demo和 springIOC - ConfigurationClassPostProcessor - full / lite 里面是同一个.
暂且先不管 full , lite 有什么作用, 也不管spring是如何做到的, 如果是自己做, 怎么可以实现那种效果.
demo:
public class Parent { public IndexDao1 indexDao1() { System.out.println("parent indexDao1"); return new IndexDao1(); } public IndexDao2 indexDao2() { System.out.println("parent indexDao2"); indexDao1(); return new IndexDao2(); } }
这里, 我有两个方法 indexDao1 和 indexDao2, 方法indexDao2中调用了 indexDao1方法. 现在这种情况, 会导致 IndexDao1 被创建两次.
那么通过什么办法, 可以让 IndexDao1 只创建一次呢?
方法一:
再写一个类Son, 来继承 Parent 类, 然后通过 重写他的 indexDao1 和 indexDao2 方法来改变他们的行为.
同时, 我还需要引入一个map, 来存储创建的对象. 在执行方法之前, 先从map中获取
-> 获取到了, 则直接返回这个对象
-> 没获取到, 则执行父类中的方法, 来获取对象, 存入 map 中.
public class Son extends Parent { Map<String , Object> map = new HashMap<>(); @Override public IndexDao1 indexDao1() { System.out.println("son indexDao1"); if(map.get("indexDao1") != null){ return (IndexDao1) map.get("indexDao1"); } IndexDao1 indexDao1 = super.indexDao1(); map.put("indexDao1", indexDao1); return indexDao1; } @Override public IndexDao2 indexDao2() { System.out.println("son indexDao2"); //Parent中, 执行的 indexDao1() 已经被 Son 重写, 所以会执行 Son 中的 indexDao1() if(map.get("indexDao2") != null){ return (IndexDao2) map.get("indexDao2"); } IndexDao2 indexDao2 = super.indexDao2(); map.put("indexDao2", indexDao2); return indexDao2; } }
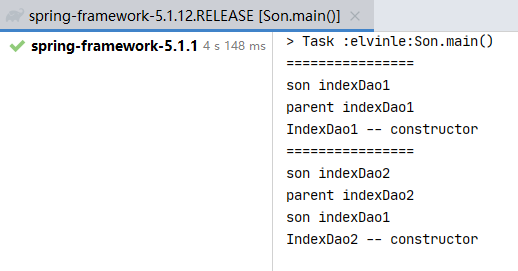
测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) { printf(); Son son = new Son(); son.indexDao1(); printf(); son.indexDao2(); } private static void printf(){ System.out.println("================"); }
结果:
方法二:
通过cglib代理的方式, 来创建一个继承Parent的类也是可以达到效果的.
public class ParentMethodInceptor implements MethodInterceptor { Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); @Override public Object intercept(Object obj, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable { System.out.println("proxy --- " + method.getName()); if (map.get(method.getName()) != null) { return map.get(method.getName()); } Object res = methodProxy.invokeSuper(obj, args); map.put(method.getName(), res); return res; } }
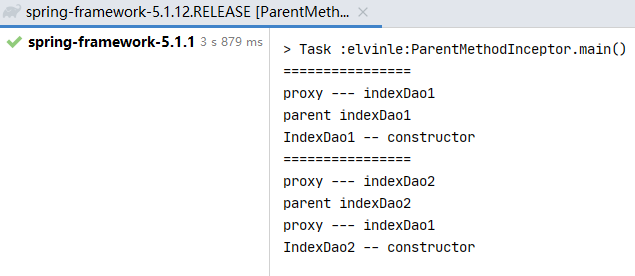
测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) { Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer(); enhancer.setSuperclass(Parent.class); enhancer.setCallback(new ParentMethodInceptor()); Parent proxy = (Parent) enhancer.create(); printf(); proxy.indexDao1(); printf(); proxy.indexDao2(); } private static void printf(){ System.out.println("================"); }
结果:
如果 Parent 类中的 indexDao1 变成一个静态方法: public static IndexDao1 indexDao1{}
那么不管是方法一,还是方法二, 都是不能实现只创建一次的效果.
方法一 中, 不能对静态方法进行重写覆盖
方法二 中, 不能对静态方法进行代理
不过, 我测试过 spring , 他也是办不到的, 也会创建两次.
源码:
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 的 postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry 调用结束之后,
就会调用他的 postProcessBeanFactory 方法.
@Override public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { int factoryId = System.identityHashCode(beanFactory); if (this.factoriesPostProcessed.contains(factoryId)) { throw new IllegalStateException( "postProcessBeanFactory already called on this post-processor against " + beanFactory); } this.factoriesPostProcessed.add(factoryId); if (!this.registriesPostProcessed.contains(factoryId)) { // BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor hook apparently not supported... // Simply call processConfigurationClasses lazily at this point then. processConfigBeanDefinitions((BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory); } //给配置类产生cglib代理 //为什么需要产生cglib代理? enhanceConfigurationClasses(beanFactory); beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ImportAwareBeanPostProcessor(beanFactory)); }
除了产生了一次 cglib 代理外, 还向容器中注册了一个后置处理器: ImportAwareBeanPostProcessor
这里主要还是看这个 cglib 代理, 它是根据是否有 @Configuration 注解来判断是否要进行的.
此例中, 主要是对 配置类 StartConfig 产生cglib代理的.
那么为什么要对 StartConfig 产生 cglib 代理呢?
是不是想要达到 上面 demo 中的效果呢? 让 IndexDao1 只创建一遍?
public void enhanceConfigurationClasses(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { Map<String, AbstractBeanDefinition> configBeanDefs = new LinkedHashMap<>();
//解析拿到容器中的配置类(加了@Configuration注解的), 放在 configBeanDefs 中 for (String beanName : beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames()) { BeanDefinition beanDef = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition(beanName); //判断是否是一个全注解类 //扫描是全注解类?full和lite的关系 if (ConfigurationClassUtils.isFullConfigurationClass(beanDef)) { if (!(beanDef instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition)) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Cannot enhance @Configuration bean definition '" + beanName + "' since it is not stored in an AbstractBeanDefinition subclass"); } else if (logger.isInfoEnabled() && beanFactory.containsSingleton(beanName)) { logger.info("Cannot enhance @Configuration bean definition '" + beanName + "' since its singleton instance has been created too early. The typical cause " + "is a non-static @Bean method with a BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor " + "return type: Consider declaring such methods as 'static'."); } configBeanDefs.put(beanName, (AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDef); } } if (configBeanDefs.isEmpty()) { // nothing to enhance -> return immediately return; } ConfigurationClassEnhancer enhancer = new ConfigurationClassEnhancer(); for (Map.Entry<String, AbstractBeanDefinition> entry : configBeanDefs.entrySet()) { AbstractBeanDefinition beanDef = entry.getValue(); // If a @Configuration class gets proxied, always proxy the target class beanDef.setAttribute(AutoProxyUtils.PRESERVE_TARGET_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, Boolean.TRUE); try { // Set enhanced subclass of the user-specified bean class Class<?> configClass = beanDef.resolveBeanClass(this.beanClassLoader); if (configClass != null) { //完成对全注解类的cglib代理 Class<?> enhancedClass = enhancer.enhance(configClass, this.beanClassLoader); if (configClass != enhancedClass) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace(String.format("Replacing bean definition '%s' existing class '%s' with " + "enhanced class '%s'", entry.getKey(), configClass.getName(), enhancedClass.getName())); } beanDef.setBeanClass(enhancedClass); } } } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot load configuration class: " + beanDef.getBeanClassName(), ex); } } }
从上面这段代码来看, 只有加载了 @Configuration 的配置类, 才会进行cglib代理.
那前面的 full / lite 属性设置的意义, 在这里就体现出来了.
1. full 模式下, 会进行配置类的 cglib 代理.
2. lite模式下, 此处就直接返回了.
enhance
org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassEnhancer#enhance
public Class<?> enhance(Class<?> configClass, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { //判断是否被代理过 if (EnhancedConfiguration.class.isAssignableFrom(configClass)) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug(String.format("Ignoring request to enhance %s as it has " + "already been enhanced. This usually indicates that more than one " + "ConfigurationClassPostProcessor has been registered (e.g. via " + "<context:annotation-config>). This is harmless, but you may " + "want check your configuration and remove one CCPP if possible", configClass.getName())); } return configClass; } //没有被代理cglib代理 Class<?> enhancedClass = createClass(newEnhancer(configClass, classLoader)); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace(String.format("Successfully enhanced %s; enhanced class name is: %s", configClass.getName(), enhancedClass.getName())); } return enhancedClass; }
EnhancedConfiguration
这里通过 EnhancedConfiguration 来判断, 配置类是否被代理过.
为什么能这么判断呢?
org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassEnhancer.EnhancedConfiguration
public interface EnhancedConfiguration extends BeanFactoryAware {}
看源码, 知道他是一个空接口, 啥也不干.
如果在进行 cglib 代理的时候, 让生成的动态代理类实现这个接口, 那么就可以通过判断配置类是否实现这个接口, 来确定是否被代理了.
newEnhancer
这里做了创建代理类前的属性配置
org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassEnhancer#newEnhancer
private Enhancer newEnhancer(Class<?> configSuperClass, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer(); //增强父类,cglib是基于继承来的 enhancer.setSuperclass(configSuperClass); //增强接口,为什么要增强接口? //便于判断,表示一个类以及被增强了 enhancer.setInterfaces(new Class<?>[] {EnhancedConfiguration.class}); //不继承Factory接口 enhancer.setUseFactory(false); enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE); // BeanFactoryAwareGeneratorStrategy是一个生成策略 // 主要为生成的CGLIB类中添加成员变量$$beanFactory // 同时基于接口EnhancedConfiguration的父接口BeanFactoryAware中的setBeanFactory方法, // 设置此变量的值为当前Context中的beanFactory,这样一来我们这个cglib代理的对象就有了beanFactory //有了factory就能获得对象,而不用去通过方法获得对象了,因为通过方法获得对象不能控制器过程 //该BeanFactory的作用是在this调用时拦截该调用,并直接在beanFactory中获得目标bean enhancer.setStrategy(new BeanFactoryAwareGeneratorStrategy(classLoader)); //过滤方法,不能每次都去new enhancer.setCallbackFilter(CALLBACK_FILTER); enhancer.setCallbackTypes(CALLBACK_FILTER.getCallbackTypes()); return enhancer; }
从这段代码看, spring确实是, 将 EnhancedConfiguration 放到了动态代理类中. 让动态代理类实现它.
createClass
正式创建代理类, 设置 MethodInterceptor
org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassEnhancer#createClass
private Class<?> createClass(Enhancer enhancer) { Class<?> subclass = enhancer.createClass(); // Registering callbacks statically (as opposed to thread-local) // is critical for usage in an OSGi environment (SPR-5932)... Enhancer.registerStaticCallbacks(subclass, CALLBACKS); return subclass; }
org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassEnhancer#CALLBACKS
private static final Callback[] CALLBACKS = new Callback[] { //增强方法,主要控制 bean 的作用域 //不每一次都去调用new new BeanMethodInterceptor(), //设置一个beanFactory new BeanFactoryAwareMethodInterceptor(), NoOp.INSTANCE };
BeanMethodInterceptor 实现了 MethodInterceptor
熟悉cglib的应该知道, 他是一个方法拦截器, 会对被代理的目标方法进行拦截包装.
其效果跟 上面demo中的方法二一样. 可以改变目标方法的逻辑
BeanMethodInterceptor
public Object intercept(Object enhancedConfigInstance, Method beanMethod, Object[] beanMethodArgs, MethodProxy cglibMethodProxy) throws Throwable { //enhancedConfigInstance 代理 // 通过enhancedConfigInstance中cglib生成的成员变量$$beanFactory获得beanFactory。 ConfigurableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(enhancedConfigInstance); String beanName = BeanAnnotationHelper.determineBeanNameFor(beanMethod); // Determine whether this bean is a scoped-proxy if (BeanAnnotationHelper.isScopedProxy(beanMethod)) { String scopedBeanName = ScopedProxyCreator.getTargetBeanName(beanName); if (beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(scopedBeanName)) { beanName = scopedBeanName; } } // To handle the case of an inter-bean method reference, we must explicitly check the // container for already cached instances. // First, check to see if the requested bean is a FactoryBean. If so, create a subclass // proxy that intercepts calls to getObject() and returns any cached bean instance. // This ensures that the semantics of calling a FactoryBean from within @Bean methods // is the same as that of referring to a FactoryBean within XML. See SPR-6602. if (factoryContainsBean(beanFactory, BeanFactory.FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName) && factoryContainsBean(beanFactory, beanName)) { Object factoryBean = beanFactory.getBean(BeanFactory.FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName); if (factoryBean instanceof ScopedProxyFactoryBean) { // Scoped proxy factory beans are a special case and should not be further proxied } else { // It is a candidate FactoryBean - go ahead with enhancement return enhanceFactoryBean(factoryBean, beanMethod.getReturnType(), beanFactory, beanName); } } //一个非常牛逼的判断 //判断到底是new 还是get //判断执行的方法和调用方法是不是同一个方法 if (isCurrentlyInvokedFactoryMethod(beanMethod)) { // The factory is calling the bean method in order to instantiate and register the bean // (i.e. via a getBean() call) -> invoke the super implementation of the method to actually // create the bean instance. if (logger.isInfoEnabled() && BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class.isAssignableFrom(beanMethod.getReturnType())) { logger.info(String.format("@Bean method %s.%s is non-static and returns an object " + "assignable to Spring's BeanFactoryPostProcessor interface. This will " + "result in a failure to process annotations such as @Autowired, " + "@Resource and @PostConstruct within the method's declaring " + "@Configuration class. Add the 'static' modifier to this method to avoid " + "these container lifecycle issues; see @Bean javadoc for complete details.", beanMethod.getDeclaringClass().getSimpleName(), beanMethod.getName())); }
//调用父类的相应方法 return cglibMethodProxy.invokeSuper(enhancedConfigInstance, beanMethodArgs); } return resolveBeanReference(beanMethod, beanMethodArgs, beanFactory, beanName); }
isCurrentlyInvokedFactoryMethod
//org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassEnhancer.BeanMethodInterceptor#isCurrentlyInvokedFactoryMethod private boolean isCurrentlyInvokedFactoryMethod(Method method) { Method currentlyInvoked = SimpleInstantiationStrategy.getCurrentlyInvokedFactoryMethod(); return (currentlyInvoked != null && method.getName().equals(currentlyInvoked.getName()) && Arrays.equals(method.getParameterTypes(), currentlyInvoked.getParameterTypes())); }
在上面的demo中, 判断是否要执行创建过程的逻辑是: 从map中获取对象, 有则不创建, 没有则创建.
显然, spring在这里, 并不是这么干的.
执行 indexDao1() 时, 通过调试可以知道, method 是indexDao1(), currentlyInvoked 也是 indexDao1().
执行 indexDao2() 时, 会进入此方法两次, 第一次是对 indexDao2() 本身的拦截, 第二次是对 他调用的 indexDao1() 的拦截.
第一次时: method 是indexDao2(), currentlyInvoked 也是 indexDao2().
第二次时: method 是indexDao1(), 但是 currentlyInvoked 却变成了 indexDao2().
从这里可以看出, spring 是通过方法名, 来进行是否要走父类方法的判断的.
resolveBeanReference
这里是通过spring工厂来获取对象的. 暂时可以理解成, 上面demo中的map.
private Object resolveBeanReference(Method beanMethod, Object[] beanMethodArgs, ConfigurableBeanFactory beanFactory, String beanName) { // The user (i.e. not the factory) is requesting this bean through a call to // the bean method, direct or indirect. The bean may have already been marked // as 'in creation' in certain autowiring scenarios; if so, temporarily set // the in-creation status to false in order to avoid an exception. //判断他是否正在创建 boolean alreadyInCreation = beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(beanName); try { if (alreadyInCreation) { beanFactory.setCurrentlyInCreation(beanName, false); } boolean useArgs = !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(beanMethodArgs); if (useArgs && beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) { // Stubbed null arguments just for reference purposes, // expecting them to be autowired for regular singleton references? // A safe assumption since @Bean singleton arguments cannot be optional... for (Object arg : beanMethodArgs) { if (arg == null) { useArgs = false; break; } } } //beanFactory.getBean 通过容器来拿 Object beanInstance = (useArgs ? beanFactory.getBean(beanName, beanMethodArgs) : beanFactory.getBean(beanName)); if (!ClassUtils.isAssignableValue(beanMethod.getReturnType(), beanInstance)) { // Detect package-protected NullBean instance through equals(null) check if (beanInstance.equals(null)) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug(String.format("@Bean method %s.%s called as bean reference " + "for type [%s] returned null bean; resolving to null value.", beanMethod.getDeclaringClass().getSimpleName(), beanMethod.getName(), beanMethod.getReturnType().getName())); } beanInstance = null; } else { String msg = String.format("@Bean method %s.%s called as bean reference " + "for type [%s] but overridden by non-compatible bean instance of type [%s].", beanMethod.getDeclaringClass().getSimpleName(), beanMethod.getName(), beanMethod.getReturnType().getName(), beanInstance.getClass().getName()); try { BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanFactory.getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName); msg += " Overriding bean of same name declared in: " + beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(); } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { // Ignore - simply no detailed message then. } throw new IllegalStateException(msg); } } Method currentlyInvoked = SimpleInstantiationStrategy.getCurrentlyInvokedFactoryMethod(); if (currentlyInvoked != null) { String outerBeanName = BeanAnnotationHelper.determineBeanNameFor(currentlyInvoked); beanFactory.registerDependentBean(beanName, outerBeanName); } return beanInstance; } finally { if (alreadyInCreation) { beanFactory.setCurrentlyInCreation(beanName, true); } } }