Problem:
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null.
To represent a cycle in the given linked list, we use an integer pos which represents the position (0-indexed) in the linked list where tail connects to. If pos is -1, then there is no cycle in the linked list.
Note: Do not modify the linked list.
Example 1:
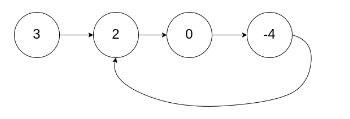
Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
Output: tail connects to node index 1
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the second node.
Example 2:
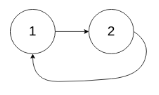
Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0
Output: tail connects to node index 0
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the first node.
Example 3:
Input: head = [1], pos = -1
Output: no cycle
Explanation: There is no cycle in the linked list.

思路:
和141题类似的思路,也是设置fast和slow2个指针,fast每次移动2个节点,slow每次移动一个节点。设链表开始节点为start,环开始的节点为entry,fast和slow相遇的节点为meet。从start到entry距离为(x_1),从entry到meet的距离为(x_2),然后从meet沿环到entry的距离为(x_3)。则fast指针移动的距离为(x_1+x_2+x_3+x_2),slow指针移动的距离为(x_1+x_2),可以得出等式:(x_1+x_2+x_3+x_2 = 2(x_1+x_2)),可以推出(x_1=x_3)。也就是说,若设置一个新的节点to_entry从start开始移动,slow从meet开始移动,2者移动相同的距离就会在entry节点相遇,而此时移动的节点数也就是entry的下标,即找到了环开始的节点。
Solution:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
if (!head) return NULL;
ListNode *fast = head, *slow = head, *entry = head;
while (fast->next && fast->next->next) {
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if (fast == slow) {
while (slow != entry) {
slow = slow->next;
entry = entry->next;
}
return entry;
}
}
return NULL;
}
性能:
Runtime: 12 ms Memory Usage: 9.9 MB
