顺序栈
代码:
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include<malloc.h> typedef struct stack{ int *top; int *base; int size; }stack,*Pstack; init_stack(Pstack p,int size){ p->base=(Pstack)malloc(sizeof(stack)*size); p->top=p->base; p->size=size; } push_stack(Pstack p,int data){ *p->top=data; p->top++; } pop_stack(Pstack p){ int val; val=*--p->top; printf("出栈:%d ",val); } travel_stack(Pstack p){ while(p->top!=p->base){ printf("值:%d ",*(p->top-1)); p->top--; } } int main() { stack p; init_stack(&p,10); travel_stack(&p); push_stack(&p,11); push_stack(&p,22); push_stack(&p,33); push_stack(&p,44); pop_stack(&p); pop_stack(&p); travel_stack(&p); }
结果:
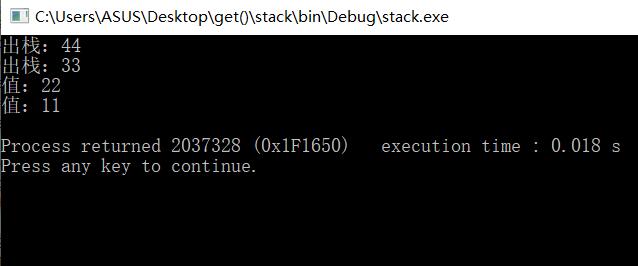
唯一要注意的是栈的出栈和入栈时指针是先增还是后增,这直接影响程序结果。
众所周知,入栈时,top指针后增,出栈时top指针先减。
队列
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include<malloc.h>
typedef struct Node{
int data;
struct Node * next;
}Node,*PNode;
typedef struct Queue{
PNode front;
PNode rear;
}Queue,*PQueue;
init_Queue(PQueue p){
p->front=(PNode)malloc(sizeof(Node));
p->front=p->rear;
p->front->next=NULL;
}
enQueue(PQueue p,int data){
PNode pNew;
pNew=(PNode)malloc(sizeof(Node));
pNew->data=data;
pNew->next=NULL;
p->rear->next=pNew;
p->rear=pNew;
}
exQueue(PQueue p){
PNode q;
q=p->front->next;
p->front->next=q->next;
free(q);
}
travel_Queue(PQueue p){
PNode q;
q=p->front->next;
while(q!=NULL){
printf("值:%d
",q->data);
q=q->next;
}
}
int main(){
Queue p;
init_Queue(&p);
enQueue(&p,10);
enQueue(&p,13);
enQueue(&p,4);
enQueue(&p,9);
exQueue(&p);
travel_Queue(&p);
}
队列有队头和队尾,这边是分别给队头和队尾一个独立的空间,所以定义了两个结构体,队头和队尾的结构体有front和rear两个指针,空间用的是Node结构体的空间
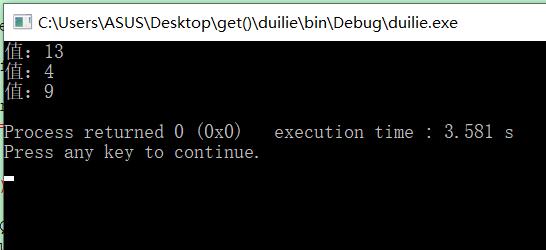
运行结果:
入队列3个数,出队列1个数,剩2个数