolean copyThisXml = isCopyXML(); boolean deployThisXML = isDeployThisXML(dir, cn); try { if (deployThisXML && xml.exists()) { synchronized (digesterLock) { try { //StandardContext context = (Context) digester.parse(xml); } catch (Exception e) { ...... } finally { digester.reset(); if (context == null) { context = new FailedContext(); } } } if (copyThisXml == false && context instanceof StandardContext) { // Host is using default value. Context may override it. copyThisXml = ((StandardContext) context).getCopyXML(); } if (copyThisXml) { Files.copy(xml.toPath(), xmlCopy.toPath()); context.setConfigFile(xmlCopy.toURI().toURL()); } else { context.setConfigFile(xml.toURI().toURL()); } } else if (!deployThisXML && xml.exists()) { // Block deployment as META-INF/context.xml may contain security // configuration necessary for a secure deployment. log.error(sm.getString("hostConfig.deployDescriptor.blocked", cn.getPath(), xml, xmlCopy)); context = new FailedContext(); } else { context = (Context) Class.forName(contextClass).getConstructor().newInstance(); } // 实例化 ContextConfig,作为 LifecycleListener 添加到 Context 容器中,这和 StandardHost 的套路一样,都是使用 XXXConfig Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(host.getConfigClass()); LifecycleListener listener = (LifecycleListener) clazz.getConstructor().newInstance(); context.addLifecycleListener(listener); context.setName(cn.getName()); context.setPath(cn.getPath()); context.setWebappVersion(cn.getVersion()); context.setDocBase(cn.getBaseName()); // 实例化 StandardContext 之后,为 Host 添加子节点 // 这里调用的是 StandardHost#addChild() host.addChild(context); } catch (Throwable t) { ...... } finally { ...... } ...... }
这里出现了 host.addChild(context) 方法, 需要回到 StandardHost 类中去看
//org.apache.catalina.core.StandardHost#addChild public void addChild(Container child) { if (!(child instanceof Context)) throw new IllegalArgumentException (sm.getString("standardHost.notContext")); //加入一个监听器 child.addLifecycleListener(new MemoryLeakTrackingListener()); // Avoid NPE for case where Context is defined in server.xml with only a // docBase Context context = (Context) child; if (context.getPath() == null) { ContextName cn = new ContextName(context.getDocBase(), true); context.setPath(cn.getPath()); } super.addChild(child); }
接着看父类中的 addChild()
//org.apache.catalina.core.ContainerBase#addChild public void addChild(Container child) { if (Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED) { PrivilegedAction<Void> dp = new PrivilegedAddChild(child); AccessController.doPrivileged(dp); } else { addChildInternal(child); } } private void addChildInternal(Container child) { if( log.isDebugEnabled() ) log.debug("Add child " + child + " " + this); synchronized(children) { if (children.get(child.getName()) != null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("addChild: Child name '" + child.getName() + "' is not unique"); child.setParent(this); // May throw IAE children.put(child.getName(), child); } // Start child // Don't do this inside sync block - start can be a slow process and // locking the children object can cause problems elsewhere try { if ((getState().isAvailable() || LifecycleState.STARTING_PREP.equals(getState())) && startChildren) { //addChild的时候, 调用启动方法, 解析Server.xml时, 不会进此方法 //StandardHost的时候, 会进此方法, 调用的是 StandardContext.start() -> StandardContext.startInternal() //StandardContext的时候, 会进此方法, 调用的是 StandardWrapper.start() -> StandardWrapper.startInternal() child.start(); } } catch (LifecycleException e) { log.error("ContainerBase.addChild: start: ", e); throw new IllegalStateException("ContainerBase.addChild: start: " + e); } finally { fireContainerEvent(ADD_CHILD_EVENT, child); } }
此时 child 是 StandardContext. 所以会调用
org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase#start() :
public final synchronized void start() throws LifecycleException { if (LifecycleState.STARTING_PREP.equals(state) || LifecycleState.STARTING.equals(state) || LifecycleState.STARTED.equals(state)) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { Exception e = new LifecycleException(); log.debug(sm.getString("lifecycleBase.alreadyStarted", toString()), e); } else if (log.isInfoEnabled()) { log.info(sm.getString("lifecycleBase.alreadyStarted", toString())); } return; } if (state.equals(LifecycleState.NEW)) { //results.add(startStopExecutor.submit(new StartChild(child))); //异步执行 StandardHost.start() 方法时, 会走这里 init(); } else if (state.equals(LifecycleState.FAILED)) { stop(); } else if (!state.equals(LifecycleState.INITIALIZED) && !state.equals(LifecycleState.STOPPED)) { invalidTransition(Lifecycle.BEFORE_START_EVENT); } try { setStateInternal(LifecycleState.STARTING_PREP, null, false); startInternal(); if (state.equals(LifecycleState.FAILED)) { // This is a 'controlled' failure. The component put itself into the // FAILED state so call stop() to complete the clean-up. stop(); } else if (!state.equals(LifecycleState.STARTING)) { // Shouldn't be necessary but acts as a check that sub-classes are // doing what they are supposed to. invalidTransition(Lifecycle.AFTER_START_EVENT); } else { setStateInternal(LifecycleState.STARTED, null, false); } } catch (Throwable t) { // This is an 'uncontrolled' failure so put the component into the // FAILED state and throw an exception. handleSubClassException(t, "lifecycleBase.startFail", toString()); } }
StandardContext 就是在这个方法中进行初始化, 以及启动的.