You are given a permutation of integers from 1 to n. Exactly once you apply the following operation to this permutation: pick a random segment and shuffle its elements. Formally:
- Pick a random segment (continuous subsequence) from l to r. All
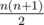 segments are equiprobable.
segments are equiprobable. - Let k = r - l + 1, i.e. the length of the chosen segment. Pick a random permutation of integers from 1 to k, p1, p2, ..., pk. All k!permutation are equiprobable.
- This permutation is applied to elements of the chosen segment, i.e. permutation a1, a2, ..., al - 1, al, al + 1, ..., ar - 1, ar, ar + 1, ..., an is transformed to a1, a2, ..., al - 1, al - 1 + p1, al - 1 + p2, ..., al - 1 + pk - 1, al - 1 + pk, ar + 1, ..., an.
Inversion if a pair of elements (not necessary neighbouring) with the wrong relative order. In other words, the number of inversion is equal to the number of pairs (i, j) such that i < j and ai > aj. Find the expected number of inversions after we apply exactly one operation mentioned above.
The first line contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 100 000) — the length of the permutation.
The second line contains n distinct integers from 1 to n — elements of the permutation.
Print one real value — the expected number of inversions. Your answer will be considered correct if its absolute or relative error does not exceed 10 - 9.
Namely: let's assume that your answer is a, and the answer of the jury is b. The checker program will consider your answer correct, if 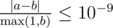 .
.
3
2 3 1
1.916666666666666666666666666667
分析:仔细分析可知答案为
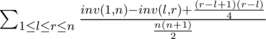 ,inv(l,r)代表[l,r]逆序数;
,inv(l,r)代表[l,r]逆序数;
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <cmath> #include <algorithm> #include <climits> #include <cstring> #include <string> #include <set> #include <map> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <vector> #include <list> #define rep(i,m,n) for(i=m;i<=n;i++) #define rsp(it,s) for(set<int>::iterator it=s.begin();it!=s.end();it++) #define mod 1000000007 #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f #define vi vector<int> #define pb push_back #define mp make_pair #define fi first #define se second #define ll long long #define pi acos(-1.0) #define pii pair<int,int> #define Lson L, mid, ls[rt] #define Rson mid+1, R, rs[rt] #define sys system("pause") #define intxt freopen("in.txt","r",stdin) const int maxn=1e5+10; using namespace std; ll gcd(ll p,ll q){return q==0?p:gcd(q,p%q);} ll qpow(ll p,ll q){ll f=1;while(q){if(q&1)f=f*p;p=p*p;q>>=1;}return f;} inline void umax(int &p,int q){if(p<q)p=q;} inline void umin(int &p,int q){if(p>q)p=q;} inline ll read() { ll x=0;int f=1;char ch=getchar(); while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')f=-1;ch=getchar();} while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){x=x*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar();} return x*f; } int n,m,k,t; ll a[maxn],d[maxn]; double ans,now,pre; void add(int x,int y) { for(int i=x;i<=n;i+=i&(-i)) d[i]+=y; } ll get(int x) { ll ret=0; for(int i=x;i;i-=i&(-i)) ret+=d[i]; return ret; } void init() { ll cnt=0; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { cnt+=get(n)-get(a[i]); add(a[i],1); } for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) ans+=(n-i+1)*((double)i*(i-1)/4+cnt); memset(d,0,sizeof(d)); } int main() { int i,j; scanf("%d",&n); rep(i,1,n)a[i]=read(); init(); rep(i,1,n) { now=get(n)-get(a[i])+pre; ans-=now; pre=now; add(a[i],i); } ans/=(double)n*(n+1)/2; printf("%.10f ",ans); //system("Pause"); return 0; }