1.Mini-batch 梯度下降(Mini-batch gradient descent)
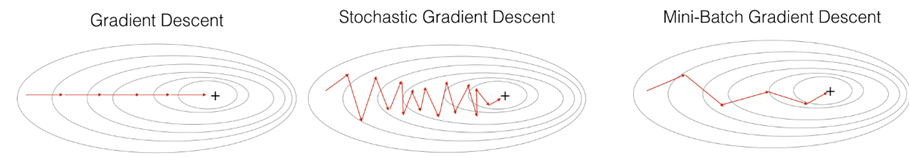
batch gradient descent :一次迭代同时处理整个train data
Mini-batch gradient descent: 一次迭代处理单一的mini-batch (X{t} ,Y{t})

Choosing your mini-batch size : if train data m<2000 then batch ,else mini-batch=64~512 (2的n次方),需要多次尝试来确定mini-batch size
A variant of this is Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD), which is equivalent to mini-batch gradient descent where each mini-batch has just 1 example. The update rule that you have just implemented does not change. What changes is that you would be computing gradients on just one training example at a time, rather than on the whole training set. The code examples below illustrate the difference between stochastic gradient descent and (batch) gradient descent.
- (Batch) Gradient Descent:
X = data_input
Y = labels
parameters = initialize_parameters(layers_dims)
for i in range(0, num_iterations):
# Forward propagation
a, caches = forward_propagation(X, parameters)
# Compute cost.
cost = compute_cost(a, Y)
# Backward propagation.
grads = backward_propagation(a, caches, parameters)
# Update parameters.
parameters = update_parameters(parameters, grads)
- Stochastic Gradient Descent:
X = data_input
Y = labels
parameters = initialize_parameters(layers_dims)
for i in range(0, num_iterations):
for j in range(0, m):
# Forward propagation
a, caches = forward_propagation(X[:,j], parameters)
# Compute cost
cost = compute_cost(a, Y[:,j])
# Backward propagation
grads = backward_propagation(a, caches, parameters)
# Update parameters.
parameters = update_parameters(parameters, grads)
1 def random_mini_batches(X, Y, mini_batch_size = 64, seed = 0): 2 """ 3 Creates a list of random minibatches from (X, Y) 4 5 Arguments: 6 X -- input data, of shape (input size, number of examples) 7 Y -- true "label" vector (1 for blue dot / 0 for red dot), of shape (1, number of examples) 8 mini_batch_size -- size of the mini-batches, integer 9 10 Returns: 11 mini_batches -- list of synchronous (mini_batch_X, mini_batch_Y) 12 """ 13 14 np.random.seed(seed) # To make your "random" minibatches the same as ours 15 m = X.shape[1] # number of training examples 16 mini_batches = [] 17 18 # Step 1: Shuffle (X, Y) 19 permutation = list(np.random.permutation(m)) 20 shuffled_X = X[:, permutation] 21 shuffled_Y = Y[:, permutation].reshape((1,m)) 22 23 # Step 2: Partition (shuffled_X, shuffled_Y). Minus the end case. 24 num_complete_minibatches = math.floor(m/mini_batch_size) # number of mini batches of size mini_batch_size in your partitionning 25 for k in range(0, num_complete_minibatches): 26 ### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 2 lines) 27 mini_batch_X = shuffled_X[:,k*mini_batch_size:(k+1)*mini_batch_size] 28 mini_batch_Y = shuffled_Y[:,k*mini_batch_size:(k+1)*mini_batch_size] 29 ### END CODE HERE ### 30 mini_batch = (mini_batch_X, mini_batch_Y) 31 mini_batches.append(mini_batch) 32 33 # Handling the end case (last mini-batch < mini_batch_size) 34 if m % mini_batch_size != 0: 35 ### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 2 lines) 36 mini_batch_X =shuffled_X[:,(k+1)*mini_batch_size:m] 37 mini_batch_Y =shuffled_Y[:,(k+1)*mini_batch_size:m] 38 ### END CODE HERE ### 39 mini_batch = (mini_batch_X, mini_batch_Y) 40 mini_batches.append(mini_batch) 41 42 return mini_batches
2.指数加权平均数(Exponentially weighted averages):
指数加权平均数的公式: 在计算时可视Vt 大概是1/(1-B)的每日温度,如果B是0.9,那么就是十天的平均值,当B较大时, 指数加权平均值适应更缓慢
在计算时可视Vt 大概是1/(1-B)的每日温度,如果B是0.9,那么就是十天的平均值,当B较大时, 指数加权平均值适应更缓慢
指数加权平均的偏差修正:

3.动量梯度下降法(Gradinent descent with Momentum)

1 def initialize_velocity(parameters): 2 """ 3 Initializes the velocity as a python dictionary with: 4 - keys: "dW1", "db1", ..., "dWL", "dbL" 5 - values: numpy arrays of zeros of the same shape as the corresponding gradients/parameters. 6 Arguments: 7 parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters. 8 parameters['W' + str(l)] = Wl 9 parameters['b' + str(l)] = bl 10 11 Returns: 12 v -- python dictionary containing the current velocity. 13 v['dW' + str(l)] = velocity of dWl 14 v['db' + str(l)] = velocity of dbl 15 """ 16 17 L = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural networks 18 v = {} 19 20 # Initialize velocity 21 for l in range(L): 22 ### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 2 lines) 23 v["dW" + str(l+1)] = np.zeros(parameters["W"+str(l+1)].shape) 24 v["db" + str(l+1)] = np.zeros(parameters["b"+str(l+1)].shape) 25 ### END CODE HERE ### 26 27 return v
1 def update_parameters_with_momentum(parameters, grads, v, beta, learning_rate): 2 """ 3 Update parameters using Momentum 4 5 Arguments: 6 parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters: 7 parameters['W' + str(l)] = Wl 8 parameters['b' + str(l)] = bl 9 grads -- python dictionary containing your gradients for each parameters: 10 grads['dW' + str(l)] = dWl 11 grads['db' + str(l)] = dbl 12 v -- python dictionary containing the current velocity: 13 v['dW' + str(l)] = ... 14 v['db' + str(l)] = ... 15 beta -- the momentum hyperparameter, scalar 16 learning_rate -- the learning rate, scalar 17 18 Returns: 19 parameters -- python dictionary containing your updated parameters 20 v -- python dictionary containing your updated velocities 21 """ 22 23 L = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural networks 24 25 # Momentum update for each parameter 26 for l in range(L): 27 28 ### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 4 lines) 29 # compute velocities 30 v["dW" + str(l+1)] = beta*v["dW" + str(l+1)]+(1-beta)*grads["dW" + str(l+1)] 31 v["db" + str(l+1)] = beta*v["db" + str(l+1)]+(1-beta)*grads["db" + str(l+1)] 32 # update parameters 33 parameters["W" + str(l+1)] = parameters["W" + str(l+1)]-learning_rate*v["dW" + str(l+1)] 34 parameters["b" + str(l+1)] = parameters["b" + str(l+1)]-learning_rate*v["db" + str(l+1)] 35 ### END CODE HERE ### 36 37 return parameters, v
#β=0.9 is often a reasonable default.
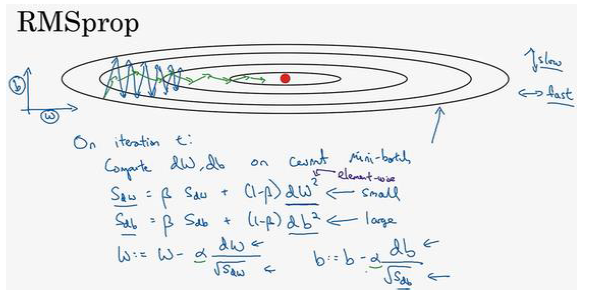
4.RMSprop算法(root mean square prop):
5.Adam 优化算法(Adam optimization algorithm):
Adam 优化算法基本上就是将Momentum 和RMSprop结合在一起



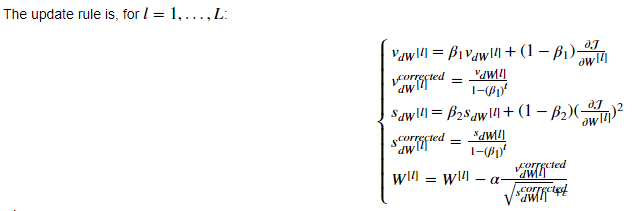
1 def initialize_adam(parameters) : 2 """ 3 Initializes v and s as two python dictionaries with: 4 - keys: "dW1", "db1", ..., "dWL", "dbL" 5 - values: numpy arrays of zeros of the same shape as the corresponding gradients/parameters. 6 7 Arguments: 8 parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters. 9 parameters["W" + str(l)] = Wl 10 parameters["b" + str(l)] = bl 11 12 Returns: 13 v -- python dictionary that will contain the exponentially weighted average of the gradient. 14 v["dW" + str(l)] = ... 15 v["db" + str(l)] = ... 16 s -- python dictionary that will contain the exponentially weighted average of the squared gradient. 17 s["dW" + str(l)] = ... 18 s["db" + str(l)] = ... 19 20 """ 21 22 L = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural networks 23 v = {} 24 s = {} 25 26 # Initialize v, s. Input: "parameters". Outputs: "v, s". 27 for l in range(L): 28 ### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 4 lines) 29 v["dW" + str(l+1)] = np.zeros(parameters["W" + str(l+1)].shape) 30 v["db" + str(l+1)] = np.zeros(parameters["b" + str(l+1)].shape) 31 s["dW" + str(l+1)] = np.zeros(parameters["W" + str(l+1)].shape) 32 s["db" + str(l+1)] = np.zeros(parameters["b" + str(l+1)].shape) 33 ### END CODE HERE ### 34 35 return v, s
1 def update_parameters_with_adam(parameters, grads, v, s, t, learning_rate = 0.01, 2 beta1 = 0.9, beta2 = 0.999, epsilon = 1e-8): 3 """ 4 Update parameters using Adam 5 6 Arguments: 7 parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters: 8 parameters['W' + str(l)] = Wl 9 parameters['b' + str(l)] = bl 10 grads -- python dictionary containing your gradients for each parameters: 11 grads['dW' + str(l)] = dWl 12 grads['db' + str(l)] = dbl 13 v -- Adam variable, moving average of the first gradient, python dictionary 14 s -- Adam variable, moving average of the squared gradient, python dictionary 15 learning_rate -- the learning rate, scalar. 16 beta1 -- Exponential decay hyperparameter for the first moment estimates 17 beta2 -- Exponential decay hyperparameter for the second moment estimates 18 epsilon -- hyperparameter preventing division by zero in Adam updates 19 20 Returns: 21 parameters -- python dictionary containing your updated parameters 22 v -- Adam variable, moving average of the first gradient, python dictionary 23 s -- Adam variable, moving average of the squared gradient, python dictionary 24 """ 25 26 L = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural networks 27 v_corrected = {} # Initializing first moment estimate, python dictionary 28 s_corrected = {} # Initializing second moment estimate, python dictionary 29 30 # Perform Adam update on all parameters 31 for l in range(L): 32 # Moving average of the gradients. Inputs: "v, grads, beta1". Output: "v". 33 ### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 2 lines) 34 v["dW" + str(l+1)] = beta1* v["dW" + str(l+1)]+(1-beta1)*grads["dW" + str(l+1)] 35 v["db" + str(l+1)] = beta1* v["db" + str(l+1)]+(1-beta1)*grads["db" + str(l+1)] 36 ### END CODE HERE ### 37 38 # Compute bias-corrected first moment estimate. Inputs: "v, beta1, t". Output: "v_corrected". 39 ### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 2 lines) 40 v_corrected["dW" + str(l+1)] = (v["dW" + str(l+1)])/(1-np.power(beta1,t)) 41 v_corrected["db" + str(l+1)] = (v["db" + str(l+1)])/(1-np.power(beta1,t)) 42 ### END CODE HERE ### 43 44 # Moving average of the squared gradients. Inputs: "s, grads, beta2". Output: "s". 45 ### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 2 lines) 46 s["dW" + str(l+1)] = beta2* s["dW" + str(l+1)]+(1-beta2)*np.power(grads["dW" + str(l+1)],2) 47 s["db" + str(l+1)] = beta2* s["db" + str(l+1)]+(1-beta2)*np.power(grads["db" + str(l+1)],2) 48 ### END CODE HERE ### 49 50 # Compute bias-corrected second raw moment estimate. Inputs: "s, beta2, t". Output: "s_corrected". 51 ### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 2 lines) 52 s_corrected["dW" + str(l+1)] = s["dW" + str(l+1)]/(1-np.power(beta2,t)) 53 s_corrected["db" + str(l+1)] = s["db" + str(l+1)]/(1-np.power(beta2,t)) 54 ### END CODE HERE ### 55 56 # Update parameters. Inputs: "parameters, learning_rate, v_corrected, s_corrected, epsilon". Output: "parameters". 57 ### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 2 lines) 58 parameters["W" + str(l+1)] = parameters["W" + str(l+1)]-learning_rate*v_corrected["dW" + str(l+1)]/(s_corrected["dW" + str(l+1)]+epsilon) 59 parameters["b" + str(l+1)] = parameters["b" + str(l+1)]-learning_rate*v_corrected["db" + str(l+1)]/(s_corrected["db" + str(l+1)]+epsilon) 60 ### END CODE HERE ### 61 62 return parameters, v, s
6.学习率衰减(Learning rate decay):
加快学习算法的一个办法就是随时间慢慢减少学习率,这样在学习初期,你能承受较大的步伐,当开始收敛的时候,小一些的学习率能让你步伐小一些。


综合练习:
1 def model(X, Y, layers_dims, optimizer, learning_rate = 0.0007, mini_batch_size = 64, beta = 0.9, 2 beta1 = 0.9, beta2 = 0.999, epsilon = 1e-8, num_epochs = 10000, print_cost = True): 3 """ 4 3-layer neural network model which can be run in different optimizer modes. 5 6 Arguments: 7 X -- input data, of shape (2, number of examples) 8 Y -- true "label" vector (1 for blue dot / 0 for red dot), of shape (1, number of examples) 9 layers_dims -- python list, containing the size of each layer 10 learning_rate -- the learning rate, scalar. 11 mini_batch_size -- the size of a mini batch 12 beta -- Momentum hyperparameter 13 beta1 -- Exponential decay hyperparameter for the past gradients estimates 14 beta2 -- Exponential decay hyperparameter for the past squared gradients estimates 15 epsilon -- hyperparameter preventing division by zero in Adam updates 16 num_epochs -- number of epochs 17 print_cost -- True to print the cost every 1000 epochs 18 19 Returns: 20 parameters -- python dictionary containing your updated parameters 21 """ 22 23 L = len(layers_dims) # number of layers in the neural networks 24 costs = [] # to keep track of the cost 25 t = 0 # initializing the counter required for Adam update 26 seed = 10 # For grading purposes, so that your "random" minibatches are the same as ours 27 28 # Initialize parameters 29 parameters = initialize_parameters(layers_dims) 30 31 # Initialize the optimizer 32 if optimizer == "gd": 33 pass # no initialization required for gradient descent 34 elif optimizer == "momentum": 35 v = initialize_velocity(parameters) 36 elif optimizer == "adam": 37 v, s = initialize_adam(parameters) 38 39 # Optimization loop 40 for i in range(num_epochs): 41 42 # Define the random minibatches. We increment the seed to reshuffle differently the dataset after each epoch 43 seed = seed + 1 44 minibatches = random_mini_batches(X, Y, mini_batch_size, seed) 45 46 for minibatch in minibatches: 47 48 # Select a minibatch 49 (minibatch_X, minibatch_Y) = minibatch 50 51 # Forward propagation 52 a3, caches = forward_propagation(minibatch_X, parameters) 53 54 # Compute cost 55 cost = compute_cost(a3, minibatch_Y) 56 57 # Backward propagation 58 grads = backward_propagation(minibatch_X, minibatch_Y, caches) 59 60 # Update parameters 61 if optimizer == "gd": 62 parameters = update_parameters_with_gd(parameters, grads, learning_rate) 63 elif optimizer == "momentum": 64 parameters, v = update_parameters_with_momentum(parameters, grads, v, beta, learning_rate) 65 elif optimizer == "adam": 66 t = t + 1 # Adam counter 67 parameters, v, s = update_parameters_with_adam(parameters, grads, v, s, 68 t, learning_rate, beta1, beta2, epsilon) 69 70 # Print the cost every 1000 epoch 71 if print_cost and i % 1000 == 0: 72 print ("Cost after epoch %i: %f" %(i, cost)) 73 if print_cost and i % 100 == 0: 74 costs.append(cost) 75 76 # plot the cost 77 plt.plot(costs) 78 plt.ylabel('cost') 79 plt.xlabel('epochs (per 100)') 80 plt.title("Learning rate = " + str(learning_rate)) 81 plt.show() 82 83 return parameters