Apache MINA 2 是一个开发高性能和高可伸缩性网络应用程序的网络应用框架。它提供了一个抽象的事件驱动的异步 API,可以使用 TCP/IP、UDP/IP、串口和虚拟机内部的管道等传输方式。
首先,mina server端acceptor启动方法:
1、NioSocketAcceptor.bind(InetSocketAddress)或者NioSocketAcceptor.bind(SocketAddress...)方法。
例如:
acceptor.bind(new InetSocketAddress(1234));
mina底层的调用链:
NioSocketAcceptor.bind(InetSocketAddress)-->
AbstractIoAcceptor.bind(SocketAddress localAddress) -->
AbstractIoAcceptor.bind(Iterable<? extends SocketAddress> localAddresses)-->
AbstractPollingIoAcceptor.bindInternal(List<? extends SocketAddress> localAddresses)-->
AbstractPollingIoAcceptor.startupAcceptor()
1、创建线程Acceptor线程-->
acceptor线程启动run()
1、初始化acceptor端的Selector,即NioSocketAcceptor.Selector
2、NioSocketAcceptor.open(SocketAddress localAddress)
// Register the channel within the selector for ACCEPT event
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
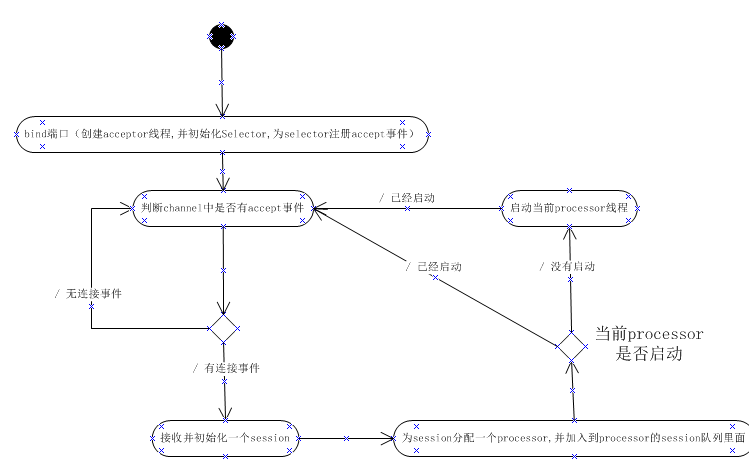
acceptor工作流程:
一、IoService类图
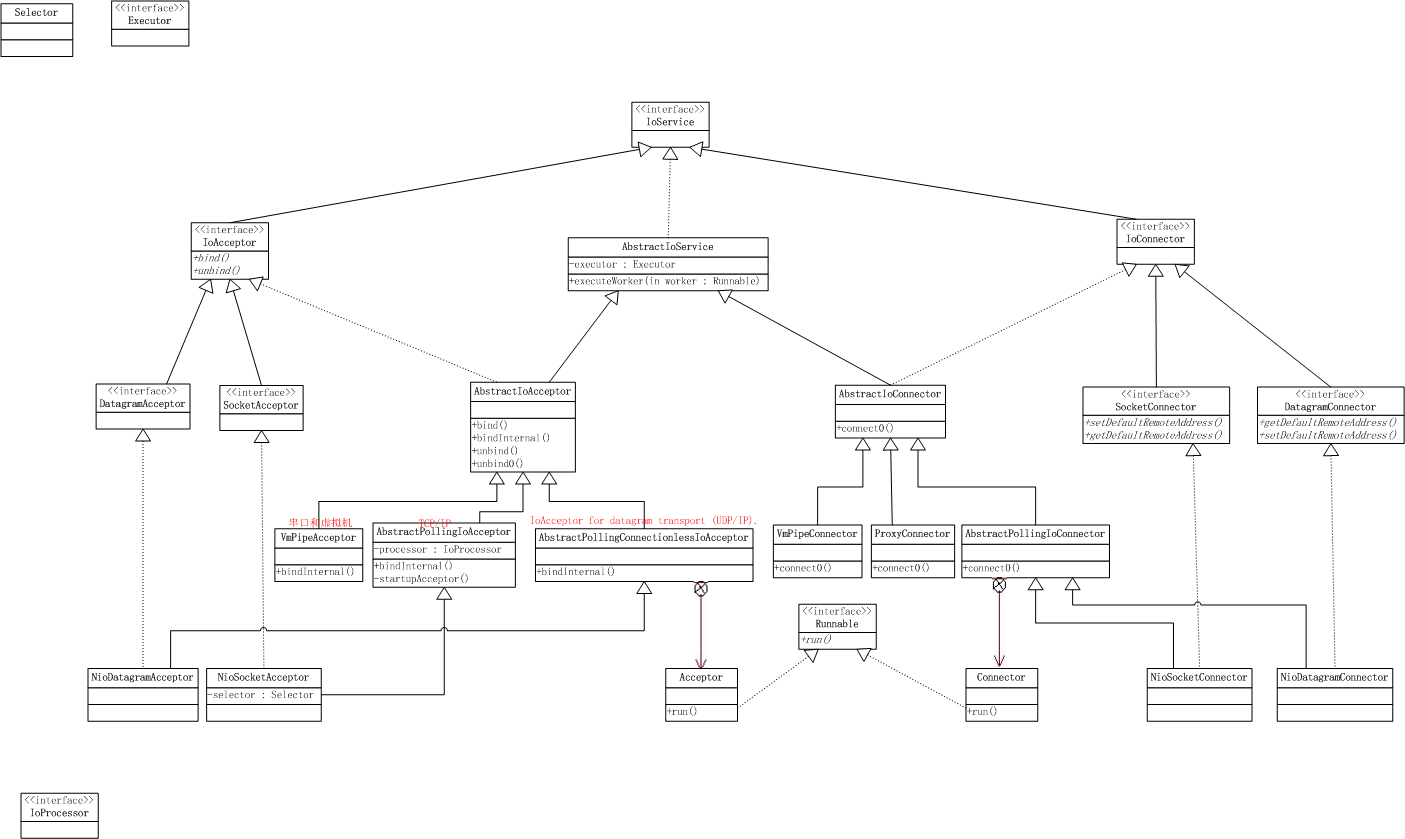
如上图所示,IOService层根据不同的角色又分为IOAcceptor(服务端左半部分)和IOConnector (客户端右半部分),分别用于接受连接与请求连接操作。
二、服务端
2.1、IoAcceptor接口
IoAcceptor相当于是对ServerSocketChannel的封装,最重要的两个操作是绑定(解绑)与接受连接,IoAcceptor接口中有多个重载的bind()方法,当然呼应有多个重载的unbind()方法。
public interface IoAcceptor extends IoService { void bind() throws IOException; void bind(SocketAddress localAddress) throws IOException; void bind(SocketAddress firstLocalAddress, SocketAddress... addresses) throws IOException; void bind(Iterable<? extends SocketAddress> localAddresses) throws IOException; void unbind(); void unbind(SocketAddress localAddress); void unbind(SocketAddress firstLocalAddress, SocketAddress... otherLocalAddresses); void unbind(Iterable<? extends SocketAddress> localAddresses); }
2.2、IoAcceptor的实现类AbstractIOAcceptor
IoAcceptor其方法的实现在抽象类AbstractIOAcceptor的bind方法中,这个方法在做了参数检查等操作后,将真正的绑定操作交给abstract bindInternal()来完成。对于bindInternal有基于TCP/IP,UDP/IP,VMPipe三种实现类,分别对应
- AbstractPollingIoAcceptor对应TCP/IP
- AbstractPollingConnectionlessIoAcceptor对应UDP/IP
- VmPipeAcceptor对应串口和虚拟机内部的管道
以TCP/IP为例来看绑定过程,见AbstractPollingIoAcceptor.java的源码:
protected final Set<SocketAddress> bindInternal(List<? extends SocketAddress> localAddresses) throws Exception { // Create a bind request as a Future operation. When the selector // have handled the registration, it will signal this future. AcceptorOperationFuture request = new AcceptorOperationFuture(localAddresses); // adds the Registration request to the queue for the Workers // to handle registerQueue.add(request); // creates the Acceptor instance and has the local // executor kick it off. startupAcceptor(); // As we just started the acceptor, we have to unblock the select() // in order to process the bind request we just have added to the // registerQueue. try { lock.acquire(); // Wait a bit to give a chance to the Acceptor thread to do the select() Thread.sleep(10); wakeup(); } finally { lock.release(); } // Now, we wait until this request is completed. request.awaitUninterruptibly(); if (request.getException() != null) { throw request.getException(); } // Update the local addresses. // setLocalAddresses() shouldn't be called from the worker thread // because of deadlock. Set<SocketAddress> newLocalAddresses = new HashSet<SocketAddress>(); for (H handle : boundHandles.values()) { newLocalAddresses.add(localAddress(handle)); } return newLocalAddresses;
主要做了以下几件事情:
1、将绑定请求放入registerQueue中
2、启动Acceptor,从Acceptor类的run方法可以看到,这一步会阻塞在Acceptor选择器的选择操作中
3、调用wakeup让选择器返回
4、等待请求处理完成,这一步会阻塞在ready变量中,当ready变量为true时才会返回,当接受连接后ready会被设置为true.
现在重点看一下AbstractPollingIoAcceptor$Acceptor的run方法:
public void run() { assert (acceptorRef.get() == this); int nHandles = 0; // Release the lock lock.release(); while (selectable) { try { // Detect if we have some keys ready to be processed // The select() will be woke up if some new connection // have occurred, or if the selector has been explicitly // woke up int selected = select(); // this actually sets the selector to OP_ACCEPT, // and binds to the port on which this class will // listen on nHandles += registerHandles(); // Now, if the number of registred handles is 0, we can // quit the loop: we don't have any socket listening // for incoming connection. if (nHandles == 0) { acceptorRef.set(null); if (registerQueue.isEmpty() && cancelQueue.isEmpty()) { assert (acceptorRef.get() != this); break; } if (!acceptorRef.compareAndSet(null, this)) { assert (acceptorRef.get() != this); break; } assert (acceptorRef.get() == this); } if (selected > 0) { // We have some connection request, let's process // them here. processHandles(selectedHandles()); } // check to see if any cancellation request has been made. nHandles -= unregisterHandles(); } catch (ClosedSelectorException cse) { // If the selector has been closed, we can exit the loop break; } catch (Throwable e) { ExceptionMonitor.getInstance().exceptionCaught(e); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e1) { ExceptionMonitor.getInstance().exceptionCaught(e1); } } } // Cleanup all the processors, and shutdown the acceptor. if (selectable && isDisposing()) { selectable = false; try { if (createdProcessor) { processor.dispose(); } } finally { try { synchronized (disposalLock) { if (isDisposing()) { destroy(); } } } catch (Exception e) { ExceptionMonitor.getInstance().exceptionCaught(e); } finally { disposalFuture.setDone(); } } } }
(1)、selector被wakeup唤醒后,调用registerHandles方法从registerQueue中取出请求依次调用open方法
private int registerHandles() { for (;;) { // The register queue contains the list of services to manage // in this acceptor. AcceptorOperationFuture future = registerQueue.poll(); if (future == null) { return 0; } // We create a temporary map to store the bound handles, // as we may have to remove them all if there is an exception // during the sockets opening. Map<SocketAddress, H> newHandles = new ConcurrentHashMap<SocketAddress, H>(); List<SocketAddress> localAddresses = future.getLocalAddresses(); try { // Process all the addresses for (SocketAddress a : localAddresses) { H handle = open(a); newHandles.put(localAddress(handle), handle); } // Everything went ok, we can now update the map storing // all the bound sockets. boundHandles.putAll(newHandles); // and notify. future.setDone(); return newHandles.size(); } catch (Exception e) { // We store the exception in the future future.setException(e); } finally { // Roll back if failed to bind all addresses. if (future.getException() != null) { for (H handle : newHandles.values()) { try { close(handle); } catch (Exception e) { ExceptionMonitor.getInstance().exceptionCaught(e); } } // TODO : add some comment : what is the wakeup() waking up ? wakeup(); } } } }
open方法完成了ServerSocket的绑定和注册(NioSocketAcceptor.open(SocketAddress localAddress)方法如下)
protected ServerSocketChannel open(SocketAddress localAddress) throws Exception { // Creates the listening ServerSocket ServerSocketChannel channel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); boolean success = false; try { // This is a non blocking socket channel channel.configureBlocking(false); // Configure the server socket, ServerSocket socket = channel.socket(); // Set the reuseAddress flag accordingly with the setting socket.setReuseAddress(isReuseAddress()); // and bind. socket.bind(localAddress, getBacklog()); // Register the channel within the selector for ACCEPT event channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); success = true; } finally { if (!success) { close(channel); } } return channel; }
(2)、从(1)中可以知道selector上注册了ServerSocketChannel的OP_ACCEPT键,注册后nHandles==0,selected==0,进行下一次循环,同样是阻塞在select方法上
(3)、当连接到来时,select方法返回,selected>0,执行processHandles方法
private void processHandles(Iterator<H> handles) throws Exception { while (handles.hasNext()) { H handle = handles.next(); handles.remove(); // Associates a new created connection to a processor, // and get back a session S session = accept(processor, handle); if (session == null) { continue; } initSession(session, null, null); // add the session to the SocketIoProcessor session.getProcessor().add(session); } }
该方法在完成真正的接受连接操作后,创建session并扔到processor中,后续的工作交给processor来完成。每个session中其实有一个SocketChannel,这个socketChannel实际上是被注册到了processor的selector上。注册代码在NioProcessor类中可以找到
总结一下:Acceptor线程专门负责接受连接,在其上有一个selector,轮询是否有连接建立上来,当有连接建立上来,调用ServerSocketChannel.accept方法来接受连接,这个方法返回一个session对象,然后将这个session对象加入processor中,由processor遍历每个session来完成真正的IO操作。processor上也有一个selector与一个Processor线程,selector用于轮询session,Processor线程处理每个session的IO操作。