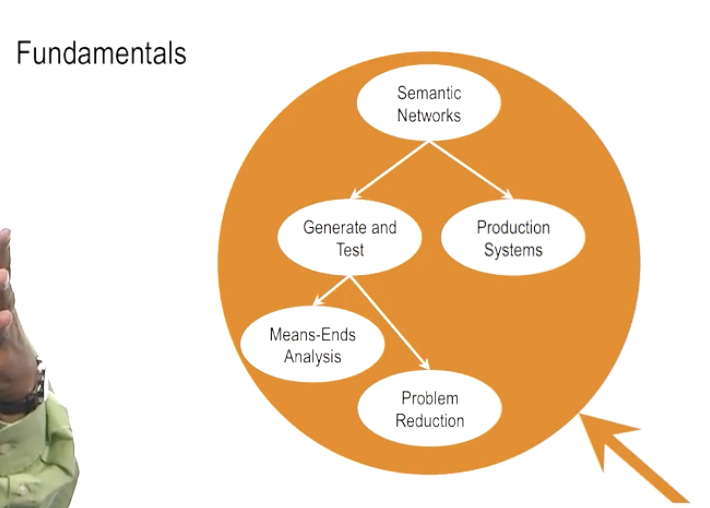


This example is adapted from the following paper:
Lehman, J. F., Laird, J. E., & Rosenbloom, P. S. (1996). A gentle introduction to Soar, an architecture for human cognition. Invitation to Cognitive Science, 4, 212-249.

David is using his knowledge to make a decision.
- How is he using his knowledge to make a decision?
- What is the architecture?
- what is the reasoning that leads him to make that specific decision?
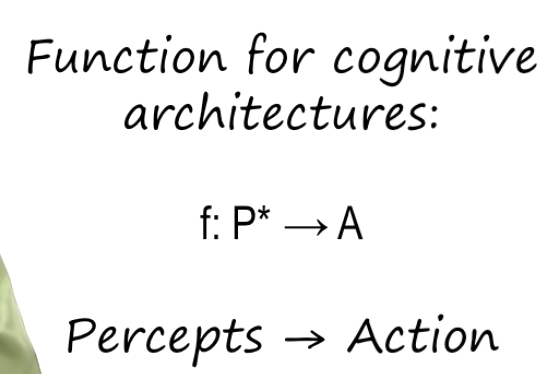
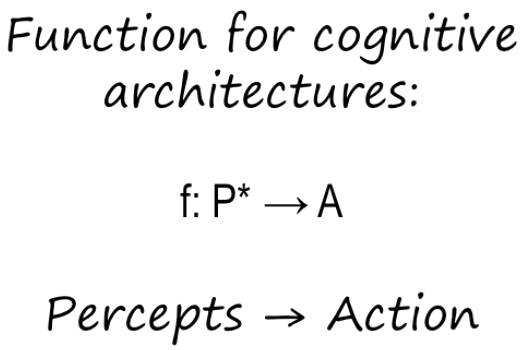
Function of a Cognitive Architecture
Production Systems:
Winston Chapter 7, pages 119-137 can be found at:http://courses.csail.mit.edu/6.034f/ai3/rest.pdf
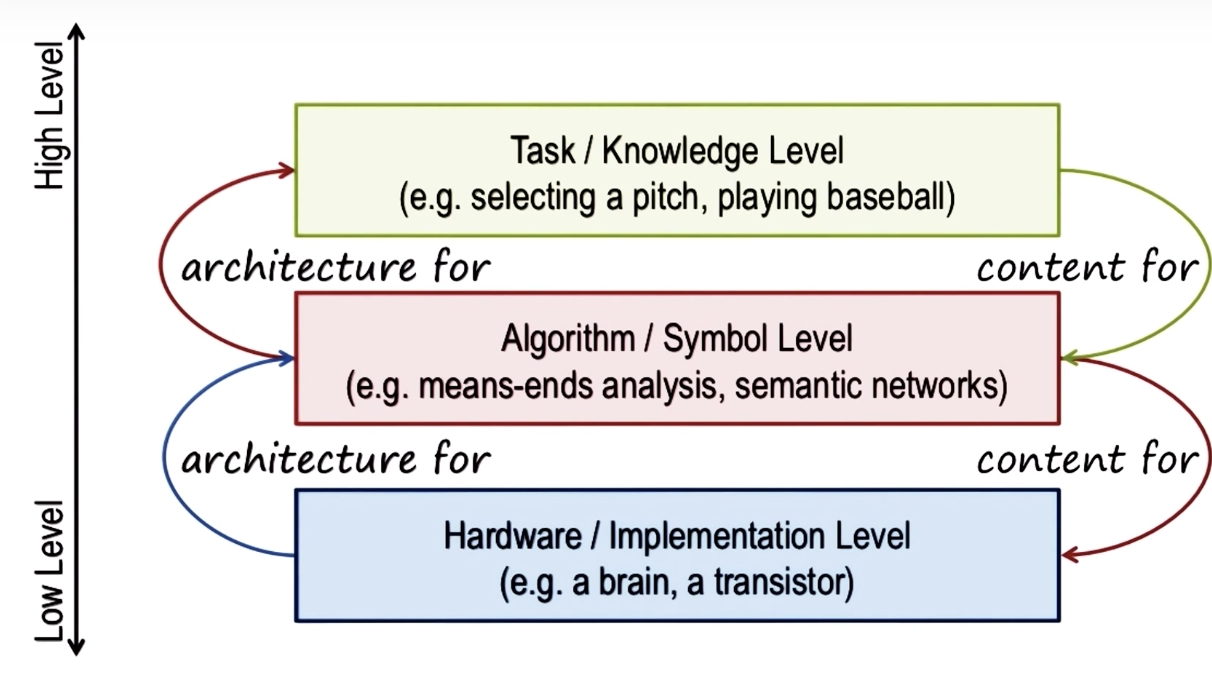
Levels of Cognitive Architectures

Assumptions of Cognitive Architectures

This list is adapted from the following paper:
Lehman, J. F., Laird, J. E., & Rosenbloom, P. S. (1996). A gentle introduction to Soar, an architecture for human cognition. Invitation to Cognitive Science, 4, 212-249.
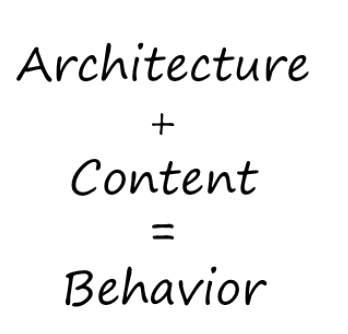
Architecture + Content = Behavior
A Cognitive Architecture for Production Systems

A general architecture of Cognitive system
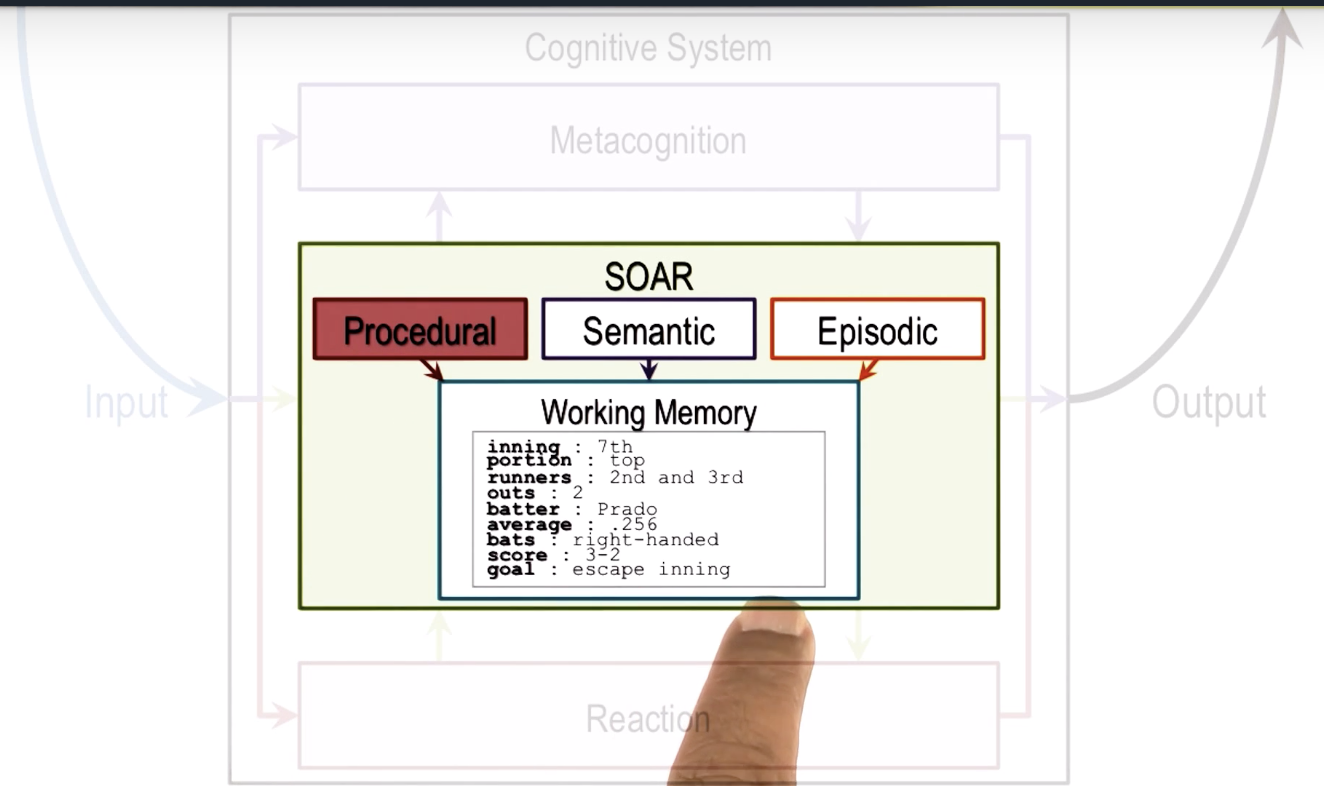
Next is a specific kind of Cognitive system: SOAR

This example is adapted from the following paper:
Lehman, J. F., Laird, J. E., & Rosenbloom, P. S. (1996). A gentle introduction to Soar, an architecture for human cognition. Invitation to Cognitive Science, 4, 212-249.
Here we first only focus on the deliberation of SOAR => long-term memory and working memory
Thre are three parts of knowledge in long-term memory:
- Procedural: how to do certain things
- Sematic: generalization in the form of concepts and models of the world
- Episodic: events, eg. what happened yesterday
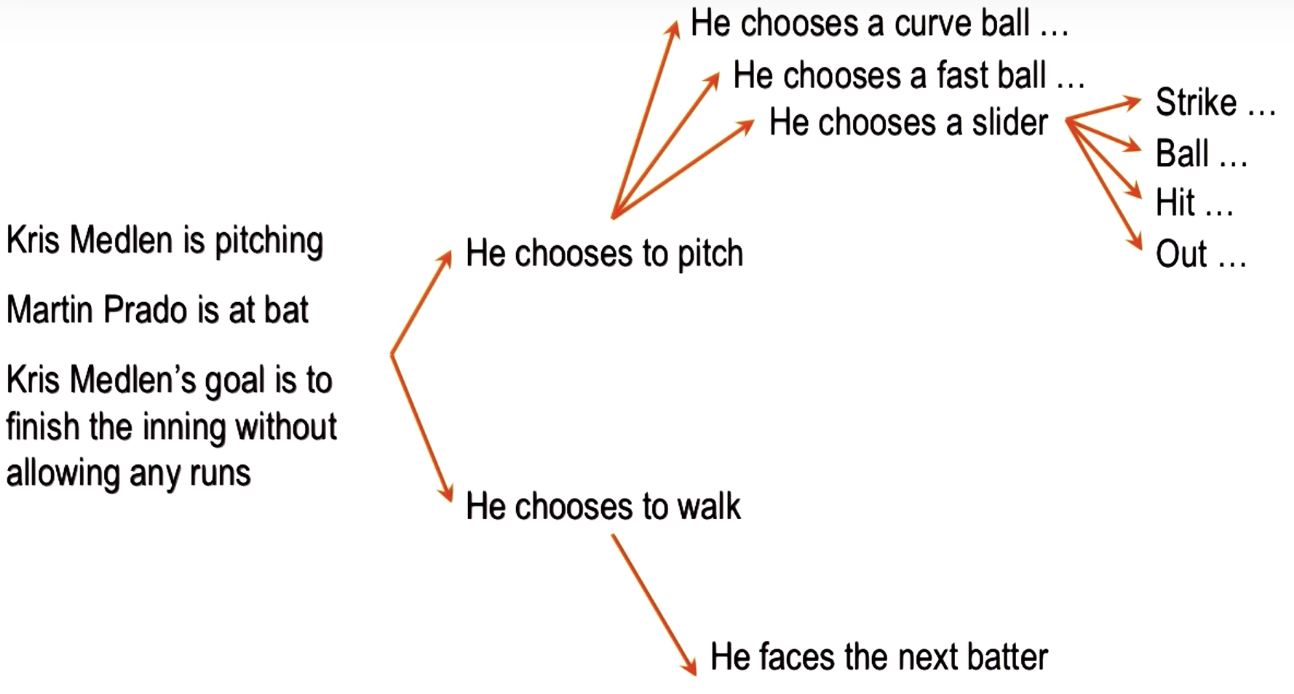
Return to the Pitcher

Action Selection
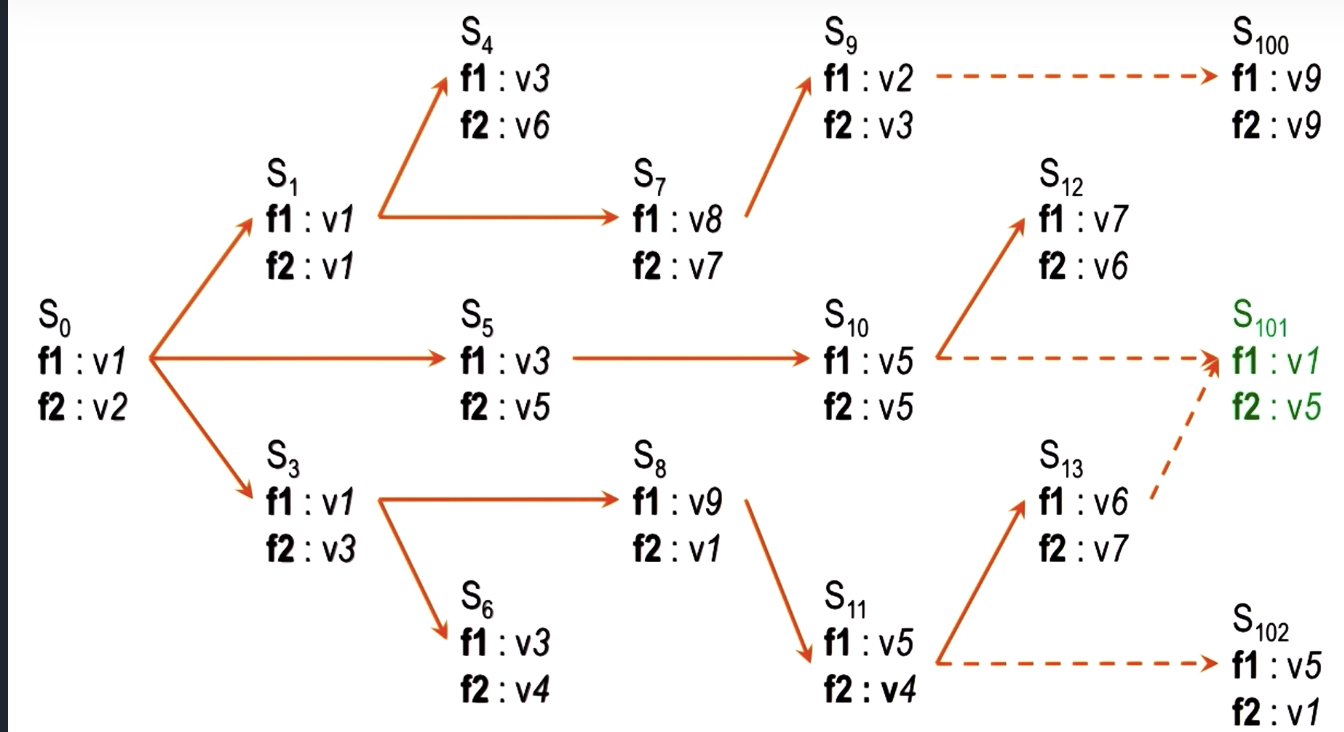
decision making => find a path from S0 to S101 => havent perform any action, just thinking
(comment: model predictive control?)
Putting Content in the Architecture

simple representation of information
Bringing in Memory
production rules:

Exercise: Production System in Action I
left: situation; right: knowledge (rules)

r2 => end

r2 => r4 => r5 => end

r2 => r4 => r5 & r6 => conflict
Chunking
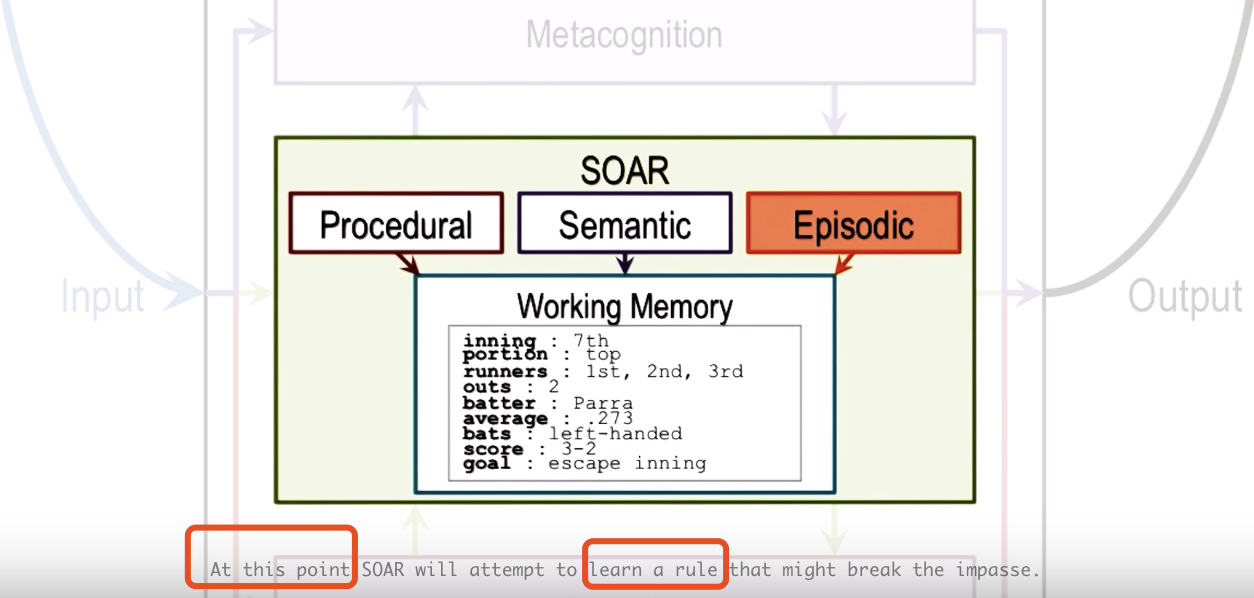
r2 => r4 => r5 & r6 => conflict => learn to choice r5 or r6 here
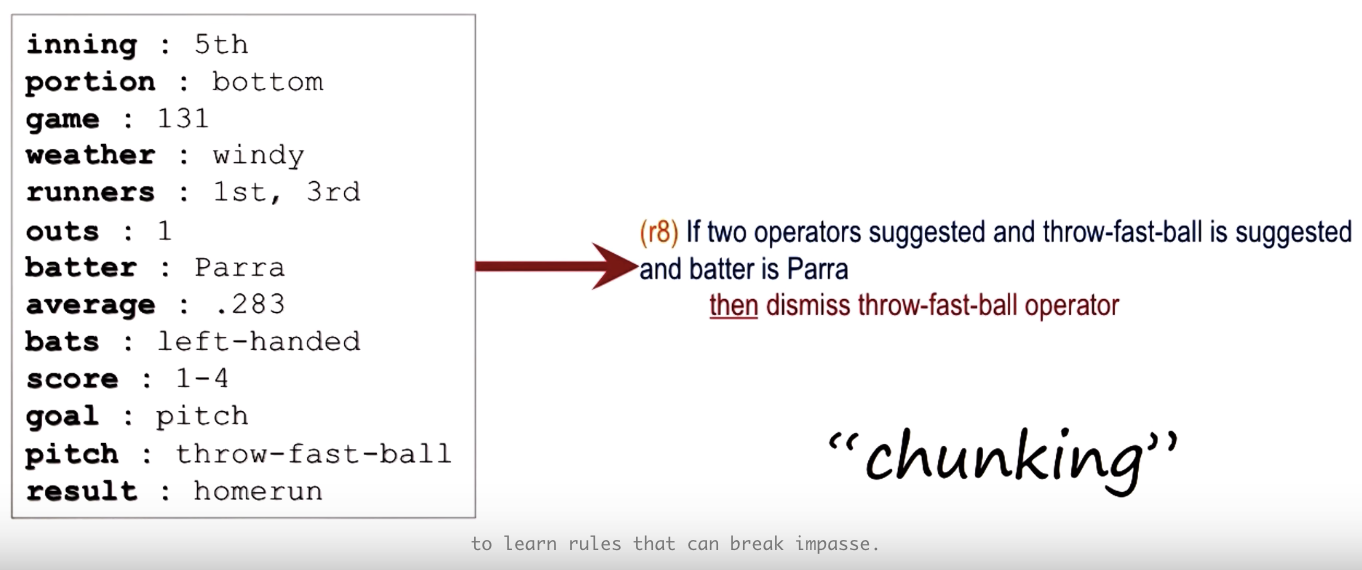
here, reasoning, learning and memory are closely connected.

Fundamentals of Learning
reason first, if reach an impasse, turn back to learning
We are trying to build a unified theory of reasoning, memory and learning, where the demands of memory and reasoning constrain the processing of learning

