本文列举常见的java定时任务实现方式,并做一定比较。
1. 循环内部sleep实现周期执行
创建一个thread,run() while循环里sleep()来实现周期性执行; 简单粗暴,作为一个初学者很容易想到。
public class Task1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// run in a second
final long timeInterval = 1000;
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
while (true) {
System.out.println("Hello !!");
// 使用线程休眠来实现周期执行,
try {
Thread.sleep(timeInterval);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
};
Thread thread = new Thread(runnable);
thread.start();
}
}
2. 使用Timer类调度TimerTask任务
改进:当启动和去取消任务时可以控制; 第一次执行任务时可以指定你想要的delay时间
不足:
- Timer的调度是基于绝对时间的,所以当系统时间改变时会影响Timer。
- Timer只有一个工作线程,所以当一个任务执行时间很长的时候,会影响后续任务的调度。
而ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor通过线程池的方式配置更灵活。 - 如果任务抛出了一个未检查的异常,将会导致Timer的工作线程被终止,使Timer无法在继续运行。
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
public class HelperTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 具体任务。
TimerTask task = new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
// task to run goes here
System.out.println("Hello !!!");
}
};
// Timer类可以调度任务。 Timer实例可以调度多任务,它是线程安全的。
Timer timer = new Timer();
long delay = 0;
long intevalPeriod = 1 * 1000;
// schedules the task to be run in an interval
timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(task, delay, intevalPeriod);
}
}
3. 使用j.u.c.ScheduledExecutorService定时任务接口
- 相比于Timer的单线程,它是通过线程池的方式来执行任务的
- 可以灵活的设定第一次执行任务delay时间
- 提供了良好的约定,以便设定执行的时间间隔
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class Task3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ScheduledExecutorService service = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1);
// 初始化延迟0ms开始执行,每隔200ms重新执行一次任务。
ScheduledExecutorService pool = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1);
pool.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// task to run goes here
System.out.println("Hello !");
}
}, 0, 200L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
实现类使用的是ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor。该类继承自ThreadPoolExecutor read more,阻塞队列使用的是DelayedWorkQueue,是ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor的内部类。
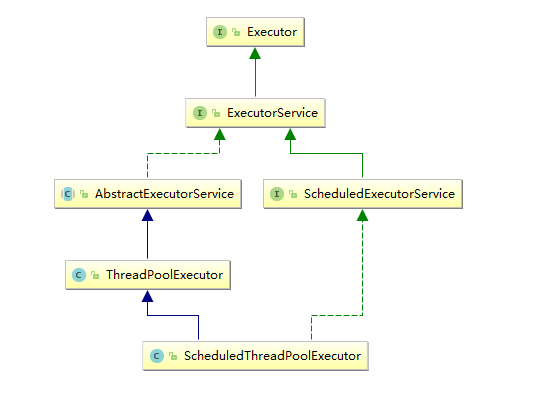
ScheduledExecutorService接口方法说明:

其中scheduleAtFixedRate和scheduleWithFixedDelay在实现定时程序时比较方便。
-
scheduleAtFixedRate(runnable, 0, 200L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) 按指定周期执行某个任务
初始化延迟0ms开始执行,每隔200ms重新执行一次任务。 -
scheduleWithFixedDelay(runnable, 0, 200L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) 按指定间隔执行某个任务
初始化时延时0ms开始执行,下次执行时间是(本次执行结束 + 延迟200ms)后开始执行。 -
schedule(Runnable command, long delay, TimeUnit unit) 在delay延时后执行一次性任务
备注:对于scheduleAtFixedRate,实际上如果当前线程阻塞执行时间t > 设置的间隔时间period,下次是在t时间后执行,并非period时间后立即开始。
ScheduledExecutorService的spring配置
>> spring.xml
<bean id="gkHeartBeatScheduler" class="org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorFactoryBean">
<property name="poolSize" value="4"/>
<property name="threadNamePrefix" value="gkHeartBeat"/>
</bean>
>> xxx.java
@Autowired
@Qualifier("gkHeartBeatScheduler")
ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService;
scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(
new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("do sth");
}
}, 1l, 2l, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
spring ScheduledExecutorFactoryBean内部同样使用的ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor,并对其做了包装处理。
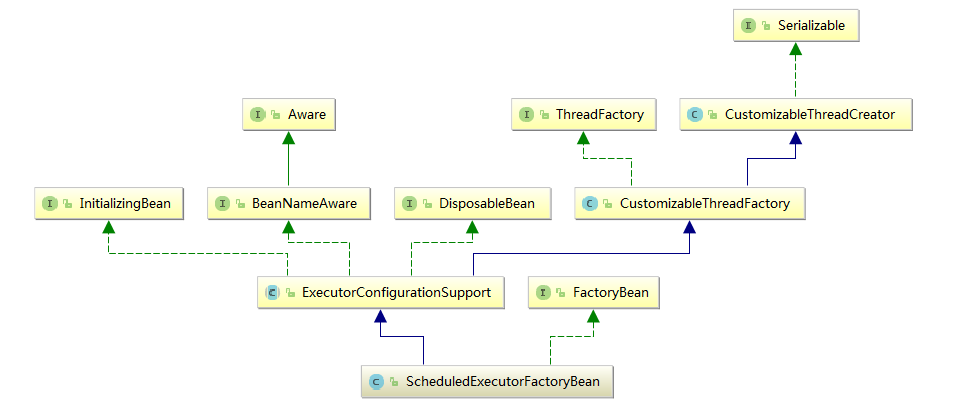
public class ScheduledExecutorFactoryBean extends ExecutorConfigurationSupport implements FactoryBean<ScheduledExecutorService>
4. @Sheduled注解方式
@Sheduled内部也使用了ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor。具体源代码可参见:spring-context包中的ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor。
用法就很简单了,举例:
- pom文件引入spring-context依赖
- 使用注解方式配置定时任务即可
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableScheduling;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@EnableScheduling
public class ScheduledAnnotationDemo {
// @Scheduled和触发器元素一起添加到方法上.
@Scheduled(fixedDelay=5000)
public void doSomething() {
System.out.println("like scheduleWithFixedDelay");
}
@Scheduled(fixedRate=5000)
public void doSomething() {
System.out.println("like scheduleAtFixedRate");
}
// fixed-delay、fixed-rate任务都可以设置初始delay。
@Scheduled(initialDelay=1000, fixedRate=5000)
public void doSomething() {
// something that should execute periodically
}
// 也支持cron表达式
@Scheduled(cron = "0/5 * * * * ?")
public void doSomething() {
// something that should execute on weekdays only
System.out.println("5s执行一次");
}
//cron举例:(秒 - 分 - 时 - 日 - 月- 星期)
// */5 * * * * ? 每隔5秒执行一次
// 0 */1 * * * ? 每隔1分钟执行一次
// 0 0 1 * * ? 每天1点执行一次
// 0 0 1 1 * ? 每月1号1点执行一次
// 0 0 1 L * ? 每月最后一天1点执行一次
// 0 0 1 ? * L 每周星期天1点执行一次
}
上面使用@EnableScheduling的方式启动定时任务,等价于在spring xml中配置<task:annotation-driven />元素。
5. 开源任务调度框架Quartz
Quartz , 功能强大的任务调度库。适用于具有更复杂调度要求的场景。
提供了对持久化任务调度信息、事务、分布式的支持。与spring无缝对接。
参见:quartz调度基础: Job/Trigger/Schedule.
6. 小结
- 使用ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor完成简单定时任务,是比较理想和常用的实现方式。书写时更容易理解其过程实现。
- 也可以用@Sheduled注解的形式,更加轻量化,看起来更简洁。
- 对复杂的任务调度,可以使用Quartz框架。