Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null.
Follow up:
Can you solve it without using extra space?
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/x1957/p/3406448.html
比I麻烦点的就是找到循环开始点TAT
I只是判断是否循环。要求不使用额外空间(不然hash就可以了
按I的思路,我们又慢指针S和快指针F。。。F走两步,S走一步。。。若有环,必定相遇。
画个图(很丑勿喷
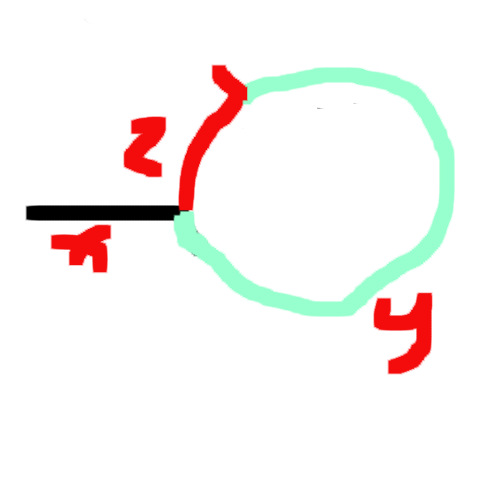
假设在红色凸起的地方相遇了。
F走的路程应该是S的两倍
S = x + y
F = x + y + z + y = x + 2y + z
2*S = F
2x+2y = x + 2y + z
得到x = z
也就是从head到环开始的路程 = 从相遇到环开始的路程
那么。。。只要S和F相遇了,我们拿一个从头开始走,一个从相遇的地方开始走
两个都走一步,那么再次相遇必定是环的开始节点!
代码也很精简,值得学习一下。
1 /** 2 * Definition for singly-linked list. 3 * struct ListNode { 4 * int val; 5 * ListNode *next; 6 * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} 7 * }; 8 */ 9 class Solution { 10 public: 11 ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) { 12 // IMPORTANT: Please reset any member data you declared, as 13 // the same Solution instance will be reused for each test case. 14 if(head == NULL) return NULL; 15 ListNode* S = head; 16 ListNode* F = head; 17 18 while(F != NULL){ 19 if(F) F = F -> next; 20 if(F) F = F -> next; 21 if(S) S = S -> next; 22 if(F != NULL && F == S){ 23 S = head; 24 while(S != F){ 25 S = S -> next; 26 F = F -> next; 27 } 28 return S; 29 } 30 } 31 return NULL; 32 } 33 };
下面是自己写的:
1 /** 2 * Definition for singly-linked list. 3 * struct ListNode { 4 * int val; 5 * ListNode *next; 6 * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} 7 * }; 8 */ 9 class Solution { 10 public: 11 ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) { 12 if (head == NULL) return NULL; 13 ListNode *slow = head, *fast = head; 14 while (slow != NULL && fast != NULL) { 15 if (slow->next != NULL) { 16 slow = slow->next; 17 } else { 18 return NULL; 19 } 20 if (fast->next != NULL) { 21 fast = fast->next; 22 } else { 23 return NULL; 24 } 25 if (fast->next != NULL) { 26 fast = fast->next; 27 } else { 28 return NULL; 29 } 30 if (slow == fast) { 31 break; 32 } 33 } 34 slow = head; 35 while (slow != fast) { 36 slow = slow->next; 37 fast = fast->next; 38 } 39 return slow; 40 } 41 };