在接上一篇之前, 我想先写几个测试demo, 应该能帮助更好的理解.
demo:
com.study.elvinle.ioc.xml.IndexService:
public class IndexService { private String name = "index";public String getName() { System.out.println("IndexService.getName() --> " + name); return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
com.study.elvinle.ioc.fac.IndexFactoryBean:
@Component("index")
public class IndexFactoryBean implements FactoryBean<Object> {
public void printf(){
System.out.println("IndexFactoryBean printf");
}
@Override
public Object getObject() throws Exception {
return new IndexService("小明");
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
}
com.study.elvinle.ioc.scan.TempDao:
@Component public class TempDao { public TempDao() { System.out.println("tempDao constructor"); } private String name = "tempDao"; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
com.study.elvinle.ioc.scan.TempScan:
// 这里使用 Configuration 也是能被扫描到的, 因为 Configuration中, 也有Component注解 //@Configuration @Component @ComponentScan("com.study.elvinle.ioc.fac") public class TempScan { }
com.study.elvinle.ioc.StartConfig:
@Configuration @ComponentScan("com.study.elvinle.ioc.scan") public class StartConfig { public StartConfig() { System.out.println("startConfig Constructor ... "); } }
从这里的扫描范围来看, IndexFactoryBean 并不在这个配置的扫描范围内.
测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext acac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(StartConfig.class); System.out.println("---------------------"); IndexService index = (IndexService) acac.getBean("index"); index.getName(); IndexFactoryBean bean = (IndexFactoryBean) acac.getBean("&index"); bean.printf(); System.out.println("====================="); TempDao tempDao = acac.getBean(TempDao.class); System.out.println(tempDao.getName()); }
结果:
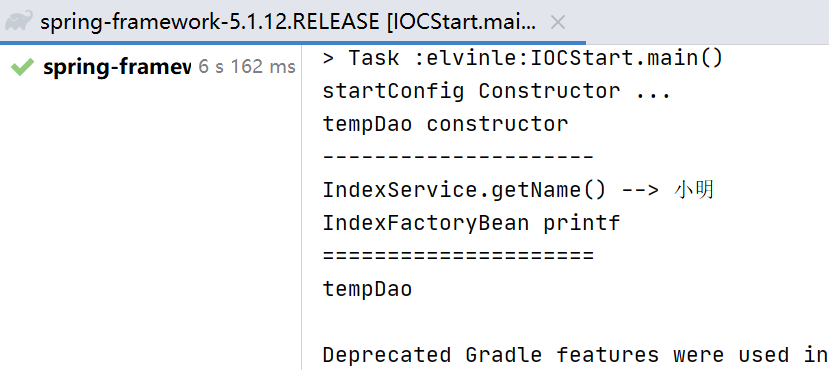
从这个结果看, 扫描发生了接力, 也就是说,
1. StartConfig 扫描的时候, 扫到了 TempScan
2. 解析 TempScan 的时候, 发现 TempScan 上面, 有@Component 和 ComponentScan 注解
3. 解析 TempScan的@ComponentScan注解, 再次进行扫描操作
4. TempScan 扫描到了 IndexFactoryBean, 然后对 IndexFactoryBean 进行解析
源码:
org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassParser#doProcessConfigurationClass
//region 处理 @ComponnentScan 注解 // Process any @ComponentScan annotations Set<AnnotationAttributes> componentScans = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable( sourceClass.getMetadata(), ComponentScans.class, ComponentScan.class); if (!componentScans.isEmpty() && !this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN)) { for (AnnotationAttributes componentScan : componentScans) { // The config class is annotated with @ComponentScan -> perform the scan immediately //扫描普通类 //这里扫描出来所有 @Component //并且把扫描的出来的普通bean放到 map 当中 Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> scannedBeanDefinitions = this.componentScanParser.parse(componentScan, sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName()); // Check the set of scanned definitions for any further config classes and parse recursively if needed //检查扫描出来的类当中是否还有configuration for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : scannedBeanDefinitions) { BeanDefinition bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition().getOriginatingBeanDefinition(); if (bdCand == null) { bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition(); } //检查扫描出来的类中, 是否还有加载了 @Configuration 的类, 如果有, 则接着递归处理 if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bdCand, this.metadataReaderFactory)) { parse(bdCand.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName()); } } } } //endregion
在spring源码里面, 会经常看到 递归调用. 因为不确定性. 此方法里面, 对扫描出来的类, 还需要进行递归处理.
因为被扫描出来的类, 可能并不是一个普通的类, 他也可能会加一些需要解析的注解, 如 @ComponentScan, @Import
进入 parse 方法看:
org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScanAnnotationParser#parse
public Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> parse(AnnotationAttributes componentScan, final String declaringClass) { //扫描的时候, spring 自己new了一个ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner来使用, 此处证实, 前面那个new出来的 reader , 确实不是给自己用的 //默认情况下, useDefaultFilters 是true,
//创建ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner的时候, 会默认使用一个过滤器: AnnotationTypeFilter(Component.class) ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this.registry, componentScan.getBoolean("useDefaultFilters"), this.environment, this.resourceLoader); //BeanNameGenerator // 获取 bean 的名字生成器, ComponentScan 默认的是 BeanNameGenerator, 也可以自定义覆盖 Class<? extends BeanNameGenerator> generatorClass = componentScan.getClass("nameGenerator"); boolean useInheritedGenerator = (BeanNameGenerator.class == generatorClass); scanner.setBeanNameGenerator(useInheritedGenerator ? this.beanNameGenerator : BeanUtils.instantiateClass(generatorClass)); //web当中在来讲 ScopedProxyMode scopedProxyMode = componentScan.getEnum("scopedProxy"); if (scopedProxyMode != ScopedProxyMode.DEFAULT) { scanner.setScopedProxyMode(scopedProxyMode); } else { Class<? extends ScopeMetadataResolver> resolverClass = componentScan.getClass("scopeResolver"); scanner.setScopeMetadataResolver(BeanUtils.instantiateClass(resolverClass)); } scanner.setResourcePattern(componentScan.getString("resourcePattern")); //遍历当中的过滤 for (AnnotationAttributes filter : componentScan.getAnnotationArray("includeFilters")) { for (TypeFilter typeFilter : typeFiltersFor(filter)) { scanner.addIncludeFilter(typeFilter); } } for (AnnotationAttributes filter : componentScan.getAnnotationArray("excludeFilters")) { for (TypeFilter typeFilter : typeFiltersFor(filter)) { scanner.addExcludeFilter(typeFilter); } } //默认false boolean lazyInit = componentScan.getBoolean("lazyInit"); if (lazyInit) { scanner.getBeanDefinitionDefaults().setLazyInit(true); } Set<String> basePackages = new LinkedHashSet<>(); String[] basePackagesArray = componentScan.getStringArray("basePackages"); for (String pkg : basePackagesArray) { String[] tokenized = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(this.environment.resolvePlaceholders(pkg), ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS); Collections.addAll(basePackages, tokenized); } for (Class<?> clazz : componentScan.getClassArray("basePackageClasses")) { basePackages.add(ClassUtils.getPackageName(clazz)); } if (basePackages.isEmpty()) { basePackages.add(ClassUtils.getPackageName(declaringClass)); } scanner.addExcludeFilter(new AbstractTypeHierarchyTraversingFilter(false, false) { @Override protected boolean matchClassName(String className) {
//排除自己 return declaringClass.equals(className); } }); return scanner.doScan(StringUtils.toStringArray(basePackages)); }
这个方法, 不用细看, 主要是设置一些属性的默认值, 只是有几个地方需要注意一下:
1. 这里new 了一个 ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner 出来, 进行扫描的工作, 也印证了前面篇幅说的,
在创建 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 的时候, 其构造函数中, 创建的 scanner , 并不是给spring自己用的, 而是给开发人员使用的.
2. 在创建这里的 scanner 的时候, 默认了一个 AnnotationTypeFilter , 并且在创建他的时候, 默认给了一个 @Component,
然后将这个设置到了 IncludeFilter 属性中.
Filter顾名思义, 就是过滤器, 这个关系到扫描出来的内容是否符合我们的要求
3. 这里还设置了一个匿名的 AbstractTypeHierarchyTraversingFilter 实现类, 并设置给了 ExcludeFilter 属性
4. 真正的扫描工作是 doScan 来完成的.
接着来看 doScan 方法:
org.springframework.context.annotation.ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner#doScan
protected Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) { Assert.notEmpty(basePackages, "At least one base package must be specified"); Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = new LinkedHashSet<>(); for (String basePackage : basePackages) { //扫描basePackage路径下的java文件, 并进行过滤, 获取加载了 @Component 注解的部分 //符合条件的并把它转成BeanDefinition类型 Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = findCandidateComponents(basePackage); for (BeanDefinition candidate : candidates) { //解析scope属性 ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(candidate); candidate.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName()); String beanName = this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(candidate, this.registry); if (candidate instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) { //如果这个类是AbstractBeanDefinition的子类 //则为他设置默认值,比如lazy,init destory postProcessBeanDefinition((AbstractBeanDefinition) candidate, beanName); } if (candidate instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) { //检查并且处理常用的注解 //这里的处理主要是指把常用注解的值设置到AnnotatedBeanDefinition当中 //当前前提是这个类必须是AnnotatedBeanDefinition类型的,说白了就是加了注解的类 AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) candidate); } if (checkCandidate(beanName, candidate)) { BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(candidate, beanName); definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry); beanDefinitions.add(definitionHolder); //将这个扫描到的 bd 注册到 spring 容器中(this.beanDefinitionMap) registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry); } } } return beanDefinitions; }
findCandidateComponents 这个方法, 内部会调用 scanCandidateComponents 方法.
scanCandidateComponents
org.springframework.context.annotation.ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider#scanCandidateComponents
private Set<BeanDefinition> scanCandidateComponents(String basePackage) { Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>(); try { String packageSearchPath = ResourcePatternResolver.CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX + resolveBasePackage(basePackage) + '/' + this.resourcePattern; Resource[] resources = getResourcePatternResolver().getResources(packageSearchPath); boolean traceEnabled = logger.isTraceEnabled(); boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled(); for (Resource resource : resources) { if (traceEnabled) { logger.trace("Scanning " + resource); } if (resource.isReadable()) { try { MetadataReader metadataReader = getMetadataReaderFactory().getMetadataReader(resource); if (isCandidateComponent(metadataReader)) { ScannedGenericBeanDefinition sbd = new ScannedGenericBeanDefinition(metadataReader); sbd.setResource(resource); sbd.setSource(resource); if (isCandidateComponent(sbd)) { if (debugEnabled) { logger.debug("Identified candidate component class: " + resource); } candidates.add(sbd); } else { if (debugEnabled) { logger.debug("Ignored because not a concrete top-level class: " + resource); } } } else { if (traceEnabled) { logger.trace("Ignored because not matching any filter: " + resource); } } } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "Failed to read candidate component class: " + resource, ex); } } else { if (traceEnabled) { logger.trace("Ignored because not readable: " + resource); } } } } catch (IOException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("I/O failure during classpath scanning", ex); } return candidates; }
从这段代码看, spring是通过扫描 java 文件的方式, 来加载的, 然后根据规则进行转换和过滤.
isCandidateComponent 方法, 如果能满足, 就会为加载的资源来创建 bd .
所以主要看一下
org.springframework.context.annotation.ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider#isCandidateComponent
方法.
protected boolean isCandidateComponent(MetadataReader metadataReader) throws IOException { for (TypeFilter tf : this.excludeFilters) { if (tf.match(metadataReader, getMetadataReaderFactory())) { return false; } } for (TypeFilter tf : this.includeFilters) { if (tf.match(metadataReader, getMetadataReaderFactory())) { return isConditionMatch(metadataReader); } } return false; }
这里的 excluderFilters 里面装的, 就是前面的那个AbstractTypeHierarchyTraversingFilter 的匿名实现类
includeFilters 里面装的, 就是前面的 AnnotationTypeFilter 类
AbstractTypeHierarchyTraversingFilter
这个匿名实现类, 对 match 进行了重写覆盖, 判断条件为:
declaringClass.equals(className)
主要就是为了将自己排除.
declaringClass 是方法传入的类, 也就是被解析的类
className 是扫描到的类.
AnnotationTypeFilter
这个类中, 并没有重写match 方法, 但是重写了 matchSlef 方法, 所以会先进父类中的 match 方法.
在其父类方法
org.springframework.core.type.filter.AbstractTypeHierarchyTraversingFilter#match
中, 调用了 matchSelf 方法, 这个方法就是 AnnotationTypeFilter 的方法了.
@Override protected boolean matchSelf(MetadataReader metadataReader) { AnnotationMetadata metadata = metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata(); //这里判断的其实就是 自己加了 指定的注解, 如 @Component, 或者 自己加的注解里面, 有指定的注解,
//如 @Configuration 中, 就有 @Component return metadata.hasAnnotation(this.annotationType.getName()) || (this.considerMetaAnnotations && metadata.hasMetaAnnotation(this.annotationType.getName())); }
还记的前面提到过, 在创建这个类的时候, 传了一个 @Component 进来了, 所以这里判断的其实是,
被扫描到的类, 是否直接或者间接的有 @Component 注解.
如果没有这个注解, scanner 是会将这个类丢弃的.
看源码的时候, 有个技巧:
1. 很多方法是不需要看的, 先看主要方法, 不能钻牛角尖
2. 看源码之前, 必须对要看的的功能, 起码有个大致的了解, 否则会看的云里雾里, 不知其意.