前言
之前在分析spring boot 源码时导出可见@ConditionalOnBean 之类的注解,那么它到底是如何使用的以及其工作流程如何,我们这里就围绕以下几点来分析:
- @Conditional系列与Condition的关系:@ConditionalXxx是注解,XxxCondition是对前面注解的对应处理类。
- @Conditional与Condition的源码分析
- 总结
一、@Conditional系列与Condition的关系
@ConditionalXxx是注解,XxxCondition是对前面注解的对应处理类。
spring boot 中有关Condition的代码在org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition中,如图:
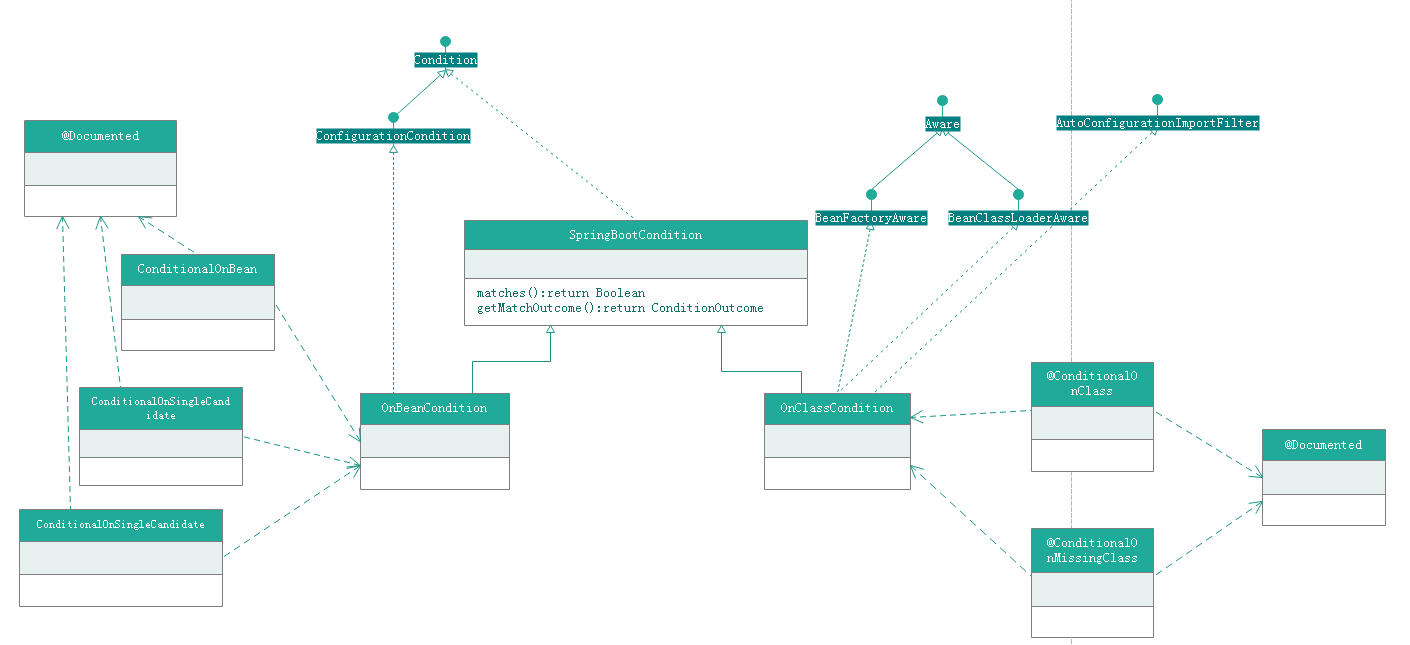
可以看到类还是很多的,但是基本上,都是一个注解对应一个condition实现类.拿其中@ConditionalOnBean,@ConditionalOnClass 为例,其类图如下:
二、@Conditional与Condition的源码分析
从以上的类图可以知道,所有的contidon类都是通过继承SpringBootCondition的方式实现的(实现了Condition接口).Condition接口定义如下:
package org.springframework.context.annotation; public interface Condition { boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata); }
matches方法判断其条件是否成立,如果不成立,则会阻止该bean的注册。
SpringBootCondition实现了Condition接口,将一些模板处理定义在该类中,声明了getMatchOutcome这么一个抽象方法,子类只需实现该方法即可实现业务逻辑.是模板方法的典型使用。代码如下:
public abstract class SpringBootCondition implements Condition { public final boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) { // 1. 得到类名或者方法名(条件注解可以作用的类或者方法上) String classOrMethodName = getClassOrMethodName(metadata); // 2. 抽象方法,具体子类实现。ConditionOutcome记录了匹配结果boolean和log信息 ConditionOutcome outcome = getMatchOutcome(context, metadata); // 3. 打印日志,Trace 级别 logOutcome(classOrMethodName, outcome); // 4. 记录结果 recordEvaluation(context, classOrMethodName, outcome); return outcome.isMatch(); } //抽象方法 public abstract ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata); }
详解:
1、getClassOrMethodName方法
//matches中1的调用:得到类名或者方法名(条件注解可以作用的类或者方法上) private static String getClassOrMethodName(AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) { // 1. 如果metadata 是ClassMetadata的实例,则返回类名,否则返回全类名#方法名 if (metadata instanceof ClassMetadata) { ClassMetadata classMetadata = (ClassMetadata) metadata; return classMetadata.getClassName(); } MethodMetadata methodMetadata = (MethodMetadata) metadata; return methodMetadata.getDeclaringClassName() + "#" + methodMetadata.getMethodName(); }
2、getMatchOutcome()抽象方法,由子类实现。
ConditionOutcome类是抽象方法的返回结果类:对匹配结果boolean和log信息的封装。
public class ConditionOutcome { private final boolean match; private final ConditionMessage message;
3、logOutcome()方法:
打印日志,Trace 级别.代码如下:
protected final void logOutcome(String classOrMethodName, ConditionOutcome outcome) { if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) { this.logger.trace(getLogMessage(classOrMethodName, outcome)); } }
4、记录结果.代码如下:
private void recordEvaluation(ConditionContext context, String classOrMethodName, ConditionOutcome outcome) { if (context.getBeanFactory() != null) { ConditionEvaluationReport.get(context.getBeanFactory()) .recordConditionEvaluation(classOrMethodName, this, outcome); } }
最终,保存在ConditionEvaluationReport的SortedMap<String, ConditionAndOutcomes> outcomes缓存里。
此外,SpringBootCondition 还声明了2个比较有用的方法,供子类使用:
anyMatches。当有任意一个Condition符号条件时返回true.代码如下:
protected final boolean anyMatches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata, Condition... conditions) { for (Condition condition : conditions) { if (matches(context, metadata, condition)) { return true; } } return false; }
matches()方法,代码如下:
protected final boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata, Condition condition) {
//如果Condition是SpringBootCondition的实例,则强转后调用getMatchOutcome进行判断(抽象方法--子类实现的方法).然后返回结果. if (condition instanceof SpringBootCondition) { return ((SpringBootCondition) condition).getMatchOutcome(context, metadata) .isMatch(); }
//否则直接调用matches即可。
return condition.matches(context, metadata);
}
接下来,我们就依次分析org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition中的源码.
2.1、@ConditionalOnBean
@ConditionalOnBean代码如下:
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD }) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Conditional(OnBeanCondition.class) public @interface ConditionalOnBean { // bean的类型,当ApplicationContext包含给定类的bean时返回true Class<?>[] value() default {}; // bean的类型名,当ApplicationContext包含给定的id时返回true String[] type() default {}; // bean所声明的注解,当ApplicationContext中存在声明该注解的bean时返回true Class<? extends Annotation>[] annotation() default {}; // bean的id,,当ApplicationContext中存在给定id的bean时返回true String[] name() default {}; // 默认是所有上下文搜索 SearchStrategy search() default SearchStrategy.ALL; }
其中, SearchStrategy是枚举类,其代码如下:
public enum SearchStrategy { // 查询当前的context CURRENT, // 查询所有的祖先和父辈容器,但是不包含当前容器,从1.5开始废弃,推荐使用ANCESTORS @Deprecated PARENTS, // 搜索所有的祖先,不搜索当前的context ANCESTORS, // 搜索整个上下文 ALL }
@Conditional对应的处理类是OnBeanCondition,
2.2、OnBeanCondition处理类
OnBeanCondition其除了继承SpringBootCondition外,还实现了ConfigurationCondition接口.类图如下:

可以看到OnBeanCondition是@ConditionalOnBean,@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate,@ConditionalOnMissingBean三个注解的处理类,这里我们只分析@ConditionalOnBean的想关的,其他部分,我们在解析到相关注解时在分析.
ConfigurationCondition接口定义如下:
public interface ConfigurationCondition extends Condition { // 返回该condition应该在哪个阶段执行 ConfigurationPhase getConfigurationPhase(); enum ConfigurationPhase { // 当前的Condition在配置类解析时执行.如果该condition返回false,则该配置类不会被解析 PARSE_CONFIGURATION, // 当前的Condition在注册bean时执行 REGISTER_BEAN } }
OnBeanCondition
A、OnBeanCondition--对于ConfigurationCondition的实现如下:
public ConfigurationPhase getConfigurationPhase() { return ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN; }
说明该bean是在注册bean时执行的。
B、OnBeanCondition--的 getMatchOutcome 实现如下:
public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) { ConditionMessage matchMessage = ConditionMessage.empty(); if (metadata.isAnnotated(ConditionalOnBean.class.getName())) { BeanSearchSpec spec = new BeanSearchSpec(context, metadata, ConditionalOnBean.class); // 构造一个BeanSearchSpec,会从@ConditionalOnBean注解中获取属性,然后设置到BeanSearchSpec中 List<String> matching = getMatchingBeans(context, spec); if (matching.isEmpty()) { // 如果没有匹配的bean,返回一个没有匹配成功的ConditionalOutcome return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(ConditionMessage.forCondition(ConditionalOnBean.class, spec).didNotFind("any beans").atAll()); } // 如果找到匹配的bean,匹配信息进行记录 matchMessage = matchMessage.andCondition(ConditionalOnBean.class, spec).found("bean", "beans").items(Style.QUOTE, matching); } return ConditionOutcome.match(matchMessage); }
1)构造一个BeanSearchSpec,会从@ConditionalOnBean注解中获取属性,然后设置到BeanSearchSpec中.其构造器如下:
BeanSearchSpec(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata, Class<?> annotationType) { // 1. 对annotationType进行赋值 this.annotationType = annotationType; // 获得metadata所有的属性所对应的值,封装为MultiValueMap,key-->属性名,value-->所对应的值,class 转换为String MultiValueMap<String, Object> attributes = metadata .getAllAnnotationAttributes(annotationType.getName(), true); // 从attributes中提取出name的值,赋值为names collect(attributes, "name", this.names); // 从attributes中提取出value的值,赋值为value collect(attributes, "value", this.types); collect(attributes, "type", this.types); collect(attributes, "annotation", this.annotations); collect(attributes, "ignored", this.ignoredTypes); collect(attributes, "ignoredType", this.ignoredTypes); // 赋值SearchStrategy this.strategy = (SearchStrategy) metadata .getAnnotationAttributes(annotationType.getName()).get("search"); BeanTypeDeductionException deductionException = null; try { if (this.types.isEmpty() && this.names.isEmpty()) { // 2. 如果types没有设置并且names也没有设置,则如果该metadata是MethodMetadata的实例并且该metadata被@Bean注解 // 则将该方法的返回值类型作为types addDeducedBeanType(context, metadata, this.types); } } catch (BeanTypeDeductionException ex) { deductionException = ex; } // 3. 检验,如果types,names,annotations 都为空,则抛出IllegalStateException异常 validate(deductionException); }
1、对annotationType进行赋值
2、获得metadata所有的属性所对应的值,封装为MultiValueMap,key–>属性名,value–>所对应的值,class 转换为String
3、调用collect方法对names,types,annotations,ignoredTypes,ignoredTypes进行赋值.collect方法从attributes中取出所给定的key的value,进行赋值即可,如果值为String[],则将其强转为String[]后添加.代码如下:
protected void collect(MultiValueMap<String, Object> attributes, String key, List<String> destination) { List<?> values = attributes.get(key); if (values != null) { for (Object value : values) { if (value instanceof String[]) { Collections.addAll(destination, (String[]) value); } else { destination.add((String) value); } } } }
4、如果types没有设置并且names也没有设置,则如果该metadata是MethodMetadata的实例并且该metadata被@Bean注解则将该方法的返回值类型作为types
5、检验,如果types,names,annotations 都为空,则抛出IllegalStateException异常
2)调用getMatchingBeans 获得匹配的bean的名称.代码如下:
private List<String> getMatchingBeans(ConditionContext context, BeanSearchSpec beans) { // 1. 如果搜索策略为PARENTS或者ANCESTORS,则beanFactory为当前容器的父容器中获取.否则beanFactory从当前容器获取 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory(); if (beans.getStrategy() == SearchStrategy.PARENTS || beans.getStrategy() == SearchStrategy.ANCESTORS) { BeanFactory parent = beanFactory.getParentBeanFactory(); Assert.isInstanceOf(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory.class, parent, "Unable to use SearchStrategy.PARENTS"); beanFactory = (ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) parent; } // 2. 如果beanFactory等于空,则返回空集合.该情况是对于父容器才会发生的 if (beanFactory == null) { return Collections.emptyList(); } List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<String>(); boolean considerHierarchy = beans.getStrategy() != SearchStrategy.CURRENT; // 3. 从beanFactory中获得给定类型的beanIds,如果需要从父容器中搜索,则该方法会合并父容器的接口 for (String type : beans.getTypes()) { beanNames.addAll(getBeanNamesForType(beanFactory, type, context.getClassLoader(), considerHierarchy)); } // 4. 从beanNames删除给定忽略类型的bean,如果需要从父容器中搜索,则该方法会将父容器中包含给定type的bean删除 for (String ignoredType : beans.getIgnoredTypes()) { beanNames.removeAll(getBeanNamesForType(beanFactory, ignoredType, context.getClassLoader(), considerHierarchy)); } // 5. 遍历给定的Annotations,依次从beanFactory中获取声明了该Annotation的bean,如果需要从父容器中搜索,则也会将父容器包含的添加进去 for (String annotation : beans.getAnnotations()) { beanNames.addAll(Arrays.asList(getBeanNamesForAnnotation(beanFactory, annotation, context.getClassLoader(), considerHierarchy))); } // 6. 遍历给定的ids,从当前容器和父容器中(如果需要)查找,如果包含的话,则加入到beanNames for (String beanName : beans.getNames()) { if (containsBean(beanFactory, beanName, considerHierarchy)) { beanNames.add(beanName); } } // 注意,如果同时指定了Types,Names 其返回的结果不是and,而是or return beanNames; }
1、如果搜索策略为PARENTS或者ANCESTORS,则beanFactory为当前容器的父容器中获取.否则beanFactory从当前容器获取
2、如果beanFactory等于空,则返回空集合.该情况是对于父容器才会发生的
3、从beanFactory中获得给定类型的beanIds,如果需要从父容器中搜索,则该方法会合并父容器的接口
4、从beanNames删除给定忽略类型的bean,如果需要从父容器中搜索,则该方法会将父容器中包含给定type的bean删除
5、遍历给定的Annotations,依次从beanFactory中获取声明了该Annotation的bean,如果需要从父容器中搜索,则也会将父容器包含的添加进去
6、遍历给定的ids,从当前容器和父容器中(如果需要)查找,如果包含的话,则加入到beanNames
注意,如果同时指定了Types,Names 其返回的结果不是and,而是or
如果没有匹配的bean,返回一个没有匹配成功的ConditionalOutcome.最终返回false.
否则,返回匹配.最终返回true.
使用案例:
在CacheStatisticsAutoConfiguration类中声明了如下注解:
@ConditionalOnBean(CacheManager.class)
标识当 CacheManager类型的bean存在时才对CacheStatisticsAutoConfiguration进行处理。
ConditionalOnSingleCandidate
1)@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate 代码如下:
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD }) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Conditional(OnBeanCondition.class) public @interface ConditionalOnSingleCandidate { /** * * bean的类型,当ApplicationContext包含给定类的bean时并且如果有多个该类型的bean并且指定为primary的 * 存在则返回true. * * @return the class type of the bean to check */ Class<?> value() default Object.class; /** * * bean的类型名,当ApplicationContext包含给定的id并且如果有多个该类型的bean并且指定为primary的 * 存在则返回true. * @return the class type name of the bean to check */ String type() default ""; /** * * 默认是所有上下文搜索 * @return the search strategy */ SearchStrategy search() default SearchStrategy.ALL; }
注意: value ,type 属性不能同时出现,只能使用一个
2)所对应的处理类为OnBeanCondition.代码如下:
if (metadata.isAnnotated(ConditionalOnSingleCandidate.class.getName())) { BeanSearchSpec spec = new SingleCandidateBeanSearchSpec(context, metadata, ConditionalOnSingleCandidate.class); List<String> matching = getMatchingBeans(context, spec); if (matching.isEmpty()) { return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(ConditionMessage .forCondition(ConditionalOnSingleCandidate.class, spec) .didNotFind("any beans").atAll()); } else if (!hasSingleAutowireCandidate(context.getBeanFactory(), matching, spec.getStrategy() == SearchStrategy.ALL)) { return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(ConditionMessage .forCondition(ConditionalOnSingleCandidate.class, spec) .didNotFind("a primary bean from beans") .items(Style.QUOTE, matching)); } matchMessage = matchMessage .andCondition(ConditionalOnSingleCandidate.class, spec) .found("a primary bean from beans").items(Style.QUOTE, matching); } return ConditionOutcome.match(matchMessage);
1、实例化SingleCandidateBeanSearchSpec,SingleCandidateBeanSearchSpec继承了BeanSearchSpec.其复写了validate方法,在该方法中校验types只能指定一个.同时,复写了collect方法,这样在实例化的时候,会去除”“, Object类型的bean.即 @ConditionalOnSingleCandidate 必须指定type,value中的一个,且不能使用默认值 代码如下:
@Override protected void collect(MultiValueMap<String, Object> attributes, String key, List<String> destination) { super.collect(attributes, key, destination); destination.removeAll(Arrays.asList("", Object.class.getName())); } @Override protected void validate(BeanTypeDeductionException ex) { Assert.isTrue(getTypes().size() == 1, annotationName() + " annotations must " + "specify only one type (got " + getTypes() + ")"); }
2、获得给定type的beanNames
3、如果不存在,则返回不匹配
4、如果给定类型的bean存在多个但是指定为Primary的不存在,则返回不匹配
5、返回匹配
3)使用案例:
在DataSourceTransactionManagerConfiguration 声明了如下注解:
@Configuration @ConditionalOnSingleCandidate(DataSource.class) static class DataSourceTransactionManagerConfiguration
标识:当DataSource类型的bean存在并且指定为Primary的DataSource存在时,加载DataSourceTransactionManagerConfiguration的配置
ConditionalOnMissingBean
1)@ConditionalOnMissingBean 注解如下:
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD }) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Conditional(OnBeanCondition.class) public @interface ConditionalOnMissingBean { // bean的类型,当ApplicationContext不包含给定类的bean时返回true Class<?>[] value() default {}; // bean的类型名,当ApplicationContext不包含给定的id时返回true String[] type() default {}; // 给定的类型当进行匹配时进行忽略 Class<?>[] ignored() default {}; // 给定的类型名当进行匹配时进行忽略 String[] ignoredType() default {}; // bean所声明的注解,当ApplicationContext中不存在声明该注解的bean时返回true Class<? extends Annotation>[] annotation() default {}; // bean的id,,当ApplicationContext中不存在给定id的bean时返回true String[] name() default {}; // 默认是所有上下文搜索 SearchStrategy search() default SearchStrategy.ALL; }
2)@ConditionalOnMissingBean 对应的处理类是OnBeanCondition,其相关代码如下:
if (metadata.isAnnotated(ConditionalOnMissingBean.class.getName())) { // 3.1 实例化BeanSearchSpec BeanSearchSpec spec = new BeanSearchSpec(context, metadata, ConditionalOnMissingBean.class); // 3.2 获得给定条件的beanNames List<String> matching = getMatchingBeans(context, spec); if (!matching.isEmpty()) { // 3.3 如果不为空,返回不匹配,否则返回匹配 return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(ConditionMessage .forCondition(ConditionalOnMissingBean.class, spec) .found("bean", "beans").items(Style.QUOTE, matching)); } matchMessage = matchMessage.andCondition(ConditionalOnMissingBean.class, spec) .didNotFind("any beans").atAll(); } return ConditionOutcome.match(matchMessage);
1、实例化BeanSearchSpec
2、获得给定条件的beanNames
3、如果不为空,返回不匹配,否则返回匹配
3)使用案例:
在DataSourceAutoConfiguration中声明了如下方法:
@Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public DataSourceInitializer dataSourceInitializer(DataSourceProperties properties, ApplicationContext applicationContext) { return new DataSourceInitializer(properties, applicationContext); }
表明当beanFactory中不存在DataSourceInitializer类型的bean时,才进行注册。
2.3、ConditionalOnClass与ConditionalOnMissingClass
@ConditionalOnClass与@ConditionalOnMissingClass 对应的处理类都是OnClassCondition.这里就一起分析了。

2.3.1、@ConditionalOnClass注解如下:
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD }) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Conditional(OnClassCondition.class) public @interface ConditionalOnClass { /** * * 给定的类必须存在 * @return the classes that must be present */ Class<?>[] value() default {}; /** * * 给定的类名,该类名必须存在 * @return the class names that must be present. */ String[] name() default {}; }
@ConditionalOnMissingClass 注解如下:
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD }) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Conditional(OnClassCondition.class) public @interface ConditionalOnMissingClass { // 给定的类名在当前类路径下不存在时返回true String[] value() default {}; }
2.3.2、OnClassCondition
1、OnClassCondition类图如上图的右边部分。
2、其上的接口AutoConfigurationImportFilter的作用是将在spring.factories中定义的auto-configuration 的类名进行过滤.该接口的目标是快速去除不需要的类在对其配置解析前.一个AutoConfigurationImportFilter接口的实现可能需要实现EnvironmentAware,BeanFactoryAware,BeanClassLoaderAware,ResourceLoaderAware接口中的任意个.这些接口会在调用match方法前进行注入.该方法的调用链如下:

在AutoConfigurationImportSelector中会加载spring.factories中配置的org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportFilter,其配置的刚好就是OnClassCondition.因此该类会在此刻被实例化,进行处理.代码如下:
# Auto Configuration Import Filters org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportFilter= org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnClassCondition
3、OnClassCondition 中的match 实现如下:
public boolean[] match(String[] autoConfigurationClasses, AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata) { // 1. 获得ConditionEvaluationReport--上面的代码往这里存,这个下面是取 ConditionEvaluationReport report = getConditionEvaluationReport(); // 2. 调用getOutcomes 获得ConditionOutcome[] ConditionOutcome[] outcomes = getOutcomes(autoConfigurationClasses, autoConfigurationMetadata); // 3. 初始化match,该数组只保存符合要求的 boolean[] match = new boolean[outcomes.length]; // 4. 依次遍历outcomes for (int i = 0; i < outcomes.length; i++) { // 4.1 对match中的数组进行赋值,当outcomes对应下标的ConditionOutcome匹配时为true.其他情况,返回false. match[i] = (outcomes[i] == null || outcomes[i].isMatch()); if (!match[i] && outcomes[i] != null) { // 4.2 如果outcome是不满足的,则打印日志并进行记录. logOutcome(autoConfigurationClasses[i], outcomes[i]); if (report != null) { report.recordConditionEvaluation(autoConfigurationClasses[i], this, outcomes[i]); } } } return match; }
1、获得ConditionEvaluationReport.该ConditionEvaluationReport只会在beanFactory中实例化1个.
2、调用getOutcomes 获得ConditionOutcome[].
3、初始化match,该数组只保存符合要求的
4、依次遍历outcomes
4.1、对match中的数组进行赋值,当outcomes等于null 或者 对应下标的ConditionOutcome匹配时为true.其他情况,返回false.一般outcomes都是null.
4.2、如果outcome是不满足的,则打印日志并进行记录.
其中的核心是第2步–> getOutcomes 方法.代码如下:
private ConditionOutcome[] getOutcomes(String[] autoConfigurationClasses, AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata) { int split = autoConfigurationClasses.length / 2; OutcomesResolver firstHalfResolver = createOutcomesResolver( autoConfigurationClasses, 0, split, autoConfigurationMetadata); OutcomesResolver secondHalfResolver = new StandardOutcomesResolver( autoConfigurationClasses, split, autoConfigurationClasses.length, autoConfigurationMetadata, this.beanClassLoader); ConditionOutcome[] secondHalf = secondHalfResolver.resolveOutcomes(); ConditionOutcome[] firstHalf = firstHalfResolver.resolveOutcomes(); ConditionOutcome[] outcomes = new ConditionOutcome[autoConfigurationClasses.length]; System.arraycopy(firstHalf, 0, outcomes, 0, firstHalf.length); System.arraycopy(secondHalf, 0, outcomes, split, secondHalf.length); return outcomes; }
这里有必要说明一下在OnClassCondition类中中声明的内部接口:OutcomesResolver接口:
private interface OutcomesResolver { ConditionOutcome[] resolveOutcomes(); }
该接口就是在第2步–> getOutcomes 中有用到. 实现类有2个:
1、StandardOutcomesResolver实现类
1、字段如下:
// 在META-INFspring.factories/中配置的org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration的类名 private final String[] autoConfigurationClasses; // 处理开始的下标 private final int start; // 处理结束的下标 private final int end; // 自动配置的元数据类,从 META-INF/spring-autoconfigure-metadata.properties private final AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata; // 类加载器 private final ClassLoader beanClassLoader;
2、resolveOutcomes 方法如下:
public ConditionOutcome[] resolveOutcomes() { return getOutcomes(this.autoConfigurationClasses, this.start, this.end, this.autoConfigurationMetadata); }
3、调用:
private ConditionOutcome[] getOutcomes(final String[] autoConfigurationClasses, int start, int end, AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata) { ConditionOutcome[] outcomes = new ConditionOutcome[end - start]; for (int i = start; i < end; i++) { String autoConfigurationClass = autoConfigurationClasses[i]; Set<String> candidates = autoConfigurationMetadata .getSet(autoConfigurationClass, "ConditionalOnClass"); if (candidates != null) { outcomes[i - start] = getOutcome(candidates); } } return outcomes; }
3.1、实例化ConditionOutcome[],大小为end - start
3.2、遍历给定的autoConfigurationClasses,依次从autoConfigurationMetadata中获得通过autoConfigurationClass+”.“+ ConditionalOnClass 所对应的配置(即autoConfigurationClass要生效所需要的类),如果存在的话,则进入第3步
3.3、调用getOutcome处理.在该方法最终调用了getMatches方法.代码如下:
private List<String> getMatches(Collection<String> candidates, MatchType matchType, ClassLoader classLoader) { List<String> matches = new ArrayList<String>(candidates.size()); for (String candidate : candidates) { if (matchType.matches(candidate, classLoader)) { matches.add(candidate); } } return matches; }
通过遍历给定的candidates,依次调用MatchType#matches方法判断是否匹配,如果匹配,则加入到matches中.此处使用的是MISSING.其matches最终调用isPresent方法.代码如下:
public boolean matches(String className, ClassLoader classLoader) { return !isPresent(className, classLoader); }
private static boolean isPresent(String className, ClassLoader classLoader) { if (classLoader == null) { classLoader = ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader(); } try { forName(className, classLoader); return true; } catch (Throwable ex) { return false; } }
通过加载该类的方式进行判断,如果有不存在,则返回false.(这里比较绕,仔细想一下就明白了)。
2、ThreadedOutcomesResolver实现类
ThreadedOutcomesResolver 是对OutcomesResolver的封装,其字段如下:
// 该线程负责调用OutcomesResolver的resolveOutcomes private final Thread thread; private volatile ConditionOutcome[] outcomes;
在实例化的时候初始化了Thread,在该线程中调用OutcomesResolver#resolveOutcomes.如下:
private ThreadedOutcomesResolver(final OutcomesResolver outcomesResolver) { this.thread = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { ThreadedOutcomesResolver.this.outcomes = outcomesResolver .resolveOutcomes(); } }); this.thread.start(); }
resolveOutcomes实现如下:
public ConditionOutcome[] resolveOutcomes() { try { this.thread.join(); } catch (InterruptedException ex) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } return this.outcomes; }
通过线程join的方式,等待outcomesResolver#resolveOutcomes运行完。
4、OnClassCondition 关于getMatchOutcome的实现如下:
public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) { ClassLoader classLoader = context.getClassLoader(); ConditionMessage matchMessage = ConditionMessage.empty(); // 1.1 得到@ConditionalOnClass注解的属性 List<String> onClasses = getCandidates(metadata, ConditionalOnClass.class); if (onClasses != null) { List<String> missing = getMatches(onClasses, MatchType.MISSING, classLoader); if (!missing.isEmpty()) { // 1.2. 如果存在类加载器中不存在对应的类,返回一个匹配失败的ConditionalOutcome return ConditionOutcome .noMatch(ConditionMessage.forCondition(ConditionalOnClass.class) .didNotFind("required class", "required classes") .items(Style.QUOTE, missing)); } // 1.3 如果类加载器中存在对应的类的话,匹配信息进行记录 matchMessage = matchMessage.andCondition(ConditionalOnClass.class) .found("required class", "required classes").items(Style.QUOTE, getMatches(onClasses, MatchType.PRESENT, classLoader)); } // 对@ConditionalOnMissingClass注解做相同的逻辑处理(说明@ConditionalOnClass和@ConditionalOnMissingClass可以一起使用) List<String> onMissingClasses = getCandidates(metadata, ConditionalOnMissingClass.class); if (onMissingClasses != null) { List<String> present = getMatches(onMissingClasses, MatchType.PRESENT, classLoader); if (!present.isEmpty()) { return ConditionOutcome.noMatch( ConditionMessage.forCondition(ConditionalOnMissingClass.class) .found("unwanted class", "unwanted classes") .items(Style.QUOTE, present)); } matchMessage = matchMessage.andCondition(ConditionalOnMissingClass.class) .didNotFind("unwanted class", "unwanted classes").items(Style.QUOTE, getMatches(onMissingClasses, MatchType.MISSING, classLoader)); } // 返回全部匹配成功的ConditionalOutcome return ConditionOutcome.match(matchMessage); }
1、得到@ConditionalOnClass注解的属性,注意: value和name的属性可以不一样,是and的关系
2、如果onClasses不为空的话,则调用getMatches进行处理,getMatches方法我们之前已经分析过了,如果有给定的类在当前的类路径上不存在的话,则返回不匹配.否则进行记录
3、得到@ConditionalOnMissingClass注解的属性.如果不为空的话,则调用getMatches进行处理,getMatches方法我们之前已经分析过了,如果有给定的类在当前的类路径上存在的话,则返回不匹配.否则进行记录.这里调用的是PRESENT#matches方法.代码如下:
@Override public boolean matches(String className, ClassLoader classLoader) { return isPresent(className, classLoader); }
4、最终,返回匹配.
5、使用案例:
5.1、AopAutoConfiguration声明了如下注解:
@ConditionalOnClass({ EnableAspectJAutoProxy.class, Aspect.class, Advice.class })
表明当在当前类路径存在EnableAspectJAutoProxy.class, Aspect.class, Advice.class时才对AopAutoConfiguration进行解析
5.2、Thymeleaf2Configuration 声明了如下注解:
@ConditionalOnMissingClass("org.thymeleaf.templatemode.TemplateMode")
表明当在当前类路径不存在org.thymeleaf.templatemode.TemplateMode时才对Thymeleaf2Configuration进行解析
2.4、@ConditionalOnCloudPlatform与OnCloudPlatformCondition
2.4.1、@ConditionalOnCloudPlatform
@ConditionalOnCloudPlatform 代码如下:
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD }) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Conditional(OnCloudPlatformCondition.class) public @interface ConditionalOnCloudPlatform { // 给定的CloudPlatform必须是激活状态时才返回true CloudPlatform value(); }
CloudPlatform是一个枚举,其声明了2个方法以供枚举使用:
1、isUsingForwardHeaders–>表明当前的平台是否使用X-Forwarded-For这个头部来进行负载均衡.默认为true.代码如下:
public boolean isUsingForwardHeaders() { return true; }
2、getActive–>遍历CloudPlatform枚举类型,返回一个激活的CloudPlatform,如果不存在,则返回null.表明不在默认的云平台中运行(Cloud Foundry,Heroku). 代码如下:
public static CloudPlatform getActive(Environment environment) { if (environment != null) { for (CloudPlatform cloudPlatform : values()) { if (cloudPlatform.isActive(environment)) { return cloudPlatform; } } } return null; }
3、声明了一个isActive抽象方法–>枚举实现,如果返回true,则表明该spirng boot 应用运行在枚举所对应的云平台中.CloudPlatform有2个枚举类型,其实现分别如下:
3.1、CLOUD_FOUNDRY–>Cloud Foundry 平台. 通过判断当前给定环境变量是否存在VCAP_APPLICATION或者VCAP_SERVICES对应的属性.代码如下:
CLOUD_FOUNDRY { @Override public boolean isActive(Environment environment) { return environment.containsProperty("VCAP_APPLICATION") || environment.containsProperty("VCAP_SERVICES"); } }
3.2、HEROKU–> Heroku 平台.通过判断当前给定环境变量是否存在DYNO对应的属性.代码如下:
HEROKU { @Override public boolean isActive(Environment environment) { return environment.containsProperty("DYNO"); } }
2.4.2、OnCloudPlatformCondition处理类
@ConditionalOnCloudPlatform 对应的处理类为OnCloudPlatformCondition.代码如下:
public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) { Map<String, Object> attributes = metadata .getAnnotationAttributes(ConditionalOnCloudPlatform.class.getName()); CloudPlatform cloudPlatform = (CloudPlatform) attributes.get("value"); return getMatchOutcome(context.getEnvironment(), cloudPlatform); }
获得@ConditionalOnCloudPlatform 所配置的CloudPlatform
调用getMatchOutcome进行处理,在该方法中是通过调用CloudPlatform的isActive来判断.如果isActive返回true,则返回匹配,否则返回不匹配.
使用案例:
CloudFoundryActuatorAutoConfiguration声明了如下注解:
@ConditionalOnCloudPlatform(CloudPlatform.CLOUD_FOUNDRY)
表明了 只有在Cloud Foundry平台时才加载CloudFoundryActuatorAutoConfiguration的配置.
2.5、@ConditionalOnExpression 与OnExpressionCondition
2.5.1、@ConditionalOnExpression 代码如下:
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD }) @Documented @Conditional(OnExpressionCondition.class) public @interface ConditionalOnExpression { // 如果该表达式返回true则代表匹配,否则返回不匹配 String value() default "true"; }
2.5.2、OnExpressionCondition处理类
conditionalOnExpression 对应的处理类为OnExpressionCondition.代码如下:
public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) { // 1. 获得@ConditionalOnExpression 所配置的表达式,并尝试对其包装--> 如果表达式不是#{ // 开头的,则返回 #{+expression+} String expression = (String) metadata .getAnnotationAttributes(ConditionalOnExpression.class.getName()) .get("value"); expression = wrapIfNecessary(expression); String rawExpression = expression; // 2. 对占位符进行处理 expression = context.getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(expression); ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory(); BeanExpressionResolver resolver = (beanFactory != null) ? beanFactory.getBeanExpressionResolver() : null; // 3. 获得BeanExpressionContext, BeanExpressionResolver BeanExpressionContext expressionContext = (beanFactory != null) ? new BeanExpressionContext(beanFactory, null) : null; if (resolver == null) { resolver = new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(); } // 4. 对该表达式进行解析,如果结果返回true,则返回匹配,否则,返回不匹配 boolean result = (Boolean) resolver.evaluate(expression, expressionContext); return new ConditionOutcome(result, ConditionMessage .forCondition(ConditionalOnExpression.class, "(" + rawExpression + ")") .resultedIn(result)); }
1、获得@ConditionalOnExpression 所配置的表达式,并尝试对其包装–> 如果表达式不是#{的,则返回 #{+expression+}
2、对占位符进行处理
3、获得BeanExpressionContext, BeanExpressionResolver
4、对该表达式进行解析,如果结果返回true,则返回匹配,否则,返回不匹配
注意: 这里涉及了spring spel的知识,读者可查询相关资料
使用案例:
spring boot 源码中没有使用案例,但是在ConditionalOnExpressionTests该测试类中声明了BasicConfiguration,其声明了如下注解:
@ConditionalOnExpression("true")
1
表明为永远加载BasicConfiguration的配置
2.6、@ConditionalOnJava 与OnJavaCondition
2.6.1、ConditionalOnJava
@ConditionalOnJava 声明了如下属性:
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Conditional(OnJavaCondition.class)
public @interface ConditionalOnJava {
/**
*
* 表明是大于等于配置的JavaVersion还是小于配置的JavaVersion
*/
Range range() default Range.EQUAL_OR_NEWER;
/**
*
* 配置要检查的java版本.使用range属性来表明大小关系
* @return the java version
*/
JavaVersion value();
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
Range(枚举).代码如下:
enum Range {
/**
* 大于或者等于给定的JavaVersion
*/
EQUAL_OR_NEWER,
/**
* 小于给定的JavaVersion
*/
OLDER_THAN
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
JavaVersion(枚举):
属性如下:
// 1.6--> 对应6,不知道java2.0 出来所对应的value是多少...
private final int value;
// 版本号
private final String name;
// 表明该版本号是否可用
private final boolean available;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
构造器如下:
JavaVersion(int value, String name, String className) {
this.value = value;
this.name = name;
this.available = ClassUtils.isPresent(className, getClass().getClassLoader());
}
1
2
3
4
5
通过加载各版本所特有的类来判断所对应的java版本是否可用.
2个方法:
isWithin–>判断给定的JavaVersion是否包含当前所对应的JavaVersion
public boolean isWithin(Range range, JavaVersion version) {
Assert.notNull(range, "Range must not be null");
Assert.notNull(version, "Version must not be null");
switch (range) {
case EQUAL_OR_NEWER:
return this.value >= version.value;
case OLDER_THAN:
return this.value < version.value;
}
throw new IllegalStateException("Unknown range " + range);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
getJavaVersion–> 返回spring boot 应用运行环境所对应的JavaVersion,默认为1.6 .代码如下:
public static JavaVersion getJavaVersion() {
for (JavaVersion candidate : JavaVersion.values()) {
if (candidate.available) {
return candidate;
}
}
return SIX;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
@ConditionalOnJava 所对应的处理类为OnJavaCondition.其实现如下:
private static final JavaVersion JVM_VERSION = JavaVersion.getJavaVersion();
@Override
public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context,
AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
Map<String, Object> attributes = metadata
.getAnnotationAttributes(ConditionalOnJava.class.getName());
Range range = (Range) attributes.get("range");
// 1. 获得@ConditionalOnJava配置的版本号
JavaVersion version = (JavaVersion) attributes.get("value");
// 2. 判断运行时的环境是否包含给定的版本.如果包含,返回匹配,否则,返回不匹配
return getMatchOutcome(range, JVM_VERSION, version);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
获得@ConditionalOnJava配置的版本号
判断运行时的环境是否包含给定的版本.如果包含,返回匹配,否则,返回不匹配
使用案例:
ThymeleafJava8TimeDialect声明了如下注解:
@ConditionalOnJava(ConditionalOnJava.JavaVersion.EIGHT)
1
表明只有在1.8及以上的java环境下才加载ThymeleafJava8TimeDialect的配置
ConditionalOnJndi
@ConditionalOnJndi 注解如下:
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Conditional(OnJndiCondition.class)
public @interface ConditionalOnJndi {
// 给定的jndi的Location 必须存在一个.否则,返回不匹配
String[] value() default {};
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
@ConditionalOnJndi 对应的处理类为 OnJndiCondition,其首先获得@ConditionalOnJndi注解配置的jndi location.然后调用getMatchOutcome进行处理,代码如下:
private ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(String[] locations) {
if (!isJndiAvailable()) {
return ConditionOutcome
.noMatch(ConditionMessage.forCondition(ConditionalOnJndi.class)
.notAvailable("JNDI environment"));
}
if (locations.length == 0) {
return ConditionOutcome.match(ConditionMessage
.forCondition(ConditionalOnJndi.class).available("JNDI environment"));
}
JndiLocator locator = getJndiLocator(locations);
String location = locator.lookupFirstLocation();
String details = "(" + StringUtils.arrayToCommaDelimitedString(locations) + ")";
if (location != null) {
return ConditionOutcome
.match(ConditionMessage.forCondition(ConditionalOnJndi.class, details)
.foundExactly(""" + location + """));
}
return ConditionOutcome
.noMatch(ConditionMessage.forCondition(ConditionalOnJndi.class, details)
.didNotFind("any matching JNDI location").atAll());
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
如果jndi 不可用,则返回不匹配:
加载/META-INF/spring.properties中配置的spring.jndi.ignore,如果配置为true,则表明jndi不可用.否则进入第2步
实例化InitialContext并调用getEnvironment方法.如果调用成功,则表明jndi可用.否则,如果出现异常,则表明不可用
如果jndi location 没有配置,返回匹配
实例化JndiLocator,依次遍历给定的locations,尝试查找,如果查找到一个,则返回匹配,否则,返回不匹配
注意: 这里涉及了jndi的知识,读者可查询相关资料
使用案例:
JndiJtaConfiguration声明了如下注解:
@ConditionalOnJndi({ JtaTransactionManager.DEFAULT_USER_TRANSACTION_NAME,
"java:comp/TransactionManager", "java:appserver/TransactionManager",
"java:pm/TransactionManager", "java:/TransactionManager" })
1
2
3
表明当jndi 在java:comp/UserTransaction,java:comp/TransactionManager,java:appserver/TransactionManager,java:pm/TransactionManager,java:/TransactionManager 路径上只要存在一个资源,则加载JndiJtaConfiguration的配置
ConditionalOn(Not)WebApplication
@ConditionalOnNotWebApplication与@ConditionalOnWebApplication 所对应的处理类都是OnWebApplicationCondition,这里就一起分析了
@ConditionalOnNotWebApplication 是一个标记注解.代码如下:
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Conditional(OnWebApplicationCondition.class)
public @interface ConditionalOnNotWebApplication {
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
@ConditionalOnWebApplication 也是一个标记注解.代码如下:
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Conditional(OnWebApplicationCondition.class)
public @interface ConditionalOnWebApplication {
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
OnWebApplicationCondition 中getMatchOutcome 实现如下:
public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context,
AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
// 1. 检查是否被@ConditionalOnWebApplication 注解
boolean required = metadata
.isAnnotated(ConditionalOnWebApplication.class.getName());
// 2. 判断是否是WebApplication
ConditionOutcome outcome = isWebApplication(context, metadata, required);
if (required && !outcome.isMatch()) {
// 3. 如果有@ConditionalOnWebApplication 注解,但是不是WebApplication环境,则返回不匹配
return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(outcome.getConditionMessage());
}
if (!required && outcome.isMatch()) {
// 4. 如果没有被@ConditionalOnWebApplication 注解,但是是WebApplication环境,则返回不匹配
return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(outcome.getConditionMessage());
}
// 5. 如果被@ConditionalOnWebApplication 注解,并且是WebApplication环境,则返回不匹配
return ConditionOutcome.match(outcome.getConditionMessage());
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
检查是否被@ConditionalOnWebApplication 注解
调用isWebApplication方法判断是否是web环境
如果有@ConditionalOnWebApplication 注解,但是不是Web环境,则返回不匹配
如果没有被@ConditionalOnWebApplication 注解,但是是WebApplication环境,则返回不匹配.即被ConditionalOnNotWebApplication注解处理的情况.
其他情况,返回匹配.如下:
如果被@ConditionalOnWebApplication 注解,并且是WebApplication环境,则返回不匹配
如果被@ ConditionalOnNotWebApplication 注解,并且不是WebApplication环境,则返回不匹配
其中,最重要的是第2步–>判断是否是web环境.代码如下:
private ConditionOutcome isWebApplication(ConditionContext context,
AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata, boolean required) {
ConditionMessage.Builder message = ConditionMessage.forCondition(
ConditionalOnWebApplication.class, required ? "(required)" : "");
// 1. 判断GenericWebApplicationContext是否在类路径中,如果不存在,则返回不匹配
if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS, context.getClassLoader())) {
return ConditionOutcome
.noMatch(message.didNotFind("web application classes").atAll());
}
// 2. 容器里是否有名为session的scope,如果存在,则返回匹配
if (context.getBeanFactory() != null) {
String[] scopes = context.getBeanFactory().getRegisteredScopeNames();
if (ObjectUtils.containsElement(scopes, "session")) {
return ConditionOutcome.match(message.foundExactly("'session' scope"));
}
}
// 3. Environment是否为StandardServletEnvironment,如果是的话,则返回匹配
if (context.getEnvironment() instanceof StandardServletEnvironment) {
return ConditionOutcome
.match(message.foundExactly("StandardServletEnvironment"));
}
// 4. 当前ResourceLoader是否为WebApplicationContext,如果是,则返回匹配
if (context.getResourceLoader() instanceof WebApplicationContext) {
return ConditionOutcome.match(message.foundExactly("WebApplicationContext"));
}
// 5. 其他情况,返回不匹配.
return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(message.because("not a web application"));
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
判断GenericWebApplicationContext是否在类路径中,如果不存在,则返回不匹配
容器里是否有名为session的scope,如果存在,则返回匹配
ConditionContext中的Environment是否为StandardServletEnvironment,如果是的话,则返回匹配
当前ResourceLoader是否为WebApplicationContext,如果是,则返回匹配
其他情况,返回不匹配.
使用案例:
FreeMarkerWebConfiguration 声明了如下注解:
@ConditionalOnWebApplication
1
表明在web环境时加载该配置
FreeMarkerNonWebConfiguration声明了如下注解:
@ConditionalOnNotWebApplication
1
表明不在web环境时加载该配置
ConditionalOnProperty
@ConditionalOnProperty 代码如下:
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })
@Documented
@Conditional(OnPropertyCondition.class)
public @interface ConditionalOnProperty {
// name属性的别名
String[] value() default {};
// 属性前缀,如果该前缀不是.结尾的,则会自动加上
String prefix() default "";
// 属性名,如果前缀被声明了,则会拼接为prefix+name 去查找.通过-进行分割单词,name需要为小写
String[] name() default {};
// 表明所期望的结果,如果没有指定该属性,则该属性所对应的值不为false时才匹配
String havingValue() default "";
// 表明配置的属性如果没有指定的话,是否匹配,默认不匹配
boolean matchIfMissing() default false;
// 是否支持relaxed(松散匹配). 默认支持
boolean relaxedNames() default true;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
OnPropertyCondition 代码如下:
public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context,
AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
// 1. 获得@ConditionalOnProperty 注解所声明的属性
List<AnnotationAttributes> allAnnotationAttributes = annotationAttributesFromMultiValueMap(
metadata.getAllAnnotationAttributes(
ConditionalOnProperty.class.getName()));
List<ConditionMessage> noMatch = new ArrayList<ConditionMessage>();
List<ConditionMessage> match = new ArrayList<ConditionMessage>();
// 2. 遍历allAnnotationAttributes 依次调用determineOutcome进行处理.
// 如果返回不匹配,则加入到noMatch中,否则加入到match中
for (AnnotationAttributes annotationAttributes : allAnnotationAttributes) {
ConditionOutcome outcome = determineOutcome(annotationAttributes,
context.getEnvironment());
(outcome.isMatch() ? match : noMatch).add(outcome.getConditionMessage());
}
// 3. 如果noMatch 不为空,则返回不匹配.否则返回匹配
if (!noMatch.isEmpty()) {
return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(ConditionMessage.of(noMatch));
}
return ConditionOutcome.match(ConditionMessage.of(match));
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
获得@ConditionalOnProperty 注解所声明的属性
遍历allAnnotationAttributes 依次调用determineOutcome进行处理. 如果返回不匹配,则加入到noMatch中,否则加入到match中
如果noMatch 不为空,则返回不匹配.否则返回匹配
其中第2步–> determineOutcome 代码如下:
private ConditionOutcome determineOutcome(AnnotationAttributes annotationAttributes,
PropertyResolver resolver) {
// 1. 实例化Spec
Spec spec = new Spec(annotationAttributes);
List<String> missingProperties = new ArrayList<String>();
List<String> nonMatchingProperties = new ArrayList<String>();
// 2.
spec.collectProperties(resolver, missingProperties, nonMatchingProperties);
// 3. 如果missingProperties不为空,返回不匹配
if (!missingProperties.isEmpty()) {
return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(
ConditionMessage.forCondition(ConditionalOnProperty.class, spec)
.didNotFind("property", "properties")
.items(Style.QUOTE, missingProperties));
}
// 4. 如果nonMatchingProperties不为空,则返回不匹配
if (!nonMatchingProperties.isEmpty()) {
return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(
ConditionMessage.forCondition(ConditionalOnProperty.class, spec)
.found("different value in property",
"different value in properties")
.items(Style.QUOTE, nonMatchingProperties));
}
// 5. 返回匹配
return ConditionOutcome.match(ConditionMessage
.forCondition(ConditionalOnProperty.class, spec).because("matched"));
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
实例化Spec, Spec就是对@ConditionalOnProperty的封装
调用Spec#collectProperties
如果missingProperties不为空,返回不匹配
如果nonMatchingProperties不为空,则返回不匹配
返回匹配
其中第2步–> collectProperties 代码如下:
private void collectProperties(PropertyResolver resolver, List<String> missing,
List<String> nonMatching) {
// 1. 如果支持relaxed(松散匹配),则实例化RelaxedPropertyResolver
if (this.relaxedNames) {
resolver = new RelaxedPropertyResolver(resolver, this.prefix);
}
// 2. 遍历names
for (String name : this.names) {
// 2.1 key等于 如果支持松散匹配,则使用所配置的name,否则等于prefix+name
String key = (this.relaxedNames ? name : this.prefix + name);
// 2.2 如果resolver包含该属性,在RelaxedPropertyResolver#containsProperty其中通过prefix和name拼接的方式查找的
if (resolver.containsProperty(key)) {
// 2.2.1 如果requiredValue配置了,则通过value是否和requiredValue相同进行比较,否则,如果value
// 不与"false"相同的时候匹配. 如果不匹配,则加入到nonMatching
if (!isMatch(resolver.getProperty(key), this.havingValue)) {
nonMatching.add(name);
}
}
else {
// 2.3 如果配置了配置的属性如果没有指定的话,不进行匹配,则加入到missing
if (!this.matchIfMissing) {
missing.add(name);
}
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
如果支持relaxed(松散匹配),则实例化RelaxedPropertyResolver.默认支持
遍历names
key等于 如果支持松散匹配,则使用所配置的name,否则等于prefix+name. 默认等于name
如果resolver包含该属性,在RelaxedPropertyResolver#containsProperty其中通过prefix和name拼接的方式查找的
如果requiredValue配置了,则通过value是否和requiredValue相同进行比较,否则,如果value不与”false”相同的时候匹配. 如果不匹配,则加入到nonMatching
如果配置了配置的属性如果没有指定的话,不进行匹配,则加入到missing
注意: 这里使用了RelaxedPropertyResolver,关于这个,在spring boot 源码解析13-@ConfigurationProperties是如何生效的 中有详细分析
使用案例:
在AopAutoConfiguration声明了如下注解:
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "auto", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true)
1
表明: 如果配置了spring.aop.auto并且值为true时匹配,或者spring.aop.auto没配置时匹配
ConditionalOnResource
@ConditionalOnResource 注解如下:
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Conditional(OnResourceCondition.class)
public @interface ConditionalOnResource {
// 指定的资源必须存在,否则返回不匹配
String[] resources() default {};
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
@ConditionalOnResource 所对应的处理类为OnResourceCondition,代码如下:
public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context,
AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
// 1. 获得@ConditionalOnResource配置的属性
MultiValueMap<String, Object> attributes = metadata
.getAllAnnotationAttributes(ConditionalOnResource.class.getName(), true);
// 2. 获得ResourceLoader,如果ConditionContext中不存在ResourceLoader,则使用默认的ResourceLoader
// 否则使用ConditionContext中的
ResourceLoader loader = context.getResourceLoader() == null
? this.defaultResourceLoader : context.getResourceLoader();
// 3. 获得@ConditionalOnResource中配置的resources的值
List<String> locations = new ArrayList<String>();
collectValues(locations, attributes.get("resources"));
Assert.isTrue(!locations.isEmpty(),
"@ConditionalOnResource annotations must specify at "
+ "least one resource location");
List<String> missing = new ArrayList<String>();
// 4. 依次遍历, 首先进行占位符处理,然后通过加载资源的方式查看是否存在,如果不存在,则加入到missing中
for (String location : locations) {
String resource = context.getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(location);
if (!loader.getResource(resource).exists()) {
missing.add(location);
}
}
// 5. 如果missing不为空,则返回不匹配,否则返回匹配.
if (!missing.isEmpty()) {
return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(ConditionMessage
.forCondition(ConditionalOnResource.class)
.didNotFind("resource", "resources").items(Style.QUOTE, missing));
}
return ConditionOutcome
.match(ConditionMessage.forCondition(ConditionalOnResource.class)
.found("location", "locations").items(locations));
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
获得@ConditionalOnResource配置的属性
获得ResourceLoader,如果ConditionContext中不存在ResourceLoader,则使用默认的ResourceLoader,否则使用ConditionContext中的
获得@ConditionalOnResource中配置的resources的值
遍历resources,依次进行占位符处理,然后通过加载资源的方式查看是否存在,如果不存在,则加入到missing中
如果missing不为空,则返回不匹配,否则返回匹配.
使用案例
在ProjectInfoAutoConfiguration中声明了如下方法:
@ConditionalOnResource(resources = "${spring.info.build.location:classpath:META-INF/build-info.properties}")
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@Bean
public BuildProperties buildProperties() throws Exception {
return new BuildProperties(
loadFrom(this.properties.getBuild().getLocation(), "build"));
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
表示: 当spring.info.build.location配置的资源如果存在的话 或者 spring.info.build.location没配置的话并且classpath:META-INF/build-info.properties 存在的话,则 进行进一步的处理–> @ConditionalOnMissingBean 注解的处理
---------------------
作者:一个努力的码农
来源:CSDN
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_26000415/article/details/79008745
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请附上博文链接!