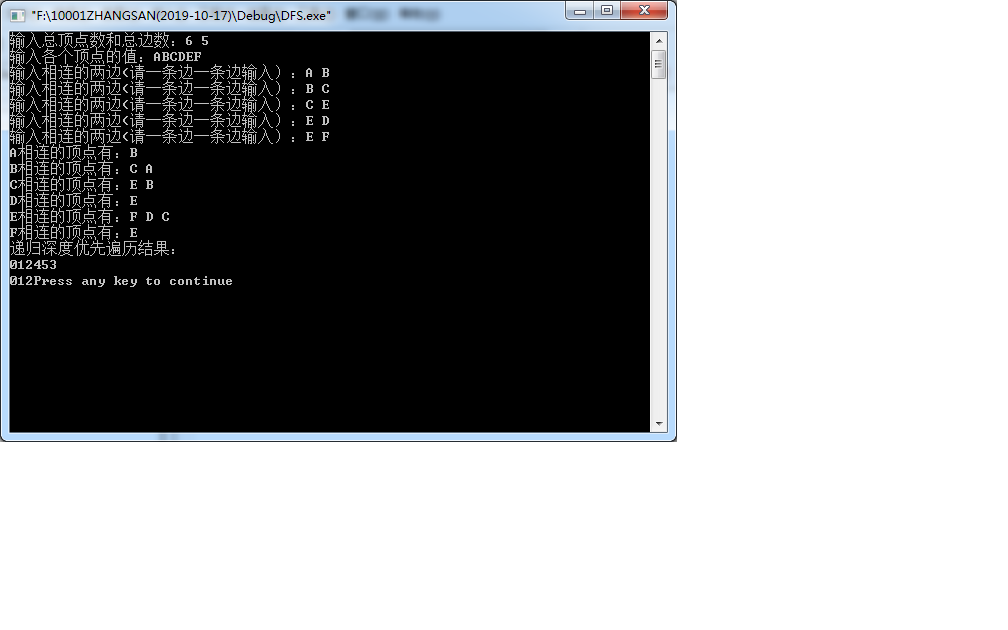
源程序:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define vnum 100
typedef char VerTexType;
//定义链接队列的结点
typedef struct LinkQueueNode
{
int data1;
struct LinkQueueNode *next;
}LKQueNode;
//定义队列,队列有头指针和尾指针
typedef struct LKQueue
{
LinkQueueNode *front,*rear;
}LKQue;
typedef struct arcnode
{
int adjvex; //下一条边的顶点编号
struct arcnode *nextarc; //指向下一条边的指针
int weight; //带权图的权值域
}ArcNode;
typedef struct vexnode
{
VerTexType data; //顶点编号
arcnode *firstarc; //指向第一条边的指针
}VNode,AdjList[vnum]; //全部顶点的数组
typedef struct gp{
AdjList adjlist;
int vexnum, arcnum; //顶点数和边数
}Graph;
int visited[vnum];
//arcnode作为顶点的边的结构体,储存着该边的另一个顶点的下标、下一条边的指针、以及与边相关的数据。vexnode是每一个顶点的结构体,
//保存着每个顶点的数据和第一个与它相连接的顶点的边的指针。Graph图的结构体,包含了所有顶点和边,储存顶点和边的数量。
//确定顶点位置:
int LocateVex(Graph *G, VerTexType v)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < (G->vexnum); i++)
{
if (G->adjlist[i].data == v)
return i;
}
}
//创建邻接表:
int CreateAdjlist(Graph *G)
{
int i, j, k;
VerTexType v1, v2;
arcnode *p1, *p2;
printf("输入总顶点数和总边数:");
scanf("%d %d", &G->vexnum, &G->arcnum);
printf("输入各个顶点的值:");
fflush(stdin);
for (i = 0; i < G->vexnum; i++)
{
scanf("%c", &G->adjlist[i].data); //输入各顶点的值
G->adjlist[i].firstarc = NULL; //初始化i的第一个邻接点为NULL
}
for (k = 0; k < G->arcnum; k++)
{
printf("输入相连的两边(请一条边一条边输入):");
fflush(stdin);
scanf("%c %c", &v1, &v2); //输入弧尾和弧头
i = LocateVex(G, v1);
j = LocateVex(G, v2);
p1 = (arcnode *)malloc(sizeof(arcnode));
p2 = (arcnode *)malloc(sizeof(arcnode));
p1->adjvex = j;
p1->nextarc = G->adjlist[i].firstarc;
G->adjlist[i].firstarc = p1;
p2->adjvex = i;
p2->nextarc = G->adjlist[j].firstarc;
G->adjlist[j].firstarc = p2;
}
return 1;
}
//从v出发深度优先遍历的递归函数
void DFS(Graph *g,int v)
{
ArcNode *p;
printf("%d",v);
visited[v]=1;
p=g->adjlist[v].firstarc;
while(p!=NULL)
{
if(!visited[p->adjvex])
DFS(g,p->adjvex);
p=p->nextarc;
}
}
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//链队列
//初始化队列
void InitQueue(LKQue * LQ)
{
LKQueNode *p;
p=(LinkQueueNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkQueueNode));
LQ->front=p;
LQ->rear=p;
LQ->front->next=NULL;
}
//判断队列是否为空队列
int EmptyQueue(LKQue *LQ)
{
if(LQ->front==LQ->rear)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
//入队操作
void EnQueue(LKQue *LQ,int x)
{
LKQueNode *p;
p=(LinkQueueNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkQueueNode));
p->data1=x;
p->next=NULL;
LQ->rear->next=p;
LQ->rear=p;
}
//出队操作
int OutQueue(LKQue *LQ,int x)
{
LKQueNode *s;
if(EmptyQueue(LQ))
{
exit(0);
return 0;
}
else
{
s=(LQ->front)->next;
x=s->data1;
(LQ->front)->next=s->next;
if(s->next==NULL)
LQ->rear=LQ->front;
free(s);
return 1;
}
}
//取队列首元素
int GetHead(LKQue *LQ)
{
LKQueNode *p;
int q;
if(EmptyQueue(LQ))
return q;
else
{
p=(LQ->front)->next;
return p->data1;
}
}
//从v出发广度优先遍历,利用链队列作为缓冲
void BFS(Graph *g,int v)
{
LKQue Q;
ArcNode *p;
InitQueue(&Q);
printf("%d",v);
visited[v]=1;
EnQueue(&Q,v);
while(!EmptyQueue(&Q))
{
v=GetHead(&Q);
OutQueue(&Q,v);
p=g->adjlist[v].firstarc;
while(p!=NULL)
{
if(!visited[p->adjvex])
{
printf("%d",p->adjvex);
visited[p->adjvex]=1;
EnQueue(&Q,p->adjvex);
}
p=p->nextarc;
}
}
}
//先确定(输入)邻接表的顶点数和边数,然后依次输入各个顶点的值。由于此时未知其有没有与其他顶点连接,故将其第一条边的指针赋值为NULL。
//之后,再根据边数,输入要连接起来的顶点的值,先得到两个顶点的下标i、j,为边指针p1、p2分配空间。
//将p1边的另一个顶点下标赋值为j,并将p1插入到表头结点和第一条边之间。、对p2执行相同操作。
int main()
{
int i;
Graph G;
arcnode *p;
CreateAdjlist(&G);
for (i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++)
{
p = G.adjlist[i].firstarc;
printf("%c相连的顶点有:", G.adjlist[i].data);
while (p != NULL)
{
printf("%c ", G.adjlist[p->adjvex].data);
p = p->nextarc;
}
printf("
");
}
printf("递归深度优先遍历结果:
");
DFS(&G,0);
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
visited[i]=0;
printf(" ");
BFS(&G,0);//邻接表的广度优先遍历
return 0;
}
运行结果: