1.1 流的简单介绍和分类
Java流操作的相关的类和接口:
- File: 文件类
- RandomAccessFile: 随机存取文件类
- InputStream: 字节输出流
- OutputStream: 字符输出流
- Reader: 字符输入流
- Writer: 字符输出流
四个抽象基类分别为:InputStream 、OutputStream 、Reader 、Writer;
Java流类图结构:
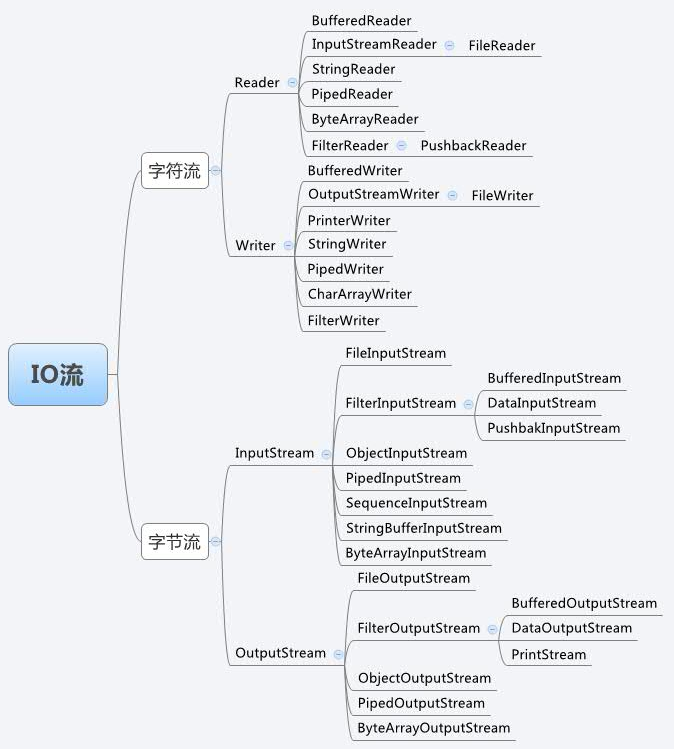
注:若用字节流操作文本文件,会引起乱码和效率低的问题。若用字符流去操作非文本文件,不会报错,但什么也获取不了。
1.2 常见节点流和处理流的使用方法
1.2.1 只使用节点流的复制粘贴
非文本文件
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
//1.创建 FileInputStream 的实例,同时打开指定文件
fis = new FileInputStream("1.jpg");
fos = new FileOutputStream("2.jpg");
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len = fis.read(b)) != -1){
fos.write(b,0,len);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(fis != null){
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(fos != null){
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
文本文件
FileReader fr = null;
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
fr = new FileReader("1.txt");
fw = new FileWriter("2.txt");
char[] c = new char[100];
int len = 0;
while((len = fr.read(c)) != -1){
fw.write(c, 0, len);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(fw != null){
try {
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(fr != null){
try {
fr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
1.2.2 带上缓冲流的复制粘贴
非文本文件
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("1.jpg");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("2.jpg");
bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len = bis.read(b)) != -1){
bos.write(b, 0, len);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
if(bos != null){
bos.close();
}
if(bis != null){
bis.close();
}
}
文本文件
BufferedReader br = null;
BufferedWriter bw = null;
try {
FileReader fr = new FileReader("newFile.txt");
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("newFile2.txt");
br = new BufferedReader(fr);
bw = new BufferedWriter(fw);
String str = null;
while( (str = br.readLine()) != null){
bw.write(str);
bw.newLine();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(bw != null){
bw.close();
}
if(br != null){
br.close();
}
}
1.3 序列化与反序列化
主要使用对象流进行操作: ObjectInputStream 、ObjectOutputStream
序列化:将内存中的对象以二进制的形式保存在磁盘中
反序列化:将磁盘的对象读取
准备工作: 需要提供一个序列化接口。序列号如果不显示给出, 则会默认根据类信息自动生成一个序列号,一旦类信息发送变动与序列化前不同,对象的反序列化将会抛出异常,所以还是建议 显示给出一个序列号。
关键字: transient 和 static修饰的属性不会被序列化
1.3.1 序列化反序列化多个值
序列化
//3. 创建对象流,包装缓冲流,用于完成序列化
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
try {
int num = 10;
boolean flag = false;
String str = "abcde";
//1.创建节点流,同时打开指定文件
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("./data.dat");
//2.(可选)使用缓冲流包装节点流,用于提高传输效率。
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeInt(num);
oos.writeBoolean(flag);
oos.writeUTF(str);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(oos != null){
//5.关闭流
try {
oos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
反序列化
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("./data.dat");
ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
//反序列化的顺序务 必和 序列化的顺序保持一致
int num = ois.readInt();
boolean flag = ois.readBoolean();
String str = ois.readUTF();
System.out.println(num);
System.out.println(flag);
System.out.println(str);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(ois != null){
try {
ois.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
1.3.2 序列化和反序列化多个对象
准备工作
public class Person implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 134628734823487283L;
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Person() {}
public int getAge(){
return age;
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
}
序列化
//Person 务必要实现序列化接口
Person p1 = new Person("张三",19);
Person p2 = new Person("李四",20);
Person p3 = new Person("王五",16);
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
try {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("person.dat");
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(p1);
oos.writeObject(p2);
oos.writeObject(p3);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(oos != null){
try {
oos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
反序列化
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("person.dat");
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis);
Person p1 = (Person)ois.readObject();
Person p2 = (Person)ois.readObject();
Person p3 = (Person)ois.readObject();
System.out.println(p1);
System.out.println(p2);
System.out.println(p3);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(ois != null){
try {
ois.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
1.4 转换流
转换流:InputStreamReader & OutStreamWriter
编码:字符串 -> 字节数组
解码:字节数组 -> 字符串
BufferedReader br = null;
BufferedWriter bw = null;
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("hello.txt");
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);
br = new BufferedReader(isr);
FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter("hello1.txt");
bw = new BufferedWriter(fileWriter);
String str = null;
while((str = br.readLine()) != null){
bw.write(str);
bw.newLine();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(bw != null){
try {
bw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(br != null){
try {
br.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
1.5 随机存取文件类
RandomAccessFile 类支持"随机访问"的方式,程序可以跳到文件的任意地方来读写文件
支持只访问文件的部分内容
可以向已存在的文件后追加内容
RandomAccessFile 对象包含一个记录指针,用以标示当前读写处的位置。
RandomAccessFile 类对象可以自由移动记录指针:
long getFilePointer():获取文件记录指针的位置
void seek(long pos):将文件记录指针定位到pos位置
- 构造器
public RandomAccessFile(File file,String mode)
public RandomAccessFile(String name,String mode)
- 创建RandomAccessFile 类实例需要制定一个mode 参数, 该参数指定 RandomAccessFile的访问模式:
r:以只读方式打开
rw:打开以便读取和写入
rwd:打开以便读取和写入;同步文件内容的更新
rws:打开以便读取和写入;同步文件内容和元数据的更新
/**
* 在abcdef写入文件 再向abc中间 插入hello
*/
@Test
public void test4() throws IOException{
RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile("hell.txt", "rw");
String str = "abcdef";
randomAccessFile.write(str.getBytes());
randomAccessFile.seek(3);
String line = randomAccessFile.readLine();
randomAccessFile.seek(3);
randomAccessFile.write("hello".getBytes());
randomAccessFile.write(line.getBytes());
randomAccessFile.close();
}