Java File类的功能非常强大,利用java基本上可以对文件进行所有操作。
首先来看File类的构造函数的源码
/** * Internal constructor for already-normalized pathname strings. */ private File(String pathname, int prefixLength) { this.path = pathname; this.prefixLength = prefixLength; } /** * Internal constructor for already-normalized pathname strings. * The parameter order is used to disambiguate this method from the * public(File, String) constructor. */ private File(String child, File parent) { assert parent.path != null; assert (!parent.path.equals("")); this.path = fs.resolve(parent.path, child); this.prefixLength = parent.prefixLength; } /** * Creates a new <code>File</code> instance by converting the given * pathname string into an abstract pathname. If the given string is * the empty string, then the result is the empty abstract pathname. * * @param pathname A pathname string * @throws NullPointerException * If the <code>pathname</code> argument is <code>null</code> */ public File(String pathname) { if (pathname == null) { throw new NullPointerException(); } this.path = fs.normalize(pathname); this.prefixLength = fs.prefixLength(this.path); } /** * @param parent The parent pathname string * @param child The child pathname string * @throws NullPointerException * If <code>child</code> is <code>null</code> */ public File(String parent, String child) { if (child == null) { throw new NullPointerException(); } if (parent != null && !parent.isEmpty()) { this.path = fs.resolve(fs.normalize(parent), fs.normalize(child)); } else { this.path = fs.normalize(child); } this.prefixLength = fs.prefixLength(this.path); } /** * @param parent The parent abstract pathname * @param child The child pathname string * @throws NullPointerException * If <code>child</code> is <code>null</code> */ public File(File parent, String child) { if (child == null) { throw new NullPointerException(); } if (parent != null) { if (parent.path.equals("")) { this.path = fs.resolve(fs.getDefaultParent(), fs.normalize(child)); } else { this.path = fs.resolve(parent.path, fs.normalize(child)); } } else { this.path = fs.normalize(child); } this.prefixLength = fs.prefixLength(this.path); } /** * @param uri * An absolute, hierarchical URI with a scheme equal to * <tt>"file"</tt>, a non-empty path component, and undefined * authority, query, and fragment components * * @throws NullPointerException * If <tt>uri</tt> is <tt>null</tt> * * @throws IllegalArgumentException * If the preconditions on the parameter do not hold */ public File(URI uri) { // Check our many preconditions if (!uri.isAbsolute()) throw new IllegalArgumentException("URI is not absolute"); if (uri.isOpaque()) throw new IllegalArgumentException("URI is not hierarchical"); String scheme = uri.getScheme(); if ((scheme == null) || !scheme.equalsIgnoreCase("file")) throw new IllegalArgumentException("URI scheme is not "file""); if (uri.getAuthority() != null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("URI has an authority component"); if (uri.getFragment() != null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("URI has a fragment component"); if (uri.getQuery() != null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("URI has a query component"); String p = uri.getPath(); if (p.equals("")) throw new IllegalArgumentException("URI path component is empty"); // Okay, now initialize p = fs.fromURIPath(p); if (File.separatorChar != '/') p = p.replace('/', File.separatorChar); this.path = fs.normalize(p); this.prefixLength = fs.prefixLength(this.path); }
从源码可以看出File类的构造函数有6个,精简如下
public File(String pathname) //文件的绝对路径 public File(URI uri) //文件的URI地址 public File(String parent, String child) //指定父文件绝对路径、子文件绝对路径 public File(File parent, String child) //指定父文件、子文件相对路径 //下面这两个是File类中私有的构造函数,外面不能调用 private File(String child, File parent) private File(String pathname, int prefixLength)
现在就看的比较清楚了,6个构造函数,可以分为2类。4个公共构造函数,2个私有构造函数。
构造函数1:
//电脑d盘中的cat.png 图片的路径 String filePath1 = "D:/cat.png" ; File file = new File( filePath1 ) ;
构造函数2:
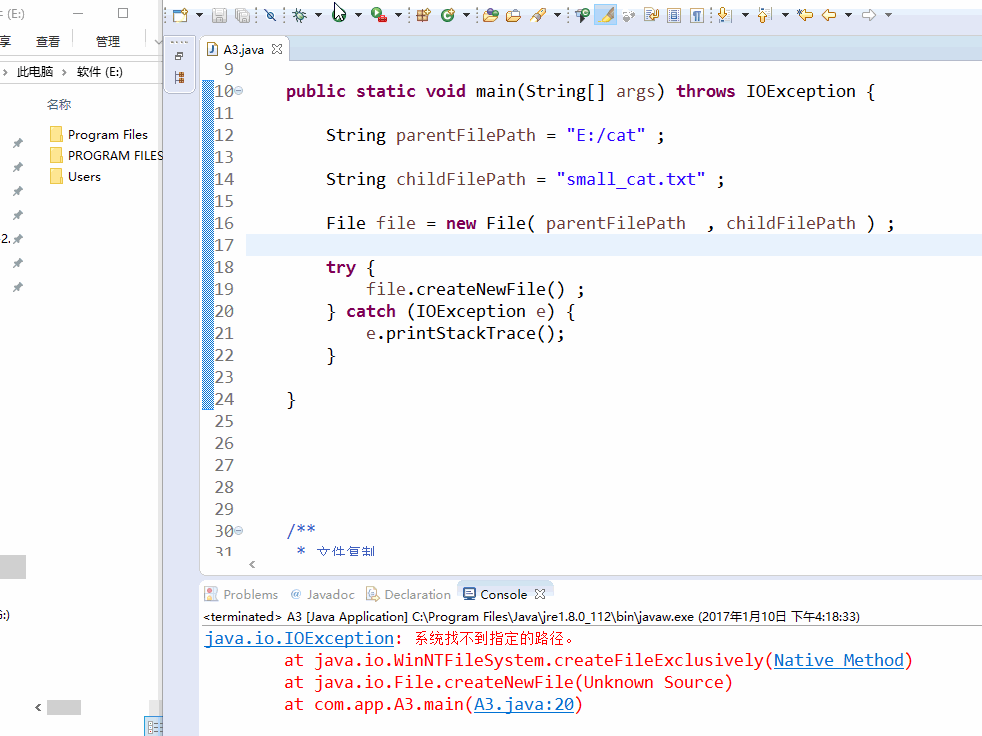
String parentFilePath = "E:/cat" ; String childFilePath = "small_cat.txt" ; //创建parentFile文件 File parentFile = new File( parentFilePath ) ; parentFile.mkdir() ; //如果parentFile不存在,就会报异常 File file = new File( parentFilePath , childFilePath ) ; try { file.createNewFile() ; } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
效果图:
构造函数3:
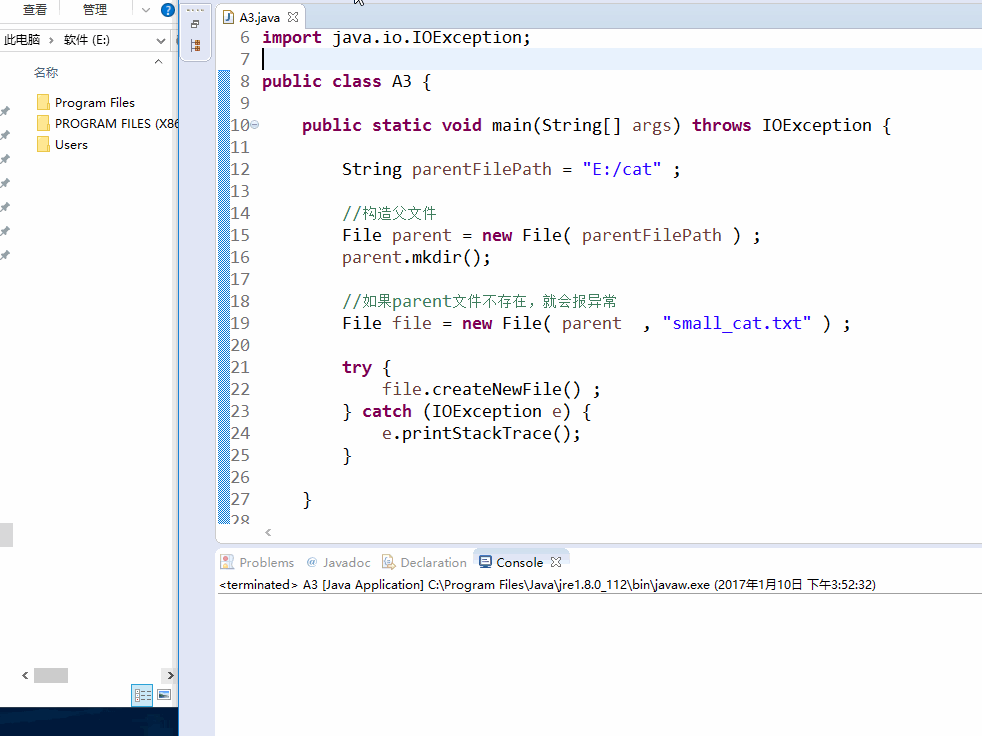
String parentFilePath = "E:/cat" ; //构造父文件 File parent = new File( parentFilePath ) ; parent.mkdir(); //如果parent文件不存在,就会报异常 File file = new File( parent , "small_cat.txt" ) ; try { file.createNewFile() ; } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
效果图:
- 创建目录
boolean file.mkdir()
如果创建成功,返回 true , 创建失败,返回false。如果这个文件夹已经存在,则返回false.
只能创建一级目录,如果父目录不存在,返回false.
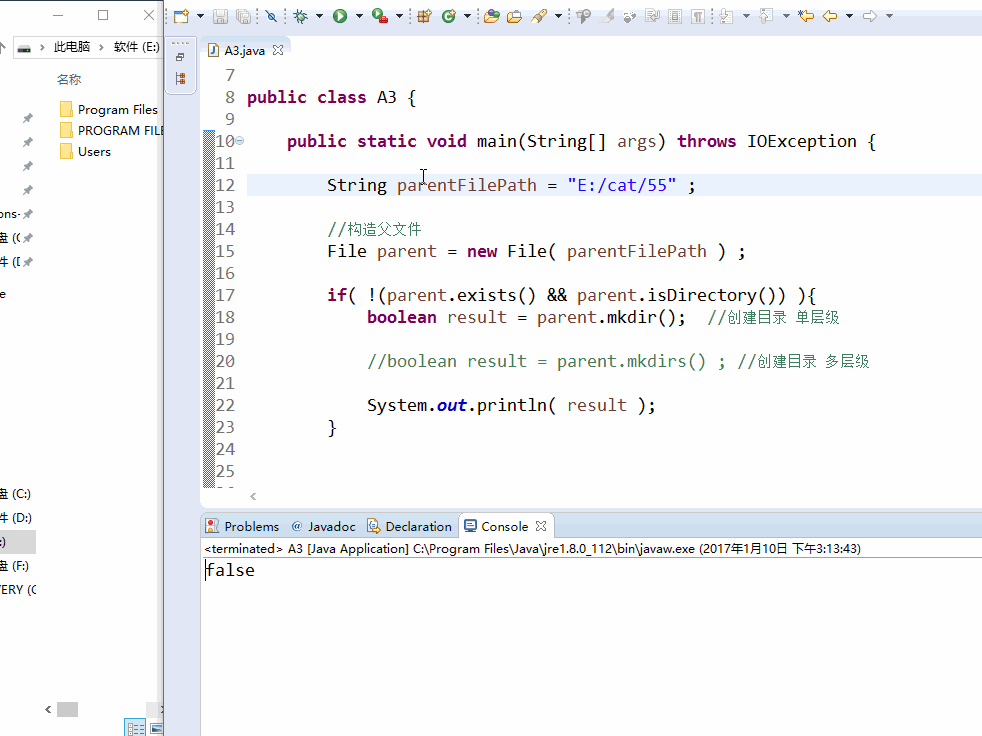
- 创建多级目录
boolean file.mkdirs()
创建多级目录,创建成功,返回true,创建失败,返回false。如果父目录不存在,就创建,并且返回true.
- 创建一个新的文件
boolean file.createNewFile() ;
如果文件不存在就创建该文件,创建成功,返回 true ;创建失败,返回false。如果这个文件已经存在,则返回false.
- 判断方法
boolean file.exists() //文件是否存在 boolean file.isFile() //是否是文件 boolean file.isDirectory() //是否是目录 boolean file.isHidden() //是否隐藏(windows上可以设置某个文件是否隐藏) boolean file.isAbsolute() //是否为绝对路径 boolean file.canRead() //是否可读 boolean file.canWrite() //是否可写 boolean file.canExecute() //是否可执行
获取文件的信息
String file.getName() //获取文件的名字,只是名字,没有路径 String file.getParent() //获取父目录的绝对路径,返回值是一个字符串。如果文件有父目录,那么返回父目录的绝对路径,(比如:`E:cat`) , 如果文件本身就在磁盘的根目录,那么返回磁盘的路径,(比如:`E:\`)。 File file.getParentFile() //获取父文件,返回值是一个File对象。 long time = file.lastModified() ; //返回文件最后一次修改的时间 Date dt = new Date(time); boolean renameTo(File file) //文件命名 long file.length() //返回文件的大小,单位字节 boolean file.delete() //删除文件 String[] file.list() //获取该目录下的所有的文件的名字。如果`file`为文件,返回值为`null`,在使用时记得判空;但是如果`file`为目录,那么返回这个目录下所有文件的名字,只是名字,不含路径;如果`file`是一个空目录,返回一个长度为0的数组;从上面的结果可以看出,`list()` 方法,只是对`file`为目录时有效,当`file`为一个文件的时候,该方法毫无意义。 File[] file.listFiles() //获取该目录下的所有的文件。如果`file`为文件,返回值为`null`,在使用时记得判空;但是如果`file`为目录,那么返回这个目录下所有的文件 ;如果`file`是一个空目录,返回一个长度为0的数组;从上面的结果可以看出,`listFiles()` 方法,只是对`file`为目录时有效,当`file`为一个文件的时候,该方法毫无意义。
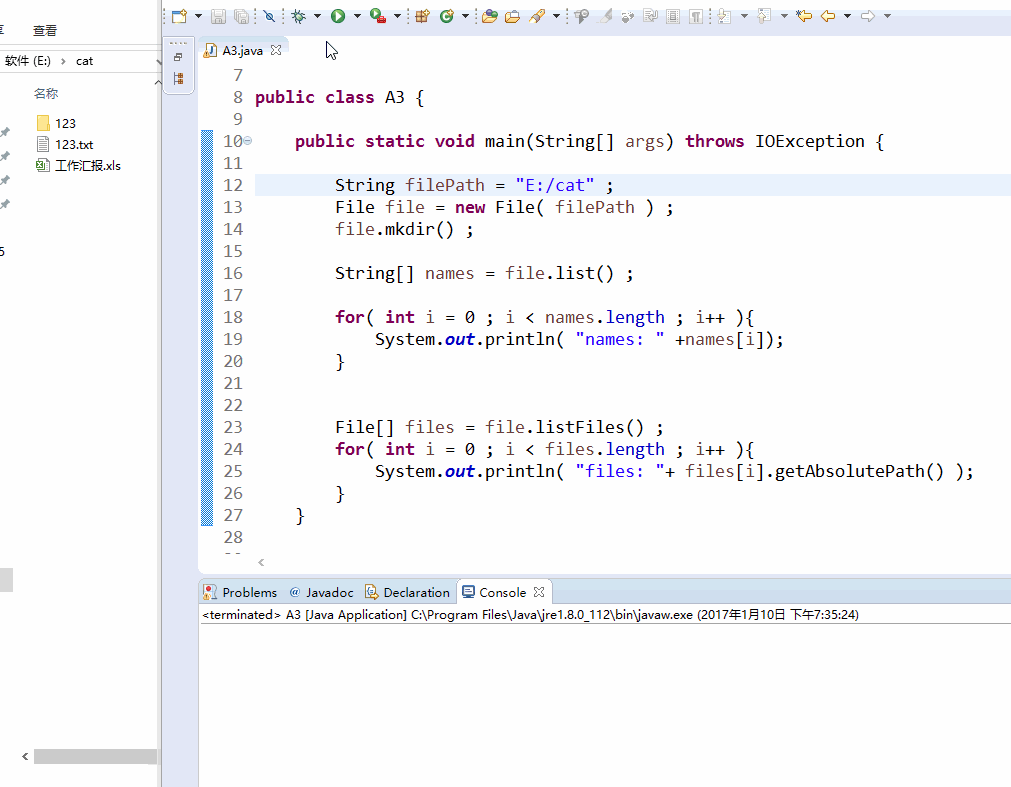
实战经验1: file.list() , file.listFiles()
String filePath = "E:/cat" ; File file = new File( filePath ) ; file.mkdir() ; String[] names = file.list() ; for( int i = 0 ; i < names.length ; i++ ){ System.out.println( "names: " +names[i]); } File[] files = file.listFiles() ; for( int i = 0 ; i < files.length ; i++ ){ System.out.println( "files: "+ files[i].getAbsolutePath() ); }
效果图:
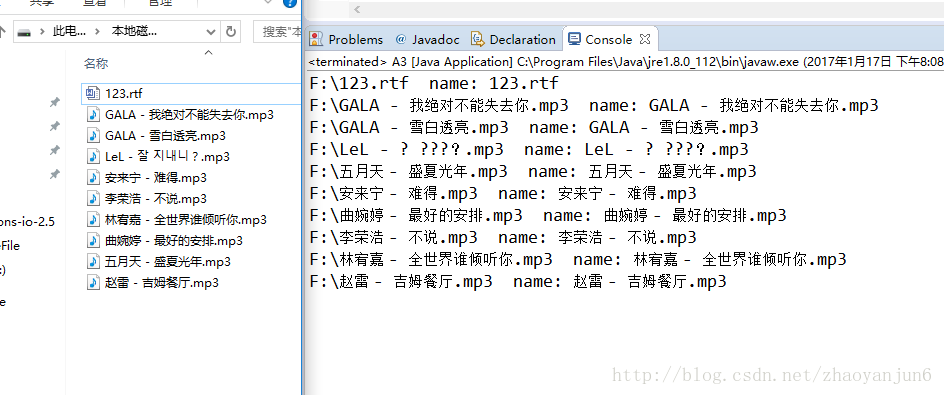
实战经验2:扫描F盘所有的文件
public class A3 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String filePath = "F:/" ; File file = new File( filePath ) ; getFile(file); } private static void getFile( File file ){ File[] files = file.listFiles() ; for( File f : files ){ if ( f.isHidden() ) continue ; if(f.isDirectory() ){ getFile( f ); }else{ System.out.println( f.getAbsolutePath() + " " + f.getName() ); } } } }
效果图:
在上面的实战演练中用到了,file.list() , file.listFiles() 。这是两个无参的方法,实际上还有两个有参的方法,分别是
file.list(FilenameFilter filter) ;
file.listFiles( FilenameFilter filter) ;
file.listFiles(FileFilter filter)
FileFilter
FileFilter是io包里面的一个接口,从名字上可以看出,这个类是文件过滤功能的。
需要重写accept方法
比如:
static class MyFileFilter implements FileFilter { MyFileFilter(){ } //pathname:文件的绝对路径+ 文件名 , 比如:F:安来宁 - 难得.mp3 , 或者: F:文件夹1 @Override public boolean accept(File pathname) { return false; } }
实战:获取指定目录的所有文件夹
package com.app; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileFilter; import java.io.IOException; public class A3 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String filePath = "F:/" ; File file = new File( filePath ) ; getFile(file); } /** * 获取指定目录的所有文件夹 * @param file */ private static void getFile( File file ){ MyFileFilter myFileFilter = new MyFileFilter() ; File[] files = file.listFiles( myFileFilter ) ; for( File f : files ){ if ( f.isHidden() ) continue ; System.out.println( f.getAbsolutePath() ); } } static class MyFileFilter implements FileFilter { MyFileFilter(){ } //pathname:文件的绝对路径+ 文件名 , 比如:F:安来宁 - 难得.mp3 , 或者: F:文件夹1 @Override public boolean accept(File pathname) { if( pathname.isDirectory() ){ return true ; } return false; } } }
FilenameFilter
FileFilter是io包里面的一个接口,从名字上可以看出,这个类是文件名字过滤功能的。
需要重写里面的accept方法。
比如:
package com.app; import java.io.File; import java.io.FilenameFilter; public class MyFilenameFilter implements FilenameFilter { //type为需要过滤的条件,比如如果type=".jpg",则只能返回后缀为jpg的文件 private String type; MyFilenameFilter( String type){ this.type = type ; } @Override public boolean accept(File dir, String name) { //dir表示文件的当前目录,name表示文件名; return name.endsWith( type ) ; } }
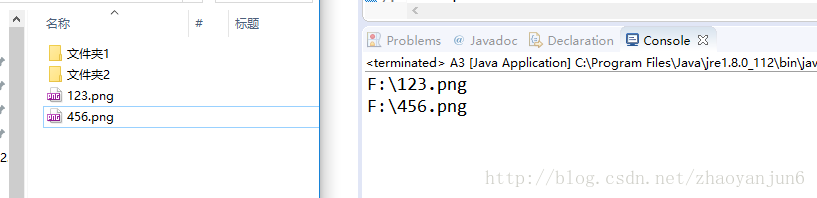
实战:扫描出指定路径的所有图片
package com.app; import java.io.File; import java.io.FilenameFilter; import java.io.IOException; public class A3 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String filePath = "F:/" ; File file = new File( filePath ) ; getFile(file); } /** * 扫描出指定路径的所有图片 * @param file */ private static void getFile( File file ){ MyFilenameFilter myFileFilter = new MyFilenameFilter( ".png") ; File[] files = file.listFiles( myFileFilter ) ; for( File f : files ){ if ( f.isHidden() ) continue ; System.out.println( f.getAbsolutePath() ); } } static class MyFilenameFilter implements FilenameFilter { //type为需要过滤的条件,比如如果type=".jpg",则只能返回后缀为jpg的文件 private String type; MyFilenameFilter( String type){ this.type = type ; } @Override public boolean accept(File dir, String name) { //dir表示文件的当前目录,name表示文件名; return name.endsWith( type ) ; } } }
运行结果:
转载 https://blog.csdn.net/zhaoyanjun6/article/details/54581478