因为在设计一个树形结构的实体中用到了多对一,一对多的映射关系,在加载其关联对象的时候,为了性能考虑,很自然的想到了懒加载。
也由此遇到了N+1的典型问题 : 通常1的这方,通过1条SQL查找得到1个对象,而JPA基于Hibernate,fetch策略默认为select(并非联表查询),由于关联的存在 ,又需要将这个对象关联的集合取出,集合数量是N,则要发出N条SQL,于是本来的1条联表查询SQL可解决的问题变成了N+1条SQL
我采取的解决方法是 : 不修改懒加载策略,JPA也不写native SQL,通过联表查询进行解决。
如果对该例子比较感兴趣或者觉得言语表达比较啰嗦,可查看完整的demo地址 : https://github.com/EalenXie/springboot-jpa-N-plus-One
场景如下 :
我设计了一个典型的二叉树结构实体叫做Area,代表的含义是区域 (省、市、区)。省是树的一级根节点,市是省的子节点,区是市的子节点。如 : 广东省,广州市,天河区
1 . Area实体设计采用自关联,关联的子集fetch策略为懒加载。
package name.ealen.entity; import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnore; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; import javax.persistence.*; import java.util.List; /** * Created by EalenXie on 2018/10/16 16:49. * 典型的 多层级 区域关系 */ @Entity @Table(name = "jpa_area") public class Area { /** * Id 使用UUID生成策略 */ @Id @GeneratedValue(generator = "UUID") @GenericGenerator(name = "UUID", strategy = "org.hibernate.id.UUIDGenerator") private String id; /** * 区域名 */ private String name; /** * 一个区域信息下面很多子区域(多级) 比如 : 广东省 (子)区域 : 广州市 (孙)子区域 : 天河区 */ @ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY) @JoinColumn(name = "parent_id") @JsonIgnore private Area parent; @OneToMany(mappedBy = "parent", fetch = FetchType.LAZY) private List<Area> children; public String getId() { return id; } public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Area getParent() { return parent; } public void setParent(Area parent) { this.parent = parent; } public List<Area> getChildren() { return children; } public void setChildren(List<Area> children) { this.children = children; } }
2 . 为Area写一个简单的dao进行数据库访问:AreaRepository
package name.ealen.dao; import name.ealen.entity.Area; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository; /** * Created by EalenXie on 2018/10/16 16:56. */ public interface AreaRepository extends JpaRepository<Area, String> { }
3. 现在来进行一波关键性的测试 : 首先我们插入数据测试 :
@Autowired private AreaRepository areaRepository; /** * 新增区域测试 */ @Test public void addArea() { // 广东省 (顶级区域) Area guangdong = new Area(); guangdong.setName("广东省"); areaRepository.save(guangdong); //广东省 下面的 广州市(二级区域) Area guangzhou = new Area(); guangzhou.setName("广州市"); guangzhou.setParent(guangdong); areaRepository.save(guangzhou); //广州市 下面的 天河区(三级区域) Area tianhe = new Area(); tianhe.setName("天河区"); tianhe.setParent(guangzhou); areaRepository.save(tianhe); //广东省 下面的 湛江市(二级区域) Area zhanjiang = new Area(); zhanjiang.setName("湛江市"); zhanjiang.setParent(guangdong); areaRepository.save(zhanjiang); //湛江市 下面的 霞山区(三级区域) Area xiashan = new Area(); xiashan.setName("霞山区"); xiashan.setParent(zhanjiang); areaRepository.save(xiashan); }
4 . 进行查询,并触发懒加载 :
/** * 触发懒加载查询 典型的 N+1 现象 */ @Test @Transactional public void findAllArea() { List<Area> areas = areaRepository.findAll(); System.out.println(JSONArray.toJSONString(areas.get(0))); }
此时,我们可以在控制台中看到,触发了懒加载,导致了N+1的问题。

上面我们首先发出 1 条SQL查出了所有的Area对象,然后为了取第一个中的关联对象发了5条SQL。
解决的方法如下 :
1 . 首先在实体上面注解@NamedEntityGraph,指明name供查询方法使用,attributeNodes 指明被标注为懒加载的属性节点
如下 : Category实体
package name.ealen.entity; import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnore; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; import javax.persistence.*; import java.util.Set; /** * Created by EalenXie on 2018/10/16 16:13. * 典型的 多层级 分类 * <p> * :@NamedEntityGraph :注解在实体上 , 解决典型的N+1问题 * name表示实体图名, 与 repository中的注解 @EntityGraph的value属性相对应, * attributeNodes 表示被标注要懒加载的属性节点 比如此例中 : 要懒加载的子分类集合children */ @Entity @Table(name = "jpa_category") @NamedEntityGraph(name = "Category.Graph", attributeNodes = {@NamedAttributeNode("children")}) public class Category { /** * Id 使用UUID生成策略 */ @Id @GeneratedValue(generator = "UUID") @GenericGenerator(name = "UUID", strategy = "org.hibernate.id.UUIDGenerator") private String id; /** * 分类名 */ private String name; /** * 一个商品分类下面可能有多个商品子分类(多级) 比如 分类 : 家用电器 (子)分类 : 电脑 (孙)子分类 : 笔记本电脑 */ @ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY) @JoinColumn(name = "parent_id") @JsonIgnore private Category parent; //父分类 @OneToMany(mappedBy = "parent", fetch = FetchType.LAZY) private Set<Category> children; //子分类集合 public String getId() { return id; } public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Category getParent() { return parent; } public void setParent(Category parent) { this.parent = parent; } public Set<Category> getChildren() { return children; } public void setChildren(Set<Category> children) { this.children = children; } }
2 . 在访问的dao的查询方法上面注解@EntityGraph,value属性值为@NamedEntityGraph的name属性值,如 CategoryRepository :
package name.ealen.dao; import name.ealen.entity.Category; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.EntityGraph; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository; import java.util.List; /** * Created by EalenXie on 2018/10/16 16:19. */ public interface CategoryRepository extends JpaRepository<Category, String> { /** * 解决 懒加载 JPA 典型的 N + 1 问题 */ @EntityGraph(value = "Category.Graph", type = EntityGraph.EntityGraphType.FETCH) List<Category> findAll(); }
3 . 进行测试 : 新增一些分类
@Autowired private CategoryRepository categoryRepository; /** * 新增分类测试 */ @Test public void addCategory() { //一个 家用电器分类(顶级分类) Category appliance = new Category(); appliance.setName("家用电器"); categoryRepository.save(appliance); //家用电器 下面的 电脑分类(二级分类) Category computer = new Category(); computer.setName("电脑"); computer.setParent(appliance); categoryRepository.save(computer); //电脑 下面的 笔记本电脑分类(三级分类) Category notebook = new Category(); notebook.setName("笔记本电脑"); notebook.setParent(computer); categoryRepository.save(notebook); //家用电器 下面的 手机分类(二级分类) Category mobile = new Category(); mobile.setName("手机"); mobile.setParent(appliance); categoryRepository.save(mobile); //手机 下面的 智能机 / 老人机(三级分类) Category smartPhone = new Category(); smartPhone.setName("智能机"); smartPhone.setParent(mobile); categoryRepository.save(smartPhone); Category oldPhone = new Category(); oldPhone.setName("老人机"); oldPhone.setParent(mobile); categoryRepository.save(oldPhone); }
进行查询 ,并触发懒加载 :
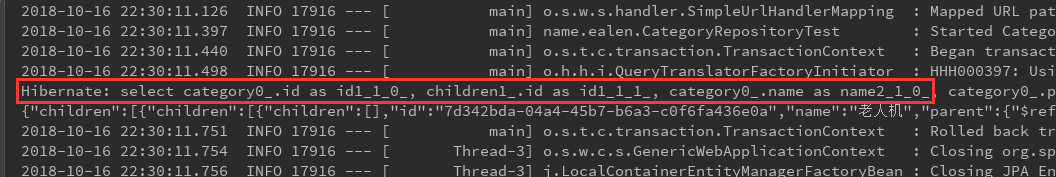
/** * 查找分类测试 已经解决了经典的 N+1 问题 */ @Test @Transactional public void findCategory() { List<Category> categories = categoryRepository.findAll(); for (Category category : categories) { System.out.println(JSONArray.toJSONString(category)); } }
此时可以看到控制台里面只发了一条联表查询就得到了关联对象。