开发环境:
System:Windows
JavaEE Server:tomcat5.0.2.8、tomcat6
JavaSDK: jdk6+
IDE:eclipse、MyEclipse 6.6
开发依赖库:
JDK6、 JavaEE5、ehcache-core-2.5.2.jar
Email:hoojo_@126.com
Blog:http://blog.csdn.net/IBM_hoojo
前面2篇文章介绍到Ehcache 整合Spring 使用页面、对象缓存 http://www.cnblogs.com/hoojo/archive/2012/07/12/2587556.html
在Spring、Hibernate中使用Ehcache缓存 http://www.cnblogs.com/hoojo/archive/2012/07/12/2587941.html
一、缓存系统简介
EhCache 是一个纯 Java 的进程内缓存框架,具有快速、精干等特点,是 Hibernate 中默认的 CacheProvider。
EhCache 应用架构图,下图是 EhCache 在应用程序中的位置:
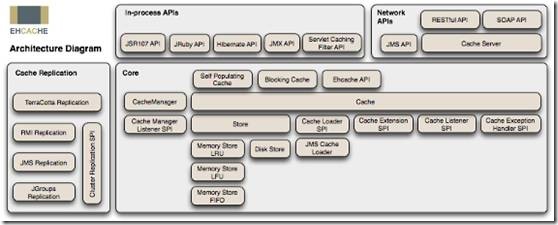
EhCache 的主要特性有:
1. 快速、精干;
2. 简单;
3. 多种缓存策略;
4. 缓存数据有两级:内存和磁盘,因此无需担心容量问题;
5. 缓存数据会在虚拟机重启的过程中写入磁盘;
6. 可以通过 RMI、可插入 API 等方式进行分布式缓存;
7. 具有缓存和缓存管理器的侦听接口;
8. 支持多缓存管理器实例,以及一个实例的多个缓存区域;
9. 提供 Hibernate 的缓存实现;
由于 EhCache 是进程中的缓存系统,一旦将应用部署在集群环境中,每一个节点维护各自的缓存数据,当某个节点对缓存数据进行更新,这些更新的数据无法在其它节点中共享,这不仅会降低节点运行的效率,而且会导致数据不同步的情况发生。例如某个网站采用 A、B 两个节点作为集群部署,当 A 节点的缓存更新后,而 B 节点缓存尚未更新就可能出现用户在浏览页面的时候,一会是更新后的数据,一会是尚未更新的数据,尽管我们也可以通过 Session Sticky 技术来将用户锁定在某个节点上,但对于一些交互性比较强或者是非 Web 方式的系统来说,Session Sticky 显然不太适合。
所以就需要用到 EhCache 的集群解决方案。
从1.2版本开始,Ehcache可以使用分布式的缓存了。EhCache 从 1.7 版本开始,支持五种集群方案,分别是:
• Terracotta
• RMI
• JMS
• JGroups
• EhCache Server
其中的三种最为常用集群方式,分别是 RMI、JGroups 以及 EhCache Server 。本文主要介绍RMI的方式。
分布式这个特性是以plugin的方式实现的。Ehcache自带了一些默认的分布式缓存插件实现,这些插件可以满足大部分应用的需要。如果需要使用其他的插件那就需要自己开发了,开发者可以通过查看distribution包里的源代码及JavaDoc来实现它。尽管不是必须的,在使用分布式缓存时理解一些ehcahce的设计思想也是有帮助的。这可以参看分布式缓存设计的页面。以下的部分将展示如何让分布式插件同ehcache一起工作。
下面列出的是一些分布式缓存中比较重要的方面:
• 你如何知道集群环境中的其他缓存?
• 分布式传送的消息是什么形式?
• 什么情况需要进行复制?增加(Puts),更新(Updates)或是失效(Expiries)?
• 采用什么方式进行复制?同步还是异步方式?
为了安装分布式缓存,你需要配置一个PeerProvider、一个CacheManagerPeerListener,
它们对于一个CacheManager来说是全局的。每个进行分布式操作的cache都要添加一个cacheEventListener来传送消息。
二、集群缓存概念及其配置
正确的元素类型
只有可序列化的元素可以进行复制。一些操作,比如移除,只需要元素的键值而不用整个元素;在这样的操作中即使元素不是可序列化的但键值是可序列化的也可以被复制。
成员发现(Peer Discovery)
Ehcache进行集群的时候有一个cache组的概念。每个cache都是其他cache的一个peer,没有主cache的存在。刚才我们问了一个问题:你如何知道集群环境中的其他缓存?这个问题可以命名为成员发现(Peer Discovery)。
Ehcache提供了两种机制用来进行成员发现,就像一辆汽车:手动档和自动档。要使用一个内置的成员发现机制要在ehcache的配置文件中指定cacheManagerPeerProviderFactory元素的class属性为
net.sf.ehcache.distribution.RMICacheManagerPeerProviderFactory。
自动的成员发现
自动的发现方式用TCP广播机制来确定和维持一个广播组。它只需要一个简单的配置可以自动的在组中添加和移除成员。在集群中也不需要什么优化服务器的知识,这是默认推荐的。
成员每秒向群组发送一个“心跳”。如果一个成员 5秒种都没有发出信号它将被群组移除。如果一个新的成员发送了一个“心跳”它将被添加进群组。
任何一个用这个配置安装了复制功能的cache都将被其他的成员发现并标识为可用状态。
要设置自动的成员发现,需要指定ehcache配置文件中cacheManagerPeerProviderFactory元素的properties属性,就像下面这样:
peerDiscovery=automaticmulticastGroupAddress=multicast address | multicast host name
multicastGroupPort=port
timeToLive=0-255 (timeToLive属性详见常见问题部分的描述)
示例
假设你在集群中有两台服务器。你希望同步sampleCache1和sampleCache2。每台独立的服务器都要有这样的配置:
配置server1和server2<cacheManagerPeerProviderFactoryclass="net.sf.ehcache.distribution.RMICacheManagerPeerProviderFactory"properties="peerDiscovery=automatic, multicastGroupAddress=230.0.0.1,multicastGroupPort=4446, timeToLive=32"/>
手动进行成员发现
进行手动成员配置要知道每个监听器的IP地址和端口。成员不能在运行时动态地添加和移除。在技术上很难使用广播的情况下就可以手动成员发现,例如在集群的服务器之间有一个不能传送广播报文的路由器。你也可以用手动成员发现进行单向的数据复制,只让server2知道server1,而server1不知道server2。
配置手动成员发现,需要指定ehcache配置文件中cacheManagerPeerProviderFactory的properties属性,像下面这样:
peerDiscovery=manual rmiUrls=//server:port/cacheName, //server:port/cacheName ...
rmiUrls配置的是服务器cache peers的列表。注意不要重复配置。
示例
假设你在集群中有两台服务器。你要同步sampleCache1和sampleCache2。下面是每个服务器需要的配置:
配置server1<cacheManagerPeerProviderFactoryclass="net.sf.ehcache.distribution.RMICacheManagerPeerProviderFactory"properties="peerDiscovery=manual,rmiUrls=//server2:40001/sampleCache11|//server2:40001/sampleCache12"/>配置server2
<cacheManagerPeerProviderFactoryclass="net.sf.ehcache.distribution.RMICacheManagerPeerProviderFactory"properties="peerDiscovery=manual,rmiUrls=//server1:40001/sampleCache11|//server1:40001/sampleCache12"/>
配置CacheManagerPeerListener
每个CacheManagerPeerListener监听从成员们发向当前CacheManager的消息。配置CacheManagerPeerListener需要指定一个CacheManagerPeerListenerFactory,它以插件的机制实现,用来创建CacheManagerPeerListener。
cacheManagerPeerListenerFactory的属性有:
class – 一个完整的工厂类名。
properties – 只对这个工厂有意义的属性,使用逗号分隔。Ehcache有一个内置的基于RMI的分布系统。它的监听器是RMICacheManagerPeerListener,这个监听器可以用
RMICacheManagerPeerListenerFactory来配置。
<cacheManagerPeerListenerFactoryclass="net.sf.ehcache.distribution.RMICacheManagerPeerListenerFactory"properties="hostName=localhost, port=40001,socketTimeoutMillis=2000"/>有效的属性是:
hostname (可选) – 运行监听器的服务器名称。标明了做为集群群组的成员的地址,同时也是你想要控制的从集群中接收消息的接口。在CacheManager初始化的时候会检查hostname是否可用。
如果hostName不可用,CacheManager将拒绝启动并抛出一个连接被拒绝的异常。
如果指定,hostname将使用InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostAddress()来得到。
警告:不要将localhost配置为本地地址127.0.0.1,因为它在网络中不可见将会导致不能从远程服务器接收信息从而不能复制。在同一台机器上有多个CacheManager的时候,你应该只用localhost来配置。
port – 监听器监听的端口。
socketTimeoutMillis (可选) – Socket超时的时间。默认是2000ms。当你socket同步缓存请求地址比较远,不是本地局域网。你可能需要把这个时间配置大些,不然很可能延时导致同步缓存失败。
配置CacheReplicators
每个要进行同步的cache都需要设置一个用来向CacheManagerr的成员复制消息的缓存事件监听器。这个工作要通过为每个cache的配置增加一个cacheEventListenerFactory元素来完成。
<!-- Sample cache named sampleCache2. --><cache name="sampleCache2"maxElementsInMemory="10"eternal="false"timeToIdleSeconds="100"timeToLiveSeconds="100"overflowToDisk="false"><cacheEventListenerFactory class="net.sf.ehcache.distribution.RMICacheReplicatorFactory"properties="replicateAsynchronously=true,replicatePuts=true, replicateUpdates=true, replicateUpdatesViaCopy=false, replicateRemovals=true "/></cache>class – 使用net.sf.ehcache.distribution.RMICacheReplicatorFactory
这个工厂支持以下属性:
replicatePuts=true | false – 当一个新元素增加到缓存中的时候是否要复制到其他的peers. 默认是true。
replicateUpdates=true | false – 当一个已经在缓存中存在的元素被覆盖时是否要进行复制。默认是true。
replicateRemovals= true | false – 当元素移除的时候是否进行复制。默认是true。
replicateAsynchronously=true | false – 复制方式是异步的(指定为true时)还是同步的(指定为false时)。默认是true。
replicatePutsViaCopy=true | false – 当一个新增元素被拷贝到其他的cache中时是否进行复制指定为true时为复制,默认是true。
replicateUpdatesViaCopy=true | false – 当一个元素被拷贝到其他的cache中时是否进行复制(指定为true时为复制),默认是true。你可以使用ehcache的默认行为从而减少配置的工作量,默认的行为是以异步的方式复制每件事;你可以像下面的例子一样减少RMICacheReplicatorFactory的属性配置:
<!-- Sample cache named sampleCache4. All missing RMICacheReplicatorFactory properties default to true --><cache name="sampleCache4"maxElementsInMemory="10"eternal="true"overflowToDisk="false"memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LFU"><cacheEventListenerFactory class="net.sf.ehcache.distribution.RMICacheReplicatorFactory"/></cache>
常见的问题
Windows上的Tomcat
有一个Tomcat或者是JDK的bug,在tomcat启动时如果tomcat的安装路径中有空格的话,在启动时RMI监听器会失败。参见http://archives.java.sun.com/cgi-bin/wa?A2=ind0205&L=rmi-users&P=797和http://www.ontotext.com/kim/doc/sys-doc/faq-howto-bugs/known-bugs.html。
由于在Windows上安装Tomcat默认是装在“Program Files”文件夹里的,所以这个问题经常发生。
广播阻断
自动的peer discovery与广播息息相关。广播可能被路由阻拦,像Xen和VMWare这种虚拟化的技术也可以阻拦广播。如果这些都打开了,你可能还在要将你的网卡的相关配置打开。一个简单的办法可以告诉广播是否有效,
那就是使用ehcache remote debugger来看“心跳”是否可用。
广播传播的不够远或是传得太远
你可以通过设置badly misnamed time to live来控制广播传播的距离。用广播IP协议时,timeToLive的值指的是数据包可以传递的域或是范围。约定如下:
0是限制在同一个服务器
1是限制在同一个子网
32是限制在同一个网站
64是限制在同一个region
128是限制在同一个大洲
255是不限制
译者按:上面这些资料翻译的不够准确,请读者自行寻找原文理解吧。
在Java实现中默认值是1,也就是在同一个子网中传播。改变timeToLive属性可以限制或是扩展传播的范围。
三、 RMI方式缓存集群/配置分布式缓存
RMI 是 Java 的一种远程方法调用技术,是一种点对点的基于 Java 对象的通讯方式。EhCache 从 1.2 版本开始就支持 RMI 方式的缓存集群。在集群环境中 EhCache 所有缓存对象的键和值都必须是可序列化的,也就是必须实现 java.io.Serializable 接口,这点在其它集群方式下也是需要遵守的。
下图是 RMI 集群模式的结构图:
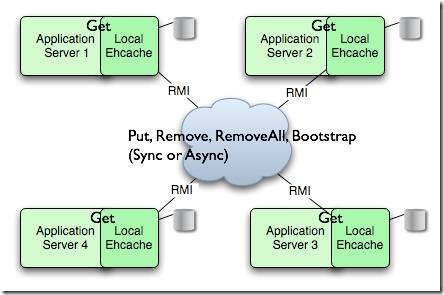
采用 RMI 集群模式时,集群中的每个节点都是对等关系,并不存在主节点或者从节点的概念,因此节点间必须有一个机制能够互相认识对方,必须知道其它节点的信息,包括主机地址、端口号等。EhCache 提供两种节点的发现方式:手工配置和自动发现。手工配置方式要求在每个节点中配置其它所有节点的连接信息,一旦集群中的节点发生变化时,需要对缓存进行重新配置。
由于 RMI 是 Java 中内置支持的技术,因此使用 RMI 集群模式时,无需引入其它的 Jar 包,EhCache 本身就带有支持 RMI 集群的功能。使用 RMI 集群模式需要在 ehcache.xml 配置文件中定义 cacheManagerPeerProviderFactory 节点。
分布式同步缓存要让这边的cache知道对方的cache,叫做Peer Discovery(成员发现) EHCache实现成员发现的方式有两种:
1、手动查找
A、 在ehcache.xml中配置PeerDiscovery成员发现对象
Server1配置,配置本地hostName、port是400001,分别监听192.168.8.32:400002的mobileCache和192.168.5.231:400003 的mobileCache。注意这里的mobileCache是缓存的名称,分别对应着server2、server3的cache的配置。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="gbk"?><ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="ehcache.xsd"><diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir"/><!--集群多台服务器中的缓存,这里是要同步一些服务器的缓存server1 hostName:192.168.8.9 port:400001 cacheName:mobileCacheserver2 hostName:192.168.8.32 port:400002 cacheName:mobileCacheserver3 hostName:192.168.8.231 port:400003 cacheName:mobileCache注意:每台要同步缓存的服务器的RMI通信socket端口都不一样,在配置的时候注意设置--><!-- server1 的cacheManagerPeerProviderFactory配置 --><cacheManagerPeerProviderFactoryclass="net.sf.ehcache.distribution.RMICacheManagerPeerProviderFactory"properties="hostName=localhost,port=400001,socketTimeoutMillis=2000,peerDiscovery=manual,rmiUrls=//192.168.8.32:400002/mobileCache|//192.168.5.231:400003/mobileCache"/></ehcache>以上注意cacheManagerPeerProviderFactory元素出现的位置在diskStore下
同样在你的另外2台服务器上增加配置
Server2,配置本地host,port为400002,分别同步192.168.8.9:400001的mobileCache和192.168.5.231:400003的mobileCache
<!-- server2 的cacheManagerPeerProviderFactory配置 --><cacheManagerPeerProviderFactoryclass="net.sf.ehcache.distribution.RMICacheManagerPeerProviderFactory"properties="hostName=localhost,port=400002,socketTimeoutMillis=2000,peerDiscovery=manual,rmiUrls=//192.168.8.9:400001/mobileCache|//192.168.5.231:400003/mobileCache"/>Server3,配置本地host,port为400003,分别同步192.168.8.9:400001的mobileCache缓存和192.168.8.32:400002的mobileCache缓存
<!-- server3 的cacheManagerPeerProviderFactory配置 --><cacheManagerPeerProviderFactoryclass="net.sf.ehcache.distribution.RMICacheManagerPeerProviderFactory"properties="hostName=localhost,port=400003,socketTimeoutMillis=2000,peerDiscovery=manual,rmiUrls=//192.168.8.9:400001/mobileCache|//192.168.8.32:400002/mobileCache"/>这样就在三台不同的服务器上配置了手动查找cache的PeerProvider成员发现的配置了。 值得注意的是你在配置rmiUrls的时候要特别注意url不能重复出现,并且端口、地址都是对的。
如果指定,hostname将使用InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostAddress()来得到。
警告:不要将localhost配置为本地地址127.0.0.1,因为它在网络中不可见将会导致不能从远程服务器接收信息从而不能复制。在同一台机器上有多个CacheManager的时候,你应该只用localhost来配置。
B、 下面配置缓存和缓存同步监听,需要在每台服务器中的ehcache.xml文件中增加cache配置和cacheEventListenerFactory、cacheLoaderFactory的配置
<defaultCache maxElementsInMemory="10000" eternal="false" timeToIdleSeconds="30" timeToLiveSeconds="30" overflowToDisk="false"/><!--配置自定义缓存maxElementsInMemory:缓存中允许创建的最大对象数eternal:缓存中对象是否为永久的,如果是,超时设置将被忽略,对象从不过期。timeToIdleSeconds:缓存数据空闲的最大时间,也就是说如果有一个缓存有多久没有被访问就会被销毁,如果该值是 0 就意味着元素可以停顿无穷长的时间。timeToLiveSeconds:缓存数据存活的时间,缓存对象最大的的存活时间,超过这个时间就会被销毁,这只能在元素不是永久驻留时有效,如果该值是0就意味着元素可以停顿无穷长的时间。overflowToDisk:内存不足时,是否启用磁盘缓存。memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:缓存满了之后的淘汰算法。每一个小时更新一次缓存(1小时过期)--><cache name="mobileCache"maxElementsInMemory="10000"eternal="false"overflowToDisk="true"timeToIdleSeconds="1800"timeToLiveSeconds="3600"memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LFU"><!--RMI缓存分布同步查找 class使用net.sf.ehcache.distribution.RMICacheReplicatorFactory这个工厂支持以下属性:replicatePuts=true | false – 当一个新元素增加到缓存中的时候是否要复制到其他的peers。默认是true。replicateUpdates=true | false – 当一个已经在缓存中存在的元素被覆盖时是否要进行复制。默认是true。replicateRemovals= true | false – 当元素移除的时候是否进行复制。默认是true。replicateAsynchronously=true | false – 复制方式是异步的�指定为true时,还是同步的,指定为false时。默认是true。replicatePutsViaCopy=true | false – 当一个新增元素被拷贝到其他的cache中时是否进行复制�指定为true时为复制,默认是true。replicateUpdatesViaCopy=true | false – 当一个元素被拷贝到其他的cache中时是否进行复制�指定为true时为复制,默认是true。asynchronousReplicationIntervalMillis=1000--><!-- 监听RMI同步缓存对象配置 注册相应的的缓存监听类,用于处理缓存事件,如put,remove,update,和expire --><cacheEventListenerFactoryclass="net.sf.ehcache.distribution.RMICacheReplicatorFactory"properties="replicateAsynchronously=true,replicatePuts=true,replicateUpdates=true,replicateUpdatesViaCopy=false,replicateRemovals=true "/><!-- 用于在初始化缓存,以及自动设置 --><bootstrapCacheLoaderFactory class="net.sf.ehcache.bootstrap.BootstrapCacheLoaderFactory"/></cache>C、 这样就完成了3台服务器的配置,下面给出server1的完整的ehcache.xml的配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="gbk"?><ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="ehcache.xsd"><diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir"/><!--集群多台服务器中的缓存,这里是要同步一些服务器的缓存server1 hostName:192.168.8.9 port:400001 cacheName:mobileCacheserver2 hostName:192.168.8.32 port:400002 cacheName:mobileCacheserver3 hostName:192.168.8.231 port:400003 cacheName:mobileCache注意每台要同步缓存的服务器的RMI通信socket端口都不一样,在配置的时候注意设置--><!-- server1 的cacheManagerPeerProviderFactory配置 --><cacheManagerPeerProviderFactoryclass="net.sf.ehcache.distribution.RMICacheManagerPeerProviderFactory"properties="hostName=localhost,port=400001,socketTimeoutMillis=2000,peerDiscovery=manual,rmiUrls=//192.168.8.32:400002/mobileCache|//192.168.5.231:400003/mobileCache"/><defaultCache maxElementsInMemory="10000" eternal="false" timeToIdleSeconds="30" timeToLiveSeconds="30" overflowToDisk="false"/><!--配置自定义缓存maxElementsInMemory:缓存中允许创建的最大对象数eternal:缓存中对象是否为永久的,如果是,超时设置将被忽略,对象从不过期。timeToIdleSeconds:缓存数据空闲的最大时间,也就是说如果有一个缓存有多久没有被访问就会被销毁,如果该值是 0 就意味着元素可以停顿无穷长的时间。timeToLiveSeconds:缓存数据存活的时间,缓存对象最大的的存活时间,超过这个时间就会被销毁,这只能在元素不是永久驻留时有效,如果该值是0就意味着元素可以停顿无穷长的时间。overflowToDisk:内存不足时,是否启用磁盘缓存。memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:缓存满了之后的淘汰算法。每一个小时更新一次缓存(1小时过期)--><cache name="mobileCache"maxElementsInMemory="10000"eternal="false"overflowToDisk="true"timeToIdleSeconds="1800"timeToLiveSeconds="3600"memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LFU"><!--RMI缓存分布同步查找 class使用net.sf.ehcache.distribution.RMICacheReplicatorFactory这个工厂支持以下属性:replicatePuts=true | false – 当一个新元素增加到缓存中的时候是否要复制到其他的peers。默认是true。replicateUpdates=true | false – 当一个已经在缓存中存在的元素被覆盖时是否要进行复制。默认是true。replicateRemovals= true | false – 当元素移除的时候是否进行复制。默认是true。replicateAsynchronously=true | false – 复制方式是异步的�指定为true时,还是同步的,指定为false时。默认是true。replicatePutsViaCopy=true | false – 当一个新增元素被拷贝到其他的cache中时是否进行复制�指定为true时为复制,默认是true。replicateUpdatesViaCopy=true | false – 当一个元素被拷贝到其他的cache中时是否进行复制�指定为true时为复制,默认是true。asynchronousReplicationIntervalMillis=1000--><!-- 监听RMI同步缓存对象配置 注册相应的的缓存监听类,用于处理缓存事件,如put,remove,update,和expire --><cacheEventListenerFactoryclass="net.sf.ehcache.distribution.RMICacheReplicatorFactory"properties="replicateAsynchronously=true,replicatePuts=true,replicateUpdates=true,replicateUpdatesViaCopy=false,replicateRemovals=true "/><!-- 用于在初始化缓存,以及自动设置 --><bootstrapCacheLoaderFactory class="net.sf.ehcache.bootstrap.BootstrapCacheLoaderFactory"/></cache></ehcache>
2、自动发现
自动发现配置和手动查找的方式有一点不同,其他的地方都基本是一样的。同样在ehcache.xml中增加配置,配置如下
<!--搜索某个网段上的缓存timeToLive0是限制在同一个服务器1是限制在同一个子网32是限制在同一个网站64是限制在同一个region128是限制在同一个大洲255是不限制--><cacheManagerPeerProviderFactoryclass="net.sf.ehcache.distribution.RMICacheManagerPeerProviderFactory"properties="peerDiscovery=automatic, multicastGroupAddress=192.168.0.1,multicastGroupPort=400004, timeToLive=32"/>其他的配置和手动查找方式的配置是一样的,这里就不再赘述了。关于ehcache的其他缓存配置方式这里将不再介绍,大家可以自己去研究。可以参考:
官方文档:http://www.ehcache.org/documentation/user-guide/cache-topologies#using-a-cache-server
ibm developerworks文档:http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-lo-ehcache/index.html
JGroups 集群模式
EhCache 从 1.5. 版本开始增加了 JGroups 的分布式集群模式。与 RMI 方式相比较, JGroups 提供了一个非常灵活的协议栈、可靠的单播和多播消息传输,主要的缺点是配置复杂以及一些协议栈对第三方包的依赖。
JGroups 也提供了基于 TCP 的单播 ( Unicast ) 和基于 UDP 的多播 ( Multicast ) ,对应 RMI 的手工配置和自动发现。使用单播方式需要指定其它节点的主机地址和端口,下面是两个节点,并使用了单播方式的配置:
<cacheManagerPeerProviderFactory
class="net.sf.ehcache.distribution.jgroups.JGroupsCacheManagerPeerProviderFactory"
properties="connect=TCP(start_port=7800):
TCPPING(initial_hosts=host1[7800],host2[7800];port_range=10;timeout=3000;
num_initial_members=3;up_thread=true;down_thread=true):
VERIFY_SUSPECT(timeout=1500;down_thread=false;up_thread=false):
pbcast.NAKACK(down_thread=true;up_thread=true;gc_lag=100;
retransmit_timeout=3000):
pbcast.GMS(join_timeout=5000;join_retry_timeout=2000;shun=false;
print_local_addr=false;down_thread=true;up_thread=true)"
propertySeparator="::" />
使用多播方式配置如下:
<cacheManagerPeerProviderFactory
class="net.sf.ehcache.distribution.jgroups.JGroupsCacheManagerPeerProviderFactory"
properties="connect=UDP(mcast_addr=231.12.21.132;mcast_port=45566;):PING:
MERGE2:FD_SOCK:VERIFY_SUSPECT:pbcast.NAKACK:UNICAST:pbcast.STABLE:FRAG:pbcast.GMS"
propertySeparator="::"
/>
从上面的配置来看,JGroups 的配置要比 RMI 复杂得多,但也提供更多的微调参数,有助于提升缓存数据复制的性能。详细的 JGroups 配置参数的具体意义可参考 JGroups 的配置手册。
JGroups 方式对应缓存节点的配置信息如下:
<cache name="sampleCache2"
maxElementsInMemory="10"
eternal="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="100"
timeToLiveSeconds="100"
overflowToDisk="false">
<cacheEventListenerFactory
class="net.sf.ehcache.distribution.jgroups.JGroupsCacheReplicatorFactory"
properties="replicateAsynchronously=true, replicatePuts=true,
replicateUpdates=true, replicateUpdatesViaCopy=false, replicateRemovals=true" />
</cache>
使用组播方式的注意事项
使用 JGroups 需要引入 JGroups 的 Jar 包以及 EhCache 对 JGroups 的封装包 ehcache-jgroupsreplication-xxx.jar 。
在一些启用了 IPv6 的电脑中,经常启动的时候报如下错误信息:
java.lang.RuntimeException: the type of the stack (IPv6) and the user supplied addresses (IPv4) don't match: /231.12.21.132.
解决的办法是增加 JVM 参数:-Djava.net.preferIPv4Stack=true。如果是 Tomcat 服务器,可在 catalina.bat 或者 catalina.sh 中增加如下环境变量即可:
SET CATALINA_OPTS=-Djava.net.preferIPv4Stack=true
经过实际测试发现,集群方式下的缓存数据都可以在 1 秒钟之内完成到其节点的复制。
EhCache Server
与前面介绍的两种集群方案不同的是, EhCache Server 是一个独立的缓存服务器,其内部使用 EhCache 做为缓存系统,可利用前面提到的两种方式进行内部集群。对外提供编程语言无关的基于 HTTP 的 RESTful 或者是 SOAP 的数据缓存操作接口。
下面是 EhCache Server 提供的对缓存数据进行操作的方法:
OPTIONS /{cache}}
获取某个缓存的可用操作的信息。
HEAD /{cache}/{element}
获取缓存中某个元素的 HTTP 头信息,例如:
curl --head http://localhost:8080/ehcache/rest/sampleCache2/2
EhCache Server 返回的信息如下:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK X-Powered-By: Servlet/2.5 Server: GlassFish/v3 Last-Modified: Sun, 27 Jul 2008 08:08:49 GMT ETag: "1217146129490" Content-Type: text/plain; charset=iso-8859-1 Content-Length: 157 Date: Sun, 27 Jul 2008 08:17:09 GMT
GET /{cache}/{element}
读取缓存中某个数据的值。
PUT /{cache}/{element}
写缓存。
由于这些操作都是基于 HTTP 协议的,因此你可以在任何一种编程语言中使用它,例如 Perl、PHP 和 Ruby 等等。
下图是 EhCache Server 在应用中的架构:
图 3. EhCache Server 应用架构图
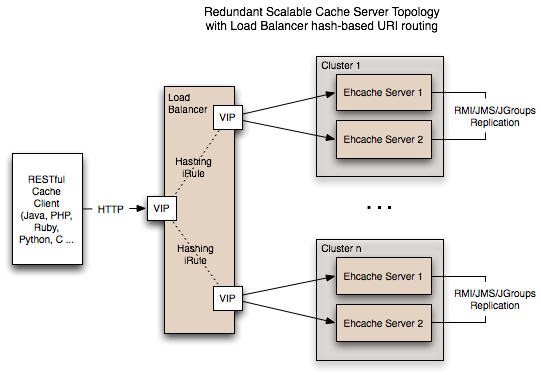
EhCache Server 同时也提供强大的安全机制、监控功能。在数据存储方面,最大的 Ehcache 单实例在内存中可以缓存 20GB。最大的磁盘可以缓存 100GB。通过将节点整合在一起,这样缓存数据就可以跨越节点,以此获得更大的容量。将缓存 20GB 的 50 个节点整合在一起就是 1TB 了。
总结
以上我们介绍了三种 EhCache 的集群方案,除了第三种跨编程语言的方案外,EhCache 的集群对应用程序的代码编写都是透明的,程序人员无需考虑缓存数据是如何复制到其它节点上。既保持了代码的轻量级,同时又支持庞大的数据集群。EhCache 可谓是深入人心。
2009 年年中,Terracotta 宣布收购 EhCache 产品。Terracotta 公司的产品 Terracotta 是一个 JVM 级的开源群集框架,提供 HTTP Session 复制、分布式缓存、POJO 群集、跨越集群的 JVM 来实现分布式应用程序协调。最近 EhCache 主要的改进都集中在跟 Terracotta 框架的集成上,这是一个真正意义上的企业级缓存解决方案。
=======================================================================
ehcache提供三种网络连接策略来实现集群,rmi,jgroup还有jms。同时ehcache可以可以实现多播的方式实现集群,也可以手动指定集群主机序列实现集群
Ehcache支持的分布式缓存支持有三种RMI,JGroups,JMS,这里介绍下MRI和JGrpups两种方式,Ehcache使用版本为1.5.0,关于ehcache的其他信息请参http://ehcache.sourceforge.net/EhcacheUserGuide.html,
关于jgroups的信息请参考http://www.jgroups.org/manual/html_single/index.html。
环境为两台机器 server1 ip:192.168.2.154,server2 ip:192.168.2.23
1. RMI方式:
rmi的方式配置要点(下面均是server1上的配置,server2上的只需要把ip兑换即可)
a. 配置PeerProvider:
<cacheManagerPeerProviderFactory class="net.sf.ehcache.distribution.RMICacheManagerPeerProviderFactory" properties="peerDiscovery=manual,rmiUrls=//192.168.2.23:40001/userCache|//192.168.2.23:40001/resourceCache" />
配置中通过手动方式同步sever2中的userCache和resourceCache。
b. 配置CacheManagerPeerListener:
<cacheManagerPeerListenerFactory class="net.sf.ehcache.distribution.RMICacheManagerPeerListenerFactory" properties="hostName=192.168.2.154, port=40001,socketTimeoutMillis=2000" />
配置中server1监听本机40001端口。
c. 在每一个cache中添加cacheEventListener,例子如下:
<cache name="userCache" maxElementsInMemory="10000" eternal="true" overflowToDisk="true" timeToIdleSeconds="0" timeToLiveSeconds="0"diskPersistent="false" diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"> <cacheEventListenerFactory class="net.sf.ehcache.distribution.RMICacheReplicatorFactory" properties="replicateAsynchronously=true, replicatePuts=true, replicateUpdates=true,replicateUpdatesViaCopy= false, replicateRemovals= true " /> </cache>
属性解释:
必须属性:
name:设置缓存的名称,用于标志缓存,惟一
maxElementsInMemory:在内存中最大的对象数量
maxElementsOnDisk:在DiskStore中的最大对象数量,如为0,则没有限制
eternal:设置元素是否永久的,如果为永久,则timeout忽略
overflowToDisk:是否当memory中的数量达到限制后,保存到Disk
可选的属性:
timeToIdleSeconds:设置元素过期前的空闲时间
timeToLiveSeconds:设置元素过期前的活动时间
diskPersistent:是否disk store在虚拟机启动时持久化。默认为false
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds:运行disk终结线程的时间,默认为120秒
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:策略关于Eviction
缓存子元素:
cacheEventListenerFactory:注册相应的的缓存监听类,用于处理缓存事件,如put,remove,update,和expire
bootstrapCacheLoaderFactory:指定相应的BootstrapCacheLoader,用于在初始化缓存,以及自动设置。
参考另外一篇学习笔记http://wozailongyou.javaeye.com/blog/230252,也有集群的说明
2. JGroups方式:
ehcache 1.5.0之后版本支持的一种方式,配置起来比较简单,要点:
a. 配置PeerProvider,使用tcp的方式,例子如下:
<cacheManagerPeerProviderFactory class="net.sf.ehcache.distribution.jgroups.JGroupsCacheManagerPeerProviderFactory" properties="connect=TCP(start_port=7800): TCPPING(initial_hosts=192.168.2.154[7800],192.168.2.23[7800];port_range=10;timeout=3000; num_initial_members=3;up_thread=true;down_thread=true): VERIFY_SUSPECT(timeout=1500;down_thread=false;up_thread=false): pbcast.NAKACK(down_thread=true;up_thread=true;gc_lag=100;retransmit_timeout=3000): pbcast.GMS(join_timeout=5000;join_retry_timeout=2000;shun=false; print_local_addr=false;down_thread=true;up_thread=true)" propertySeparator="::" />
b.为每个cache添加cacheEventListener:
<cache name="userCache" maxElementsInMemory="10000" eternal="true" overflowToDisk="true" timeToIdleSeconds="0" timeToLiveSeconds="0" diskPersistent="false" diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"> <cacheEventListenerFactory class="net.sf.ehcache.distribution.jgroups.JGroupsCacheReplicatorFactory" properties="replicateAsynchronously=true, replicatePuts=true, replicateUpdates=true, replicateUpdatesViaCopy=false, replicateRemovals=true"/> </cache>
JGroup方式配置的两个server上的配置文件一样,若有多个server,在initial_hosts中将server ip加上即可。
一个完整的ehcache.xml文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://ehcache.sf.net/ehcache.xsd"> <diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir" /> <cacheManagerPeerProviderFactory class="net.sf.ehcache.distribution.jgroups.JGroupsCacheManagerPeerProviderFactory" properties="connect=TCP(start_port=7800): TCPPING(initial_hosts=192.168.2.154[7800],192.168.2.23[7800];port_range=10;timeout=3000; num_initial_members=3;up_thread=true;down_thread=true): VERIFY_SUSPECT(timeout=1500;down_thread=false;up_thread=false): pbcast.NAKACK(down_thread=true;up_thread=true;gc_lag=100;retransmit_timeout=3000): pbcast.GMS(join_timeout=5000;join_retry_timeout=2000;shun=false; print_local_addr=false;down_thread=true;up_thread=true)" propertySeparator="::" /> <defaultCache maxElementsInMemory="10000" eternal="true" overflowToDisk="true" timeToIdleSeconds="0" timeToLiveSeconds="0" diskPersistent="false" diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"> <cacheEventListenerFactory class="net.sf.ehcache.distribution.jgroups.JGroupsCacheReplicatorFactory" properties="replicateAsynchronously=true, replicatePuts=true, replicateUpdates=true, replicateUpdatesViaCopy=false, replicateRemovals=true"/> </defaultCache> <cache name="velcroCache" maxElementsInMemory="10000" eternal="true" overflowToDisk="true" timeToIdleSeconds="0" timeToLiveSeconds="0" diskPersistent="false" diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"> <cacheEventListenerFactory class="net.sf.ehcache.distribution.jgroups.JGroupsCacheReplicatorFactory" properties="replicateAsynchronously=true, replicatePuts=true, replicateUpdates=true, replicateUpdatesViaCopy=false, replicateRemovals=true"/> </cache> <cache name="userCache" maxElementsInMemory="10000" eternal="true" overflowToDisk="true" timeToIdleSeconds="0" timeToLiveSeconds="0" diskPersistent="false" diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"> <cacheEventListenerFactory class="net.sf.ehcache.distribution.jgroups.JGroupsCacheReplicatorFactory" properties="replicateAsynchronously=true, replicatePuts=true, replicateUpdates=true, replicateUpdatesViaCopy=false, replicateRemovals=true"/> </cache> <cache name="resourceCache" maxElementsInMemory="10000" eternal="true" overflowToDisk="true" timeToIdleSeconds="0" timeToLiveSeconds="0" diskPersistent="false" diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"> <cacheEventListenerFactory class="net.sf.ehcache.distribution.jgroups.JGroupsCacheReplicatorFactory" properties="replicateAsynchronously=true, replicatePuts=true, replicateUpdates=true, replicateUpdatesViaCopy=false, replicateRemovals=true"/> </cache> </ehcache>