Lesson outline
Pandas makes it very convenient to compute various statistics on a dataframe:
- Global statistics: mean, median, std, sum, etc. [more]
- Rolling statistics: rolling_mean, rolling_std, etc. [more]
You will use these functions to analyze stock movement over time.
Specifically, you will compute:
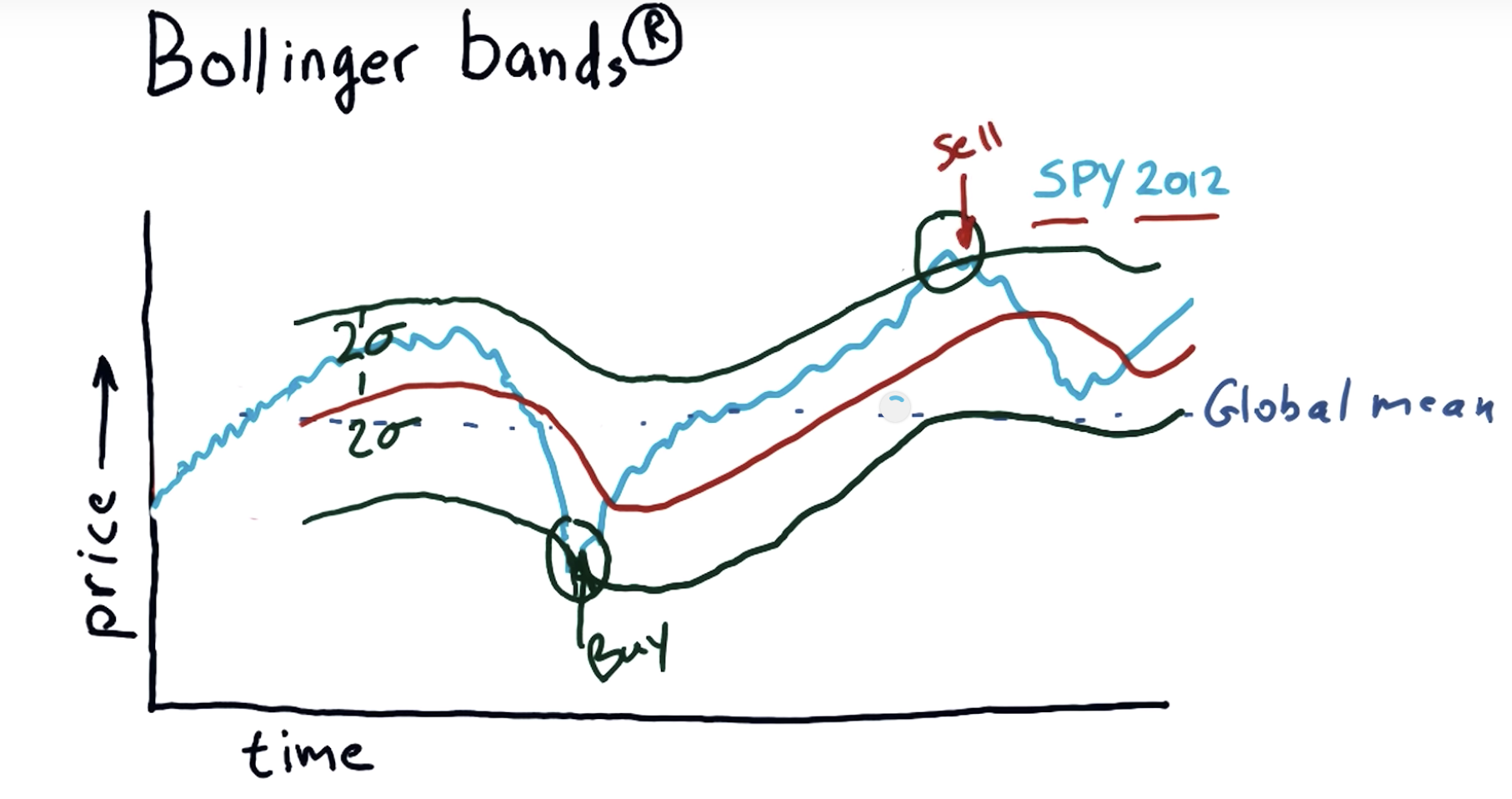
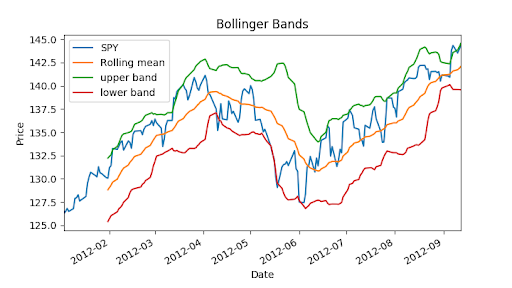
- Bollinger Bands: A way of quantifying how far stock price has deviated from some norm.
- Daily returns: Day-to-day change in stock price.
Global statistics
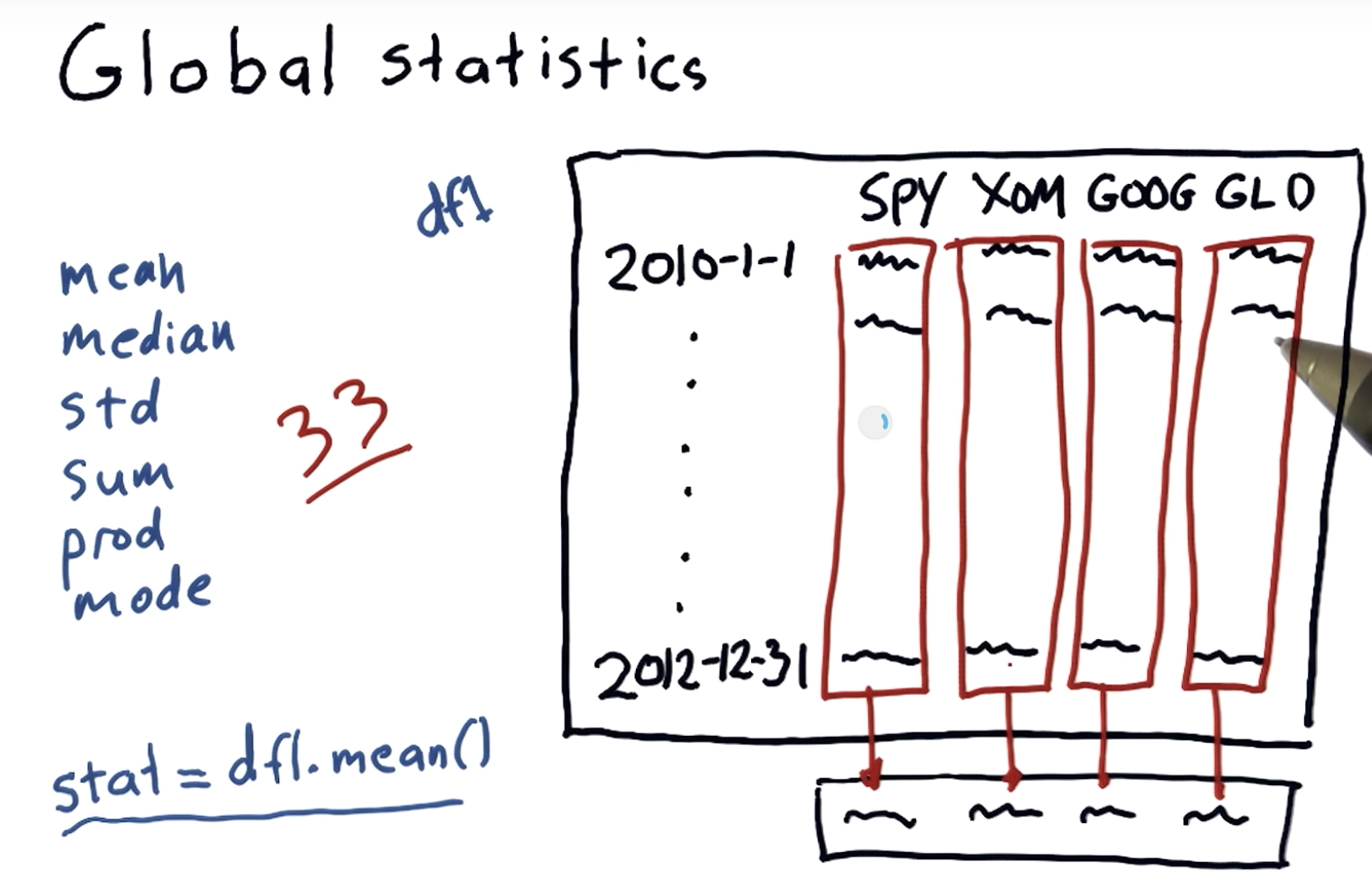
Global statistics: mean, median, std, sum, etc. [more]
Rolling statistics

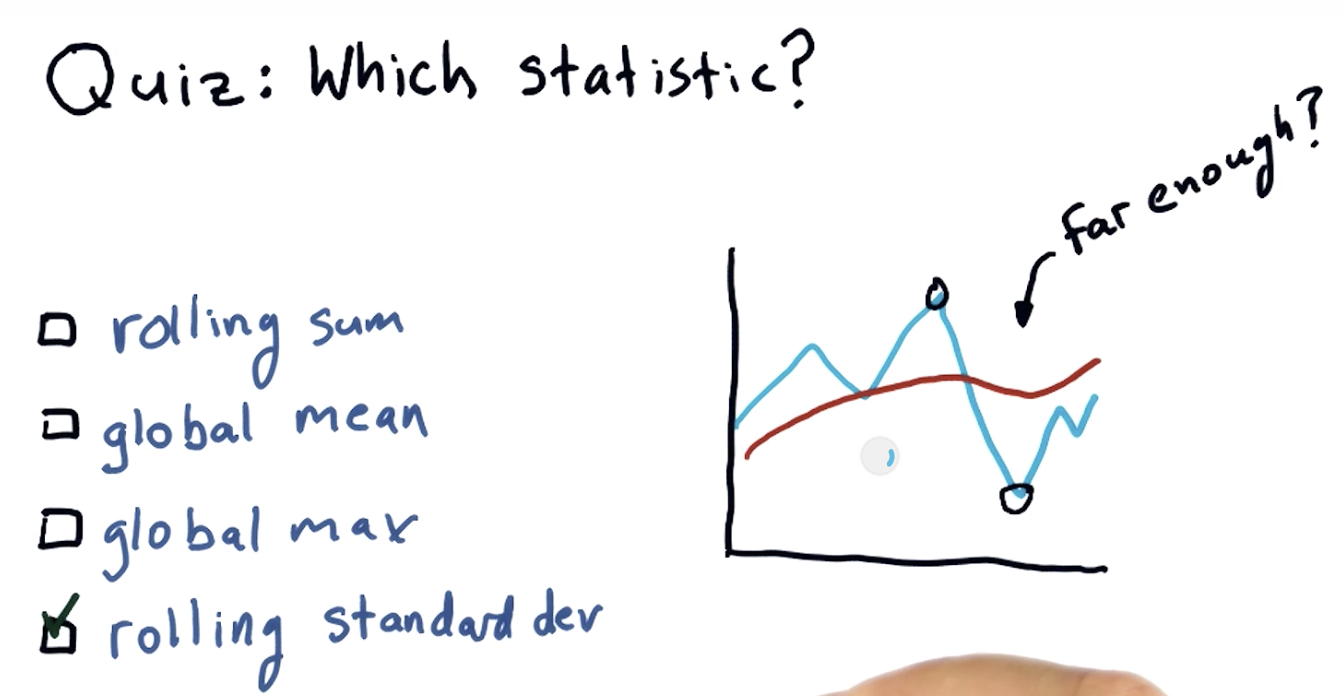
rolling mean is one of the technical indicators,
one thing it looks at is the places where the proce crosses through the rolling average , eg:

a hypothesis is that this rolling mean may be a good representation of sort of the true underlying price of a stock
and that significant deviation from that eventually result in a return to the mean

a challenge is when is that deviation significant enough: see the quiz and next slide
Which statistic to use?
Bollinger Bands (1980s)
Computing rolling statistics
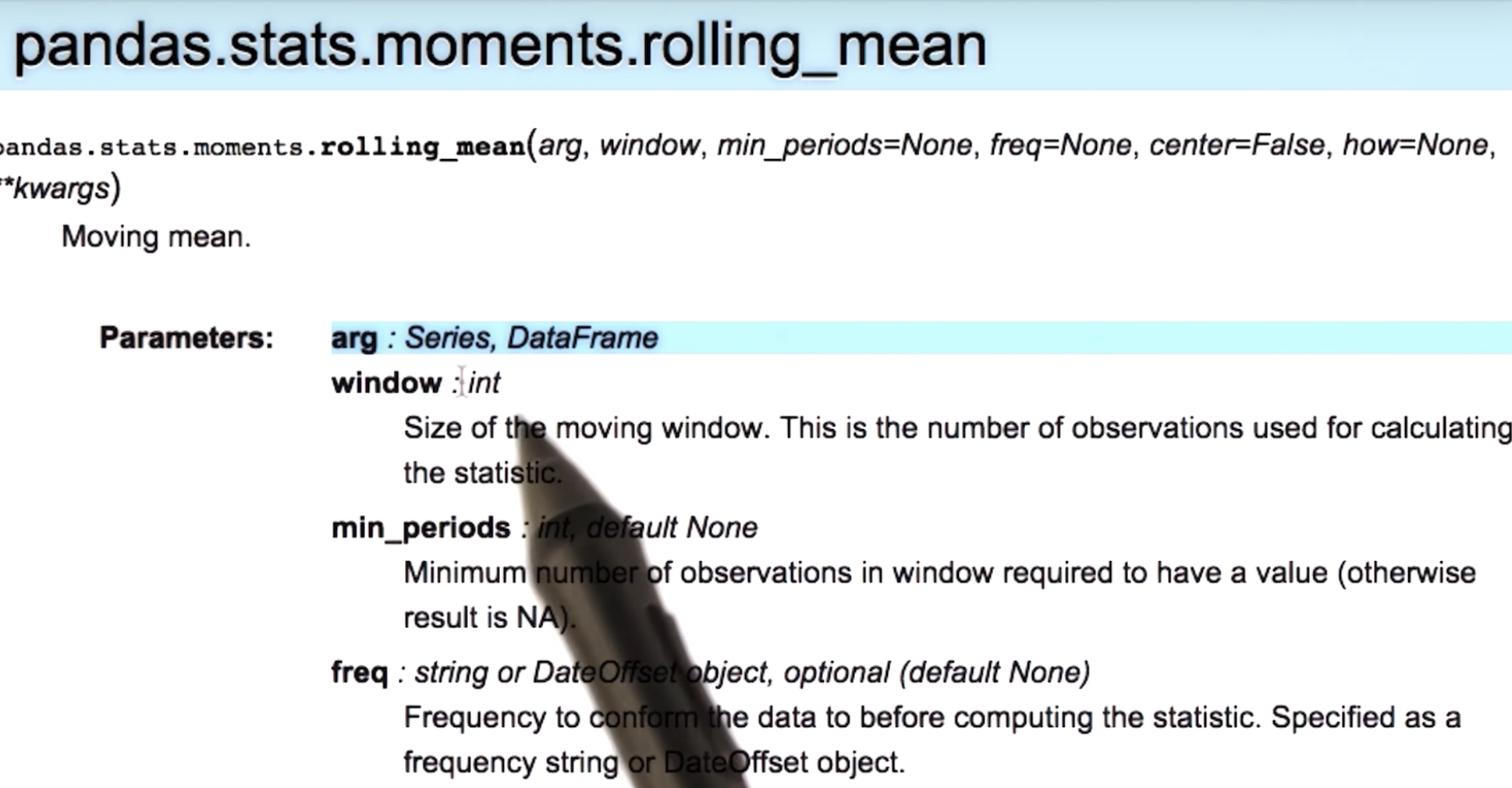
Rolling statistics: rolling_mean, rolling_std, etc. [more]
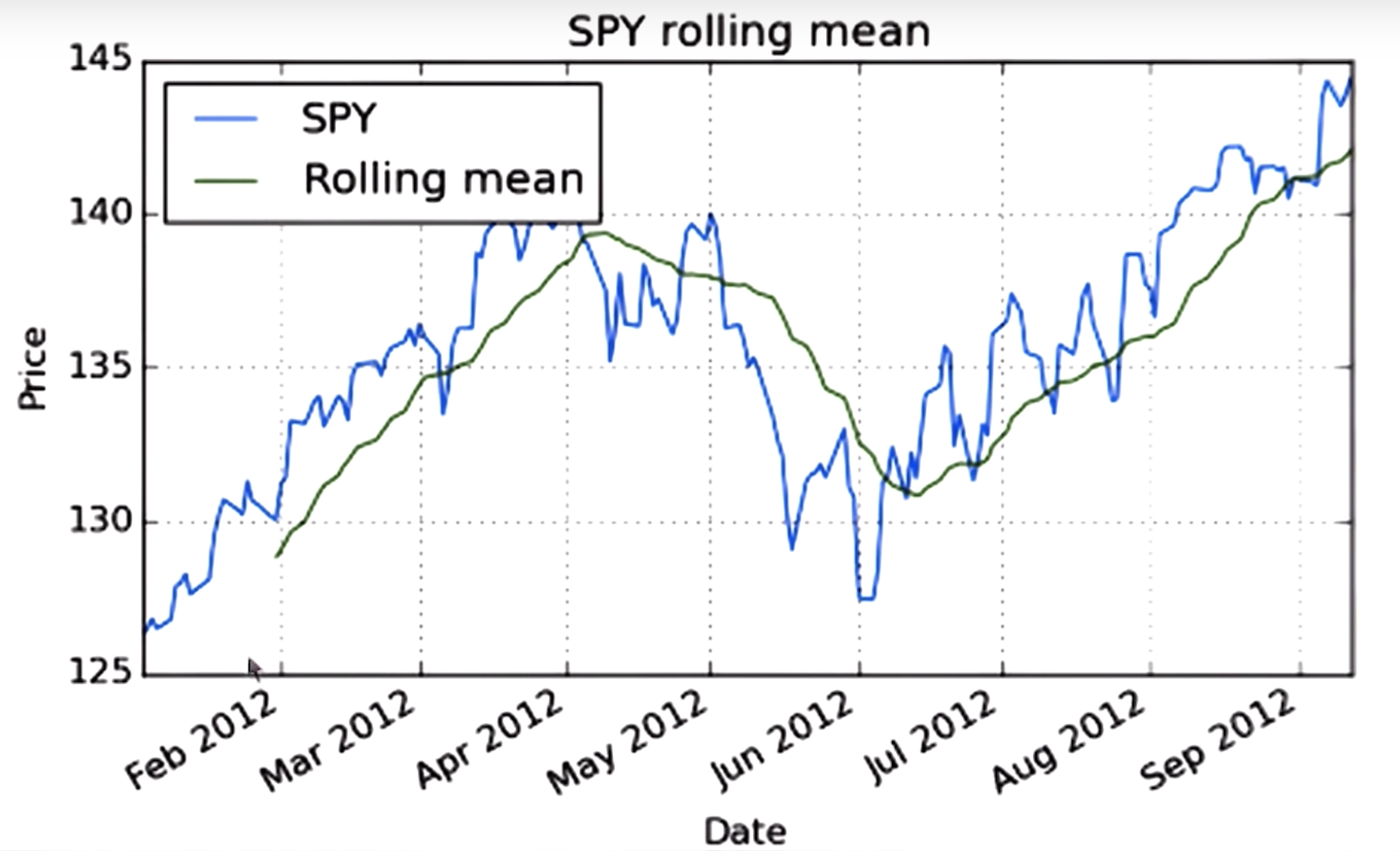
no data in the first 20 days
![]()
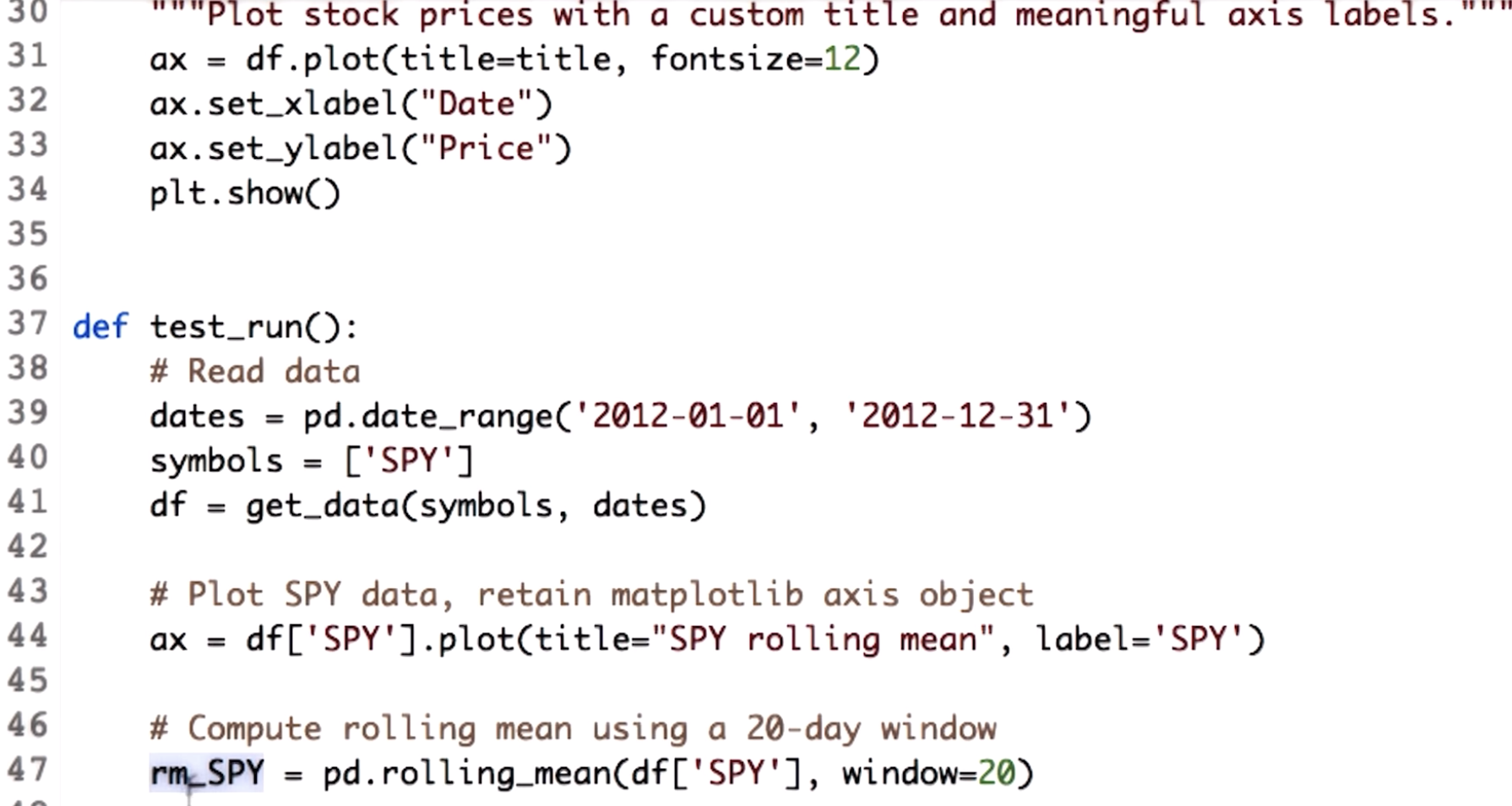
line 44 & 47
"""Bollinger Bands.""" import os import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def symbol_to_path(symbol, base_dir="data"): """Return CSV file path given ticker symbol.""" return os.path.join(base_dir, "{}.csv".format(str(symbol))) def get_data(symbols, dates): """Read stock data (adjusted close) for given symbols from CSV files.""" df = pd.DataFrame(index=dates) if 'SPY' not in symbols: # add SPY for reference, if absent symbols.insert(0, 'SPY') for symbol in symbols: df_temp = pd.read_csv(symbol_to_path(symbol), index_col='Date', parse_dates=True, usecols=['Date', 'Adj Close'], na_values=['nan']) df_temp = df_temp.rename(columns={'Adj Close': symbol}) df = df.join(df_temp) if symbol == 'SPY': # drop dates SPY did not trade df = df.dropna(subset=["SPY"]) return df def plot_data(df, title="Stock prices"): """Plot stock prices with a custom title and meaningful axis labels.""" ax = df.plot(title=title, fontsize=12) ax.set_xlabel("Date") ax.set_ylabel("Price") plt.show() def get_rolling_mean(values, window): """Return rolling mean of given values, using specified window size.""" return pd.rolling_mean(values, window=window) def get_rolling_std(values, window): """Return rolling standard deviation of given values, using specified window size.""" # TODO: Compute and return rolling standard deviation return pd.rolling_std(values,window=window) def get_bollinger_bands(rm, rstd): """Return upper and lower Bollinger Bands.""" # TODO: Compute upper_band and lower_band upper_band = rm + 2*rstd lower_band = rm - 2*rstd return upper_band, lower_band def test_run(): # Read data dates = pd.date_range('2012-01-01', '2012-12-31') symbols = ['SPY'] df = get_data(symbols, dates) # Compute Bollinger Bands # 1. Compute rolling mean rm_SPY = get_rolling_mean(df['SPY'], window=20) # 2. Compute rolling standard deviation rstd_SPY = get_rolling_std(df['SPY'], window=20) # 3. Compute upper and lower bands upper_band, lower_band = get_bollinger_bands(rm_SPY, rstd_SPY) # Plot raw SPY values, rolling mean and Bollinger Bands ax = df['SPY'].plot(title="Bollinger Bands", label='SPY') rm_SPY.plot(label='Rolling mean', ax=ax) upper_band.plot(label='upper band', ax=ax) lower_band.plot(label='lower band', ax=ax)
Daily returns
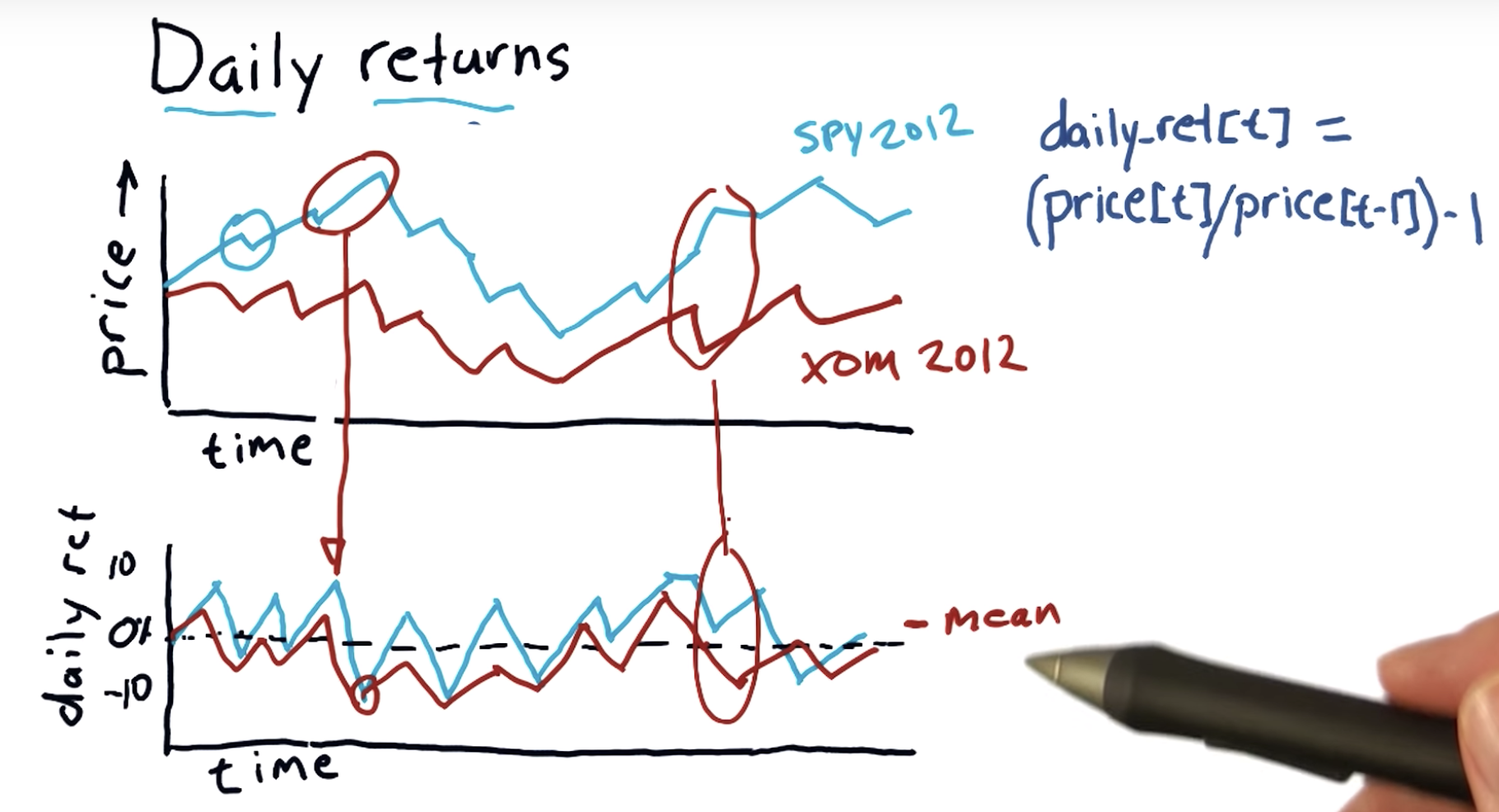
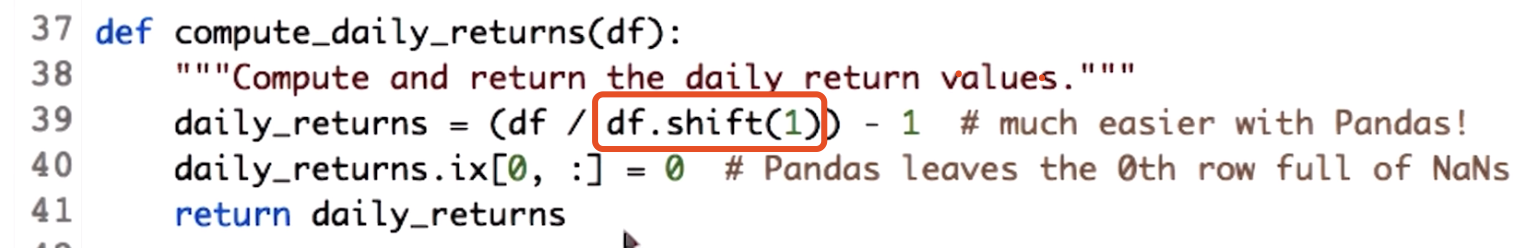
Compute daily returns

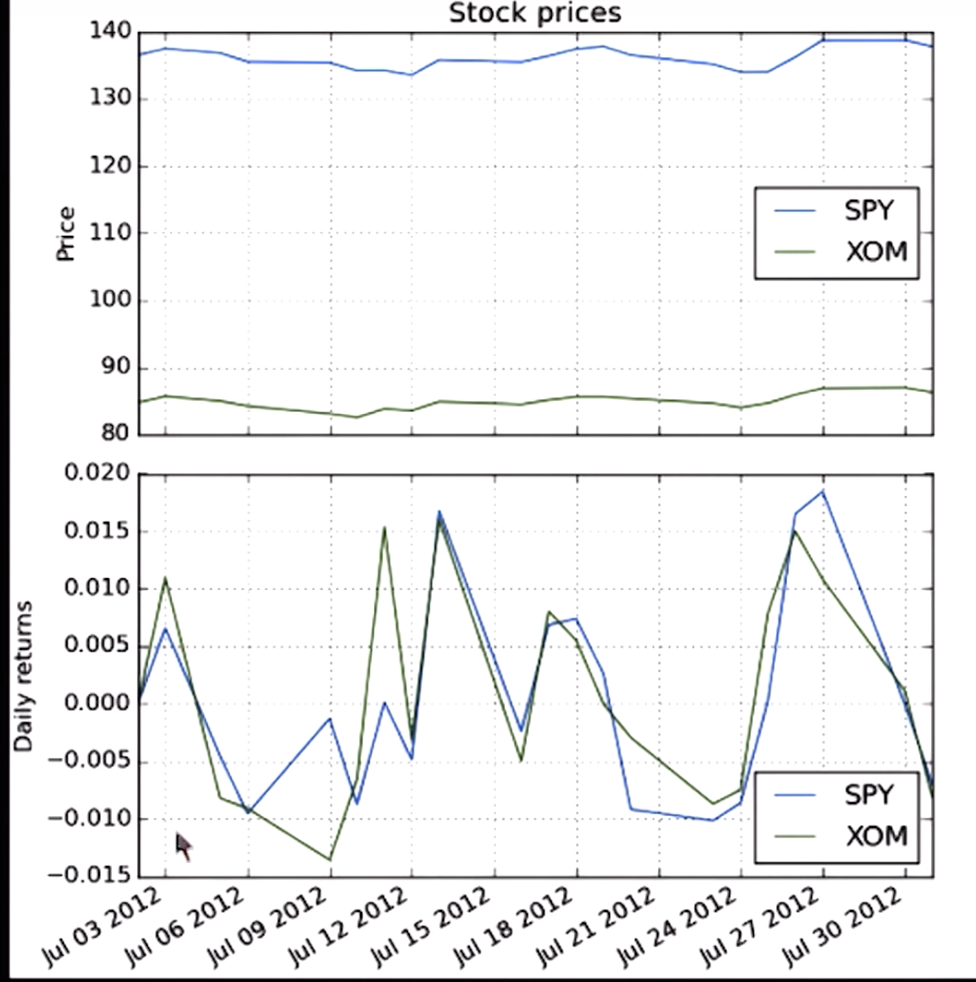
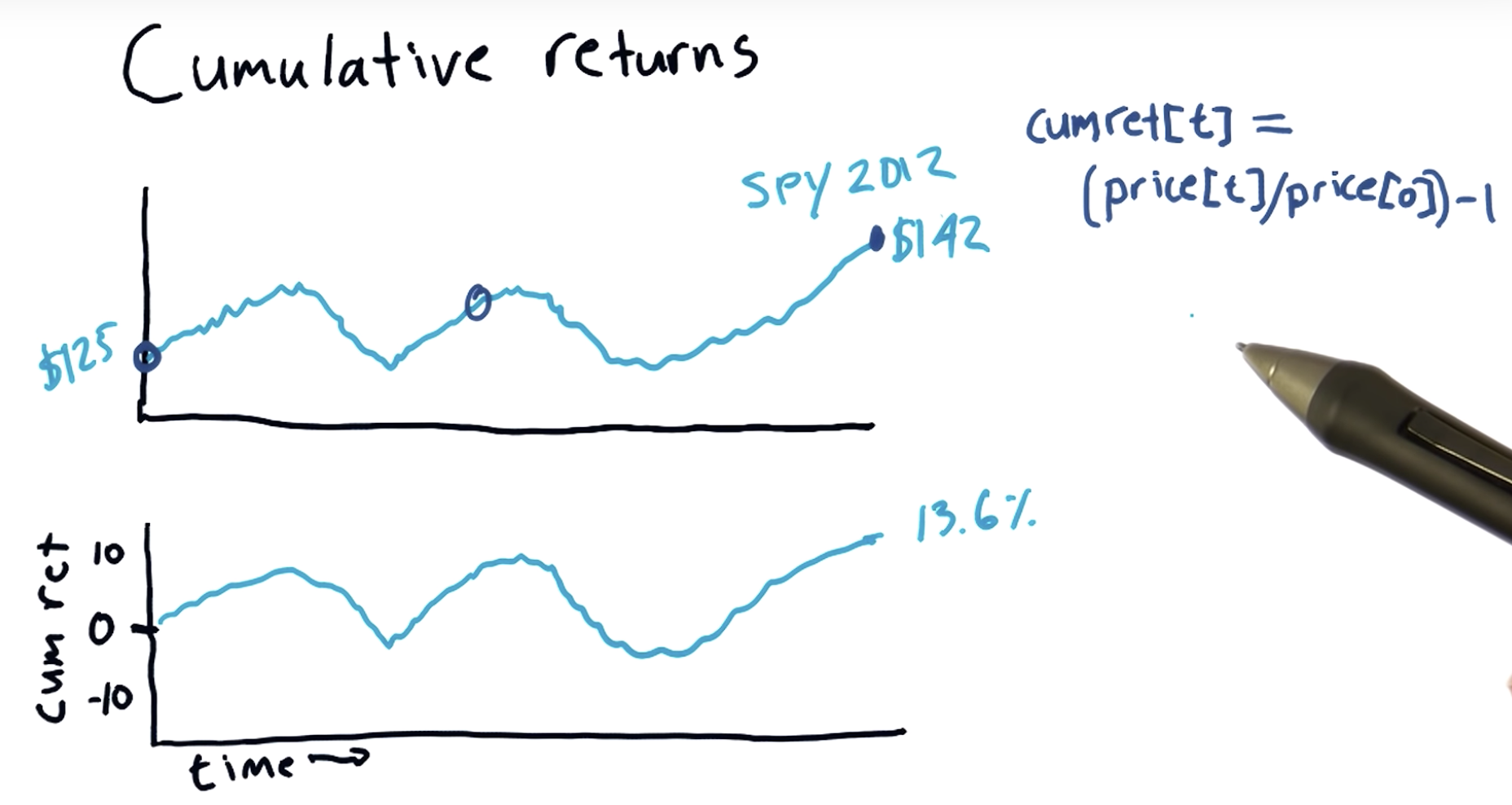
Cumulative returns
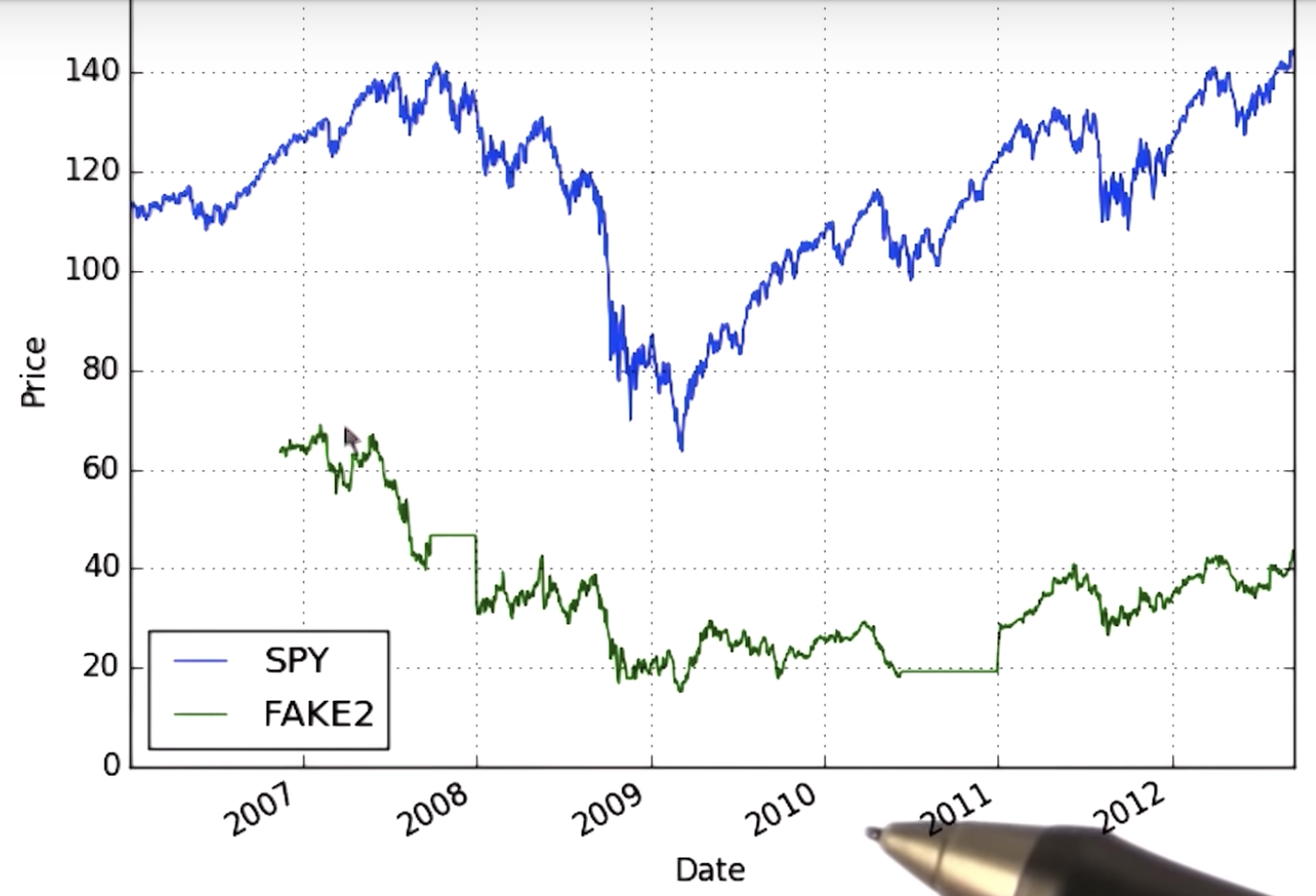
Pristine data

no exact correct price for a stock at a time point
Why data goes missing
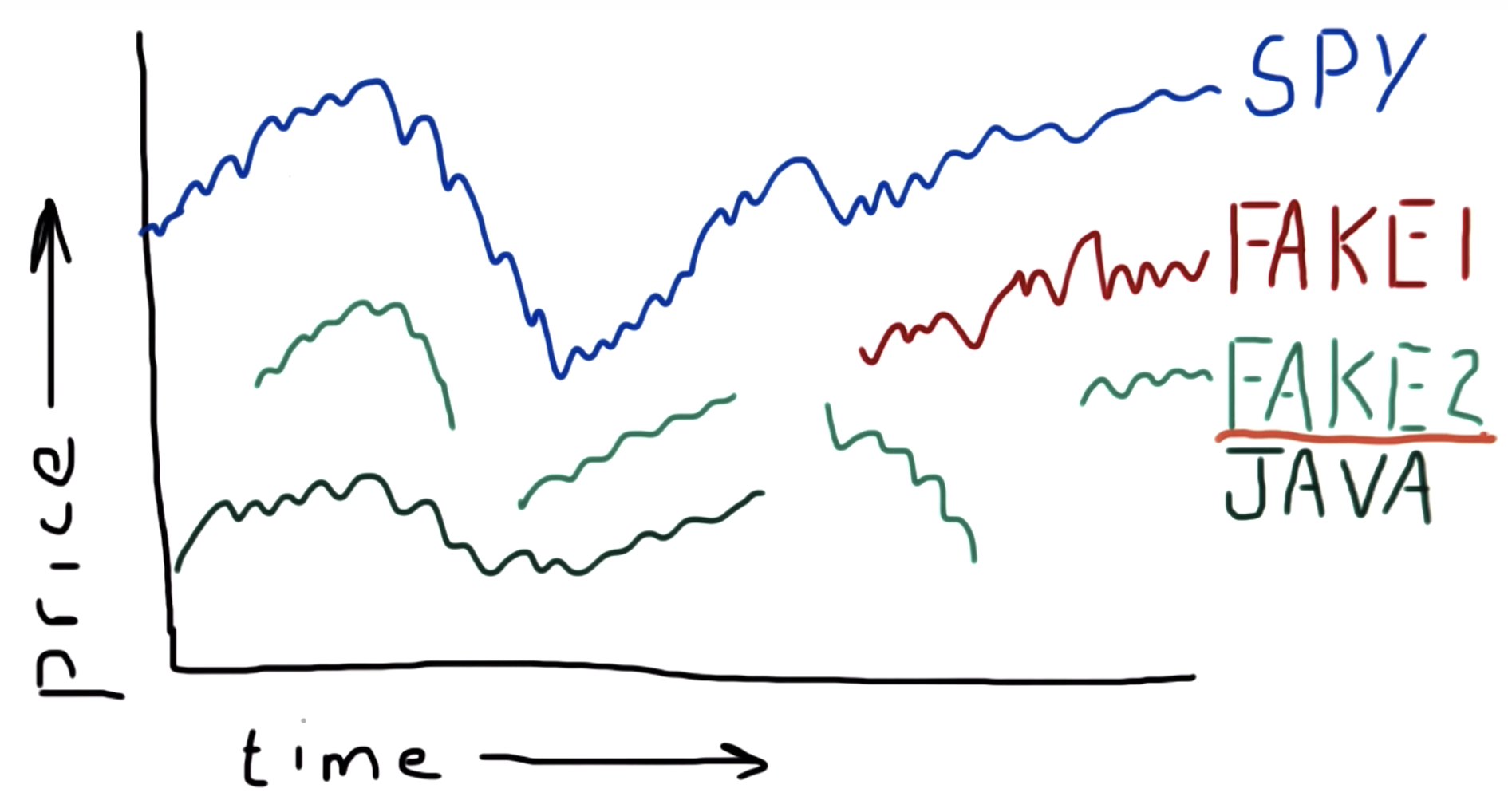
An ETF or Exchange-Traded Fund is a basket of equities allocated in such a way that the overall portfolio tracks the performance of a stock exchange index. ETFs can be bought and sold on the market like shares.
For example, SPY tracks the S&P 500 index (Standard & Poor's selection of 500 large publicly-traded companies).
You will learn more about ETFs and other funds in the second mini-course.
case1: ends
case2: starts
case3: starts and ends occasionally
Why this is bad - what can we do?
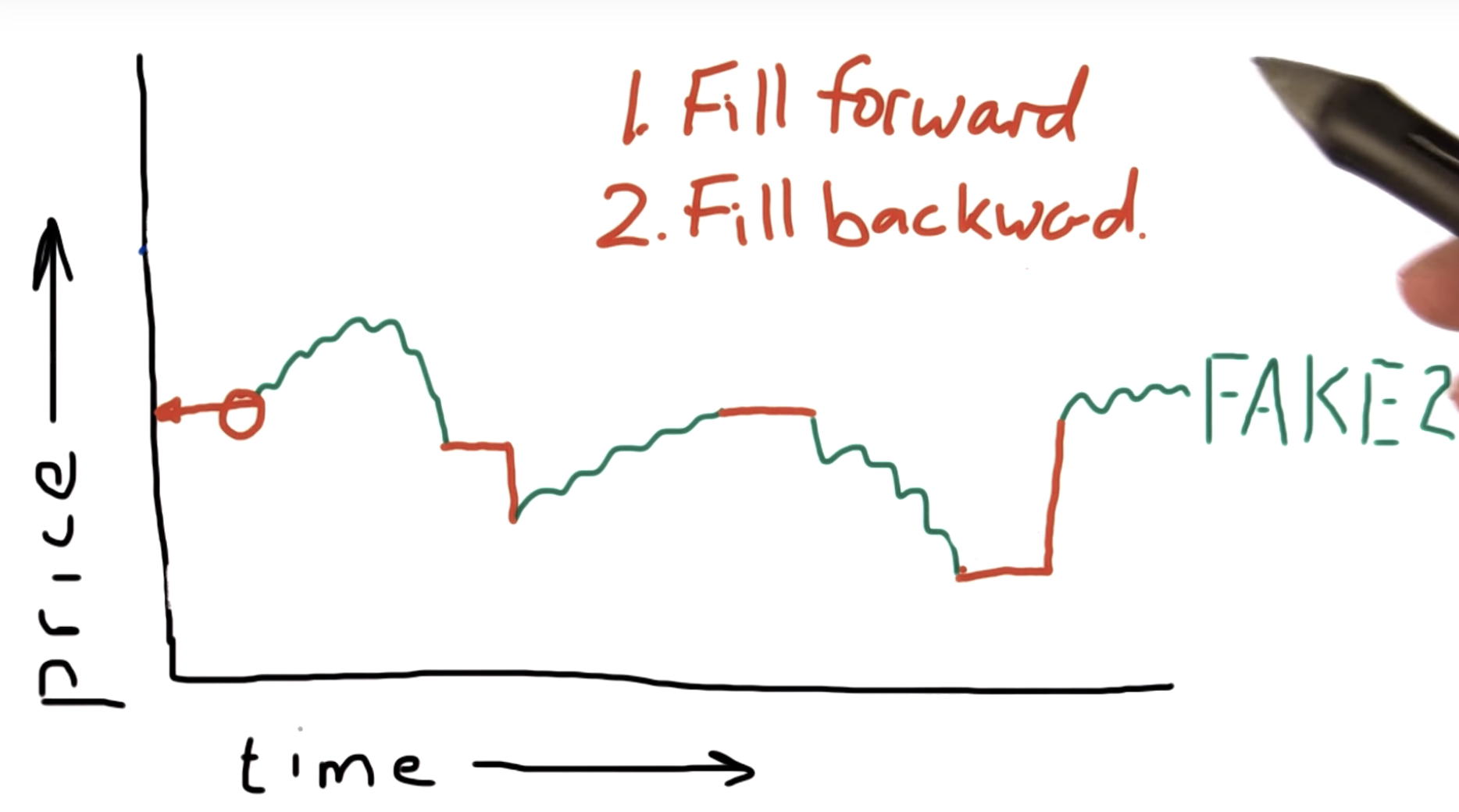
3, dont interpolate
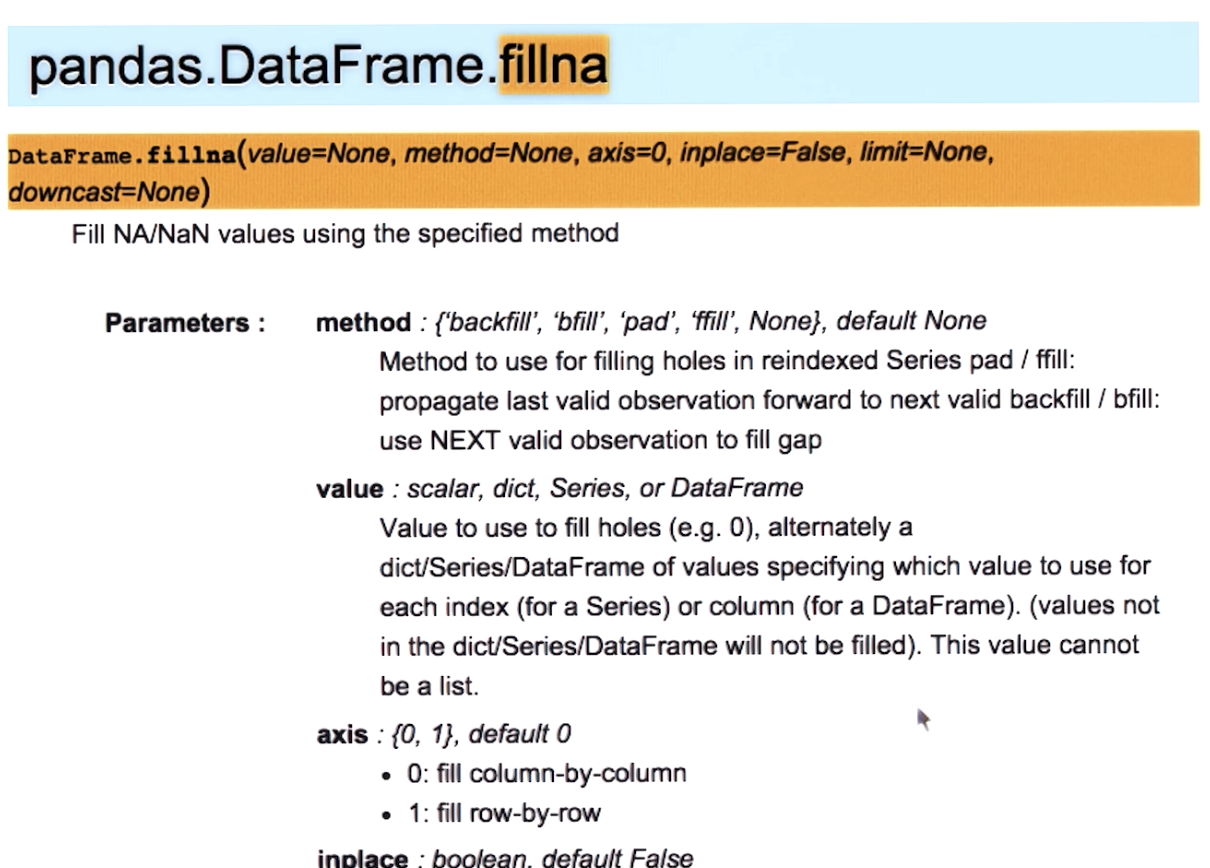
Documentation: pandas
Documentation: pandas.DataFrame.fillna()
You could also use the 'pad' method, same as 'ffill': fillna(method='pad')

Using fillna()
Read about method, inplace and other parameters: pandas.DataFrame.fillna()
Correction: The inplace parameter accepts a boolean value (whereas method accepts a string), so the function call (in line 47) should look like:
df_data.fillna(method="ffill", inplace=True)
Boolean constants in Python are True and False (without quotes).
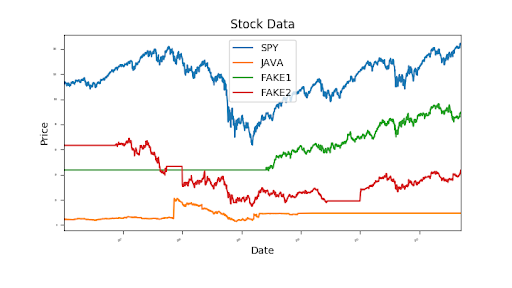
"""Fill missing values""" import numpy as np import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import os def fill_missing_values(df_data): """Fill missing values in data frame, in place.""" df_data.fillna(method="ffill",inplace=True) return df_data.fillna(method="bfill",inplace=True) def symbol_to_path(symbol, base_dir="data"): """Return CSV file path given ticker symbol.""" return os.path.join(base_dir, "{}.csv".format(str(symbol))) def get_data(symbols, dates): """Read stock data (adjusted close) for given symbols from CSV files.""" df_final = pd.DataFrame(index=dates) if "SPY" not in symbols: # add SPY for reference, if absent symbols.insert(0, "SPY") for symbol in symbols: file_path = symbol_to_path(symbol) df_temp = pd.read_csv(file_path, parse_dates=True, index_col="Date", usecols=["Date", "Adj Close"], na_values=["nan"]) df_temp = df_temp.rename(columns={"Adj Close": symbol}) df_final = df_final.join(df_temp) if symbol == "SPY": # drop dates SPY did not trade df_final = df_final.dropna(subset=["SPY"]) return df_final def plot_data(df_data): """Plot stock data with appropriate axis labels.""" ax = df_data.plot(title="Stock Data", fontsize=2) ax.set_xlabel("Date") ax.set_ylabel("Price") plt.show() def test_run(): """Function called by Test Run.""" # Read data symbol_list = ["JAVA", "FAKE1", "FAKE2"] # list of symbols start_date = "2005-12-31" end_date = "2014-12-07" dates = pd.date_range(start_date, end_date) # date range as index df_data = get_data(symbol_list, dates) # get data for each symbol # Fill missing values fill_missing_values(df_data) # Plot plot_data(df_data) if __name__ == "__main__": test_run()