采用部分快速排序算法实现数组的部分排序
Author: Eaglet
快速排序算法,网上相关文章已经介绍的很多了,数据结构教材中也有很详细的介绍。本文需要阐述的不是全排序快速排序算法,而是部分快速排序算法。所谓部分快速排序算法是指通过排序获取一个数列中最大的若干条有序记录。比如我们需要从一个有1百万记录的数组中获取前100条有序记录,并按从大到小顺序显示给用户,这种应用在搜索引擎中经常被使用,很少会有人有耐心将100万条搜索出来的记录都阅读一遍,一般阅读前几百条纪录就可以得到自己满意的答案。其实这种算法很像SQLSERVER 中的 TOP n 的实现,不过数据库是预先已经将记录通过B+树索引的方式进行了组织,实现方法完全不同。本文需要阐述的是不通过数据库,如何高效完成Top n 这种部分排序的功能。
在开始之前,我们先来分析一下2种其他的排序方法,如果进行部分排序。
1. 选择排序
选择排序方法实现部分排序非常简单,如果你需要获取长度为M的数组中前N条排序记录,你只需要对M条记录进行N次扫描,每次扫描都找出剩余序列中的最大(或最小值)就可以完成。当N 远小于 M 时,选择排序的时间复杂度大概为O(M*N)。
2. 堆排序
对排序可以说是实现部分排序时最常被用到的算法,包括著名的搜索组件Lucene在内都采用了堆排序来实现部分排序。具体算法我在网上找了一个,请参见 部分排序问题 。根据这篇文章所述,堆排序实现部分排序的实现复杂度是 O(MlogN)
现在让我们开始部分快速排序算法。
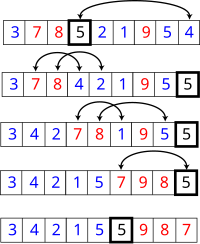
快速排序的一趟排序,可以根据一个基准值将数组分割成两个部分,基准前的所有数都比基准小,基准后的所有数都比基准大。 如上图所示,5 就是这个基准值。全排序的快速排序算法,在实现了一趟排序后,通过递归分别对基准前后的数列再进行相同的排序直到所有数据都有序。
我们可以巧妙的利用这种基准分割的方法来实现部分排序。如果要实现部分排序,我们不需要对所有的数据都进行排序,其实每次只需要对基准的一边进行一趟排序就可以了,其原理很像二分查找。如上图,如果我们希望得到最小的前2个排序数据,我们只需要在第二次排序时对5之前的数列重新做一次一趟排序,而不需要对5之后的数据做,因为5在一趟排序后被排在了第6位,其之后的数据肯定不可能出现在前2位。假设第二次我们选取5之前的数列的中间位置的值2作为基准,那么第二次一趟排序的过程如下
3 4 2 1 5 5 9 8 7
_ 4 3 1 5 5 9 8 7 (2)
1 4 3 _ 5 5 9 8 7 (2)
1 _ 3 4 5 5 9 8 7 (2)
1 2 3 4 5 5 9 8 7
两次一趟排序后,前2条排序记录已经算出,但从结果可以看出,这时整个数列并没有被完全排序,因为我们不需要完整的排序数列。 第二轮的演化过程请参考严蔚敏的数据结构教材,采用的是相同的算法。
下面来分析一下部分快速排序的时间复杂度
理想情况
我们假设理想情况下,每次基准都选择在数列的中间位置,那么其扫描的趟数是
1 + 1/2 + 1/4 + 1/8 ... 1/ K (K = log(M/N)) + NlogN
这个等比级数,如果K趋近为无穷的时候值为2,为什么是2,参考高等数学,这里不多阐述。
那么现在我们可以看出,在这种情况下时间复杂度 < O(2M + NlogN), 当N远小于M时,时间复杂度近似为小于 O(2M)
这个时间复杂度在N>4时要比部分堆排序的 O(MlogN)要小,而且随着N 的增大,部分快速排序的优势越来越明显。
最佳情况
最佳情况并不是每次基准都出现的中间位置,而是第一趟排序选择的基准正好位于第N个位置。这时时间复杂度为O(M)
最坏情况
每次基准出现在M-i 的位置,这时时间复杂度为 O (M*M)
下面是测试结果:
测试1 数组中为随机数据,数组长度M从2的16次方到2的22次方,N=100,每组长度下测试100次计算平均用时
| 平均用时(单位毫秒)/ 数组长度 |
65536 | 131072 | 262144 | 524288 | 1024857 | 2097152 | 41944304 |
| 部分快速排序 | 0.55 | 1.61 | 3.13 | 7.46 | 13.04 | 30.1 | 62.96 |
| 完全快速排序 | 10.45 | 21.85 | 45.55 | 93.97 | 197.3 | 405.54 | 841.75 |
测试2 数组中为以排序好的数据,数组长度M从2的16次方到2的22次方,N=100,每组长度下测试100次计算平均用时
| 平均用时(单位毫秒)/ 数组长度 |
65536 | 131072 | 262144 | 524288 | 1024857 | 2097152 | 41944304 |
| 部分快速排序 | 0.03 | 0 | 0.11 | 1.12 | 3.04 | 6.66 | 12.87 |
| 完全快速排序 | 2.12 | 4.9 | 10.49 | 21.6 | 44.29 | 91 | 185.77 |
从测试结果看采用部分快速排序获取前100条有序记录要比采用完全快速排序要快10到100倍。
下面给出代码,由于.Net的Array.Sort就是完全快速排序,所以直接使用,没有自己实现完全快速排序。
QuickSort 类
 using System;
using System; using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Text;
using System.Text;
 namespace Sort
namespace Sort {
{ /// <summary>
/// <summary> /// Quick Sort
/// Quick Sort /// </summary>
/// </summary> /// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>
/// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam> public class QuickSort<T>
public class QuickSort<T> {
{ //Partition for int
//Partition for int private static int PartitionInt(int[] array, int low, int high, int pivotIndex)
private static int PartitionInt(int[] array, int low, int high, int pivotIndex) {
{ int pivotValue = array[pivotIndex];
int pivotValue = array[pivotIndex]; array[pivotIndex] = array[low];
array[pivotIndex] = array[low]; array[low] = pivotValue;
array[low] = pivotValue;
 while (low < high)
while (low < high) {
{ while (array[high] >= pivotValue && high > low)
while (array[high] >= pivotValue && high > low) {
{ --high;
--high; }
}
 if (high > low)
if (high > low) {
{ array[low] = array[high];
array[low] = array[high]; }
}
 while (array[low] <= pivotValue && high > low)
while (array[low] <= pivotValue && high > low) {
{ ++low;
++low; }
}
 if (high > low)
if (high > low) {
{ array[high] = array[low];
array[high] = array[low]; }
}
 }
}
 array[low] = pivotValue;
array[low] = pivotValue;
 return low;
return low; }
}
 //Partition for long
//Partition for long  private static int PartitionLong(long[] array, int low, int high, int pivotIndex)
private static int PartitionLong(long[] array, int low, int high, int pivotIndex) {
{ long pivotValue = array[pivotIndex];
long pivotValue = array[pivotIndex]; array[pivotIndex] = array[low];
array[pivotIndex] = array[low]; array[low] = pivotValue;
array[low] = pivotValue;
 while (low < high)
while (low < high) {
{ while (array[high] >= pivotValue && high > low)
while (array[high] >= pivotValue && high > low) {
{ --high;
--high; }
}
 if (high > low)
if (high > low) {
{ array[low] = array[high];
array[low] = array[high]; }
}
 while (array[low] <= pivotValue && high > low)
while (array[low] <= pivotValue && high > low) {
{ ++low;
++low; }
}
 if (high > low)
if (high > low) {
{ array[high] = array[low];
array[high] = array[low]; }
}
 }
}
 array[low] = pivotValue;
array[low] = pivotValue;
 return low;
return low; }
}
 //Normal Partition
//Normal Partition private static int Partition(T[] array, int low, int high, int pivotIndex, IComparer<T> comparer)
private static int Partition(T[] array, int low, int high, int pivotIndex, IComparer<T> comparer) {
{ if (comparer == null)
if (comparer == null) {
{ Array arr = array;
Array arr = array;
 if (typeof(T) == typeof(int))
if (typeof(T) == typeof(int)) {
{ return PartitionInt((int[])arr, low, high, pivotIndex);
return PartitionInt((int[])arr, low, high, pivotIndex); }
} else if (typeof(T) == typeof(long))
else if (typeof(T) == typeof(long)) {
{ return PartitionLong((long[])arr, low, high, pivotIndex);
return PartitionLong((long[])arr, low, high, pivotIndex); }
} }
}
 T pivotValue = array[pivotIndex];
T pivotValue = array[pivotIndex]; T pLow = array[low];
T pLow = array[low];
 while (low < high)
while (low < high) {
{ while (comparer.Compare(array[high], pivotValue) >= 0 && high > low)
while (comparer.Compare(array[high], pivotValue) >= 0 && high > low) {
{ --high;
--high; }
}
 if (high > low)
if (high > low) {
{ array[low] = array[high];
array[low] = array[high]; }
}
 while (comparer.Compare(array[low], pivotValue) <= 0 && high > low)
while (comparer.Compare(array[low], pivotValue) <= 0 && high > low) {
{ ++low;
++low; }
}
 if (high > low)
if (high > low) {
{ array[high] = array[low];
array[high] = array[low]; }
}
 }
}
 array[low] = pLow;
array[low] = pLow;
 return low;
return low; }
}
 public static void TopSort(T[] array, int top)
public static void TopSort(T[] array, int top) {
{ TopSort(array, top, null);
TopSort(array, top, null); }
}
 public static void TopSort(T[] array, int top, IComparer<T> comparer)
public static void TopSort(T[] array, int top, IComparer<T> comparer) {
{ //If comparer is null
//If comparer is null if (comparer == null)
if (comparer == null) {
{ Array arr = array;
Array arr = array;
 if (typeof(T) != typeof(int) &&
if (typeof(T) != typeof(int) && typeof(T) != typeof(long))
typeof(T) != typeof(long)) {
{ Array.Sort(array);
Array.Sort(array); return;
return; }
} }
}
 //Judge input
//Judge input if (array.Length <= 2 || top >= array.Length / 2)
if (array.Length <= 2 || top >= array.Length / 2) {
{ Array.Sort(array, comparer);
Array.Sort(array, comparer); return;
return; }
}
 //One time partition
//One time partition int pivot = Partition(array, 0, array.Length - 1, array.Length / 2, comparer);
int pivot = Partition(array, 0, array.Length - 1, array.Length / 2, comparer); int lastPivot = pivot;
int lastPivot = pivot;
 //Run until pivot near the top
//Run until pivot near the top while ((!(lastPivot >= top && pivot <= top)))
while ((!(lastPivot >= top && pivot <= top))) {
{ lastPivot = pivot;
lastPivot = pivot;
 if (pivot > top)
if (pivot > top) {
{ pivot = Partition(array, 0, pivot, pivot/2, comparer);
pivot = Partition(array, 0, pivot, pivot/2, comparer);
 if (pivot == lastPivot)
if (pivot == lastPivot) {
{ pivot--;
pivot--; }
} }
} else
else {
{ if (pivot >= array.Length - 1)
if (pivot >= array.Length - 1) {
{ lastPivot = array.Length - 1;
lastPivot = array.Length - 1; break;
break; }
}
 pivot = Partition(array, pivot + 1, array.Length -1, (array.Length - pivot) / 2, comparer);
pivot = Partition(array, pivot + 1, array.Length -1, (array.Length - pivot) / 2, comparer); }
} }
}
 //Finally sort
//Finally sort if (lastPivot < array.Length)
if (lastPivot < array.Length) {
{ Array.Sort(array, 0, lastPivot + 1, comparer);
Array.Sort(array, 0, lastPivot + 1, comparer); }
} else
else {
{ Array.Sort(array, 0, lastPivot, comparer);
Array.Sort(array, 0, lastPivot, comparer); }
} }
} }
} }
}
测试代码
 static void Main(string[] args)
static void Main(string[] args) {
{ int[] testArr = null;
int[] testArr = null; int[] testArr1 = null;
int[] testArr1 = null; Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch();
Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch(); List<int> testValues = new List<int>();
List<int> testValues = new List<int>();
 Random rand = new Random();
Random rand = new Random();
 int pow = 16;
int pow = 16;
 int count = (int)Math.Pow(2, pow);
int count = (int)Math.Pow(2, pow); int top = 100;
int top = 100;
 while (pow < 23)
while (pow < 23) {
{ Console.WriteLine(string.Format("Test count={0}", count));
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("Test count={0}", count));
 double topSortElapsedMilliseconds = 0;
double topSortElapsedMilliseconds = 0; double fullSortElapsedMilliseconds = 0;
double fullSortElapsedMilliseconds = 0;
 for (int j = 0; j < 100; j++)
for (int j = 0; j < 100; j++) {
{
 testValues.Clear();
testValues.Clear();
 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
{ testValues.Add(rand.Next());
testValues.Add(rand.Next()); //testValues.Add(i);
//testValues.Add(i); }
}
 testArr = new int[testValues.Count];
testArr = new int[testValues.Count]; testArr1 = new int[testValues.Count];
testArr1 = new int[testValues.Count];
 testValues.CopyTo(testArr);
testValues.CopyTo(testArr); testValues.CopyTo(testArr1);
testValues.CopyTo(testArr1);
 sw.Reset();
sw.Reset(); sw.Start();
sw.Start(); Sort.QuickSort<int>.TopSort(testArr, top);
Sort.QuickSort<int>.TopSort(testArr, top);
 sw.Stop();
sw.Stop();
 topSortElapsedMilliseconds += sw.ElapsedMilliseconds;
topSortElapsedMilliseconds += sw.ElapsedMilliseconds;
 sw.Reset();
sw.Reset(); sw.Start();
sw.Start(); Array.Sort(testArr1);
Array.Sort(testArr1);
 sw.Stop();
sw.Stop();
 fullSortElapsedMilliseconds += sw.ElapsedMilliseconds;
fullSortElapsedMilliseconds += sw.ElapsedMilliseconds;
 //Compare result
//Compare result for (int i = 0; i < top; i++)
for (int i = 0; i < top; i++) {
{ if (testArr[i] != testArr1[i])
if (testArr[i] != testArr1[i]) {
{ Console.WriteLine(string.Format("Wrong at {0}! {1} {2}",
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("Wrong at {0}! {1} {2}",  i, testArr[i], testArr1[i]));
i, testArr[i], testArr1[i]));
 Console.ReadKey();
Console.ReadKey();
 //For test
//For test while (true)
while (true) {
{ testValues.CopyTo(testArr);
testValues.CopyTo(testArr); Sort.QuickSort<int>.TopSort(testArr, top);
Sort.QuickSort<int>.TopSort(testArr, top); }
} }
} }
}
 }
}
 Console.WriteLine(string.Format("Top sort elapses {0} ms",
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("Top sort elapses {0} ms",  topSortElapsedMilliseconds/100));
topSortElapsedMilliseconds/100)); Console.WriteLine(string.Format("Full sort elapses {0} ms",
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("Full sort elapses {0} ms", fullSortElapsedMilliseconds/100));
fullSortElapsedMilliseconds/100));
 count *= 2;
count *= 2; pow++;
pow++; }
}
 Console.ReadKey();
Console.ReadKey();
 }
}


